In Vivo Animal Study of a Highly Viscous N-butyl Cyanoacrylate Medical Adhesive for Intravenous Embolization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viscosity
2.2. Heat of Polymerization and Curing Time
2.3. Animal Study Design
2.4. Venous Occlusion Procedures
2.5. Measurement Procedures
2.6. Histological Examination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Viscosity of Two Adhesives
3.2. Heat of Polymerization and Curing Time
3.3. Examination of Vascular Occlusion
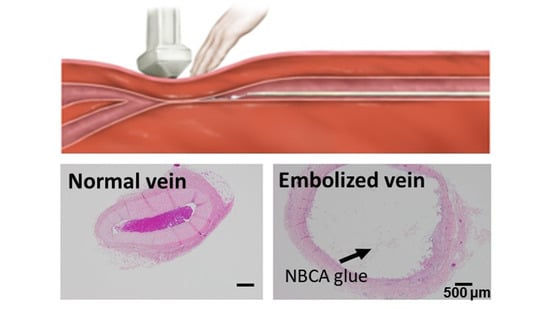
3.4. Histological Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koo, H.J.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Yoon, H.-K.; Ko, G.-Y.; Gwon, D.I. Clinical Outcome of Transcatheter Arterial Embolization With N-Butyl-2-Cyanoacrylate for Control of Acute Gastrointestinal Tract Bleeding. Am. J. Roentgen. 2015, 204, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jae, H.J.; Chung, J.W.; Jung, A.Y.; Lee, W.; Park, J.H. Transcatheter Arterial Embolization of Nonvariceal Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding with N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate. Korean J. Radiol. 2007, 8, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamatani, S.; Koike, T.; Ito, Y.; Tanaka, R. Embolization of Arteriovenous Malformation with Diluted Mixture of NBCA. Interv. Neurorad. 2000, 6, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanahashi, Y.; Kondo, H.; Osawa, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Furui, S. Transcatheter embolization of a Rasmussen aneurysm via pulmonary artery with n-butyl cyanoacrylate and iodized oil mixture injection with balloon occlusion. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2016, 2, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, A.B.; Nguyen, N.S.; Le, V.H.; Nguyen, D.D.; Phan, A.K.; Nguyen, T.X.; Pham, N.H. Preoperative embolization of high-flow peripheral AVMs using plug and push technique with low-density NBCA/Lipiodol. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 2020, rjaa316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.H.; Stephen, P.L. Characterization of N-butyl Cyanoacrylate (NBCA) Glue Polymerization for the Embolization of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs). Master’s Thesis, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2016; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, M.; Horikawa, M.; Yamagami, T.; Uchida, B.T.; Awai, K.; Kaufman, J.A. Embolization of Arteriovenous Malformations: Effect of Flow Control and Composition of n-Butyl-2 Cyanoacrylate and Iodized Oil Mixtures with and without Ethanol in an in Vitro Model. Radiology 2016, 279, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radak, D.; Djukic, N.M. Neskovic, Cyanoacrylate Embolisation: A Novelty In The Field of Varicose Veins Surgery. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 55, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, E.; Yasim, A. A Randomised Clinical Trial Comparing N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate, Radiofrequency Ablation and Endovenous Laser Ablation for the Treatment of Superficial Venous Incompetence: Two Year Follow up Results. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2018, 56, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, K.; Ferris, B. Cyanoacrylate closure of incompetent great, small and accessory saphenous veins without the use of post-procedure compression, Initial outcomes of a post-market evaluation of the VenaSeal System (the WAVES Study). Vascular 2017, 25, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Morishita, H.; Sato, Y.; Hamaguchi, S.; Sakamoto, N.; Tokue, H.; Yonemitsu, T.; Murakami, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Sofue, K.; et al. Guidelines for the use of NBCA in vascular embolization devised by the Committee of Practice Guidelines of the Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology (CGJSIR), 2012 edition. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2014, 32, 500–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takasawa, C.; Matsunaga, K.; Seiji, K.; Mastuhashi, T.; Shida, S.; Ota, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Fujishima, F.; Takahashi, S. A fundamental examination of the effect of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (NBCA)-iodized oil mixtures on arterial embolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 23, S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, N.; Sato, M.; Minamiguchi, H.; Ikoma, A.; Sanda, H.; Nakata, K.; Tanaka, F.; Nakai, M.; Sonomura, T. Basic Study of a Mixture of N-butyl Cyanoacrylate, Ethanol, and Lipiodol as a New Embolic Material. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 1516–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Barthès-Biesel, D.; Salsac, A.-V. Polymerization kinetics of n-butyl cyanoacrylate glues used for vascular embolization. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 69, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data, Histoacryl and Histoacryl Blue, Premarket Approval (PMA) Application Number, P050013S, FDA. 2007. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf5/P050013c.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2021).
