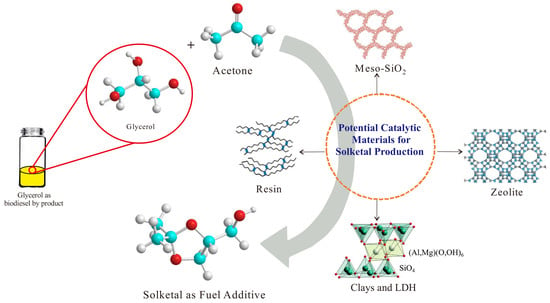
Glycerol to Solketal for Fuel Additive: Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Glycerol-to-Solketal Over Resin Catalysts
3. Glycerol-to-Solketal over Mesoporous Silica
4. Ketalization of Glycerol over Clay Minerals
5. Perspective on Ketalization of Glycerol over Hierarchical Zeolites
6. Solketal Synthesis over Carbon/Activated Carbon-Based Catalyst
7. Perspective and Conclusions
- The presence of water and impurities in the feed.
- The shift from the batch reactor to the fixed bed reactor.
- The presence of equilibrium offers other difficulties as higher acetone demand is expected. However, higher acetone to glycerol will lead to destructive instruments.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silitonga, A.S.; Atabani, A.E.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Masjuki, H.H.; Badruddin, I.A.; Mekhilef, S. A review on prospect of Jatropha curcas for biodiesel in Indonesia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 3733–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.C.; Masjuki, H.H.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Silitonga, A.S.; Chong, W.T.; Leong, K.Y. Optimization of biodiesel production and engine performance from high free fatty acid Calophyllum inophyllum oil in CI diesel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 81, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadima, A.; Muraza, O. Hydrothermal liquefaction of algae and bio-oil upgrading into liquid fuels: Role of heterogeneous catalysts. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadima, A.; Muraza, O. Biodiesel production from algae by using heterogeneous catalysts: A critical review. Energy 2014, 78, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silitonga, A.S.; Masjuki, H.H.; Ong, H.C.; Sebayang, A.H.; Dharma, S.; Kusumo, F.; Siswantoro, J.; Milano, J.; Daud, K.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; et al. Evaluation of the engine performance and exhaust emissions of biodiesel-bioethanol-diesel blends using kernel-based extreme learning machine. Energy 2018, 159, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, C.A.G.; Coronado, C.J.R.; Carvalho, J.A., Jr. Glycerol: Production, consumption, prices, characterization and new trends in combustion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.R.; Kugelmeier, C.L.; Pinheiro, R.S.; Batalha, M.O.; Da Silva César, A. Glycerol from biodiesel production: Technological paths for sustainability. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 88, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharma, S.; Masjuki, H.H.; Ong, H.C.; Sebayang, A.H.; Silitonga, A.S.; Kusumo, F.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Optimization of biodiesel production process for mixed Jatropha curcas-Ceiba pentandra biodiesel using response surface methodology. Energy Convers. Manage. 2016, 115, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.Y.; Linnekoski, J.; Amin, N.A.S. Catalyst screening for conversion of glycerol to light olefins. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 207, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadima, A.; Muraza, O. A review on glycerol valorization to acrolein over solid acid catalysts. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 67, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadima, A.; Muraza, O. Sustainable Production of Glycerol Carbonate from By-product in Biodiesel Plant. Waste Biomass Valorization 2016, 8, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.; Julkapli, N.M.; Yehye, W.A. Catalytic conversion of biodiesel derived raw glycerol to value added products. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.; Bordado, J.C.; Santos, R.G.D. Upgrading the Glycerol from Biodiesel Production as a Source of Energy Carriers and Chemicals—A Technological Review for Three Chemical Pathways. Energies 2017, 10, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J.; Smith, L.; Dummer, N.F.; Douthwaite, M.; Willock, D.J.; Howard, M.; Knight, D.W.; Taylor, S.H.; Hutchings, G.J. Investigating the Influence of Reaction Conditions and the Properties of Ceria for the Valorisation of Glycerol. Energies 2019, 12, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat, N.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Mohamed, A.R. Recent progress on innovative and potential technologies for glycerol transformation into fuel additives: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, A.; Barrio, I.; Campoy, M.; Lázaro, J.; Navarrete, B. Oxygenated fuel additives from glycerol valorization. Main production pathways and effects on fuel properties and engine performance: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 1400–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, M.R.