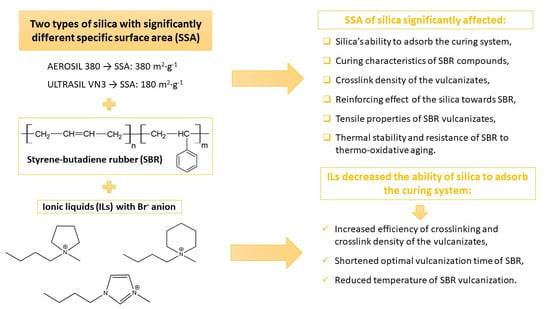
Influence of the Silica Specific Surface Area and Ionic Liquids on the Curing Characteristics and Performance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of SBR Compounds Filled with Silica
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Stability of Silica and Ionic Liquids
3.2. Dispersion of Curatives and Silica in SBR Matrix
3.3. Effect of Silica and Ionic Liquids on Cure Characteristics and Crosslink Density of SBR Composites
3.4. Effect of Silica and Ionic Liquids on Tensile Properties and Hardness of SBR Composites
3.5. Effect of Silica and Ionic Liquids on Thermo-Oxidative Aging of SBR Composites
3.6. Effect of Silica and Ionic Liquids on Thermal Stability of SBR Cmposites
3.7. Effect of Silica and Ionic Liquids on Dynamic Mechanical Properties of SBR Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da Silva, V.M.; Nunes, R.C.R.; De Sousa, A.M.F. Epoxidized natural rubber and hydrotalcite compounds: Rheological and thermal characterization. Polímeros 2017, 27, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maslowski, M.; Miedzianowska, J.; Strzelec, K. The Potential Application of Cereal Straw as a Bio-filler for Elastomer Composites. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 2021–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nihmath, A.; Ramesan, M. Hydroxyapatite as a Potential Nanofiller in Technologically Useful Chlorinated Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber. Polym. Test. 2020, 91, 106837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szadkowski, B.; Marzec, A.; Rybiński, P.; Żukowski, W.; Zaborski, M. Characterization of Ethylene–propylene Composites Filled with Perlite and Vermiculite Minerals: Mechanical, Barrier, and Flammability Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulfah, I.M.; Fidyaningsih, R.; Rahayu, S.; Fitriani, D.A.; Saputra, D.A.; Winarto, D.A.; Wisojodharmo, L.A. Influence of Carbon Black and Silica Filler on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber Compound. Procedia Chem. 2015, 16, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinrich, G.; Klüppel, M.; Vilgis, T.A. Reinforcement of elastomers. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmalska, A.; Zaborski, M.; Ślusarski, L. Adsorption of curatives and activity of silica toward elastomers. Macromol. Symp. 2003, 194, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanasom, N.; Saowapark, T.; Deeprasertkul, C. Reinforcement of natural rubber with silica/carbon black hybrid filler. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrasik, J.; Szustakiewicz, L.; Zaborski, M.; Haberko, K. Hydroxyapatite: An Environmentally Friendly Filler for Elastomers. Mol. Cryst. Liq. 2010, 483, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bevervoorde-Meilof, E.E.; van Haeringen-Trifonova, D.; Vansco, G.J.; van der Does, L.; Bantjes, A.; Noordemeer, J.W.M. Cross-link Clusters: Reality or Fiction? A Review of The State of the Art, Enlarged with Recent AFM-data. Kautsch. Gummi. Kunsts. 2000, 53, 426–433. [Google Scholar]
- Brinke, J.; Debnath, S.; Reuvekamp, L.; Noordermeer, J. Mechanistic aspects of the role of coupling agents in silica–rubber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-Oui, P.; Sirisinha, C.; Thepsuwan, U.; Hatthapanit, K. Dependence of mechanical and aging properties of chloroprene rubber on silica and ethylene thiourea loadings. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luginsland, H.D.; Niedermeien, W. New Reinforcing Materials for Rising Tire Performance Demands. Rubber World 2003, 228, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ansarifar, M.A.; Nijhawan, R. Effects of Silane on Properties of Silica Filled Natural Rubber Compounds. J. Rubb. Res. 2000, 3, 169–184. [Google Scholar]
- Noriman, N.Z.; Ismail, H. Properties of styrene butadiene rubber (SBR)/recycled acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBRr) blends: The effects of carbon black/silica (CB/Sil) hybrid filler and silane coupling agent, Si69. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.P. Reinforcing Silicas and Silicates. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1976, 49, 703–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Sowińska, A. Influence of Fillers and Ionic Liquids on the Crosslinking and Performance of Natural Rubber Biocomposites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Zaborski, M. Ionic Liquids Applied to Improve the Dispersion of Coagent Particles in an Elastomer. J. Compos. