Psychrophilic Full Scale Tubular Digester Operating over Eight Years: Complete Performance Evaluation and Microbiological Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
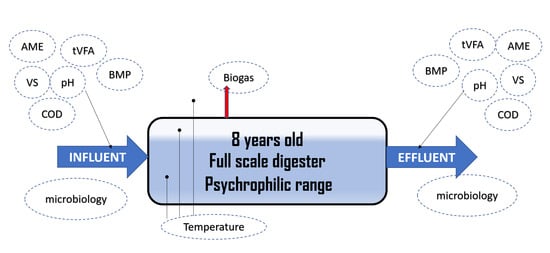
2.2. Description of Rural Biogas Plant
2.3. Monitoring Temperature in the Biodigester
2.4. Diagnosis of Anaerobic Digestion in the Pig Farm Digester
2.4.1. Biochemical Assays
2.4.2. Microbiological Analysis of Pig Farm Digester
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Behavior of the Digester
3.2. Changes in Control Parameters in Pig Farm Digester
Process Efficiency and Biogas Quality
3.3. Microbiological Analysis
3.4. Pathogen Reduction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martí-Herrero, J.; Alvarez, R.; Rojas, M.; Aliaga, L.; Céspedes, R.; Carbonell, J. Improvement through low cost biofilm carrier in anaerobic tubular digestion in cold climate regions. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfí, M.; Martí-Herrero, J.; Garwood, A.; Ferrer, I. Household anaerobic digesters for biogas production in Latin America: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sambusiti, C.; Monlau, F.; Ficara, E.; Musatti, A.; Rollini, M.; Barakat, A.; Malpei, F. Comparison of various post-treatments for recovering methane from agricultural digestate. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 137, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilayn, F.; Jimenez, J.; Martel, J.-L.; Rouez, M.; Crest, M.; Patureau, D. First fertilizing-value typology of digestates: A decision-making tool for regulation. Waste Manag. 2019, 86, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Escalante, H.; Jaimes-Estévez, J.; Díaz, L.; Vecino, K.; Rojas, G.; Mantilla, L. Low cost digester monitoring under realistic conditions: Rural use of biogas and digestate quality. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 239, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dev, S.; Saha, S.; Kurade, M.B.; Salama, E.-S.; El-Dalatony, M.M.; Ha, G.-S.; Chang, S.W.; Jeon, B.-H. Perspective on anaerobic digestion for biomethanation in cold environments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohoo, C.; Guernsey, J.R.; Gibson, M.D.; Van Leeuwen, J. Impact of biogas digesters on cookhouse volatile organic compound exposure for rural Kenyan farmwomen. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 25, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.K.; Yang, G. Determination of bicarbonate and total volatile acid concentration in anaerobic digesters using a simple titration. Water Environ. Res. 1992, 64, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, F.; Borja, R.; Cacho, J.; Mumme, J.; Orupõld, K.; Esteves, S.; Noguerol-Arias, J.; Picard, S.; Nielfa, A.; Scherer, P.; et al. First international comparative study of volatile fatty acids in aqueous samples by chromatographic techniques: Evaluating sources of error. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfì, M.; Ferrer-Martí, L.; Pérez, I.; Flotats, X.; Ferrer, I. Codigestion of cow and guinea pig manure in low-cost tubular digesters at high altitude. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 2066–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotidis, I.A.; Laranjeiro, T.F.V.C.; Angelidaki, I. Alternative co-digestion scenarios for efficient fixed-dome reactor biomethanation processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holliger, C.; Alves, M.; Andrade, D.; Angelidaki, I.; Astals, S.; Baier, U.; Bougrier, C.; Buffière, P.; Carballa, M.; De Wilde, V.; et al. Towards a standardization of biomethane potential tests. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martí-Herrero, J.; Flores, T.; Alvarez, R.; Pérez, D. How to report biogas production when monitoring small-scale digesters in field. Biomass- Bioenergy 2016, 84, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrigault, T.; Weatherford, V.; Martí-Herrero, J.; Poggio, D. Towards thermal design optimization of tubular digesters in cold climates: A heat transfer model. