An Experimental Study on the Potential Usage of Acetone as an Oxygenate Additive in PFI SI Engines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Methods
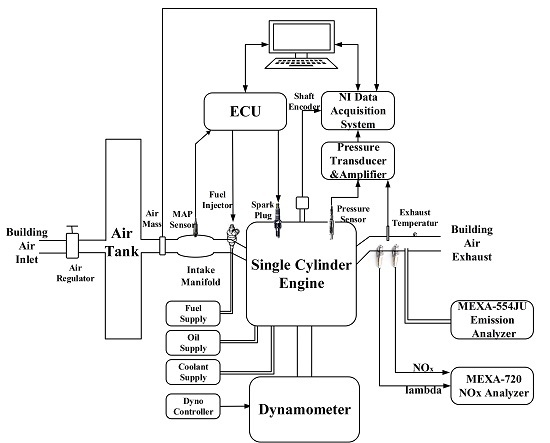
2.1. Engine Test Bench
2.2. Uncertainty Analysis
2.3. Fuels
3. Test conditions and Procedure
3.1. Test Conditions
3.2. Engine Combustion Characteristics Analysis
3.2.1. In-Cylinder Pressure Traces
3.2.2. Normalized Mass Fraction Burnt (MFB)
3.2.3. Coefficient of Variance (COV)
3.3. Engine Efficiency Analysis
3.3.1. Brake Thermal Efficiency
3.3.2. Brake Specific Fuel Consumption
3.4. Engine Emission Analysis
3.4.1. Unburned Hydrocarbon (UHC)
3.4.2. Carbon Monoxide (CO)
3.4.3. Nitrogen Oxide (NOx)
4. Conclusions
- Acetone has a relatively lower laminar flame speed than that of ethanol; AE10 and AE30 have retarded phasing compared to ethanol-gasoline blends (E10 and E30) at gasoline MBT, implying that using acetone as an oxygenate additive could narrow the differences relative to pure gasoline without any modifications on commercial engines
- There is a negligible reduction in BTE with acetone addition relative to pure gasoline and ethanol-containing gasoline; meanwhile, the BSFC can be improved relative to ethanol–gasoline due to the higher LHV of acetone.
- No combustion stability problems were caused by acetone addition based on the COV-IMEP calculation. E10 has been shown to have a relatively small COV value compare with other blends.
- AE30 shows the lowest HC emission under different equivalence ratios because of the better volatility of acetone leading to an improvement in the fuel pre-mixing, better combustion and post-flame oxidation. Compared with G100, E10 and E30 also show the improvement of HC emission as the ethanol addition increases.
- Higher CO emission from AE30 at stoichiometric ratio might be due to more unburned gases returning from the crevice and partially reacting during the expansion and exhaust stroke in the form of post-flame oxidation. In addition, the AE blends were less sensitive to the equivalence ratio at fuel-rich conditions in terms of CO emission, which might reduce CO at full load and transient accelerating.
- The NOx emissions were more influenced by engine operating conditions rather than due to different fuels (negligible changes).
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Liao, S.; Liu, G. Thermo-economic multi-objective optimization for a solar-dish Brayton system using NSGA-II and decision making. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 64, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuholt, E. Life cycle assessment of gasoline and diesel. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1995, 14, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.-Q.; Wang, J.-X.; Hao, J.-M.; Yan, X.-G.; Xiao, J.-H. A study on emission characteristics of an EFI engine with ethanol blended gasoline fuels. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, T.; Miers, S.A.; McConnell, S. A comparison of ethanol and butanol as oxygenates using a direct-injection, spark-ignition engine. J. Eng. Gas. Turbines Power 2009, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balat, M.; Balat, H. Recent trends in global production and utilization of bio-ethanol fuel. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulczyk, K.R.; McCarl, B.A.; Cornforth, G. Market penetration of ethanol. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghinezhad, E.; Kazi, S.N.; Badarudin, A.; Togun, H.; Zubir, M.N.M.; Oon, C.S.; Gharehkhani, S. Sustainability and environmental impact of ethanol as a biofuel. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2014, 30, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costagliola, M.A.; de Simio, L.; Iannaccone, S.; Prati, M.V. Combustion efficiency and engine out emissions of a S.I. engine fueled with alcohol/gasoline blends. Appl. Energy 2013, 111, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, I.C.; Seabra, J.E.A.; Silva, J.E.A.R. Green house gases emissions in the production and use of ethanol from sugarcane in Brazil: The 2005/2006 averages and a prediction for 2020. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.; Chen, R.; Wu, T.; Lin, T. Engine performance and pollutant emission of an SI engine using ethanol-gasoline blended fuels. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Choi, Y.; Kim, C.; Oh, S.; Lim, G.; Moriyoshi, Y. Performance and exhaust emission characteristics of a spark ignition engine using ethanol and ethanol-reformed gas. Fuel 2010, 89, 2118–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masum, B.M.; Kalam, M.A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Daggig, E.E. Impact of denatured anhydrous ethanol-gasoline fuel blends on a spark-ignition engine. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 51220–51227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Khatri, D.S.; Babu, M.K.G. An Investigation of Potential and Challenges with Higher Ethanol-gasoline Blend on a Single Cylinder Spark Ignition Research Engine. SAE Tech. Paper 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceviz, M.A.; Yüksel, F. Effects of ethanol-unleaded gasoline blends on cyclic variability and emissions in an SI engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2005, 25, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifter, I.; Diaz, L.; Rodriguez, R.; Gómez, J.P.; Gonzalez, U. Combustion and emissions behavior for ethanol-gasoline blends in a single cylinder engine. Fuel 2011, 90, 3586–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.; Xu, H.; Cracknell, R.F.; Natarajan, V.; Chen, X. Combustion performance of bio-ethanol at various blend ratios in a gasoline direct injection engine. Fuel 2011, 90, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsezen, A.N.; Canakci, M. Performance and combustion characteristics of alcohol-gasoline blends at wide-open throttle. Energy 2011, 36, 2747–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Shen, M.; Wang, J.; Lin, M. Influence of ethanol-gasoline blended fuel on emission characteristics from a four-stroke motorcycle engine. J. Hazard Mater. 2005, 123, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.R.; Sodré, J.R. Using Additive to Improve Cold Start in Ethanol-Fuelled Vehicles. SAE Tech. Paper 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenphonphanich, C.; Imerb, W.; Karin, P.; Chollacoop, N.; Hanamura, K. Low Temperature Starting Techniques for Ethanol Engine without Secondary Fuel Tank. SAE Tech. Paper 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Ge, L.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J.; Chen, R.; Shi, Z. Enhancing acetone biosynthesis and acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation performance by co-culturing Clostridium acetobutylicum/Saccharomyces cerevisiae integrated with exogenous acetate addition. Bioresource Technol. 2016, 200, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, M.J., Jr.; Thirmulachar, M.J. Acetone-Gasoline Mixture for Automobiles; Pollution Control; Efficiency. U.S. Patent 4,372,753, 8 February 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C. Alcohol, Ketone and Ether with Silicon Compounds. U.S. Patent 5,688,295, 18 November 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Nithyanandan, K.; Chia-fon, F.L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J. Performance and Emissions of Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol (ABE) and Gasoline Blends in a Port Fuel Injected Spark Ignition Engine. In Proceedings of the ASME 2014 Internal Combustion Engine Division Fall Technical Conference, Columbus, IN, USA, 19–22 October 2014.