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowińska, A.; Maciejewska, M.; Guo, L.; Delebecq, E. Effect of SILPs on the Vulcanization and Properties of Ethylene–Propylene–Diene Elastomer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, M.; Conzatti, L.; Costa, G.; Falqui, L.; Turturro, A.; Valenti, B.; Negroni, F. Surface modification of silica: 1. Thermodynamic aspects and effect on elastomer reinforcement. Polymer 2005, 46, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, G.; Huh, M.-Y.; Rhee, J.M.; Lee, M.-H.; Nah, C. Improvement of Properties of Silica-Filled Styrene-Butadiene Rubber Composites Through Plasma Surface Modification of Silica. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2004, 15, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chen, F.; Lei, Y.; Chen, W. Significantly improved performance of rubber/silica composites by addition of sorbic acid. Polym. J. 2010, 42, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Barrantes, I.; Rodriguez, A.; Ibarra, L.; González, L.; Valentin, J.L. Overcoming the disadvantages of fumed silica as filler in elastomer composites. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7381–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Yasin, S.; Adnan Akram, M.; Xu, H.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Influence of Ionic Liquids on Structure and Rheological Behaviors of Silica-Filled Butadiene Rubber. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 18205–18212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, X.; Jia, H.; Wang, J.; Ji, Q.; Xu, Z.-D. Influence of ionic liquid on the polymer-filler coupling and mechanical properties of nano-silica filled elastomer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 134, 44478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.D.; Tang, Z.H.; Guo, B.C.; Zhu, L.X.; Jia, D.M. Synthesis of novel functional liquid and its application as a modifier in SBR/silica composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2010, 4, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Functional thiol ionic liquids as novel interfacial modifiers in SBR/HNTs composites. Polymer 2011, 52, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Ding, Y. Piezoresistive properties of nanocomposites based on silicone rubber and ionic liquid-functionalized carbon black. Mater. Lett. 2016, 182, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6502-3:2018. Rubber—Measurement of Vulcanization Characteristics Using Curemeters—Part 3: Rotorless Rheometer; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khimi, S.R.; Pickering, K.L. A new method to predict optimum cure time of rubber compound using dynamic mechanical analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 131, 40008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.B. Rubber Basics, 1st ed.; Rapra Technology Limited: Shawbury, UK, 2002; pp. 2–30. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11357-1:2016. Plastics—Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)—Part 1: General Principles; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 1817:2015. Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic—Determination of Effect of Liquids; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Flory, P.J.; Rehner, J. Statistical Mechanics of Cross-Linked Polymer Networks II. Swelling. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, I.; Kimura, S.; Iwama, M. Physical Constants of Rubbery Polymers. In Polymer Handbook, 4th ed.; Brandrup, J., Immergut, E.H., Grulke, E.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 37:2017. Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic—Determination of Tensile Stress-Strain Properties; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 868:2003. Plastics and Ebonite—Determination of Indentation Hardness by Means of a Durometer (Shore Hardness); International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 188:2011. Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic—Accelerated Ageing and Heat Resistance Tests; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dziemidkiewicz, A.; Maciejewska, M. Manganese and Nickel Acetylacetonates as Curatives for Chloroprene Rubber Based on Heck’s Reaction. Materials 2021, 14, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szadkowski, B.; Kuśmierek, M.; Rybiński, P.; Żukowski, W.; Marzec, A. Application of Earth Pigments in Cycloolefin Copolymer: Protection against Combustion and Accelerated Aging in the Full Sunlight Spectrum. Materials 2020, 13, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masłowski, M.; Miedzianowska, J.; Strzelec, K. Natural Rubber Composites Filled with Crop Residues as an Alternative to Vulcanizates with Common Fillers. Polymers 2019, 11, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Souza, A.S.; Pantano, C.G. Hydroxylation and Dehydroxylation Behavior of Silica Glass Fracture Surfaces. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 85, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Qin, L.; Jiang, J.; Mu, T.; Gao, G. Thermal, electrochemical and radiolytic stabilities of ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 8382–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhocine, T.; Forsyth, S.A.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; Nieuwenhuyzen, M.; Nockemann, P.; Puga, A.; Seddon, K.R.; Srinivasan, G.; Whiston, K. 3-Methylpiperidinium ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 10398–10416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejewska, M.; Sowińska, A. Thermal characterization of the effect of fillers and ionic liquids on the vulcanization and properties of acrylonitrile–butadiene elastomer. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 4359–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maciejewska, M.; Zaborski, M. Ionic liquids as coagents for sulfur vulcanization of butadiene–styrene elastomer filled with carbon black. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 4499–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokobza, L. Natural Rubber Nanocomposites: A Review. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaborski, M.; Donnet, J. Activity of fillers in elastomer networks of different structure. Macromol. Symp. 2003, 194, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordermeer, J.W.M. Vulcanization. In Encyclopedia of Polymeric Nanomaterials; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 2577–2590. [Google Scholar]
- Maciejewska, M.; Walkiewicz, F.; Zaborski, M. Novel Ionic Liquids as Accelerators for the Sulfur Vulcanization of Butadiene–Styrene Elastomer Composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 8410–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaca, M.; Ilcikova, M.; Mrlik, M.; Cvek, M.; Vaulot, C.; Urbanek, P.; Pietrasik, R.; Krupa, I.; Pietrasik, J. Impact of ionic liquids on the processing and photo-actuation behavior of SBR composites containing graphene nanoplatelets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, S.; Hussain, M.; Zheng, Q.; Song, Y. Effects of ionic liquid on cellulosic nanofiller filled natural rubber bionanocomposites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 591, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzec, A.; Laskowska, A.; Boiteux, G.; Zaborski, M.; Gain, O.; Serghei, A. Properties of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber/Hydrotalcite Composites Containing Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. Macromol. Symp. 2014, 341, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mąka, H.; Spychaj, T.; Zenker, M. High performance epoxy composites cured with ionic liquids. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 31, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochoń, M.; Janowska, G.; Przepiórkowska, A.; Kucharska-Jastrzabek, A. Thermal properties and combustibility of elastomer–protein composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 109, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowińska, A.; Maciejewska, M. Thermal analysis applied to studying the influence of ionic liquids on the vulcanization, thermal stability and damping properties of ethylene-propylene-diene rubber. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 2669–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maciejewska, M.; Zaborski, M. Ionic Liquids Applied to Improve the Dispersion of Solids in Elastomers. In Ionic Liquids-Current State of the Art; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2015; pp. 557–589. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Bi, W.; Zhao, S. Influence of Crosslink Density on Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber Vulcanizates. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2011, 50, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Bai, F.; Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Hu, J.; Chen, L.; Lin, J.; Wei, G.; Du, X. Aging properties of styrene-butadiene rubber nanocomposites filled with carbon black and rectorite. Polym. Test. 2017, 64, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Dosoudil, R.; Hudec, I. Thermooxidative aging of rubber composites based on NR and NBR with incorporated strontium ferrite. J. Elastomers Plast. 2018, 50, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Zaborski, M. Effect of ionic liquids on the dispersion of zinc oxide and silica nanoparticles, vulcanisation behaviour and properties of NBR composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gwaily, S.; Badawy, M.; Hassan, H.; Madani, M. Influence of thermal aging on crosslinking density of boron carbide/natural rubber composites. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Wei, W.-L.; Hsu, K.-Y.; Ho, W.-H. Thermal stability of epoxy-silica hybrid materials by thermogravimetric analysis. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 412, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertsri, S.; Rattanasom, N. Fumed and precipitated silica reinforced natural rubber composites prepared from latex system: Mechanical and dynamic properties. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, J.; George, E.; Thomas, S.; Anas, S. Effect of filler loading on polymer chain confinement and thermomechanical properties of epoxy/boron nitride (h-BN) nanocomposites. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 4494–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.; Kim, J.Y.; Hong, U.; Oh, M.K.; Kim, M.; Han, S.B.; Nam, J.-D.; Suhr, J. Dynamic viscoelasticity of silica-filled styrene-butadiene rubber/polybutadiene rubber (SBR/BR) elastomer composites. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2020, 187, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Name | Abbreviation | CAS Number | Purity (%) | Water Content (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide | BmiBr | 85100-77-2 | ≥99.0% | <0.5% |
| 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bromide | BmpyrBr | 93457-69-3 | ≥99.0% | ≤0.5% |
| 1-butyl-1-methylpiperidinium bromide | BmpipBr | 94280-72-5 | ≥99.0% | 0.5% |
| Ingredient, phr | Unfilled Sample (R0) | SBR/A380 (R1) | SBR/VN3 (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBR | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Sulfur | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| ZnO | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| MBT | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| CBS | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Aerosil 380 | ₋ | 30 | ₋ |
| Ultrasil VN3 | ₋ | ₋ | 30 |
| Ingredient, phr | SBR/BmiBr (IL1–IL2) | SBR/BmpyrBr (IL3–IL4) | SBR/BmpipBr (IL5–IL6) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBR | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Sulfur | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| ZnO | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| MBT | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| CBS | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Silica * | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| BmiBr | 3 | ₋ | ₋ |
| BmpyrBr | ₋ | 3 | ₋ |
| BmpipBr | ₋ | ₋ | 3 |
| Compounds | Smin (dNm) | Smax (dNm) | ∆S (dNm) | t05 (min) | t95 (min) | (mol/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unfilled sample | 0.7 | 8.1 | 7.4 | 1 | 3 | 5.44 |
| Aerosil A380 | ||||||
| A380 | 4.5 | 24.5 | 20.0 | 2 | 42 | 4.36 |
| A380/BmiBr | 4.1 | 24.3 | 19.2 | 1 | 11 | 7.65 |
| A380/BmpyrBr | 4.3 | 22.0 | 17.8 | 1 | 28 | 6.09 |
| A380/BmpipBr | 3.7 | 22.2 | 18.5 | 1 | 21 | 6.55 |
| Ultrasil VN3 | ||||||
| VN3 | 2.3 | 18.0 | 15.7 | 2 | 10 | 6.19 |
| VN3/BmiBr | 1.7 | 17.0 | 15.5 | 1 | 3 | 8.84 |
| VN3/BmpyrBr | 1.9 | 16.5 | 14.6 | 1 | 17 | 7.26 |
| VN3/BmpipBr | 2.3 | 17.2 | 14.5 | 1 | 15 | 8.03 |
| Compounds | Tg (°C) | ∆Cp (J/g × K) | Tonset (°C) | Tendset (°C) | ∆H (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unfilled sample | −51.1 ± 0.9 | 0.40 ± 0.10 | 149 ± 2 | 188 ± 2 | 9.0 ± 1.5 |
| Aerosil 380 | |||||
| A380 | −51.5 ± 1.0 | 0.33 ± 0.09 | 176 ± 3 | 235 ± 3 | 8.6 ± 1.4 |
| A380/BmiBr | −51.2 ± 0.9 | 0.33 ± 0.08 | 145 ± 1 | 243 ± 1 | 7.1 ± 1.3 |
| A380/BmpyrBr | −51.9 ± 1.1 | 0.35 ± 0.09 | 148 ± 2 | 241 ± 2 | 7.3 ± 1.4 |
| A380/BmpipBr | −51.5 ± 1.0 | 0.33 ± 0.08 | 146 ± 3 | 239 ± 3 | 5.9 ± 1.5 |
| Ultrasil VN3 | |||||
| VN3 | −50.9 ± 0.9 | 0.34 ± 0.09 | 167 ± 1 | 235 ± 1 | 12.7 ± 1.5 |
| VN3/BmiBr | −50.4 ± 0.8 | 0.36 ± 0.07 | 137 ± 1 | 230 ± 1 | 3.0 ± 1.5 |
