Comparing the Bio-Hydrogen Production Potential of Pretreated Rice Straw Co-Digested with Seeded Sludge Using an Anaerobic Bioreactor under Mesophilic Thermophilic Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Pretreatment of Rice
2.2. Seeded Sludge
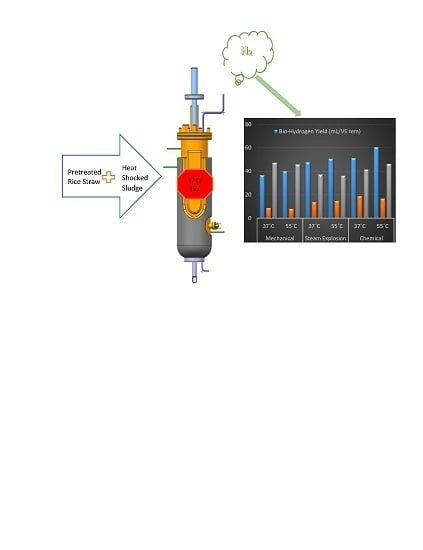
2.3. Anaerobic Bio-Reactor
2.4. Analytical and Assay Methods
2.5. Batch Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pretreatment Effect on Kinetic Parameters
3.2. Bio-Hydrogen Yield
3.3. Change in pH
3.4. VFA Production under Tested Pretreatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ni, M.; Leung, D.Y.; Leung, M.K.; Sumathy, K. An overview of hydrogen production from biomass. Fuel Process. Technol. 2006, 87, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wu, C.; Huang, H.; Lin, G. Research and development on biomass energy in china. Int. J. Energy Technol. Policy 2002, 1, 108–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, K.L.; Forrest, L.H.; Jacobson, W.A. Rice straw as a lignocellulosic resource: Collection, processing, transportation, and environmental aspects. Biomass Bioenergy 2000, 18, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sevda, S.; Abu Reesh, I.M.; Vanbroekhoven, K.; Rathore, D.; Pant, D. Biohydrogen production from lignocellulosic biomass: Technology and sustainability. Energies 2015, 8, 13062–13080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claassen, P.; Van Lier, J.; Contreras, A.L.; Van Niel, E.; Sijtsma, L.; Stams, A.; De Vries, S.; Weusthuis, R. Utilisation of biomass for the supply of energy carriers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 52, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, K.; Das, D. Improvement of fermentative hydrogen production: Various approaches. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, F.; Dinsdale, R.; Hawkes, D.; Hussy, I. Sustainable fermentative hydrogen production: Challenges for process optimisation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2002, 27, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynd, L.R.; Van Zyl, W.H.; McBride, J.E.; Laser, M. Consolidated bioprocessing of cellulosic biomass: An update. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosier, N.; Wyman, C.; Dale, B.; Elander, R.; Lee, Y.; Holtzapple, M.; Ladisch, M. Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratky, L.; Jirout, T. Biomass size reduction machines for enhancing biogas production. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, J. Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, J.; Sarikaya, A.; Rau, S.-L.; Goetz, J.; Ladisch, C.M.; Brewer, M.; Hendrickson, R.; Ladisch, M.R. Pretreatment of yellow poplar sawdust by pressure cooking in water. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1997, 68, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, F.; Li, Y. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enhanced biogas production. PrECS 2014, 42, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, M.; Kurogi, R.; Tsumagari, H.; Shiragami, T.; Matsumoto, T. New approach to fuelization of herbaceous lignocelluloses through simultaneous saccharification and fermentation followed by photocatalytic reforming. Energies 2014, 7, 4087–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Pang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, K. Physicochemical characterization of rice straw pretreated with sodium hydroxide in the solid state for enhancing biogas production. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 2775–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.H.; Li, C.; Zhang, T. Acidophilic biohydrogen production from rice slurry. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2006, 31, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-E.; Van Ginkel, S.; Logan, B.E. The relative effectiveness of pH control and heat treatment for enhancing biohydrogen gas production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5186–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, H. Biological hydrogen production from steam-exploded straw by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2007, 32, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Huang, H.; Lei, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced hydrogen production from anaerobic fermentation of rice straw pretreated by hydrothermal technology. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; El-Zawawy, W.K.; Abdel-Fattah, Y.R.; Soliman, N.A.; Agblevor, F.A. Comparison of alkaline pulping with steam explosion for glucose production from rice straw. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathao, C.; Sirisukpoka, U.; Pisutpaisal, N. Production of hydrogen and methane by one and two stage fermentation of food waste. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 15764–15769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fang, H.H. Fermentative hydrogen production from wastewater and solid wastes by mixed cultures. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reungsang, A.; Sreela-or, C. Bio-hydrogen production from pineapple waste extract by anaerobic mixed cultures. Energies 2013, 6, 2175–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Arslan, C.; Ji, C.; Chen, K.; Nasir, A.; Fang, H.; Umair, M. Optimizing the physical parameters for bio-hydrogen production from food waste co-digested with mixed consortia of clostridium. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 013107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, C.; Sattar, A.; Ji, C.; Sattar, S.; Yousaf, K.; Hashim, S. Optimizing the impact of temperature on bio-hydrogen production from food waste and its derivatives under no pH control using statistical modelling. BGeo 2015, 12, 6503–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 25th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, C.; Sattar, A.; Changying, J.; Nasir, A.; Ali Mari, I.; Zia Bakht, M. Impact of pH management interval on biohydrogen production from organic fraction of municipal solid wastes by mesophilic thermophilic anaerobic codigestion. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ververis, C.; Georghiou, K.; Danielidis, D.; Hatzinikolaou, D.; Santas, P.; Santas, R.; Corleti, V. Cellulose, hemicelluloses, lignin and ash content of some organic materials and their suitability for use as paper pulp supplements. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, C.; Buitrón, G.; Moreno-Andrade, I.; Chamy, R. Effect of the initial total solids concentration and initial pH on the bio-hydrogen production from cafeteria food waste. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 13288–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Han, S.-K.; Shin, H.-S. Optimization of continuous hydrogen fermentation of food waste as a function of solids retention time independent of hydraulic retention time. Process. Biochem. 2008, 43, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.H.; Lee, D.S.; Park, D.; Choe, W.-S.; Park, J.M. Optimization of key process variables for enhanced hydrogen production by enterobacter aerogenes using statistical methods. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Liu, C.; Noh, J.-W.; Yang, Y.; Oh, S.; Shimizu, K.; Lee, D.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Hydrogen and methane production from untreated rice straw and raw sewage sludge under thermophilic anaerobic conditions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 8648–8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemahdi, N.; Man, H.C.; Nasirian, N.; Yang, Y. Enhanced mesophilic bio-hydrogen production of raw rice straw and activated sewage sludge by co-digestion. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 16033–16044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-S.; Youn, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H. Hydrogen production from food waste in anaerobic mesophilic and thermophilic acidogenesis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2004, 29, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Chuang, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-Y.; Lay, C.-H.; Sen, B. Thermophilic dark fermentation of untreated rice straw using mixed cultures for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 15540–15546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.C.; Tu, Y.-H.; Huang, M.-H.; Lay, C.-H.; Lin, C.-Y. Hydrogen production by the anaerobic fermentation from acid hydrolyzed rice straw hydrolysate. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 14280–14288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. Plant Fiber Chemistry; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 176–182. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Durot, N.; Gaudard, F.; Kurek, B. The unmasking of lignin structures in wheat straw by alkali. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Shi, S.; Yang, R.; Niu, M.; Song, W. Modification of reed cellulose microstructure and it change in enzymatic hydrolysis of reed pulp. Trans. China Pulp. Pap. 2005, 20, 85–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.F.; Sun, R.; Tomkinson, J.; Baird, M. Preparation of sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic succinates using nbs as a catalyst. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 53, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, M.J.; Viamajala, S.; Decker, S.R.; Tucker, M.P.; Himmel, M.E.; Vinzant, T.B. Deposition of lignin droplets produced during dilute acid pretreatment of maize stems retards enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, A.; Zeeman, G. Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin DB, I.R.; Cicek, N.; Sparling, R. Hydrogen production by clostridium thermocellum 27,405 from cellulosic biomass substrates. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2006, 31, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, G. Thermophilic solid-state anaerobic digestion of alkaline-pretreated corn stover. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 3759–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadow, S.; Li, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of temperature on continuous hydrogen production of cellulose. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 15465–15472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yang, Y.; Morikawa-Sakura, M.S.; Wang, Q.; Lee, M.V.; Lee, D.-Y.; Feng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z. Hydrogen production by anaerobic co-digestion of rice straw and sewage sludge. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 3142–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, G. Bacterial Metabolism, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Zoetemeyer, R.J.; Cohen, A.; Boelhouwer, C. Product inhibition in the acid forming stage of the anaerobic digestion process. Water Res. 1982, 16, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzenbaum, G.-G.E.; Hickey, R.F. Monitoring of the anaerobic methane fermentation process. Enzyme microbial technology. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1990, 12, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Properties (%) | Mechanical | Steam Explosion | Chemical |
|---|---|---|---|
| Holocellulose | 66.79 | 56.92 | 54.53 |
| LCH | 76.51 | 70.64 | 61.51 |
| Lignin | 9.72 | 13.72 | 6.98 |
| Ash | 11.21 | 21.81 | 19.46 |
| TS | 92.05 | 20.53 | 90.49 |
| VS | 77.36 | 16.94 | 74.46 |
| Pretreatment | Temperature | P | Rm | R2 | Hydrogen Yield | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mL) | (mL/h) | (h) | (h) | (mL/VSfed) | (mL/VSremoved) | |||
| Mechanical | 37 °C | 4258 | 42.51 | 10.26 | 47.22 | 0.9973 | 7.66 | 36.62 |
| 55 °C | 5402 | 44.73 | 1.27 | 45.84 | 0.9955 | 9.72 | 40.04 | |
| Steam Explosion | 37 °C | 5570 | 66.78 | 6.53 | 37.32 | 0.9941 | 9.01 | 47.80 |
| 55 °C | 6181 | 75.17 | 5.88 | 36.23 | 0.9948 | 10.00 | 50.68 | |
| Chemical | 37 °C | 6008 | 92.44 | 17.65 | 41.63 | 0.9977 | 11.00 | 51.18 |
| 55 °C | 8361 | 96.5 | 14.36 | 46.33 | 0.9982 | 15.30 | 60.60 | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sattar, A.; Arslan, C.; Ji, C.; Sattar, S.; Ali Mari, I.; Rashid, H.; Ilyas, F. Comparing the Bio-Hydrogen Production Potential of Pretreated Rice Straw Co-Digested with Seeded Sludge Using an Anaerobic Bioreactor under Mesophilic Thermophilic Conditions. Energies 2016, 9, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9030198
Sattar A, Arslan C, Ji C, Sattar S, Ali Mari I, Rashid H, Ilyas F. Comparing the Bio-Hydrogen Production Potential of Pretreated Rice Straw Co-Digested with Seeded Sludge Using an Anaerobic Bioreactor under Mesophilic Thermophilic Conditions. Energies. 2016; 9(3):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9030198
Chicago/Turabian StyleSattar, Asma, Chaudhry Arslan, Changying Ji, Sumiyya Sattar, Irshad Ali Mari, Haroon Rashid, and Fariha Ilyas. 2016. "Comparing the Bio-Hydrogen Production Potential of Pretreated Rice Straw Co-Digested with Seeded Sludge Using an Anaerobic Bioreactor under Mesophilic Thermophilic Conditions" Energies 9, no. 3: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9030198
APA StyleSattar, A., Arslan, C., Ji, C., Sattar, S., Ali Mari, I., Rashid, H., & Ilyas, F. (2016). Comparing the Bio-Hydrogen Production Potential of Pretreated Rice Straw Co-Digested with Seeded Sludge Using an Anaerobic Bioreactor under Mesophilic Thermophilic Conditions. Energies, 9(3), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9030198