Kinetic Characterization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Apple Pomace as Feedstock for a Sugar-Based Biorefinery
Abstract
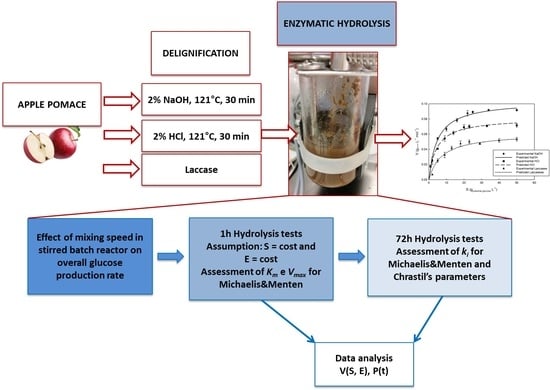
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material and Eenzymes
2.2. Biomass Pretreatment
2.2.1. Chemical Delignification
2.2.2. Laccase Catalysed Delignification
2.3. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Polysaccharides
2.4. Effect of Mixing Speed
2.5. Effect of Substrate Concentration
2.6. Effect of Product Inhibition
2.7. Analytical Methods
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Raw and Pretreated Biomass
3.2. Effect of Mixing Rate on Kinetics
3.3. Effect of Substrate Concentration on Kinetics
3.4. Effect of Product Inhibition on Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parajuli, R.; Dalgaard, T.; Jørgensen, U.; Adamsen, A.P.; Trydeman Knudsen, M.; Birkved, M.; Gylling, M.; KofodSchjørring, J. Biorefining in the prevailing energy and materials crisis: A review of sustainable pathways for biorefinery value chains and sustainability assessment methodologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arora, A.; Banerjee, J.; Vijayaraghavan , R.; Mac Farlane, D.; Patti, A.F. Process design and techno-economic analysis of an integrated mango processing waste biorefinery. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 116, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Freitas dos Santos, A.C.; Ximenes, E.; Ladisch, M. Proteins at heterogeneous (lignocellulose) interfaces. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2017, 18, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratto, B.; Alencar de Souza, R.B.; Sousa, R., Jr.; Gonçalves da Cruz, A.J. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Pretreated Sugarcane Straw: Kinetic Study and Semi-Mechanistic Modeling. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 178, 1430–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, B.T.; Al-Shannag, M.; Alnaief, M.; Singh, L.; Singsaas, E.; Alkasrawi, M. Production of multiple biofuels from Whole Camelina Material: A renewable energy crop. BioResources 2019, 13, 4870–4883. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, U.L.; Yu, E.K.C.; Campbell, N.; Saddler, J.N. Column cellulose hydrolysis reactor: An efficient cellulose hydrolysis reactor with continuous cellulase recycling. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1986, 25, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusakov, A.; Sinitsyn, A.P.; Klyosov, A.A. A Theoretical Comparison of the Reactors for the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Cellulose. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1987, 29, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Jameel, H.; Phillips, R.; Chang, H. Split addition of enzymes in enzymatic hydrolysis at high solids concentration to increase sugar concentration for bioethanol production. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Quiroga, A.; Bula Silvera, A.; Vasquez Padilla, R.; da Costa, A.C.; Maciel Filho, A.C. Continuous and semicontinuous reaction systems for high-solids enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, Q.; Cheng, G. Deconstruction of corncob by steam explosion pretreatment: Correlations between sugar conversion and recalcitrant structures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeoh, T.; Cardona, J.M.; Karuna, N.; Mudinoor, A.R.; Nill, J. Mechanistic Kinetic Models of Enzymatic Cellulose Hydrolysis—A Review. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, P.; Hall, M.; Realff, M.J.; Lee, J.H.; Bommarius, A.S. Modelling cellulase kinetics on lignocellulosic substrates. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo, F.; Lis, M.J.; Colom, X.; López-Mesas, M.; Valldeperas, J. Effect of alkali pretreatment on cellulose hydrolysis of wheat straw: Kinetic study. Proc. Biochem. 