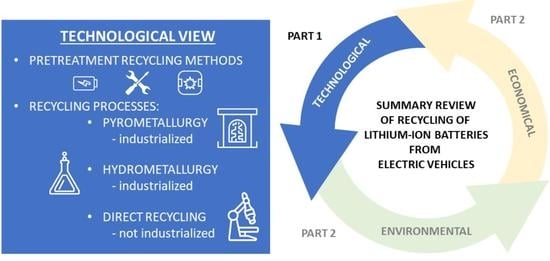
Literature Review, Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries from Electric Vehicles, Part I: Recycling Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Pretreatment of the Recycling Processes
3.1.1. Laboratory-Scale Pretreatment Methods
- Discharging
- 2.
- Dismantling
- 3.
- Separation
- High-temperature calcination is carried out between 350 °C and 600 °C to decompose the organic binders, additives, and electrolyte and release the active material in a powder form;
- Dissolution of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) supported using heat and/or sonication, subsequently following processes of drying and filtration;
3.1.2. Industrial-Scale Pretreatment Methods
- Discharging
- Distilled water;
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) water-based solution (using 10 wt% NaCl solution ensures the best discharging conditions; the extraction of the valuable metals is maximal);
- Alternative research-focused solutions such as potassium chloride (KCl), sodium nitrate (NaNO3), manganese(II) sulfate (MnSO4), magnesium sulfate (MgSO4), and iron(II) sulfate (FeSO4) [11].
- 2.
- Dismantling (disassembly)
- 3.
- Comminution (mechanical treatment)
- Dry processes—crushing is conducted in a gastight unit in an inert atmosphere, generally in a two step-method in a low-speed rotary mill and high-speed impact mill [23], or a combination of the hammer crushing combined with a two-blade rotor crusher that can maximize the efficiency of this process [11];
- Wet processes—the comminution equipment is a blade crusher with a water-based medium; firstly, the batteries are cut into pieces in a shear crusher, and the outputs are then crushed using the impact crusher. Then, water feeds into an entrance of the crusher and the particles in the form of a slurry carry the broken fractions through a selective sieve [11,23].
- 4.
- Classification (sieving)
- 5.
- Separation
- The magnetic separation removes the iron (Fe)-containing components and separates the cathode that contains active materials, the Al current collector, the anode, the steel casings, and the packaging [27].
- The eddy current separates the electrical conductors from the non-conductors or the minimally conductive materials. This method provides a high-ranking separation between Al and Cu in the electromagnetic fraction and Co and Li in the non-electromagnetic fragments [28].
- The differences in material electrical properties are utilized in the electrostatic separation. When an electric field is applied, charged or polarized particles are being moved and sorted from the LIBs crushed mass [29].
- 6.
- Dissolution
- 7.
- Thermal treatment
- A two-step thermal treatment followed by calcination. The furnace temperature range varies from process to process and affects the overall duration. The first thermal step can be conducted between 150–500 °C and lasts for 1–2 h; the second is between 500–900 °C and lasts for the same length [30,31]. The calcination at 600–700 °C lasts about 5 h [11].
3.2. Recycling Processes
3.2.1. Metallurgical and Mechanical Processes
3.2.2. Pyrometallurgical Process
3.2.3. Hydrometallurgical Process
- The first stage, “Leaching“, contains dissolving or leaching of the valuable metals by acid or basic agent in an oxidizing or reducing medium in leaching tanks [55,57]. Many inorganic acids such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and nitric acid (HNO3) [59] or organic acids, e.g., citric acid, malic acid, oxalic acid, etc., are usually used [60,61].
3.2.4. Direct Recycling Process
3.2.5. Special Recycling Methods
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Pretreatment of the Recycling Processes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Type | Publication Year | Summary Content |
| [12] | Review | 2021 | Three-step pretreatment method, pretreating flowchart of retired LIBs |
| [11] | Review | 2021 | The innovative approach to the classification of pretreatment, seven-step method |
| [103] | Article | 2020 | Investigation of incineration of LIB cell materials |
| [13] | Review | 2020 | Procedures of lab-scale and industrial-scale pretreatment |
| Metallurgical and Mechanical Processes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | Article | 2018 | Two main basic aspects of recycling battery packs: mechanical procedure and chemical recycling (metallurgical) |
| [15] | Article | 2017 | Recycling Metals from LIBs; mechanical separation; vacuum metallurgy |
| [10] | Review | 2020 | The current status of development, focusing on the metallurgical processing of LIB modules and cells |
| [104] | Article | 2017 | In-situ recovery from retired LIBs; vacuum metallurgy |
| [39] | Article | 2017 | The LithoRec projects; energy-efficient recycling mechanical process-steps |
| [105] | Article | 2019 | Mechanical and hydrometallurgical processes in HCl media |
| [106] | Article | 2020 | Leaching of LNCM cathodes in ascorbic acid lixiviant |
| [77] | Article | 2016 | Decomposing of LiFePO4 to host particles, recycling cathode powders using heat-treated at different temperatures |
| [61] | Article | 2018 | A ‘‘grave-to-cradle” process for the recycling of retired mixed-cathode materials |
| Pyrometallurgical Process | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Type | Publication Year | Summary Content |
| [107] | Article | 2020 | Erosion mechanism of refractories in a pyro-furnace |
| [43] | Review | 2021 | Overview on extractive pyrometallurgical options for recycling retired LIBs; lab-scale and industrial-scale processes |
| [72] | Review | 2020 | Overview on laboratory and industrial investigations and implementation of recycling |
| [24] | Article | 2020 | Recycling of pyrolyzed LIBs black mass, Li concentrates |
| [99] | Article | 2021 | Pyrometallurgical treating LCO in an Al2O3 and MgO crucible, concept for the treatment of LFP |
| [7] | Article | 2020 | Recycling processes; flowchart for pyrometallurgical recycling of Li-ion, Ni–Cd, and Ni–MH batteries. |
| [40] | Review | 2018 | A brief review of typical physical and chemical processes |
| [108] | Review | 2021 | Potential benefits of pretreatment; recycling processes |