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 124, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, G. Cryosphere and Psychrophiles: Insights into a Cold Origin of Life? Life 2017, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martí-Herrero, J.; Alvarez, R.; Flores, T. Evaluation of the low technology tubular digesters in the production of biogas from slaughterhouse wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Jung, S.P.; Kim, S.-H. Enhancing anaerobic digestion for rural wastewater treatment with granular activated carbon (GAC) supplementation. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansing, S.; Víquez, J.; Martínez, H.; Botero, R.; Martin, J. Quantifying electricity generation and waste transformations in a low-cost, plug-flow anaerobic digestion system. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 34, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Herrero, J.; Ceron, M.; Garcia, R.; Pracejus, L.; Alvarez, R.; Cipriano, X. The influence of users’ behavior on biogas production from low cost tubular digesters: A technical and socio-cultural field analysis. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2015, 27, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfí, M.; Ferrer-Martí, L.; Velo, E.; Ferrer, I. Evaluating benefits of low-cost household digesters for rural Andean communities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulhane, M.; Khardenavis, A.; Karia, S.; Pandit, P.; Kanade, G.S.; Lokhande, S.; Vaidya, A.N.; Purohit, H.J. Biomethanation of vegetable market waste in an anaerobic baffled reactor: Effect of effluent recirculation and carbon mass balance analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martí-Herrero, J.; Soria-Castellón, G.; Diaz-De-Basurto, A.; Alvarez, R.; Chemisana, D. Biogas from a full scale digester operated in psychrophilic conditions and fed only with fruit and vegetable waste. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAteer, P.G.; Trego, A.C.; Thorn, C.; Mahony, T.; Abram, F.; O’Flaherty, V. Reactor configuration influences microbial community structure during high-rate, low-temperature anaerobic treatment of dairy wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IDEAM. GLACIARES. 2020. Available online: http://www.ideam.gov.co/web/otros-ecosistemas/investigacion-y-publicaciones?p_p_id=31_INSTANCE_x5l2d9DnqhhZ&p_p_lifecycle=0&p_p_state=normal&p_p_mode=view&p_p_col_id=column-1&p_p_col_pos=1&p_p_col_count=3&_31_INSTANCE_x5l2d9DnqhhZ_struts_action=%2Fimage_g (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water & Wastewater; Eaton, D.A., Franson, H.M.A., Eds.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Leamington, ON, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Purser, B.J.; Thai, S.-M.; Fritz, T.; Esteves, S.; Dinsdale, R.; Guwy, A. An improved titration model reducing over estimation of total volatile fatty acids in anaerobic digestion of energy crop, animal slurry and food waste. Water Res. 2014, 61, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astals, S.; Batstone, D.; Tait, S.; Jensen, P. Development and validation of a rapid test for anaerobic inhibition and toxicity. Water Res. 2015, 81, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, T.R.; Dowd, S.E.; Wolcott, R.D.; Sun, Y.; McReynolds, J.; Edrington, T.; Byrd, J.A.; Anderson, R.C.; Krueger, N.; Nisbet, D.J. Evaluation of the bacterial diversity in cecal contents of laying hens fed various molting diets by using bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, K.; Horikoshi, K. Rapid Detection and Quantification of Members of the Archaeal Community by Quantitative PCR Using Fluorogenic Probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5066–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sotres, A.; Tey, L.; Bonmatí, A.; Viñas, M. Microbial community dynamics in continuous microbial fuel cells fed with synthetic wastewater and pig slurry. Bioelectrochemistry 2016, 111, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Martín, M.I.; Sotres, A.; Alonso, R.M.; Díaz-Marcos, J.; Morán, A.; Escapa, A. Assessing anodic microbial populations and membrane ageing in a pilot microbial