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Qin, W.; Ghaziaskar, H.S.; Xu, C. Catalytic conversion of glycerol for sustainable production of solketal as a fuel additive: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, H.I.; Irawan, E.; Nuryoto, N.; Jayanudin, J.; Sulistyo, H.; Sediawan, W.B.; Muraza, O. Glycerol Carbonate Production from Biodiesel Waste Over Modified Natural Clinoptilolite. Waste Biomass Valorization 2016, 7, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alptekin, E.; Canakci, M. Performance and emission characteristics of solketal-gasoline fuel blend in a vehicle with spark ignition engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 124, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghbashlo, M.; Hosseinpour, S.; Tabatabaei, M.; Rastegari, H.; Ghaziaskar, H.S. Multi-objective exergoeconomic and exergoenvironmental optimization of continuous synthesis of solketal through glycerol ketalization with acetone in the presence of ethanol as co-solvent. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, M.; Abdullah, A.Z. Diglycerol synthesis via solvent-free selective glycerol etherification process over lithium-modified clay catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konaka, A.; Tago, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Shitara, H.; Nakasaka, Y.; Masuda, T. Conversion of Biodiesel-Derived Crude Glycerol into Useful Chemicals over a Zirconia–Iron Oxide Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 15509–15515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, G.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Kennedy, E.M.; Stockenhuber, M. Zeolite-supported iron catalysts for allyl alcohol synthesis from glycerol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 509, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manikandan, M.; Prabu, M.; Sk, A.K.; Sangeetha, P.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Tuning the basicity of Cu-based mixed oxide catalysts towards the efficient conversion of glycerol to glycerol carbonate. Mol. Catal. 2018, 460, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadamsetti, S.; Rajan, N.P.; Rao, G.S.; Chary, K.V.R. Acetalization of glycerol with acetone to bio fuel additives over supported molybdenum phosphate catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 410, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim, H.; Fonseca, I.M.; Ramos, A.M.; Vital, J.; Castanheiro, J.E. Valorization of glycerol into fuel additives over zeolites as catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 178, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kiyan, A.M.; Bagio, J.C.; Rossi, K.A.B.; Delabio Berezuk, F.; Berezuk, M.E. Green cyclic acetals production by glycerol etherification reaction with benzaldehyde using cationic acidic resin. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsanam, P.; Mallesham, B.; Prasad, A.N.; Reddy, P.S.; Reddy, B.M. Synthesis of bio–additive fuels from acetalization of glycerol with benzaldehyde over molybdenum promoted green solid acid catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 106, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallesham, B.; Sudarsanam, P.; Raju, G.; Reddy, B.M. Design of highly efficient Mo and W-promoted SnO2solid acids for heterogeneous catalysis: Acetalization of bio-glycerol. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunathan, P.; Marakatti, V.S.; Chandra, P.; Kulal, A.B.; Umbarkar, S.B.; Ravishankar, R.; Shanbhag, G.V. Mesoporous tin oxide: An efficient catalyst with versatile applications in acid and oxidation catalysis. Catal. Today 2018, 309, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawicka, K.; Díaz-Álvarez, A.E.; Calvino-Casilda, V.; Trejda, M.; Bañares, M.A.; Ziolek, M. The Role of Brønsted and Lewis Acid Sites in Acetalization of Glycerol over Modified Mesoporous Cellular Foams. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 16699–16711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.A.; Souza, R.O.M.A.; Mota, C.J.A. Atmospheric Pressure Continuous Production of Solketal from the Acid-Catalyzed Reaction of Glycerol with Acetone. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2016, 27, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgen, O.; Yerlikaya, S.; Akyurek, F.O. Synthesis of Solketal from Glycerol and Acetone over Amberlyst-46 to Produce an Oxygenated Fuel Additive. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2016, 61, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Moteki, T.; Gokhale, A.A.; Flaherty, D.W.; Toste, F.D. Production of Fuels and Chemicals from Biomass: Condensation Reactions and Beyond. Chem 2016, 1, 32–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Li, N.; Ma, W.J.; Zhou, J.H.; Sun, H.Z. Synthesis of Solketal with Catalyst Sulfonic Acid Resin. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 830, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, S.; Noe, M.; Riello, P.; Perosa, A.; Selva, M. Towards a Rational Design of a Continuous-Flow Method for the Acetalization of Crude Glycerol: Scope and Limitations of Commercial Amberlyst 36 and AlF3.3H2O as Model Catalysts. Molecules 2016, 21, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Korányi, T.I.; Sels, B.F.; Pescarmona, P.P. Highly-efficient conversion of glycerol to solketal over heterogeneous Lewis acid catalysts. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, T.H.; Meyer, C.I.; Padró, C.; Martins, L. Acidic V-MCM-41 catalysts for the liquid-phase ketalization of glycerol with acetone. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 273, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.; Gonçalves, M.; Mandelli, D.; Pescarmona, P.P.; Carvalho, W.A. Solvent-free conversion of glycerol to solketal catalysed by activated carbons functionalised with acid groups. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, G.A.; Kurniawan, T.; Tago, T.; Bakare, I.A.; Taniguchi, T.; Nakasaka, Y.; Masuda, T.; Muraza, O. Cracking of n-hexane over hierarchical MOR zeolites derived from natural minerals. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 61, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.M.; Muraza, O.; Al-Amer, A.M.; Miyake, K.; Nishiyama, N. Development of hierarchical EU-1 zeolite by sequential alkaline and acid treatments for selective dimethyl ether to propylene (DTP). Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 497, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Nohair, B.; Zhao, D.; Kaliaguine, S. Highly Efficient Glycerol Acetalization over Supported Heteropoly Acid Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Song, H.; Chen, J. Propylsulfonic Acid Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica as Efficient Catalysts for the Acetalization of Glycerol. Catalysts 2018, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, G.; Melero, J.A.; Morales, G.; Paniagua, M.; Martín, E. Acetalisation of bio-glycerol with acetone to produce solketal over sulfonic mesostructured silicas. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, G.; Paniagua, M.; Melero, J.A.; Vicente, G.; Ochoa, C. Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized Catalysts for the Valorization of Glycerol via Transesterification with Methyl Acetate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 5898–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churipard, S.R.; Manjunathan, P.; Chandra, P.; Shanbhag, G.V.; Ravishankar, R.; Rao, P.V.C.; Sri Ganesh, G.; Halgeri, A.B.; Maradur, S.P. Remarkable catalytic activity of a sulfonated mesoporous polymer (MP-SO3H) for the synthesis of solketal at room temperature. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 5745–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konwar, L.J.; Samikannu, A.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Boström, D.; Mikkola, J.-P. Lignosulfonate-based macro/mesoporous solid protonic acids for acetalization of glycerol to bio-additives. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 220, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, M.R.; Yuan, Z.; Qin, W.; Ghaziaskar, H.S.; Poirier, M.-A.; Xu, C. A new continuous-flow process for catalytic conversion of glycerol to oxygenated fuel additive: Catalyst screening. Appl. Energy 2014, 123, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, C.J.A.; Da Silva, C.X.A.; Rosenbach, N.; Costa, J.; Da Silva, F. Glycerin Derivatives as Fuel Additives: The Addition of Glycerol/Acetone Ketal (Solketal) in Gasolines. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2733–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Tsai, S.-M. Comparison of Fuel Properties of Nanoemulsions of Diesel Fuel Dispersed with Solketal by Microwave Irradiation and Mechanical Homogenization Methods. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 11814–11820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, J.; Murasiewicz, H.; Simons, T.A.H.; Bakalis, S.; Fryer, P.J. Measuring the Density, Viscosity, Surface Tension, and Refractive Index of Binary Mixtures of Cetane with Solketal, a Novel Fuel Additive. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 7452–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, I.B.; Rajkumari, K.; Gupta, R.; Rokhum, L. Acid functionalized mesoporous polymer catalyzed acetalization of glycerol to solketal, a potential fuel additive under solvent-free conditions. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 12567–12576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, M.N.; Panchenko, V.N.; Krupskaya, V.V.; Gil, A.; Vicente, M.A. Effect of nitric acid modification of montmorillonite clay on synthesis of solketal from glycerol and acetone. Catal. Commun. 2017, 90, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Wang, S.; Wulandari, D. ZnO/montmorillonite for photocatalytic and photochemical degradation of methylene blue. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Wang, S.; Narsito; Wijaya, K. Composites of TiO2-aluminum pillared montmorillonite: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Huda, T. Preparation of cetyltrimethylammonium intercalated Indonesian montmorillonite for adsorption of toluene. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 74, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonar, S.K.; Shinde, A.S.; Asok, A.; Niphadkar, P.S.; Mayadevi, S.; Joshi, P.N.; Bokade, V.V. Solvent free acetalization of glycerol with formaldehyde over hierarchical zeolite of BEA topology. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2018, 37, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallesham, B.; Rao, B.G.; Reddy, B.M. Production of biofuel additives by esterification and acetalization of bioglycerol. C. R. Chim. 2016, 19, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, C.X.A.; Gonçalves, V.L.C.; Mota, C.J.A. Water-tolerant zeolitecatalyst for the acetalisation of glycerol. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandesh, S.; Halgeri, A.B.; Shanbhag, G.V. Utilization of renewable resources: Condensation of glycerol with acetone at room temperature catalyzed by organic–inorganic hybrid catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 401, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasabnis, A.; Mahajani, S. Acetalization of Glycerol with Formaldehyde by Reactive Distillation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 12279–12287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammaji, S.; Rao, G.S.; Chary, K.V.R. Acetalization of glycerol with acetone over various metal-modified SBA-15 catalysts. Appl. Petrochem. Res. 2018, 8, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dmitriev, G.S.; Terekhov, A.V.; Zanaveskin, L.N.; Khadzhiev, S.N.; Zanaveskin, K.L.; Maksimov, A.L. Choice of a catalyst and technological scheme for synthesis of solketal. Rus. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 89, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska-Kus, J.; Held, A.; Frankowski, M.; Nowinska, K. Solketal formation from glycerol and acetone over hierarchical zeolites of different structure as catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2017, 426, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska-Kus, J.; Held, A.; Nowinska, K. Enhancement of the catalytic activity of H-ZSM-5 zeolites for glycerol acetalization by mechanical grinding. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2015, 117, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.M.; Muraza, O.; Yoshioka, M.; Yokoi, T. Effect of multi-step desilication and dealumination treatments on the performance of hierarchical EU-1 zeolite for converting methanol to olefins. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 241, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraza, O.; Bakare, I.A.; Tago, T.; Konno, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Al-Amer, A.M.; Yamani, Z.H.; Nakasaka, Y.; Masuda, T. Selective catalytic cracking of n-hexane to propylene over hierarchical MTT zeolite. Fuel 2014, 135, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.M.; Muraza, O.; Nakaoka, S.; Jamil, A.K.; Mayoral, A.; Sebastian, V.; Yamani, Z.H.; Masuda, T. Stability Assessment of Regenerated Hierarchical ZSM-48 Zeolite Designed by Post-Synthesis Treatment for Catalytic Cracking of Light Naphtha. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 14097–14103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossa, V.; Pessanha, Y.D.S.P.; Díaz, G.C.; Câmara, L.D.T.; Pergher, S.B.C.; Aranda, D.A.G. Reaction Kinetic Study of Solketal Production from Glycerol Ketalization with Acetone. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, L.; Han, W.; Zhang, L. Energy and exergy analyses of coal gasification with supercritical water and O2-H2O. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 148, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghbashlo, M.; Tabatabaei, M.; Hosseinpour, S.; Rastegari, H.; Ghaziaskar, H.S. Multi-objective exergy-based optimization of continuous glycerol ketalization to synthesize solketal as a biodiesel additive in subcritical acetone. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 160, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesha, N.J.; Bhat, Y.S.; Prakash, B.S.J. Dealuminated BEA zeolite for selective synthesis of five-membered cyclic acetal from glycerol under ambient conditions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 18824–18833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunathan, P.; Maradur, S.P.; Halgeri, A.B.; Shanbhag, G.V. Room temperature synthesis of solketal from acetalization of glycerol with acetone: Effect of crystallite size and the role of acidity of beta zeolite. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 396, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghbashlo, M.; Tabatabaei, M.; Rastegari, H.; Ghaziaskar, H.S.; Shojaei, T.R. On the exergetic optimization of solketalacetin synthesis as a green fuel additive through ketalization of glycerol-derived monoacetin with acetone. Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Hajinezhad, A.; Pourfayaz, F.; Ahmadi, M.H. The effect of hydrodynamic and ultrasonic cavitation on biodiesel production: An exergy analysis approach. Energy 2018, 160, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, F.G.; Ollero, P.; Serrera, A.; Galera, S. Process integration and exergy analysis of the autothermal reforming of glycerol using supercritical water. Energy 2012, 42, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, F.G.; Ollero, P.; Serrera, A.; Galera, S. An energy and exergy analysis of the supercritical water reforming of glycerol for power production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjaji, N.; Baccar, I.; Pons, M.-N. Energy and exergy analysis as tools for optimization of hydrogen production by glycerol autothermal reforming. Renew. Energy 2014, 71, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presciutti, A.; Asdrubali, F.; Baldinelli, G.; Rotili, A.; Malavasi, M.; Di Salvia, G. Energy and exergy analysis of glycerol combustion in an innovative flameless power plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3817–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, Z.A.; Krouk, V.S.; Pilyuk, Y.E.; Maksimuk, Y.V.; Karpushenkava, L.S.; Krivova, M.G. Exergy analysis of canola-based biodiesel production in Belarus. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 138, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.M.; Muraza, O.; Galadima, A.; Yoshioka, M.; Yamani, Z.H.; Yokoi, T. Choreographing boron-aluminum acidity and hierarchical porosity in *BEA zeolite by in-situ hydrothermal synthesis for a highly selective methanol to propylene catalyst. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 273, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadima, A.; Muraza, O. Hydrocracking catalysts based on hierarchical zeolites: A recent progress. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 61, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Wei, R.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Shen, P.; Wang, H.; Gao, L.; Xiao, G. Synergy effect between hierarchical structured and Sn-modified H[Sn, Al]ZSM-5 zeolites on the catalysts for glycerol aromatization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 257, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliczak-Guzik, A. Hierarchical zeolites: Synthesis and catalytic properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 259, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possato, L.G.; Chaves, T.F.; Cassinelli, W.H.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V.; Martins, L. The multiple benefits of glycerol conversion to acrolein and acrylic acid catalyzed by vanadium oxides supported on micro-mesoporous MFI zeolites. Catal. Today 2017, 289, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, G.; Ji, P.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.-G.; Chen, L.; Wu, P. Fast synthesis of hierarchical Beta zeolites with uniform nanocrystals from layered silicate precursor. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 248, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Cui, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Cui, Q.; Yang, C.; Shan, H. Hierarchical ZSM-11 with intergrowth structures: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties. J. Energy Chem. 2013, 22, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadima, A.; Muraza, O. In situ fast pyrolysis of biomass with zeolite catalysts for bioaromatics/gasoline production: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 338–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawah, A.-R.; Malaibari, Z.O.; Muraza, O. Syngas production from CO2 reforming of methane over Ni supported on hierarchical silicalite-1 fabricated by microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 13177–13189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraza, O.; Bakare, I.A.; Tago, T.; Konno, H.; Adedigba, A.