| [21] | Review | 2008 | Structure of LIBs; overview of single and typical combined recycling processes; |
| [9] | Review | 2019 | Recycling process of EV LIBs |
| [17] | Review | 2021 | Reduction, reuse, and recycle (3R) of retired LIBs; pretreatment methods; technological processes |
| [48] | Review | 2018 | State-of-the-art research of recycling procedures; concept of suitability, LCA assessment of battery recycling |
| [109] | Article | 2019 | Quantitative analysis of the recycling methods |
| [100] | Review | 2020 | Improvements of recycling processes; a holistic design approach for LIBs |
| [18] | Review | 2019 | Overview of recycling commercial processes |
| [50] | Review | 2018 | Battery collection, transport, recycling commercial processes; End-of-Life (EOF) EV battery consideration |
| [110] | Article | 2016 | Recycling processes; hydrometallurgy for cathode recovery |
| [111] | Review | 2014 | Recycling procedures; problem and prospect analysis |
| Hydrometallurgical Process | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| [112] | Article | 2019 | Enhanced hydrometallurgical process; iron-precipitation, liquid-liquid extraction, innovative Li-Na separation |
| [62] | Article | 2013 | Overview of leaching and solvent extraction strategies |
| [44] | Article | 2020 | Experimental and modelling results for the hydrometallurgical recycling LiCoO2 cathodes; physicochemical model |
| [113] | Article | 2009 | A hydrometallurgical route based on leaching-crystallization steps for the separation of metals Al, Co, Cu and Li |
| [114] | Article | 2021 | Recycling processes; evaluation of effects of incineration on the leaching efficiency |
| [26] | Article | 2018 | Hydrometallurgy extraction from retired LIBs |
| [38] | Review | 2018 | The current status of hydrometallurgy recycling process; pretreatment methods |
| [115] | Article | 2015 | Efficient and product-oriented hydrometallurgical recycling of retired automotive batteries |
| [52] | Review | 2021 | Overview on the available hydrometallurgical technologies |
| [113] | Article | 2020 | Recycling process of LFP-type of LIBs |
| [116] | Article | 2019 | LCA; process-based cost model; recycling processes of LIBs |
| [117] | Review | 2017 | Current-state of retired LiFePO4 batteries recycling in China |
| [118] | Article | 2014 | Physical and chemical treatments for LIBs modules used in hybrid EV |
| [67] | Article | 2001 | A laboratory process of LIBs recycling |
| [34] | Review | 2019 | Summary of recycling processes of EOL batteries |
| [119] | Proceeding Paper | 2015 | Recycling process of retired automotive LIBs |
| [20] | Proceeding Paper | 2020 | Optimizing efficient hydrometallurgical processes of LIBs |
| [120] | Review | 2020 | Closed-loop strategy for cycling cathode materials; utilization of exhausted anode materials |
| [57] | Review | 2020 | Recovery process and products of waste LIBs |
| [121] | Article | 2014 | Solid−liquid equilibrium (SLE) phase behaviour and process optimize of retired LIBs |
| [56] | Review | 2021 | Processing of organic binders; recycling technologies |
| [38] | Review | 2018 | The current status of hydrometallurgical recycling technologies |
| [36] | Article | 2015 | Recycling concepts for retired LIBs; state-of-the-art schemes of waste treatment technology |
| Direct Recycling Process | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| [58] | Review | 2020 | Retired LIBs recycling processes |
| [19] | Article | 2021 | Direct cathode recycling of EOL LIBs |
| [73] | Article | 2020 | Industrial model for direct recycling of LIBs |
| [122] | Article | 2020 | Removal of the PVDF binder and carbon black through thermal processing |
| [123] | Article | 2019 | Characterization of aged components; direct recycling |
| [124] | Review | 2016 | The current status of graphite anodes in the present recycling technologies of retired LIBs |
| [125] | Article | 2019 | Direct recycling or two-step carbonization for LIBs anode materials |
| [126] | Article | 2020 | Revitalization of composition, structure, and electrochemical performance of LFP LIBs with different degradation conditions; LCA |
| [74] | Article | 2021 | Mathematical regression model; retrieval efficiency using Taguchi Design of Experiment (DoE) method |
| [127] | Article | 2018 | Aged cathode materials; two direct recycling methods: solid-state, and hydrothermal. |
| [128] | Article | 2018 | Four recycling steams; evolution of the precursor particles |
| [129] | Article | 2013 | Recycling mixed cathode materials |
| [130] | Review | 2018 | The whole recycling process; hydrometallurgy |
| [8] | Review | 2020 | A systematic overview of rechargeable battery sustainability |
| [131] | Review | 2020 | Current recycling status for LIBs; advancements in these methods |
| [5] | Article | 2017 | A novel approach to recycling mixed cathode materials based on a closed-loop |
| [132] | Article | 2021 | Study of 44 commercial recyclers; a novel qualitative assessment matrix termed “Strategic materials Weighting And Value Evaluation” (SWAVE) |
| Special Recycling Methods | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| [81] | Article | 2020 | Process models of state-of-the-art pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical recycling based on real data |
| [83] | Article | 2020 | Life-cycle burdens of LIBs |
| [84] | Article | 2011 | LCA; benefits of EOF batteries |
| [82] | Article | 2018 | Staklberg game theory-based model; reward-penalty mechanisms and policies—a case of Beijing |
| [85] | Review | 2020 | Safe recycling, physical processes |
| [87] | Processing Paper | 2016 | LithoRec project |
| [88] | Article | 2020 | Synthesisation and extension design for recycling (DfR) principles |
| [92] | Review | 2020 | Recycling–Molten salt approach |
| [86] | Article | 2018 | Recycling processes, dis/advantages |
| [93] | Article | 2017 | Mechanochemical process using polyvinyl chloride |
| [133] | Article | 2018 | Metal recycling using ammonium chloride |
| [94] | Article | 2020 | Metal Organic Frameworks recycling process |
| [95] | Article | 2020 | Microwave processing route |
| [89] | Article | 2013 | Wet and dry crushing methods |
| [134] | Article | 2021 | Recycling using catalytic pyrolysis or gasification of biomass |