2005, 40, 3360–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.L.; Sousa, R., Jr.; Rodríguez-Zúñiga, U.F.; Suarez, C.A.G.; Rodrigues, D.S.; Giordano, R.C.; Giordano, R.L.C. Kinetic study of the enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2005, 30, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Procentese, A.; Raganati, F.; Olivieri, G.; Russo, M.E.; Rehmann LMarzocchella, A. Deep eutectic solvents pretreatment of agro industrial food waste. Biotech. Biofuels 2018, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adney, B.; Baker, J. Measurement of Cellulase Activities; Report No.: NREL/TP-510-42628; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Denver, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass; Report No.: NREL/TP-510-42618; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Denver, CO, USA, July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chrastil, J. Enzymic product formation curves with the normal or diffusion limited reaction mechanism and in the presence of substrate receptors. Int. J. Biochem. 1988, 20, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Barrett, D.M.; Delwiche, M.J.; Stroeve, P. Methods for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient hydrolysis and biofuel production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 3713–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niglio, S.; Procentese, A.; Russo, M.E.; Piscitelli, A.; Marzocchella, A. Integrated enzymatic pretreatment and hydrolysis of apple pomace in a bubble column bioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 150, 107306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procentese, A.; Raganati, F.; Olivieri, G.; Russo, M.E.; Marzocchella, A. Pre-treatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of lettuce residues as feedstock for bio-butanol production. Biomass. Bioenergy 2017, 96, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Pre-Treatment | Recovery (%) | Composition (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucans | Xylans and Arabinans | AIL | ASL | ||
| Raw | 100 | 21.2 ± 0.01 | 14.75 ± 0.03 | 16.5 ± 0.55 | 2.1 ± 0.34 |
| NaOH | 60 | 28.0 ± 0.01 | 0.8 ± 0.05 | 5.0 ± 0.53 | n.d |
| HCL | 50 | 25.0 ± 0.01 | 0.2 ± 0.06 | 9.0 ± 0.43 | n.d |
| Laccases | 75 | 22.5 ± 0.01 | 12.04 ± 0.03 | 14.5 ± 0.54 | n.d |
| Pre-Treatment | Glucans (%) | Michaelis and Menten Model | |
|---|---|---|---|
| KM (g L−1) | VMax (g L−1 min−1) | ||
| NaOH | 28.0 | 5.5 ± 0.6 | 0.108 ± 0.003 |
| HCl | 25.0 | 4.8 ± 0.6 | 0.084 ± 0.003 |
| Laccase | 22.5 | 9.0 ± 2.1 | 0.067 ± 0.006 |
| Biomass Pre-Treatment | Glucans (%) | Lignin (%) | M&M with Product Inhibition | Chrastil’s Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vmax (g L−1 min−1) | KM (g L−1) | Ki (g L−1) | k (L g−1 min−1) | n (-) | |||
| NaOH | 28.0 | 5.0 | 0.30 | 5.5 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 2·10−3 ± 1.2·10−4 | 0.41 ± 0.02 |
| HCl | 25.5 | 9.0 | 0.24 | 4.8 | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 1.8·10−3 ± 1.2·10−4 | 0.63 ± 0.03 |
| Laccase | 22.5 | 14.5 | 0.19 | 9.0 | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 1.1·10−3 ± 8·10−5 | 0.58 ± 0.03 |
| Biomass | Pre-Treatments | Residual Lignin (%) | Chrastil’s Model | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k (L g−1 min−1) | n (-) | ||||
| Sugarcane Bagasse | 121 °C 30 min in 4% NaOH + Steam explosion | 5.4 | 2·10−5 | 0.6 | [12] |
| Sugarcane Straw | 195 °C 10min + 121 °C 30 min in 4% NaOH | 5.7 | Between 3.52·10−5 and 7.4 10−5 | 0.4 | [13] |
| Apple Pomace | 121 °C 30 min in 2% NaOH | 5.0 | 2·10−3 | 0.4 | Present work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Procentese, A.; Russo, M.E.; Di Somma, I.; Marzocchella, A. Kinetic Characterization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Apple Pomace as Feedstock for a Sugar-Based Biorefinery. Energies 2020, 13, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051051
Procentese A, Russo ME, Di Somma I, Marzocchella A. Kinetic Characterization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Apple Pomace as Feedstock for a Sugar-Based Biorefinery. Energies. 2020; 13(5):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051051
Chicago/Turabian StyleProcentese, Alessandra, Maria Elena Russo, Ilaria Di Somma, and Antonio Marzocchella. 2020. "Kinetic Characterization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Apple Pomace as Feedstock for a Sugar-Based Biorefinery" Energies 13, no. 5: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051051
APA StyleProcentese, A., Russo, M. E., Di Somma, I., & Marzocchella, A. (2020). Kinetic Characterization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Apple Pomace as Feedstock for a Sugar-Based Biorefinery. Energies, 13(5), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051051