-L.; Al-Amer, A.M.; Yamani, Z.H.; Masuda, T. Controlled and rapid growth of MTT zeolite crystals with low-aspect-ratio in a microwave reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hanache, L.; Lebeau, B.; Nouali, H.; Toufaily, J.; Hamieh, T.; Daou, T.J. Performance of surfactant-modified *BEA-type zeolite nanosponges for the removal of nitrate in contaminated water: Effect of the external surface. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammoury, H.; Toufaily, J.; Cherry, K.; Hamieh, T.; Pouilloux, Y.; Pinard, L. Desilication of *BEA zeolites using different alkaline media: Impact on catalytic cracking of n-hexane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 267, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Rodrigues, R.; Galhardo, T.S.; Carvalho, W.A. Highly selective acetalization of glycerol with acetone to solketal over acidic carbon-based catalysts from biodiesel waste. Fuel 2016, 181, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Miao, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; Si, W.; Zhuo, S. One-pot synthesis of ZrMo-KIT-6 solid acid catalyst for solvent-free conversion of glycerol to solketal. Fuel 2018, 233, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; He, D. Transformation of CO2 and glycerol to glycerol carbonate over CeO2ZrO2 solid solution—Effect of Zr doping. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 118, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaika, A.; Kozłowski, M. Glycerol conversion towards valuable fuel blending compounds with the assistance of SO3H-functionalized carbon xerogels and spheres. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 184, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Lei, Y.; Lan, G.; Liu, D.; Li, G.; Bai, R. Synthesis of glycerol carbonate from glycerol and dimethyl carbonate over DABCO embedded porous organic polymer as a bifunctional and robust catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 562, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oger, N.; Lin, Y.F.; Le Grognec, E.; Rataboul, F.; Felpin, F.-X. Graphene-promoted acetalisation of glycerol under acid-free conditions. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, D.; Sreenivasulu, P.; Konathala, L.S.; Kumar, M.; Viswanadham, N. Acid functionalized carbon–silica composite and its application for solketal production. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 179, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayoon, M.S.; Hameed, B.H. Solventless acetalization of glycerol with acetone to fuel oxygenates over Ni–Zr supported on mesoporous activated carbon catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 464, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebian-Kiakalaieh, A.; Amin, N.A.S.; Rajaei, K.; Tarighi, S. Oxidation of bio-renewable glycerol to value-added chemicals through catalytic and electro-chemical processes. Appl. Energy 2018, 230, 1347–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chol, C.G.; Dhabhai, R.; Dalai, A.K.; Reaney, M. Purification of crude glycerol derived from biodiesel production process: Experimental studies and techno-economic analyses. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 178, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.S.; Moghavvemi, M.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Techno-economic analysis of an optimized photovoltaic and diesel generator hybrid power system for remote houses in a tropical climate. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 69, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantozzi, F.; Frassoldati, A.; Bartocci, P.; Cinti, G.; Quagliarini, F.; Bidini, G.; Ranzi, E.M. An experimental and kinetic modeling study of glycerol pyrolysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norhasyima, R.S.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Advances in CO2 utilization technology: A patent landscape review. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 26, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, V.C.; Harvey, A.P. Continuous reactive coupling of glycerol and acetone—A strategy for triglyceride transesterification and in-situ valorisation of glycerol by-product. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, F.; Saxena, S.K.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.A.H.; Baawain, M.; Al-Abri, M.; Viswanadham, N.; Kumar, G.; Abu-Jrai, A.M. Valorization of waste “date seeds” bio-glycerol for synthesizing oxidative green fuel additive. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.S.; Selvakannan, P.R.; Chary, K.V.R.; Kantam, M.L.; Bhargava, S.K. Solvent-free microwave-assisted synthesis of solketal from glycerol using transition metal ions promoted mordenite solid acid catalysts. Mol. Catal. 