Birnessite: A New Oxidant for Green Rust Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Birnessite
2.2. Oxidation of Ferrous Species by Air and Birnessite
2.3. Solids Characterization
2.3.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.3.2. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.3.3. Transmission Mössbauer Spectrometry
3. Results
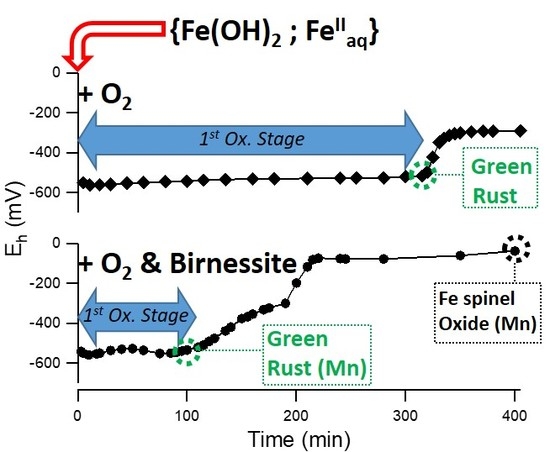
3.1. Air Oxidation of FeII Species in the Presence of Birnessite
3.1.1. Oxidation of Fe(OH)2 without Fe2+aq (R = 0.5)
3.1.2. Oxidation of a {Fe(OH)2, Fe2+aq} Mixture (R = 0.6)
3.2. Reduction of Birnessite Followed by XRD and XPS
4. Discussion
4.1. Thermodynamical Analysis of the Eh-pH Data
4.2. Kinetics of the Oxidation Reaction
4.3. Potential Substitution of Fe by Mn in the Oxidation Products
4.3.1. Powder X-ray Diffraction Analysis
4.3.2. Analysis with Mössbauer Spectroscopy
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Post, J.E. Manganese oxide minerals: Crystal structures and economic and environmental significance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3447–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaied, M.; Chutet, E.; Peulon, S.; Bellakhal, N.; Desmazières, B.; Dachraoui, M.; Chaussé, A. Spontaneous oxidative degradation of indigo carmine by thin films of birnessite electrodeposited onto SnO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 107, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, W.A.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Reaction of aqueous Cu–Citrate with MnO2 birnessite: Characterization of Mn dissolution, oxidation products and surface interactions. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.J.; Morgan, J.J. Reactions at oxide surfaces: Oxidation of As(III) by synthetic Birnessite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.H.; Zhai, L.M.; Tan, W.F.; Liu, F.; He, J.Z. Adsorption and redox reactions of heavy metals on synthesized Mn oxide minerals. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 147, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, A.; Drits, V.A.; Silvester, E.; Bartoli, C.; Lanson, B. Structural mechanism of Co2+ oxidation by the phyllomanganate buserite. Am. Miner. 1997, 82, 1150–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Chen, C.; Lv, Q.; Tan, W.; Liu, F.; Liu, C. Influence factors for the oxidation of pyrite by oxygen and birnessite in aqueous systems. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 45, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Shen, Y.; Jia, Z.; Qiu, G.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Cai, C. Interaction mechanisms and Kinetics of ferrous ion and hexagonal birnessite in aqueous systems. Geochem. Trans. 2015, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnamurti, G.S.R.; Huang, P.M. The catalytic role of birnessite in the transformation of iron. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1978, 67, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postma, D. Concentration of Mn and separation from Fe in sediments-I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of the reaction between birnessite and dissolved Fe(II) at 10 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.S.; Feng, X.H.; Tan, W.F.; Qiu, G.H. Oxidation process of dissolvable sulfide by synthesized todorokite in aqueous systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 290, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hem, J.D. Rates of manganese oxidation in aqueous systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1981, 45, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowe, A.A.; Génin, J.M.R. The mechanism of oxidation of Fe(II) hydroxide in sulfated aqueous media: Importance of the initial ratio of the reactants. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 965–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, C.; Géhin, A.; Aissa, R.; Génin, J.M.R. Mass-balance and Eh–pH diagrams of FeII–III green rust in aqueous sulfated solution. Corros.Sci. 2006, 48, 3824–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowe, A.A.; Pauron, B.; Génin, J.M.R. The influence of temperature on the oxidation of ferrous hydroxide in sulphated aqueous medium: Activation energies of formation of the products and hyperfine structure of magnetite. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 985–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Génin, J.M.R.; Olowe, A.A.; Refait, P.H.; Simon, L. On the stoichiometry and Pourbaix diagram of the Fe(II)-(III) hydroxyl-sulfate or sulphate- containing Green Rust 2: An electrochemical and Mossbauer spectroscopy study. Corros. Sci. 1996, 38, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.H.; Bon, C.; Simon, L.; Bourrie, G.; Trolard, J.B.; Génin, J.M.R. Chemical composition and Gibbs standard free energy of formation of Fe(II)-Fe(III) hydroxysulphate green rust and Fe(II) hydroxide. Clay Miner. 1999, 34, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; Michel, F.; Refait, P.; Renaudin, G.; Lelaurain, M.; Génin, J.M.R. Structure of the Fe(II-III) layered double hydroxysulphate green rust two from Rietveld analysis. Solid State Sci. 2003, 5, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaiza, H.; Coustel, R.; Ghouti, M.; Ruby, C.; Bergaoui, L. Conditions for the formation of pure birnessite during the oxidation of Mn(II) cations in aqueous alkaline medium. J. Solid State Chem. 2017, 248, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarec, K.; Rancourt, D.G. Recoil-Mossbauer Spectral Analysis Software for Windows; Version 1.05; University of Ottawa: Ottawa, ON, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Banerjee, D. Interpretation of XPS Mn(2p) spectra of Mn oxyhydroxides and constraints on the mechanism of MnO2 precipitation. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detournay, J.; De Miranda, L.; Dérie, R.; Ghodsi, M. The region of stability of GRII in the electrochemical potential-pH diagram of iron in sulphate medium. Corros. Sci. 1975, 15, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Luis, K.B.; Koch, C.B.; Hansen, H.C.B. The standard Gibbs energy of formation of Fe(II)Fe(III) hydroxide sulfate green rust. Clays Clay Miner. 2008, 56, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebecker, M.; Madison, A.S.; Luther, G.W. Reduction kinetics of poly-meric (soluble) manganese (IV) oxide (MnO2) by ferrous iron (Fe2+). Aquat. Geochem. 2015, 21, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, D.; Appelo, C.A.J. Reduction of Mn-oxides by ferrous iron in a flow system: Column experiment and reactive transport modeling. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, C.; Abdelmoula, M.; Aissa, R.; Medjahdi, G.; Brunelli, M.; François, M. Aluminium substitution in iron(II–III)-layered double hydroxides: Formation and cationic order. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 2285–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xue, D. Estimation of electronegativity values of elements in different valence states. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 11332–11337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belin, T.; Guigue-Millot, N.; Caillot, T.; Aymes, D.; Niepce, J.C. Influence of Grain Size, Oxygen Stoichiometry, and Synthesis Conditions on the γ-Fe2O3 Vacancies Ordering and Lattice Parameters. J. Solid State Chem. 2002, 163, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.V.; Ming, D.W.; Golden, D.C.; Bell, J.F. An occurrence of jarositic tephra on Mauna Kea, Hawaii: Implications for the ferric mineralogy of the martian surface. Geochem. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1996, 5, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberghe, R.E.; Barrero, C.A.; da Costa, G.M.; San, E.V.; Grave, E.D. Mössbauer characterization of iron oxides and (oxy)hydroxides: The present state of the art. Hyperfine Interact. 2000, 126, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, A.; Abdelmoula, M.; Usman, M.; Hanna, K.; Ruby, C. In situ monitoring of lepidocrocite bioreduction and magnetite formation by reflection Mössbauer spectroscopy. Am. Miner. 2011, 96, 1410–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatzky, G.A.; Van Der woude, F.; Morrish, A.H. Mössbauer Study of Several Ferrimagnetic Spinels. Phys. Rev. 1969, 187, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorescu, M.; Tarabasanu-Mihaila, D.; Diamandescu, L. A Mössbauer study of manganese-doped magnetite. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1867–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.C.A.; Fabris, J.D.; Rios, R.R.V.A.; Mussel, W.N.; Lago, R.M. Fe3−xMnxO4 catalysts: Phase transformations and carbon monoxide oxidation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 259, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Sorensen, C.M.; Klabunde, K.J.