- Jamnadas-Khoda, B.; Khan, M.A.A.; Thomas, G.P.L.; Ghosh, S.J. Histoacryl glue, A burning issue. Burns 2011, 37, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffroy, R. Glubran2®, Histoacryl® or Trufill®, Which cyanoacrylate glue for endovascular use? Diag. Interv. Imaging 2016, 97, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhat, Y.M.; Banerjee, S.; Barth, B.A.; Chauhan, S.S.; Gottlieb, K.T.; Konda, V.; Maple, J.T.; Murad, F.M.; Pfau, P.R.; Pleskow, D.K.; et al. Tissue adhesives, cyanoacrylate glue and fibrin sealant. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 78, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.C.; Park, W.; Kang, J.M.; Ryu, D.S.; Park, Y.; Seo, J.-W.; Koh, Y.G.; Park, J.-H.; Shin, J.H. Newly Developed N-butyl Cyanoacrylate (EG glue) for Arterial Embolization, A Preclinical Study in Rabbit Renal Artery. Macromol. Res. 2021, 29, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasawa, C.; Seiji, K.; Matsunaga, K.; Matsuhashi, T.; Ohta, M.; Shida, S.; Takase, K. Properties of N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate–iodized Oil Mixtures for Arterial Embolization: In Vitro and In Vivo Experiments. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, C.M.; Malek, A.M.; Kwan, E.S.; Hoit, D.A.; Weller, S.J. Embolization of Hypervascular Spinal Metastases using Percutaneous Direct Injection with N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate, Technical Case Report. Neurosurgery. 2006, 59, E431–E432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattamal, G.J.; Krause, D. Class II Special Controls Guidance Document, Tissue Adhesive with Adjunct Wound Closure Device Intended for the Topical Approximation of Skin, Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff. 2010. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/guidance-documents-medical-devices-and-radiation-emitting-products/tissue-adhesive-adjunct-wound-closure-device-intended-topical-approximation-skin-class-ii-special (accessed on 24 June 2021).
- Minqiang, X.; Jie, L.; Dali, M.; Lanhua, M. Transmidline Abdominal Skin Flap Model in Pig, Refinements and Advancements. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2012, 28, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, N.G.; Laura, B.; Ali, C.; Anant, M.; Nasir, R.; Bulent, Y. Histopathological Image Analysis: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 2, 147–171. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, C.; Murphy, K.; Gailloud, P. Improved distal distribution of n-butyl cyanoacrylate glue by simultaneous injection of dextrose 5% through the guiding catheter. Neuroradiology 2006, 48, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5, Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity (ISO 10993-5); ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Costigliola, L.; Heyes, D.M.; Schrøder, T.B.; Dyre, J.C. Revisiting the Stokes-Einstein relation without a hydrodynamic diameter. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 150, 021101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conway, R.; Aglan, A.; O’connor, E. Severe respiratory failure due to embolization of cyanoacrylate sclerosant. Q. J. Med. 2014, 107, 831–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaminuma, Y.; Tanahashi, M.; Suzuki, E.; Yoshii, N.; Niwa, H. Extensive bronchial occlusion with N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate for bronchopleural fistula and a destroyed lung. Respirol. Case Rep. 2020, 8, e00500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, P.; Horowitz, M.; Kopitnik, T.; Samson, D.; Dion, J.; Joseph, G.; Dawson, R.; Owens, D.; Barrow, D.; Barr, J.; et al. N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate Embolization of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations, Results of a Prospective, Randomized, Multi-center Trial. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2002, 23, 748–755. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, J.-W.; Park, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Koh, Y.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, I.; Lee, W. In Vivo Animal Study of a Highly Viscous N-butyl Cyanoacrylate Medical Adhesive for Intravenous Embolization. Materials 2021, 14, 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133527
Seo J-W, Park H, Kim D, Lee S, Koh YG, Kim JY, Park I, Lee W. In Vivo Animal Study of a Highly Viscous N-butyl Cyanoacrylate Medical Adhesive for Intravenous Embolization. Materials. 2021; 14(13):3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133527
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Jae-Won, Habeen Park, Dogeun Kim, Seoyun Lee, Young Gook Koh, Jang Yong Kim, Insoo Park, and Wonmok Lee. 2021. "In Vivo Animal Study of a Highly Viscous N-butyl Cyanoacrylate Medical Adhesive for Intravenous Embolization" Materials 14, no. 13: 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133527
APA StyleSeo, J. -W., Park, H., Kim, D., Lee, S., Koh, Y. G., Kim, J. Y., Park, I., & Lee, W. (2021). In Vivo Animal Study of a Highly Viscous N-butyl Cyanoacrylate Medical Adhesive for Intravenous Embolization. Materials, 14(13), 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133527