| [91] | Article | 2018 | Heat-treatment recycling of waste toner |
| [135] | Editorial Material | 2018 | Electrohydraulic crushing |
| [36] | Article | 2012 | ACCUREC Recycling and UVR-FIA a recycling process specially dedicated to portable LIBs |
References
- Searchinger, T.D.; Hamburg, S.P.; Melillo, J.; Chameides, W.; Havlik, P.; Kammen, D.M.; Likens, G.E.; Lubowski, R.N.; Obersteiner, M.; Oppenheimer, M.; et al. Climate change. Fixing a critical climate accounting error. Science 2009, 326, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, L.; Cleaver, T.; Rajaeifar, M.A.; Nguyen-Tien, V.; Elliott, R.J.R.; Heidrich, O.; Kendrick, E.; Edge, J.S.; Offer, G. Financial viability of electric vehicle lithium-ion battery recycling. iScience 2021, 24, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Afroz, R.; Safrin, M. Recycling and disposal of lithium batteries: An economical and environmental approach. IIUM Eng. J. 2017, 18, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Elliott, R.J.R.; Nguyen-Tien, V. The EV revolution: The road ahead for critical raw materials demand. Appl. Energy 2020, 280, 115072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Wang, W.; Dai, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Mu, D.; Li, R.; Ren, J.; Dai, C. A closed-loop process for recycling LiNixCoyMn(1−x−y)O2 from mixed cathode materials of lithium-ion batteries. Green Energy Environ. 2017, 2, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Krishna, T.N.V.; Zeb, K.; Rajangam, V.; Muralee Gopi, C.V.V.; Sambasivam, S.; Raghavendra, K.V.G.; Obaidat, I.M. A comprehensive review of li-ion battery materials and their recycling techniques. Electronics 2020, 9, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefi, M.; Maroufi, S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Sahajwalla, V. Pyrometallurgical recycling of Li-ion, Ni–Cd and Ni–MH batteries: A minireview. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 24, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wu, F. Sustainable Recycling Technology for Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond: Challenges and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7020–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.; Sommerville, R.; Kendrick, E.; Driscoll, L.; Slater, P.; Stolkin, R.; Walton, A.; Christensen, P.; Heidrich, O.; Lambert, S.; et al. Recycling lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles. Nature 2019, 575, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brückner, L.; Frank, J.; Elwert, T. Industrial Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries—A Critical Review of Metallurgical Process Routes. Metals 2020, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Bang, J.; Yoo, J.; Shin, Y.; Bae, J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, K.; Dong, P.; Kwon, K. A comprehensive review on the pretreatment process in lithium-ion battery recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yuan, X.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Xie, W. Recent advances in pretreating technology for recycling valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Or, T.; Gourley, S.W.D.; Kaliyappan, K.; Yu, A.; Chen, Z. Recycling of mixed cathode lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles: Current status and future outlook. Carbon Energy 2020, 2, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, L.; Linh, D.; Shui, L.; Peng, X.; Garg, A.; LE, M.L.P.; Asghari, S.; Sandoval, J. Metallurgical and mechanical methods for recycling of lithium-ion battery pack for electric vehicles. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Recycling metals from lithium ion battery by mechanical separation and vacuum metallurgy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, D.; Peuker, U.A.; Mütze, T. Recycling chain for spent lithium-ion batteries. Metals 2020, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, T.; Chen, H.; Wang, K.T.; He, C.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Dodbiba, G.; Wei, Y.-Z. Reduction, reuse and recycle of spent Li-ion batteries for automobiles: A review. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2021, 28, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinegar, H.; Smith, Y.R. Recycling of End-of-Life Lithium Ion Batteries, Part I: Commercial Processes. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Yu, J.; Coyle, J.; Dai, Q.; Frisco, S.; Zhou, M.; Burrell, A. Direct Cathode Recycling of End-Of-Life Li-Ion Batteries Enabled by Redox Mediation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 8214–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.; Malik, M.; Anawati, J.; Azimi, G. Recycling of end-of-life lithium-ion battery of electric vehicles. In Rare Metal Technology 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Thomas, H.R.; Francis, R.W.; Lum, K.R.; Wang, J.; Liang, B. A review of processes and technologies for the recycling of lithium-ion secondary batteries. J. Power Sources 2008, 177, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanitha, M.; Balasubramanian, N. Waste minimization and recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries—A review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2013, 2, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senćanski, J.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D.; Majstorović, D.; Tchernychova, E.; Papan, J.; Vujković, M. The synthesis of Li(Co[sbnd]Mn[sbnd]Ni)O2 cathode material from spent-Li ion batteries and the proof of its functionality in aqueous lithium and sodium electrolytic solutions. J. Power Sources 2017, 342, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, M.; Vonderstein, C.; Dertmann, C.; Klimko, J.; Oráč, D.; Miškufová, A.; Havlík, T.; Friedrich, B. A combined pyro-and hydrometallurgical approach to recycle pyrolyzed lithium-ion battery black mass part 1: Production of lithium concentrates in an electric arc furnace. Metals 2020, 10, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, W.; Zhu, X. Removal of Organics by Pyrolysis for Enhancing Liberation and Flotation Behavior of Electrode Materials Derived from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieceli, N.; Nogueira, C.A.; Guimarães, C.; Pereira, M.F.C.; Durão, F.O.; Margarido, F. Hydrometallurgical recycling of lithium-ion batteries by reductive leaching with sodium metabisulphite. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.M.; Kim, N.H.; Sohn, J.S.; Yang, D.H.; Kim, Y.H. Development of a metal recovery process from Li-ion battery wastes. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 79, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, H.; Zhu, H.; Zu, L.; Bai, Y.; Gao, S.; Gao, Y. A new model of trajectory in eddy current separation for recovering spent lithium iron phosphate batteries. Waste Manag. 2019, 100, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, A.V.M.; Santana, M.P.; Tanabe, E.H.; Bertuol, D.A. Recovery of valuable materials from spent lithium ion batteries using electrostatic separation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 169, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, P. Use of glucose as reductant to recover Co from spent lithium ions batteries. Waste Manag. 2017, 64, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Hu, Q.Y.; Li, X.H.; Wang, Z.X.; Guo, H.J. Recycle and synthesis of LiCoO2 from incisors bound of Li-ion batteries. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China Engl. Ed. 2006, 16, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Qiu, K. Vacuum pyrolysis and hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 194, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northic Council of Ministers. Mapping of Lithium-Ion Batteries for Vehicles; Nordisk Ministerråd: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019; ISBN 9789289362931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ma, X.; Chen, B.; Arsenault, R.; Karlson, P.; Simon, N.; Wang, Y. Recycling End-of-Life Electric Vehicle Lithium-Ion Batteries. Joule 2019, 3, 2622–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallo Tolós, H. Second Life Batteries of Electric Vehicles: Analysis of Use and Management Models. 2021. Available online: https://upcommons.upc.edu/handle/2117/346658 (accessed on 16 September 2021).
- Georgi-Maschler, T.; Friedrich, B.; Weyhe, R.; Heegn, H.; Rutz, M. Development of a recycling process for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2012, 207, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenger Method of and Apparatus for Dismantling and Storage of Objects Comprising Alkali Metals, Such as Alkali Metal Containing Batteries. IFI CLAIMS Patent Services: New Haven, USA. 2003. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US7833646B2/en (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Tong, B.; Fan, Y.; Hua, Z. Hydrometallurgical Processes for Recycling Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Critical Review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13611–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, J.; Hanisch, C.; Froböse, L.; Schälicke, G.; Loellhoeffel, T.; Fölster, A.-S.; Kwade, A. Ecological Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries from Electric Vehicles with Focus on Mechanical Processes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A6184–A6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Amine, K.; Lu, J. The Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Review of Current Processes and Technologies. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2018, 1, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayyas, A.; Steward, D.; Mann, M. The Case for Recycling: Overview and Challenges in the Material Supply Chain for Automotive Li-Ion Batteries. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2018, 19, e00087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, C. Recycling Method for Treating Used Batteries, In Particular Rechergeable Batteries, and Battery Processing Installation. Canada Patent EP3312922B1, 15 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Makuza, B.; Tian, Q.; Guo, X.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Yu, D. Pyrometallurgical options for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries: A comprehensive review. J. Power Sources 2021, 491, 229622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo-Gonzalez, M.d.M.; Villen-Guzman, M.; Acedo-Bueno, L.F.; Rodriguez-Maroto, J.M.; Paz-Garcia, J.M. Hydrometallurgical extraction of Li and Co from LiCoO2 particles-experimental and modeling. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, S.K. Mineral Processing. Miner. Explor. 2018, 259–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.; Saidi, M.Y.; Swoyer, J.L. Lithium iron(II) phospho-olivines prepared by a novel carbothermal reduction method. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2003, 6, A53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Xu, Z. Environmentally-friendly oxygen-free roasting/wet magnetic separation technology for in situ recycling cobalt, lithium carbonate and graphite from spent LiCoO2/graphite lithium batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Fan, E.; Xue, Q.; Bian, Y.; Wu, F.; Chen, R. Toward sustainable and systematic recycling of spent rechargeable batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 7239–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.Y.; Wadsworth, M.E. Rate Processes of Extractive Metallurgy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, L.; Richa, K.; Spangenberger, J. Key issues for Li-ion battery recycling. MRS Energy Sustain. 2018, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaudet, A.; Larouche, F.; Amouzegar, K.; Bouchard, P.; Zaghib, K. Key Challenges and Opportunities for Recycling Electric Vehicle Battery Materials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.C.Y.; Sui, P.C.; Zhang, J. A review of recycling spent lithium-ion battery cathode materials using hydrometallurgical treatments. J. Energy Storage 2021, 35, 102217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, T.; Liu, D.; Hu, H.; Fan, S. Hydrometallurgical recovery of metal values from sulfuric acid leaching liquor of spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo-Gonzalez, M.M.; Villen-Guzman, M.; Vereda-Alonso, C.; Gomez-Lahoz, C.; Rodriguez-Maroto, J.M.; Paz-Garcia, J.M. Recovery of Li and Co from LiCoO2 via hydrometallurgical-electrodialytic treatment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djoudi, N.; Le Page Mostefa, M.; Muhr, H. Hydrometallurgical process to recover cobalt from spent li-ion batteries. Resources 2021, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Xie, W.; Li, L. A critical review of current technologies for the liberation of electrode materials from foils in the recycling process of spent lithium-ion batteries. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.F.; Yang, D.; Du, T.; Gong, H.; Luo, W. Bin The Current Process for the Recycling of Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 578044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larouche, F.; Tedjar, F.; Amouzegar, K.; Houlachi, G.; Bouchard, P.; Demopoulos, G.P.; Zaghib, K. Progress and status of hydrometallurgical and direct recycling of Li-Ion batteries and beyond. Materials 2020, 13, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meshram, P.; Abhilash; Pandey, B.D.; Mankhand, T.R.; Deveci, H. Comparision of Different Reductants in Leaching of Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. JOM 2016, 68, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, T. Hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion batteries in citric acid media. Waste Manag. Res. 2014, 32, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Y.; Fan, E.; Wu, F.; Chen, R. Process for recycling mixed-cathode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries and kinetics of leaching. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagnes, A.; Pospiech, B. A brief review on hydrometallurgical technologies for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Process for the recovery of cobalt oxalate from spent lithium-ion batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, C.; Pasquali, M.; Dell’Era, A. Nickel and cobalt recycling from lithium-ion batteries by electrochemical processes. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabaharan, G.; Barik, S.P.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, L. Electrochemical process for electrode material of spent lithium ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Yokoyama, T.; Itabashi, O.; Suzuki, T.M.; Inoue, K. Hydrometallurgical process for recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion secondary batteries. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 47, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contestabile, M.; Panero, S.; Scrosati, B. A laboratory-scale lithium-ion battery recycling process. J. Power Sources 2001, 92, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacova, Z.; Havlik, T.; Kukurugya, F.; Orac, D. Cobalt and lithium recovery from active mass of spent Li-ion batteries: Theoretical and experimental approach. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 163, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Wu, S.H. A novel recovery process of metal values from the cathode active materials of the lithium-ion secondary batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 99, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.; Ansart, F.; Laberty-Robert, C.; Portal, J. Advances in the recovering of spent lithium battery compounds. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Rhee, K.I. Preparation of LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2002, 109, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, F.; Li, L.; Amin, K.; Fan, E.; Manurkar, N.; Ahmad, A.; Yang, J.; Wu, F.; Chen, R. A Comprehensive Review of the Advancement in Recycling the Anode and Electrolyte from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13527–13554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloop, S.; Crandon, L.; Allen, M.; Koetje, K.; Reed, L.; Gaines, L.; Sirisaksoontorn, W.; Lerner, M. A direct recycling case study from a lithium-ion battery recall. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, T.; Li, Z. Parameter optimization and yield prediction of cathode coating separation process for direct recycling of end-of-life lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 24132–24136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.N.; Swoffer, S. Smith Process for Recovering and Regenerating Lithium Cathode Material from Lithium-Ion Batteries. U.S. Patent US8882007B1, 21 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Shin, E.J. Re-synthesis and Electrochemical Characteristics of LiFePO4 Cathode Materials Recycled from Scrap Electrodes. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Song, J.; Song, D.; Zhang, L.; Shi, X. Environmentally friendly recycling and effective repairing of cathode powders from spent LiFePO4 batteries. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2500–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Huang, Z.; Tao, S.; Zhai, B.; Liu, L.; Hu, L. Regeneration cathode material mixture from spent lithium iron phosphate batteries. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 9283–9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayama, S.; Uchida, S. Degraded Performance Recovery Method for Lithium Ion Secondary Battery. U.S. Patent US9958508B2, 1 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, F.; Hailey, P. Method for Removing Copper and Aluminum from an Electrode Material, and Process for Recycling Electrode Material from Waste Lithium-Ion Batteries. U.S. Patent US10103413B2, 16 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, M.; Peters, J.F.; Baumann, M.; Weil, M. Toward a cell-chemistry specific life cycle assessment of lithium-ion battery recycling processes. J. Ind. Ecol. 2020, 24, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Y. Recycling mechanisms and policy suggestions for spent electric vehicles’ power battery -A case of Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 388–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, L.; Forcina, A.; Arcese, G.; Bella, G. Recycling technologies of nickel–metal hydride batteries: An LCA based analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, L.; Sullivan, J.; Burnham, A.; Belharouak, I. Life-cycle analysis of production and recycling of lithium ion batteries. Transp. Res. Rec. 2011, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerville, R.; Shaw-Stewart, J.; Goodship, V.; Rowson, N.; Kendrick, E. A review of physical processes used in the safe recycling of lithium ion batteries. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, L. Lithium-ion battery recycling processes: Research towards a sustainable course. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2018, 17, e00068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, J.; Hanisch, C.; Loellhoeffel, T.; Schalicke, G.; Kwade, A. (Invited) Ecologically Friendly Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries—The LithoRec Process. ECS Trans. 2016, 73, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgren, A.; Carpenter, A.; Heath, G. Design for Recycling Principles Applicable to Selected Clean Energy Technologies: Crystalline-Silicon Photovoltaic Modules, Electric Vehicle Batteries, and Wind Turbine Blades. J. Sustain. Metall. 2020, 6, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; He, Y.; Ge, L.; Fu, R.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y. Characteristics of wet and dry crushing methods in the recycling process of spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 240, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, L. Profitable Recycling of Low-Cobalt Lithium-Ion Batteries Will Depend on New Process Developments. One Earth 2019, 1, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mao, J.; Xie, H.; Li, J. Heat-treatment recycling of waste toner and its applications in lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Ortiz, R. Alternative recycling process for lithium-ion batteries: Molten salt approach. Johnson Matthey Technol. Rev. 2020, 64, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Zhang, C.C.; Zhang, F.S. Recycling of spent lithium-ion battery with polyvinyl chloride by mechanochemical process. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cognet, M.; Condomines, J.; Cambedouzou, J.; Madhavi, S.; Carboni, M.; Meyer, D. An original recycling method for Li-ion batteries through large scale production of Metal Organic Frameworks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindar, S.; Dhawan, N. Recycling of mixed discarded lithium-ion batteries via microwave processing route. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotak, Y.; Fernández, C.M.; Casals, L.C.; Kotak, B.S.; Koch, D.; Geisbauer, C.; Trilla, L.; Gómez-Núñez, A.; Schweiger, H.G. End of Electric Vehicle Batteries: Reuse vs. Recycle. Energies 2021, 14, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.A.; Groesser, S.N. A Systematic Literature Review of the Solar Photovoltaic Value Chain for a Circular Economy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.; Kim, Y. Technologies of lithium recycling from waste lithium ion batteries: A review. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 3234–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, A.; Windisch-Kern, S.; Ponak, C.; Raupenstrauch, H. A novel pyrometallurgical recycling process for lithium-ion batteries and its application to the recycling of lco and lfp. Metals 2021, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitre, A.; Freake, D.; Lander, L.; Edge, J.; Titirici, M. Towards a More Sustainable Lithium-Ion Battery Future: Recycling LIBs from Electric Vehicles. Batter. Supercaps 2020, 3, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Ager-Wick Ellingsen, L.; Roxanne Hung, C. Research for TRAN Committee-Battery-Powered Electric Vehicles: Market Development and Lifecycle Emissions. 2018. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/thinktank/en/document/IPOL_STU(2018)617457 (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Meng, F.; McNeice, J.; Zadeh, S.S.; Ghahreman, A. Review of Lithium Production and Recovery from Minerals, Brines, and Lithium-Ion Batteries. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 42, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.; Ebin, B.; Mark, M.R.; Steenari, B.M.; Petranikova, M. Incineration of EV Lithium-ion batteries as a pretreatment for recycling—Determination of the potential formation of hazardous by-products and effects on metal compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Novel Approach for in Situ Recovery of Lithium Carbonate from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries Using Vacuum Metallurgy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11960–11966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porvali, A.; Aaltonen, M.; Ojanen, S.; Velazquez-Martinez, O.; Eronen, E.; Liu, F.; Wilson, B.P.; Serna-Guerrero, R.; Lundström, M. Mechanical and hydrometallurgical processes in HCl media for the recycling of valuable metals from Li-ion battery waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 142, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, H.; Srivastava, R.R.; Kim, H.; Ilyas, S.; Khosa, M.K.; Yameen, B. Leaching of exhausted LNCM cathode batteries in ascorbic acid lixiviant: A green recycling approach, reaction kinetics and process mechanism. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Kamimura, T.; Nishiura, T.; Masuda, K.; Shibayama, A.; Inoue, R. Erosion mechanism of refractories in a pyro-processing furnace for recycling lithium-ion secondary batteries. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 9281–9288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, Z.A.; Marshall, A.; Kennedy, J. A review on sustainable recycling technologies for lithium-ion batteries. Emergent Mater. 2021, 4, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Huang, K.; Wang, L. Development tendency and future response about the recycling methods of spent lithium-ion batteries based on bibliometrics analysis. J. Energy Storage 2020, 27, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heelan, J.; Gratz, E.