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Devlin, E.; Kostikas, A. Size-dependent magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 fine particles synthesized by coprecipitation. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 9288–9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Shafi, K.V.P.M.; Loos, K.; Ulman, A.; Lee, Y.; Vogt, T.; Estournès, C. Doping γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles with Mn(III) Suppresses the Transition to the α-Fe2O3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11470–11471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendo, S.G.; Alves, A.F.; Ferreira, L.P.; Cruz, M.M.; Mendonça, M.H.; Godinho, M.; Carvalho, M.D. Hyperthermia studies of ferrite nanoparticles synthesized in the presence of cotton. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 7182–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.C.; Von Dreele, R.B. GSAS. Los Alamos National Laboratory Report; Los Alamos National Laboratoy: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Toby, B.H. Development of a methodology for the application of the Warren-Averbach method. J. Appl. Cryst. 2001, 34, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bard, A.J.; Parsons, R.; Jordan, J. Standard Potentials in Aqueous Solution; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Beverskog, B.; Puidomenech, I. Revised Pourbaix diagrams for iron at 25–300 °C. Corros. Sci. 1996, 38, 2121–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Major Phase | Minor Phases | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Parameters (Å) | ||||
| Final Products | R06B05F | Magnetite | a = 8.412 (3) | Hausmannite Mn3O4 Suspected: Manganite MnO(OH) Suspected: Lepidocrocite FeO(OH) |
| R06B02F | a = 8.3814(5) | None | ||
| R06F | a = 8.3828(11) | Goethite FeO(OH) Natrojarosite NaFe3(SO4)2(OH)6 Suspected: Lepidocrocite FeO(OH) | ||
| R05B05F | a = 8.3846(12) | Na Birnessite | ||
| R05F | a = 8.3722(5) | None | ||
| Intermediate Products | R06I | Green rust | a = 3.1776(3) c = 10.9638(23) | Magnetite Fe3O4 |
| R06B02I | a = 3.1841(12) c = 10.976(7) | None | ||
| R06B05I | a = 3.1912(17) c = 10.973(9) | Na Birnessite Magnetite Fe3O4 | ||
| R06B05IN2 | a = 3.1874(16) c = 10.954(8) | Na Birnessite Hausmannite Mn3O4 Magnetite Fe3O4 | ||
| Sample | Site | CS (mm s−1) | <Δ> or ε (mm s−1) | <Hhf> (T) | RA (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R06F | D1 | 0.36 | 0.56 | - | 9 | Lepidocrocite |
| - | D2 | 0.37 | 1.20 | - | 6 | Natrojarosite |
| - | S1 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 48.9 | 23 | Fe3-δO4 [Fe3+]A |
| - | S2 | 0.66 | 0.02 | 45.4 | 26 | Fe3-δO4 [Fe2.5+]B |
| - | S3 | 0.42 | −0.03 | 49.5 | 12 | Fe3-δO4 [Fe3+]B |
| - | S4 | 0.43 | −0.06 | 27.2 | 24 | Goethite |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| R06B02F | D | 0.40 | 0.58 | - | 4 | Lepidocrocite |
| - | S1 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 47.5 | 37 | MnxFe3-x-δO4 [Fe3+]A |
| - | S2 | 0.51 | −0.06 | 39.9 | 37 | MnxFe3-x-δO4 [Fe2.5+]B |
| - | S3 | 0.38 | −0.06 | 48.4 | 23 | MnxFe3-x-δO4 [Fe3+]B |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| R06B05F | D | 0.36 | 0.66 | - | 53 | - |
| - | S1 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 43.7 | 24 | - |
| - | S2 | 0.42 | -0.08 | 35.0 | 23 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doggaz, A.; Coustel, R.; Durand, P.; Humbert, F.; Ruby, C. Birnessite: A New Oxidant for Green Rust Formation. Materials 2020, 13, 3777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173777
Doggaz A, Coustel R, Durand P, Humbert F, Ruby C. Birnessite: A New Oxidant for Green Rust Formation. Materials. 2020; 13(17):3777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173777
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoggaz, Amira, Romain Coustel, Pierrick Durand, François Humbert, and Christian Ruby. 2020. "Birnessite: A New Oxidant for Green Rust Formation" Materials 13, no. 17: 3777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173777
APA StyleDoggaz, A., Coustel, R., Durand, P., Humbert, F., & Ruby, C. (2020). Birnessite: A New Oxidant for Green Rust Formation. Materials, 13(17), 3777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173777