- Nithyanandan, K.; Zhang, J.; Yuqiang, L.; Wu, H.; Lee, C. Investigating the Impact of Acetone on the Performance and Emissions of Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol (ABE) and Gasoline Blends in an SI Engine. SAE Tech. Paper 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Li, Y. Experimental Study on Performance and Emission of Acetone-Ethanol and Gasoline Blends in a PFI Spark Ignition Engine. SAE Tech. Paper 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Nithyanandan, K.; Zhou, N.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, C.F.; Zhang, C. Impacts of acetone on the spray combustion of Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol (ABE)-Diesel blends under low ambient temperature. Fuel 2015, 142, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, H. Current status and prospects of biobutanol manufacturing technology. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 914–923. [Google Scholar]
- Wigg, B.; Coverdill, R.; Lee, C.; Kyritsis, D. Emissions Characteristics of Neat Butanol Fuel Using a Port Fuel-Injected, Spark-Ignition Engine. SAE Tech. Paper 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithyanandan, K.; Wu, H.; Huo, M.; Lee, C. A Preliminary Investigation of the Performance and Emissions of a Port-Fuel Injected SI Engine Fueled with Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol (ABE) and Gasoline. SAE Tech. Paper 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy, T.; Gakkhar, R.P.; Murugesan, K. Influence of injection timing on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of Jatropha biodiesel engine. APPL ENERG 2011, 88, 4376–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, J.P. Experimental methods for engineers. In McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mani, M.; Nagarajan, G. Influence of injection timing on performance, emission and combustion characteristics of a DI diesel engine running on waste plastic oil. Energy 2009, 34, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devan, P.K.; Mahalakshmi, N.V. Performance, emission and combustion characteristics of poon oil and its diesel blends in a DI diesel engine. Fuel 2009, 88, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, T.; Miers, S.A. Combustion Behavior of Gasoline and Gasoline/Ethanol Blends in a Modern Direct-Injection 4-Cylinder Engine. SAE Tech. Paper 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.T.; Hochgreb, S. Measurements of laminar flame speeds of acetone/methane/air mixtures. Combust Flame 2011, 158, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataluña, R.; Da Silva, R.; de Menezes, E.W.; Ivanov, R.B. Specific consumption of liquid biofuels in gasoline fuelled engines. Fuel 2008, 87, 3362–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwaja, S.; Naber, J.D. Combustion of n-butanol in a spark-ignition IC engine. Fuel 2010, 89, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Nithyanandan, K.; Li, Y.; Lee, C.; Huang, Z. Comparative Study of High-Alcohol-Content Gasoline Blends in an SI Engine. SAE Tech. Paper 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleiferis, P.G.; Malcolm, J.S.; Todd, A.R.; Cairns, A.; Hoffmann, H. An optical study of spray development and combustion of ethanol, Iso-octane and gasoline blends in a DISI engine. SAE Tech. Paper 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Lee, W.; Lin, S.; Wang, L. Green energy: Water-containing acetone-butanol-ethanol diesel blends fueled in diesel engines. Appl. Energy 2013, 109, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassweiler, G.M.; Withrow, L. Motion pictures of engine flames correlated with pressure cards. SAE Tech. Paper 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, J.B. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals; Mcgraw-hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 930. [Google Scholar]
- Price, P.; Twiney, B.; Stone, R.; Kar, K.; Walmsley, H. Particulate and hydrocarbon emissions from a spray guided direct injection spark ignition engine with oxygenate fuel blends. SAE Tech. Paper 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, C.P.; Yeliana; Worm, J.J.; Naber, J.D. Combustion Characterization in an Internal Combustion Engine with Ethanol-Gasoline Blended Fuels Varying Compression Ratios and Ignition Timing. Energy Fuel 2009, 23, 2319–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, C.; Wallner, T.; McConnell, S.; Gillen, J.C.; Abell, C.; Miers, S.A.; Naber, J.D. Effects of blending gasoline with ethanol and butanol on engine efficiency and emissions using a direct-injection, spark-ignition engine. In Proceedings of the ASME 2009 Internal Combustion Engine Division Spring Technical Conference, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 3–6 May 2009.