2017, 434, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifoi, A.R.; Agachi, P.Ş.; Pap, T. Glycerol acetals and ketals as possible diesel additives. A review of their synthesis protocols. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remón, J.; Ruiz, J.; Oliva, M.; García, L.; Arauzo, J. Effect of biodiesel-derived impurities (acetic acid, methanol and potassium hydroxide) on the aqueous phase reforming of glycerol. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 299, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Conversion | Catalyst | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Etherification | Li/clay | Diglycerol isomer was also increased from 35% to 55% while the selectivity to aa isomer was decreased from 65% to 35% | [21] |
| Conversion glycerol to allyl Alcohol | K/Al2O3-ZrO2-FeOX Alkali metals supported to ZrO2-FeOx | Improvement in conversion With the increase of the K content in the catalyst, allyl alcohol yield increased up to 27%-C | [22] |
| Allyl alcohol | ZSM-5-supported iron catalysts | The prepared catalyst performed better for allyl alcohol production as compared to catalysts synthesized by other methods | [23] |
| Conversion alcohol to glycerol carbonate | Mg3−xAl1Cux | Transesterification of glycerol to glycerol carbonate (GC) increased to 96% of yields | [24] |
| Acetalization glycerol with acetone | MoPO supported to SBA-15 | A 40% MoPO/SBA-15 showed a conversion of 100% and selectivity of 98% | [25] |
| Acetalization of glycerol with butanal | BEA zeolite with the ratio Si/Al of 40 | Showed conversion of 88% and selectivity 80% of five member rings acetal (2-propyl-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methanol | [26] |
| Glycerol etherification with benzaldehyde | Cationic acidic resin | Achieving conversion of 93% and selectivity above 80% of 2-phenyl-1,3-di-oxan-5-ol | [27] |
| Acetalization of glycerol with mono-substitude benzaldehyde | MoOx/TiO2-ZrO2 | Glycerol conversion to 1,3-dioxolane (74%) within 30 min | [28] |
| Acetalization of glycerol with acetone | MoO3 and WO3 supported to SnO2 | A 71% glycerol conversion and a 96% solketal selectivity were achieved. | [29] |
| Others | Heteropolyacid | Resin | Meso-SiO2 | Double Layer Hydroxide and Clay | Zeolites |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co/CNT | Si-W (tungstosilisic) | Amberlyst | KIT-6 | ZrO2 dolomite | Zeolite X |
| Na-lignosulfonate | HMQ-SJW | Cat. Ex. | Me-SBA-5J | Nb, AlOx | VnOx/FER MOR |
| SnF2 | H3PW12040 | Amberlyst-46 | Hf-SBA-15 | Nb oxy OH | BEA |
| Ionic liquid | Amberlyst-46 | Mo-SBA-15 | COK-S | Hierarchical | |
| Carbon | KU-2-8 | Sn TUD-1 | MgLDH | BEA, MOR | |
| Lewatit GF101 | Al-MCM-41 | Montmorillonite | ZSM-5 (MFI) | ||
| Sulfonic | Ga-MCM-4 | DeAl BEA | |||
| Amberlyst-35 | Acidity BEA |
| Source | Catalyst | Condition | Conversion | Selectivity to Solketal | Remark | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerol and Acetone | Amberlyst-15 | 50 °C | 92% | 96% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:2, 7.0 g of amberlyst-15 in 96 min | [32] |
| Glycerol and Acetone | Amberlyst-46 | 60 °C | 84% | 97% | %1 (w/w) catalyst, 30 min | [33] |
| Glycerol and Acetone | Amberlyst DPT-1 | 70 °C | 97% | 98% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:2 at ambient pressure | [34] |
| Glycerol and Acetone | DT-851 sulfonic acid resin | 58 °C | 95% | 99% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:20, catalyst DT-851 sulfonic acid resin dosage is 5% (wt., calculated by glycerol), reaction time is 2 h. | [35] |
| Glycerol and acetone | Amberlyst-36 | 25 °C | 85%–97% | 99% | At 10 barr and 25 °C, A36 was a highly active catalyst allowing good-to-excellent conversion (85%–97%) and selectivity (99%) when either pure or wet glycerol was used as a reagent. | [36] |
| Source | Catalyst | Condition | Conversion | Selectivity to Solketal | Remark | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerol and Acetone | Cs 2.5/KIT-6 | 25 °C | 95% in 15 min | 98% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:6, catalyst loading was 5 wt.%. | [42] |
| Glycerol and formaldehyde | Propylsulfonic Acid Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica | 90 °C | 91.5 in 8 h | 98% | Glycerol:formaldehyde = 1:1.5 with 4 wt.% catalyst loading | [43] |
| Glycerol and Acetone | arenesulfonic acid-functionalized silica | 70 °C | 84% in 30 min | 81% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:6 | [44] |
| methyl acetate to glycerol | Sulfonic acid-functionalized mesostructured SBA-15 silicas | 170 °C | 99.5% in 4 h | 74.2% | Glycerol:methyl acetate = 1:50 and catalyst loading (7.5 wt.% based on glycerol) | [45] |