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Apelian, D.; Wang, Y. Current and Prospective Li-Ion Battery Recycling and Recovery Processes. JOM 2016, 68, 2632–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Singh, N. Recycling of spent lithium-ion battery: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 1129–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, T.A.; Elia, G.; Hahn, R.; Altimari, P.; Pagnanelli, F. Closed-loop hydrometallurgical treatment of end-of-life lithium ion batteries: Towards zero-waste process and metal recycling in advanced batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 35, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, D.A.; Prados, L.M.Z.; Majuste, D.; Mansur, M.B. Hydrometallurgical separation of aluminium, cobalt, copper and lithium from spent Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2009, 187, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieceli, N.; Casasola, R.; Lombardo, G.; Ebin, B.; Petranikova, M. Hydrometallurgical recycling of EV lithium-ion batteries: Effects of incineration on the leaching efficiency of metals using sulfuric acid. Waste Manag. 2021, 125, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Friedrich, B. Development of a Highly Efficient Hydrometallurgical Recycling Process for Automotive Li–Ion Batteries. J. Sustain. Metall. 2015, 1, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciez, R.E.; Whitacre, J.F. Examining different recycling processes for lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Y. An overview of recycling and treatment of spent LiFePO4 batteries in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, H.; Jung, Y.; Jo, M.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Yang, D.; Rhee, K.; An, E.M.; Sohn, J.; Kwon, K. Recycling of spent lithium-ion battery cathode materials by ammoniacal leaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 313, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoc, A.; Jeswiet, J. A review of lithium supply and demand and a preliminary investigation of a room temperature method to recycle lithium ion batteries to recover lithium and other materials. Procedia CIRP 2014, 15, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; An, N.; Wen, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Hou, F.; Yin, Y.; Liang, J. Recent progress on the recycling technology of Li-ion batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 55, 391–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Fung, K.Y.; Ng, K.M.; Wibowo, C. Process development for the recycle of spent lithium ion batteries by chemical precipitation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18245–18259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, B.J.; Leresche, M.; Liu, D.; Durham, J.L.; Dahl, E.U.; Lipson, A.L. Mitigating the Impact of Thermal Binder Removal for Direct Li-Ion Battery Recycling. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12511–12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, K.; Santhanagopalan, S.; Hartig, J.; Cao, L. Characterization of Aged Li-Ion Battery Components for Direct Recycling Process Design. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A3775–A3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, B.; Botte, G.G. Recycling of graphite anodes for the next generation of lithium ion batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2016, 46, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Dai, Z.; Liu, X.; Yao, Y.; Yu, C.; Li, D. Direct and indirect recycling strategies of expired oxytetracycline for the anode material in lithium ion batteries. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Dai, Q.; Gao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; An, K.; Meng, Y.S.; Liu, P.; et al. Efficient Direct Recycling of Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes by Targeted Healing. Joule 2020, 4, 2609–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Whitacre, J.F. Direct Recycling of Aged LiMn2O4 Cathode Materials used in Aqueous Lithium-ion Batteries: Processes and Sensitivities. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 2429–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Shen, C.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Gionet, P.; et al. High Performance Cathode Recovery from Different Electric Vehicle Recycling Streams. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13977–13982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, E.; Sa, Q.; Apelian, D.; Wang, Y. A closed loop process for recycling spent lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Wang, Z.; Cao, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. A Critical Review and Analysis on the Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1504–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garole, D.J.; Hossain, R.; Garole, V.J.; Sahajwalla, V.; Nerkar, J.; Dubal, D.P. Recycle, Recover and Repurpose Strategy of Spent Li-ion Batteries and Catalysts: Current Status and Future Opportunities. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 3079–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerville, R.; Zhu, P.; Rajaeifar, M.A.; Heidrich, O.; Goodship, V.; Kendrick, E. A qualitative assessment of lithium ion battery recycling processes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 165, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Wang, Z.; Cao, H.; Zheng, X.; Jin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. A sustainable process for metal recycling from spent lithium-ion batteries using ammonium chloride. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, P.; Shen, Y.; Guo, M. Spent lithium-ion battery materials recycling for catalytic pyrolysis or gasification of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokelmann, K.; Horn, D.; Zimmermann, J.; Gellermann, C.; Stauber, R. Recycling von Li-Ionen-Batterien: Elektrohydraulische Zerkleinerung. Chem. Unserer Zeit 2018, 52, 284–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Section | Description | Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Recycling Processes | Individual steps of the recycling process; description of special methods | Pretreatment Metallurgy/Mechanical Pyrometallurgy Hydrometallurgy Direct Recycling Special Method |
| Battery Composition | Characterization of recycling and recovery processes of the individual battery components | Cathode Anode Electrolyte |