electrolysis cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 17304–17315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Herrero, J.; Chipana, M.; Cuevas, C.; Paco, G.; Serrano, V.; Zymla, B.; Heising, K.; Sologuren, J.; Gamarra, A. Low cost tubular digesters as appropriate technology for widespread application: Results and lessons learned from Bolivia. Renew. Energy 2014, 71, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Molano, L.D.P.; Parrales-Ramírez, Y.A.; Escalante-Hernández, H. Co-digestión anaerobia de estiércoles bovino, porcino y equino como alternativa para mejorar el potencial energético en digestores domésticos. Rev. ION 2019, 32, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Huang, G.; An, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Xin, X.; Shen, J.; Agnew, J. Anaerobic digestion of livestock manure in cold regions: Technological advancements and global impacts. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza, G.; Chará, J.; Conde, N.; Giraldo, S.; Giraldo, L. Evaluation of polyethylene and PVC tubular biodigesters in the treatment of swine wastewater. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2002, 14. Available online: http://www.lrrd.org/lrrd14/1/Pedr141.htm (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Lansing, S.; Martin, J.F.; Botero, R.B.; Da Silva, T.N.; Da Silva, E.D. Methane production in low-cost, unheated, plug-flow digesters treating swine manure and used cooking grease. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4362–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardi, M.H. Temperature. In The Microbiology of Anaerobic Digesters; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Nozhevnikova, A.N.; Rebak, S.; Kotsyurbenko, O.R.; Parshina, S.; Holliger, C.; Lettinga, G. Anaerobic production and degradation of volatile fatty acids in low temperature environments. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.T.; Cobb, S.A.; Bolte, J.P. Using Volatile Fatty Acid Relationships to Predict Anaerobic Digester Failure. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 0496–0501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes-Estévez, J.; Castro, L.; Escalante, H.; Carrillo, D.; Portillo, S.; Sotres, A.; Morán, A. Cheese whey co-digestion treatment in a tubular system: Microbiological behaviour along the axial axis. Biomass Convers Biorefin. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenigun, O.; Demirel, B. Ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion: A review. Process. Biochem. 2013, 48, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, P.; Shaw, B. Inhibition of methane production by Methanobacterium formicicum. Water Res. 1976, 10, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massé, D.I.; Rajagopal, R.; Singh, G. Technical and operational feasibility of psychrophilic anaerobic digestion biotechnology for processing ammonia-rich waste. Appl. Energy 2014, 120, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Guo, Y. Comparative study of reactor performance and microbial community in psychrophilic and mesophilic biogas digesters under solid state condition. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 125, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, G.K.; Chen, L. Comparison on batch anaerobic digestion of five different livestock manures and prediction of biochemical methane potential (BMP) using different statistical models. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Cummins, C.S.; Johnson, J.L. Family Propionibacteriaceae: The Genus Propionibacterium. Prokaryotes 2006, 2006, 400–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuever, J. The Family Syntrophaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Deltaproteobacteria and Epsilonproteobacteria; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 9783642390, pp. 1–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Tang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, J.; Tang, J. Methanogenic Activity and Microbial Community Structure in Response to Different Mineralization Pathways of Ferrihydrite in Paddy Soil. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Prokaryotes. The Prokaryotes; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 2014, pp. 298–305. [Google Scholar]