- Dernotte, J.; Mounaim-Rousselle, C.; Halter, F.; Seers, P. Evaluation of butanol-gasoline blends in a port fuel-injection, spark-ignition engine. Oil Gas. Sci. Technol. Revue Inst. Français. Pétrole 2010, 65, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhas, A.S.; Muraleedharan, C.; Jayaraj, S. Performance and emission evaluation of a diesel engine fueled with methyl esters of rubber seed oil. Renew Energy 2005, 30, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.K.; Hamrin, D.; Heywood, J.B.; Hochgreb, S.; Min, K.; Norris, M. An overview of hydrocarbon emissions mechanisms in spark-ignition engines. SAE Tech. Paper 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, J.; Ghandhi, J. Investigation of Post-Flame Oxidation of Unburned Hydrocarbons in Small Engines. SAE Tech. Paper 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, M.; Sekmen, Y.; Topgül, T.; Yücesu, H.S. The effects of ethanol-unleaded gasoline blends on engine performance and exhaust emissions in a spark-ignition engine. Renew Energy 2009, 34, 2101–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cuty Clemente, E.R.; Hu, T.; Wei, Y. Study of spark ignition engine fueled with methanol/gasoline fuel blends. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 1904–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, Ö.; Celikten, I.; Usta, N. Effects of ethanol addition on performance and emissions of a turbocharged indirect injection diesel engine running at different injection pressures. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masum, B.M.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Rizwanul Fattah, I.M.; Palash, S.M.; Abedin, M.J. Effect of ethanol-gasoline blend on NOx emission in SI engine. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Yu, H.; Li, Q.; Gong, J.; Huang, Z. Laminar Flame Characteristics of Iso-Octane/n-Butanol Blend—Air Mixtures at Elevated Temperatures. Energy Fuel 2013, 27, 2327–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Displaced Volume | 575 cc |
| Stroke | 90.1 mm |
| Bore | 90.3 mm |
| Connecting Rod Length | 150.7 mm |
| Compression Ratio | 9.6:1 |
| Number of Valves | 4 |
| Fuel Injection | Port Fuel Injection (PFI) |
| Measurements | Measuring Range | Accuracy (±) | Percentage Uncertainties (± %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine speed | 1–5000 RPM | 0.2% | 0.1 |
| Torque | 0–300 N∙m | 0.5% FS | 0.3 |
| Exhaust Gas Temperature | 0–900 °C | 1 °C | 0.15 |
| CO emission | 0%–10% volume | 0.06% | 0.6 |
| HC emission | 0–10,000 ppm | 12 ppm | 0.12 |
| CO2 emission | 0%–20% volume | 0.5% | 0.5 |
| NOx emission | 0–3000 ppm | 3% | 0.18 |
| AFR | 4–200 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Air flow mass | 0–800 g/min | 1% | 1.8 |
| Parameter | Gasoline | Acetone | Ethanol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4–C12 | C3H6O | C2H5OH |
| Oxygen (Mass %) | 0 | 27 | 35 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 715-765 | 790 | 790 |
| Energy Density (MJ/l) | 32.20 | 23.38 | 21.17 |
| Lower Heating Value (MJ/kg) | 43.4 | 29.6 | 26.8 |
| Octane Number | 92 | 117 | 100 |
| Self-ignition temperature (°C) | ~300 | 465 | 420 |
| Boiling Temperature(°C) | 25–215 | 56.2 | 78 |
| Stoichiometric A/F ratio | 14.7 | 9.5 | 9 |
| Latent Heat of Vaporization (25 °C) (kJ/kg) | 380-500 | 518 | 904 |
| Laminar Flame Speed (LFS) (cm/s) | ~33 a | ~34 b | ~48 c |
| Ignition Limits in Air (volume %) [Lower-Upper] | 0.6–8 | 2.6–12.8 | 3.5–15 |
| Fuel Type | Lower Heating Value (MJ/kg) | Density (kg/m3) | Energy Density of Stoichiometric Air-Fuel Mixture (MJ/L) | Stoichiometric Air/Fuel Ratio | Oxygen (Mass %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G100 | 43.4 | 730 | 31.7 | 14.7 | 0 |
| E10 | 41.6 | 736 | 30.6 | 13.90 | 3.75 |
| E30 | 38.1 | 748 | 28.5 | 12.73 | 11.06 |
| AE10(3:1) | 41.8 | 736 | 30.8 | 13.94 | 3.17 |
| AE30(3:1) | 38.8 | 748 | 29.0 | 12.85 | 9.36 |
| Engine Speed | 1200 RPM |
|---|---|
| Throttle Position | 100% |
| Engine Load (BMEP) | 3 bar, 5 bar |
| Equivalence Ratio | 0.83–1.25 |
| Spark Timing | Gasoline MBT |
| Fuel Pressure | 3 bar |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, L.; Zeng, C.; Li, Y.; Nithyanandan, K.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, C.-f. An Experimental Study on the Potential Usage of Acetone as an Oxygenate Additive in PFI SI Engines. Energies 2016, 9, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9040256
Meng L, Zeng C, Li Y, Nithyanandan K, Lee TH, Lee C-f. An Experimental Study on the Potential Usage of Acetone as an Oxygenate Additive in PFI SI Engines. Energies. 2016; 9(4):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9040256
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Lei, Chunnian Zeng, Yuqiang Li, Karthik Nithyanandan, Timothy H. Lee, and Chia-fon Lee. 2016. "An Experimental Study on the Potential Usage of Acetone as an Oxygenate Additive in PFI SI Engines" Energies 9, no. 4: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9040256
APA StyleMeng, L., Zeng, C., Li, Y., Nithyanandan, K., Lee, T. H., & Lee, C. -f. (2016). An Experimental Study on the Potential Usage of Acetone as an Oxygenate Additive in PFI SI Engines. Energies, 9(4), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9040256