| Environmental Impact | Issues related to the environment: general impact, Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) studies, focus on raw/reused materials | Envi/Ecological Impact Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Recovery of Materials Recycling of Materials |
| Economic Assessment | Various types of economic evaluation, mainly including cost-benefit analysis | Economic Assessment |
| Recycling & Rest | Studies describing: the whole recycling cycle or approach it in a specific way; focus on EVs | Recycling EV LIBs Recycling LIBs |
| Section | Technological | Environmental | Economical |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recycling Processes | x | ||
| Battery Composition | x | x | |
| Environmental Impact | x | ||
| Economic Assessment | x | ||
| Recycling & Rest | x | x | x |
| Section | No. of Articles in Section | % of Total LR | Category/Keyword | No. of Articles in Category | No. of Overlapped Articles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycling Processes | 61 | 23 | Pretreatment | 3 | 0 |
| Metallurgy/Mechanical | 6 | 1 | |||
| Pyrometallurgy | 4 | 0 | |||
| Hydrometallurgy | 19 | 11 | |||
| Direct Recycling | 6 | 3 | |||
| Special Method | 23 | 9 | |||
| Battery Composition | 63 | 24 | Cathode | 51 | 51 |
| Anode | 10 | 10 | |||
| Electrolyte | 2 | 2 | |||
| Environmental Impact | 76 | 28 | Envi/Ecological Impact | 10 | 2 |
| Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) | 8 | 3 | |||
| Recovery of Materials | 35 | 1 | |||
| Recycling of Materials | 23 | 0 | |||
| Economical Assessment | 15 | 6 | Economical Evaluation | 15 | 3 |
| Recycling & Rest | 48 | 18 | Recycling EV LIBs | 11 | 6 |
| Recycling LIBs | 37 | 19 |
| Company | Country | Process | Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accurec | Germany | Mechanical, electric furnace | Co alloy, Li2Co3 |
| Albemarle | USA | Hydrometallurgical | - |
| AkkureSer + Boliden | Finland | Mechanical (AS), Copper refining (Boliden) | Black Mass |
| Battery Resourcers | USA | Hydrometallurgycal | - |
| BatRec | Switzerland | Mechanical, pyrometallurgycal | Material fractures |
| Brunp | China | Hydrometallurgycal | - |
| Duesenfeld | Germany | Mechanical, hydrometallurgycal | Co, Ni, Mn (active mat.), electrolyte |
| Eramet | France | Pyrometallurgy | Ferro-Ni/Ferro-Mn alloy |
| Farasis Energy | USA | Mechanical | - |
| GEM | China | Hydrometallurgycal | - |
| GHTECH | China | Hydrometallurgycal | - |
| Inmetco | USA | Pyrometallurgycal | - |
| Highpower International | China | Hydrometallurgycal | - |
| Neometals | Austria | Mechanical, hydrometallurgycal | Co, Ni, Cu, Li, Gr (less quality) |
| OnTo Technology | USA | Mechanical | - |
| Recupyl | France | Mechanical, hydrometallurgycal | Mn, Co, Li, Ni (less quality) |
| Redux | Germany, Austria | Mechanical, hydrometallurgycal | Co, Ni, Cu, Li, Gr (less quality) |
| Retriev | Canada, USA | Mechanical, hydrometallurgycal | - |
| SNAM | France | Pyrometallurgy | Black mass, Co, Cu, Ni |
| Sony/Sumitomo | Japan | Pyrometallurgycal | - |
| SungEel HiTech | South Korea | Hydrometallurgycal | - |
| TES-AMM | Singapore | Hydrometallurgycal | - |
| Umicore | Belgium | Pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy | Co, Ni, Cu (chemical form) |
| uRecycle | Sweden | Mechanical | Black mass |
| Elements | Content [wt %] |
|---|---|
| Aluminum (Al) | 1–5 |
| Cobalt (Co) | 3–33 |
| Copper (Cu) | 1–3 |
| Iron (Fe) | 0.1–0.3 |
| Lithium (Li) | 3.5–4 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 3–11 |
| Graphite | approx. 35 |
| Fluor (F) | 2–4 |
| Oxide (O) | 0.5–1 |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Application flexibility; all battery compositions, and configurations | Not possible to obtain products based on: Li, Al, organic materials |
| Not required pretreatment (sorting, mechanical processing) | Unable to recycle Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) |
| High proportion of recovery metals in products | High energy and capacity requirements |
| Proven technology; existing equipment can be used | Expensive gas cleaning; prevention of toxic emissions in the air |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Application flexibility; all battery compositions and configurations | Necessary to crush the batteries; high safety requirements |
| Flexibility of separation process; a desired product (metal) can be obtained | Uneconomical for Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) |
| High efficiency of the recycling process (especially for Li) | High volume of waste water; necessary disposal or further recycling |
| High purity of products | Impossibility of recycling anode materials (graphite, conductive additives) |
| Emission-free | High operating costs |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Recycling of all materials: anodes, cathodes, electrolytes, foils, … | Difficult mechanical pretreatment, necessary material separation |
| Suitable for Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) | The mix of materials reduces the quality of the process |
| Energy efficient | Low quality of output products |
| Production residues can be recycled | Not yet fully industrially applied |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pražanová, A.; Knap, V.; Stroe, D.-I. Literature Review, Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries from Electric Vehicles, Part I: Recycling Technology. Energies 2022, 15, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15031086
Pražanová A, Knap V, Stroe D-I. Literature Review, Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries from Electric Vehicles, Part I: Recycling Technology. Energies. 2022; 15(3):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15031086
Chicago/Turabian StylePražanová, Anna, Vaclav Knap, and Daniel-Ioan Stroe. 2022. "Literature Review, Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries from Electric Vehicles, Part I: Recycling Technology" Energies 15, no. 3: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15031086
APA StylePražanová, A., Knap, V., & Stroe, D. -I. (2022). Literature Review, Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries from Electric Vehicles, Part I: Recycling Technology. Energies, 15(3), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15031086