| VN3/BmpyrBr | −50.3 ± 0.9 | 0.34 ± 0.09 | 140 ± 2 | 235 ± 2 | 4.8 ± 1.4 |
| VN3/BmpipBr | −50.6 ± 0.9 | 0.32 ± 0.10 | 140 ± 2 | 235 ± 2 | 4.7 ± 1.3 |
| SBR Vulcanizates | Se100 (MPa) | Se300 (MPa) | TS (MPa) | Eb (%) | H (Shore A) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unfilled sample | 1.2 ± 0.1 | - | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 222 ± 14 | 43 ± 1 |
| Aerosil 380 | |||||
| A380 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 18.2 ± 0.9 | 749 ± 17 | 63 ± 1 |
| A380/BmiBr | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 17.5 ± 0.5 | 560 ± 17 | 70 ± 1 |
| A380/BmpyrBr | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 12.0 ± 0.6 | 600 ± 16 | 67 ± 1 |
| A380/BmpipBr | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 16.7 ± 0.8 | 590 ± 10 | 68 ± 1 |
| Ultrasil VN3 | |||||
| VN3 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 2.8 ± 0.1 | 18.7 ± 0.9 | 690 ± 10 | 58 ± 1 |
| VN3/BmiBr | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 18.4 ± 1.0 | 590 ± 17 | 63 ± 1 |
| VN3/BmpyrBr | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.3 | 15.0 ± 1.0 | 600 ± 16 | 61 ± 1 |
| VN3/BmpipBr | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 3.8 ± 0.3 | 17.5 ± 0.5 | 587 ± 20 | 62 ± 1 |
| SBR Vulcanizates | AF (-) |
|---|---|
| Unfilled sample | 0.7 |
| Aerosil 380 | |
| A380 | 0.3 |
| A380/BmiBr | 0.4 |
| A380/BmpyrBr | 0.6 |
| A380/BmpipBr | 0.5 |
| Ultrasil VN3 | |
| VN3 | 0.2 |
| VN3/BmiBr | 0.2 |
| VN3/BmpyrBr | 0.2 |
| VN3/BmpipBr | 0.3 |
| SBR Vulcanizates | T5% (°C) | TDTG (°C) | ∆m25–600 °C (%) | ∆m600–800 °C (%) | Residue at 800 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unfilled sample | 331 ± 1 | 481 ± 1 | 94.1 ± 1.2 | 0.4 ± 1.2 | 5.5 ± 1.0 |
| Aerosil 380 | |||||
| A380 | 363 ± 1 | 478 ± 1 | 74.8 ± 1.1 | 0.7 ± 1.1 | 24.5 ± 0.8 |
| A380/BmiBr | 357 ± 1 | 469 ± 1 | 74.9 ± 1.0 | 1.4 ± 1.0 | 23.7 ± 0.7 |
| A380/BmpyrBr | 337 ± 2 | 477 ± 2 | 75.3 ± 1.3 | 1.2 ± 1.3 | 23.5 ± 0.9 |
| A380/BmpipBr | 347 ± 1 | 477 ± 1 | 75.4 ± 1.3 | 1.2 ± 1.3 | 23.4 ± 0.9 |
| Ultrasil VN3 | |||||
| VN3 | 347 ± 1 | 479 ± 1 | 75.7 ± 1.0 | 0.8 ± 1.0 | 23.5 ± 0.8 |
| VN3/BmiBr | 339 ± 1 | 474 ± 1 | 76.1 ± 0.9 | 1.2 ± 0.9 | 22.7 ± 0.8 |
| VN3/BmpyrBr | 319 ± 2 | 477 ± 2 | 75.9 ± 1.3 | 1.1 ± 1.3 | 23.0 ± 0.9 |
| VN3/BmpipBr | 301 ± 1 | 475 ± 1 | 76.3 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 22.7 ± 0.9 |
| SBR Vulcanizates | Tg (°C) | Tan δTg (-) | Tan δ25 °C (-) | Tan δ50 °C (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unfilled sample | −46.6 ± 1.1 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 |
| Aerosil A380 | ||||
| A380 | −49.4 ± 1.2 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 |
| A380/BmiBr | −49.1 ± 1.0 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| A380/BmpyrBr | −47.4 ± 1.2 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.02 |
| A380/BmpipBr | −50.0 ± 1.2 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.01 |
| Ultrasil VN3 | ||||
| VN3 | −48.9 ± 1.0 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.02 |
| VN3/BmiBr | −49.2 ± 1.0 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 |
| VN3/BmpyrBr | −47.2 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 |
| VN3/BmpipBr | −48.8 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sowińska-Baranowska, A.; Maciejewska, M. Influence of the Silica Specific Surface Area and Ionic Liquids on the Curing Characteristics and Performance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 5302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185302
Sowińska-Baranowska A, Maciejewska M. Influence of the Silica Specific Surface Area and Ionic Liquids on the Curing Characteristics and Performance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Composites. Materials. 2021; 14(18):5302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185302
Chicago/Turabian StyleSowińska-Baranowska, Anna, and Magdalena Maciejewska. 2021. "Influence of the Silica Specific Surface Area and Ionic Liquids on the Curing Characteristics and Performance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Composites" Materials 14, no. 18: 5302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185302
APA StyleSowińska-Baranowska, A., & Maciejewska, M. (2021). Influence of the Silica Specific Surface Area and Ionic Liquids on the Curing Characteristics and Performance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Composites. Materials, 14(18), 5302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185302