- McIlroy, S.J.; Kirkegaard, R.H.; Dueholm, M.S.; Fernando, E.; Karst, S.M.; Albertsen, M.; Nielsen, P.H. Culture-Independent Analyses Reveal Novel Anaerolineaceae as Abundant Primary Fermenters in Anaerobic Digesters Treating Waste Activated Sludge. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Enviromental Regulations and Technology. Control of Pathogens and Vector Attraction in Sewage Sludge; United States Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Ju, F.; Liping, M.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, D.; Zhang, T. Antibiotic resistance genes and human bacterial pathogens: Co-occurrence, removal, and enrichment in municipal sewage sludge digesters. Water Res. 2016, 91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Name | Data | Location | Equipment | Resolution | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tamt (sensor 1) | ambient temperature | around the greenhouse | HOBO UA-001-08 Pendant® Waterproof Data Logger | 0.14° | ±0.53 °C from 0 °C to 50 °C |
| Tga (sensor 2) | air temperature/solar luminosity | inside greenhouse | HOBO UA-002-64 Pendant® Temperature/Light 64K Data Logger | 0.14°/Designed for relative light levels | |
| Ts (sensor 3) | Slurry temperature | one meter into the biodigester bag | HOBO UA-001-08 Pendant® Waterproof Data Logger | 0.14° | |
| Tgr (sensor 4) | Soil temperature | one meter underground | HOBO UA-001-08 Pendant® Waterproof Data Logger | 0.14° |
| Operational Conditions | Units | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Working years | years | 8 | |
| Volume | m3 | 103.1 | |
| Daily mean load | m3/d | 4.16 | |
| Mean slurry temperature | °C | 17.7 | |
| Mean ambient temperature | °C | 16.6 | |
| ORL | kg VS/m3digester d | 0.34 to 0.76 (mean 0.52) | |
| HRT | d | 25 | |
| Parameters | Units | Influent value | Effluent value |
| COD | g COD/L | 9.94 ± 3.25 | 3.31 ± 1.20 |
| VS | gVS/kg | 12.74 ± 3.52 | 2.86 ± 1.2 |
| pH | --- | 6.15 ± 0.77 | 7.6 ± 0.3 |
| tVFA | g CODVFA/L | 2.9 ± 1.3 | 0.3 ± 0.08 |
| TA | g CaCO3/L | 3.72 ± 1.3 | 1.95 ± 0.25 |
| Ammonium | g NH4-N/L | 0.34 ± 0.05 | 0.28 ± 0.03 |
| BMP | Nm3 CH4/kgVS | 0.46 ± 0.017 | 0.13 ± 0.06 |
| Coliforms | × 106 CFU/mL | 3.99 | 3.57 |
| Performance characterization | |||
| CH4 | % | 63.1 ± 5.3 | |
| SMP | Nm3 CH4/kg VS | 0.40 | |
| MPR | Nm3 CH4/m3digester d | 0.21 | |
| COD reduction | % | 66.7% | |
| VS reduction | % | 77.6% | |
| Coliforms reduction | % | 10.5% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaimes-Estévez, J.; Zafra, G.; Martí-Herrero, J.; Pelaz, G.; Morán, A.; Puentes, A.; Gomez, C.; Castro, L.d.P.; Escalante Hernández, H. Psychrophilic Full Scale Tubular Digester Operating over Eight Years: Complete Performance Evaluation and Microbiological Population. Energies 2021, 14, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010151
Jaimes-Estévez J, Zafra G, Martí-Herrero J, Pelaz G, Morán A, Puentes A, Gomez C, Castro LdP, Escalante Hernández H. Psychrophilic Full Scale Tubular Digester Operating over Eight Years: Complete Performance Evaluation and Microbiological Population. Energies. 2021; 14(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaimes-Estévez, Jaime, German Zafra, Jaime Martí-Herrero, Guillermo Pelaz, Antonio Morán, Alejandra Puentes, Christian Gomez, Liliana del Pilar Castro, and Humberto Escalante Hernández. 2021. "Psychrophilic Full Scale Tubular Digester Operating over Eight Years: Complete Performance Evaluation and Microbiological Population" Energies 14, no. 1: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010151
APA StyleJaimes-Estévez, J., Zafra, G., Martí-Herrero, J., Pelaz, G., Morán, A., Puentes, A., Gomez, C., Castro, L. d. P., & Escalante Hernández, H. (2021). Psychrophilic Full Scale Tubular Digester Operating over Eight Years: Complete Performance Evaluation and Microbiological Population. Energies, 14(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010151