| Glycerol and acetone | A sulfonic acid-functionalized mesoporous polymer (MP-SO3H) | 30 °C | 94% | 98.5% | The MP-SO3H catalyst performed better than other conventional solid acid catalysts | [46] |
| Glycerol and acetone | Zr-TUD-1 | 80 °C | 64% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:2, 25 mg of catalyst, at room temperature, for 6 h. | [37] | |
| Glycerol and acetone | Hf-TUD-1 | 80 °C | 65% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:2, 25 mg of catalyst, at room temperature, for 6 h. | [37] |
| Source | Catalyst | Condition | Conversion | Selectivity to Solketal | Remark | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerol and acetone | Montmorilonite modified by HNO3 | T = 25 °C | 94% | 95.4% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:4, 10 mg of catalyst, time at 10 min | [53] |
| Glycerol and benzaldehyde | K10 Montmorillonite | T = 40 °C | 83% | 99% | Glycerol:benzaldehyde dimethyl acetal = 1:1.1 at 6 h. | [17] |
| Glycerol and acetone | K10 clays | T = 30 °C | 87% | 85% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:6, catalyst loading was 3 wt.% of total reactant weight, time at 120 min | [60] |
| Glycerol and formaldehyde | K10 Montmorillonite | T = 70 °C | 80% | - | Glycerol: formaldehyde = 1:1.2 | [61] |
| Glycerol and acetone | K10 Montmorillonite | T = 40 °C | 69% | 68% | Glycerol:acetone = 2:6, P=600 psi, The amount of catalyst in each run was determined by the selected weight hourly space velocity (WHSV) at 4 h−1 | [48] |
| Source | Catalyst | Condition | Conversion | Selectivity to Solketal | Remark | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerol and acetone | hierarchical (micro-mesoporous) MFI zeolites (pore diameter 0.51–0.55 nm) | T = 70 °C | 80% | 100% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:1, catalyst in the amount of 1% related to glycerol. | [64] |
| Glycerol and acetone | H-B-1 zeolites | T = 28 °C (room temperature) | 86% | 98.5% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:2, catalyst amount = 5 wt.% referred to glycerol in 1 h. | [73] |
| Glycerol and acetone | Dealumination of BEA Zeolites | T = 30 °C | 80% | 100% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:1, t = 30 min, catalyst loading was 0.5 g | [72] |
| Glycerol and acetone | H-Zeolite (pore size 4.10 nm) | T = 70 °C | 75% | 92% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:3 were used with 0.05 g of catalyst for 2 h | [65] |
| Glycerol and acetone | H-BEA Zeolite | T = 60 °C | 70% | 97.9% | Glycerol:acetone = 1:4, catalyst amount was loading at 5 wt.% for 1 h. | [69] |
| Source | Catalyst | Condition | Conversion | Selectivity to Solketal | Remark | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| acetone and glycerol | acid functionalized activated carbon | Room temperature, glycerol to acetone molar ratio of 1:4 | 97% | 96% | The highest number and strength of acid sites generated by the acid treatments onto activated carbon gave better yield and selectivity | [39] |
| glycerol with benzaldehyde at | Graphene | 100 °C and 120 °C | 97% | Graphene catalyst produced 76% yield at 100 °C and 85% yield at 120 °C, selectivity 100% | [98] | |
| acetone and glycerol | sulfonated carbon-silica-meso composite materials | acetone and glycerol molar ratio of 1:6, re- fluxed at 70 °C | 82% | 99% | [99] | |
| acetone and glycerol | acidic carbon-based catalysts | 80% | 95% | [93] | ||
| acetone and glycerol | Ni-Zr supported on mesoporous activated carbon | Room Temperature glycerol/acetone ratio of 1:10 | 75% | 100% | Conversion and selectivity are affected by glycerol/acetone ratio and temperature | [100] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fatimah, I.; Sahroni, I.; Fadillah, G.; Musawwa, M.M.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Muraza, O. Glycerol to Solketal for Fuel Additive: Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts. Energies 2019, 12, 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12152872
Fatimah I, Sahroni I, Fadillah G, Musawwa MM, Mahlia TMI, Muraza O. Glycerol to Solketal for Fuel Additive: Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts. Energies. 2019; 12(15):2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12152872
Chicago/Turabian StyleFatimah, Is, Imam Sahroni, Ganjar Fadillah, Muhammad Miqdam Musawwa, Teuku Meurah Indra Mahlia, and Oki Muraza. 2019. "Glycerol to Solketal for Fuel Additive: Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts" Energies 12, no. 15: 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12152872
APA StyleFatimah, I., Sahroni, I., Fadillah, G., Musawwa, M. M., Mahlia, T. M. I., & Muraza, O. (2019). Glycerol to Solketal for Fuel Additive: Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts. Energies, 12(15), 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12152872