A Robust and Wearable Triboelectric Tactile Patch as Intelligent Human-Machine Interface
Abstract
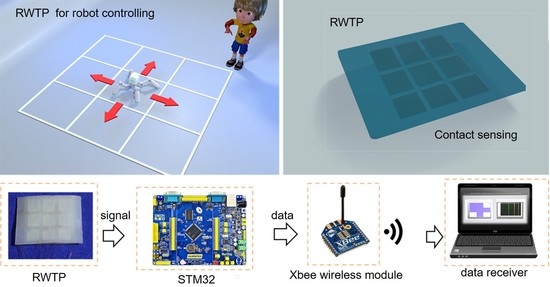
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
3. Conclusions
4. Methods
4.1. Signal Acquisition Circuit and Signal Processing Design
4.2. Fabrication of Device
4.3. Characterization and Electrical Measurements
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




References
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ren, C.; Zhang, H.; Cai, H.; Ding, G.; Yang, Z.; et al. Regulation of nanocrystals structure for high-performance magnetic triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Yang, F.; Zhou, F.; He, J.; Lu, W.; Xiao, P.; Yan, H.; Pan, C.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.L. bioinspired self-healing human-machine interactive touch pad with pressure-sensitive adhesiveness on targeted substrates. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Yu, G.; Zhai, D.; Lee, H.R.; Zhao, W.; Liu, N.; Wang, H.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Shi, Y.; Cui, Y. Hierarchical nanostructured conducting polymer hydrogel with high electrochemical activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2012, 109, 9287–9292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.G.; Nie, J.; Han, C.; Jiang, T.; Yang, Z.; Pang, Y.; Xu, L.; Guo, T.; Bu, T.; Zhang, C. Self-powered electrostatic adsorption face mask based on a triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7126–7133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Shang, J.; Jiang, X. Multilayered electronic transfer tattoo that can enable the crease amplification effect. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MMirvakili, S.M.; Hunter, I.W. Artificial muscles: Mechanisms, applications, and challenges. Adv. Mater. 2017, 30, 1704407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wu, F.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C.; Yuce, M.R. Sensors and control interface methods based on triboelectric nanogenerator in IoT applications. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 92745–92757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Hjort, K.; Hilborn, J.; Wu, Z. PDMS-based elastomer tuned soft, stretchable, and sticky for epidermal electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5830–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, C.K.; Chortos, A.; Berndt, A.; Nguyen, A.K.; Tom, A.; Mcguire, A.; Lin, Z.C.; Tien, K.; Bae, W.G.; Wang, H. A skin-inspired organic digital mechanoreceptor. Science 2015, 2, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, A.; Sanchez, V.; Atalay, O.; Vogt, D.M.; Haufe, F.; Wood, R.J.; Walsh, C.J. Batch fabrication of customizable silicone-textile composite capacitive strain sensors for human motion tracking. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 350, 1700136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannsfeld, S.C.; Tee, B.C.; Stoltenberg, R.M.; Chen, C.V.H.; Barman, S.; Muir, B.V.; Sokolov, A.N.; Reese, C.; Bao, Z. Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensors with microstructured rubber dielectric layers. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, R.; Ma, C.; Tang, Z.; Bao, N.; Wu, W.; Fan, F.; Wu, W. Solution-synthesized chiral piezoelectric selenium nanowires for wearable self-powered human-integrated monitoring. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.K.; Chou, S.A.; Hsu, C.H.; Mathew, R.J.; Chen, Y.T. Tin disulfide piezoelectric nanogenerators for biomechanical energy harvesting and intelligent human-robot interface applications. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Pu, X.; Yang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Hu, C.; Xi, Y. A flutter-effect-based triboelectric nanogenerator for breeze energy collection from arbitrary directions and self-powered wind speed sensor. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 3018–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Q.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, M.; Lee, C. Ultrathin noncontact-mode triboelectric nanogenerator triggered by giant dielectric material adaption. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, T.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, W.; Xu, M.; Tao, J.; Xie, G. A triboelectric-based artificial whisker for reactive obstacle avoidance and local mapping. Research 2021, 2021, 9864967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. Electron transfer mechanism of graphene/Cu heterostructure for improving the stability of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zou, H.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Rationally designed sea snake structure based triboelectric nanogenerators for effectively and efficiently harvesting ocean wave energy with minimized water screening effect. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, T.; Dong, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Liu, C.; Pan, X.; Zhao, Y. Sandwich-like triboelectric nanogenerators integrated self-powered buoy for navigation safety. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, E.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Mi, J.; Pan, X.; Xu, M. A novel humidity resisting and wind direction adapting flag-type triboelectric nanogenerator for wind energy harvesting and speed sensing. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudem, B.; Ko, Y.H.; Leem, J.W.; Lim, J.H.; Yu, J.S. Hybrid energy cell with hierarchical nano/micro-architectured polymer film to harvest mechanical, solar, and wind energies individually/simultaneously. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30165–30175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.X.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, J.X.; Liang, X.; Xu, L.; Shao, J.J.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Silicone-based triboelectric nanogenerator for water wave energy harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3616–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, M.; Ma, Z.; Ouyang, H.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Niu, H.; Pan, X.; Xu, M.; Li, Z. Self-powered distributed water level sensors based on liquid-solid triboelectric nanogenerators for ship draft detecting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.S.; Chhetry, A.; Maharjan, P.; Rasel, M.S.; Park, J.Y. A laser ablated graphene-based flexible self-powered pressure sensor for human gestures and finger pulse monitoring. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.L.; Ding, W.; Kien, P.T.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. A highly-sensitive wave sensor based on liquid-solid interfacing triboelectric nanogenerator for smart marine equipment. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Hu, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Du, T.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, T.; et al. A triboelectric-nanogenerator-based gas-solid two-phase flow sensor for pneumatic conveying system detecting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2001270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xie, Z.; Yao, K.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Lu, W.; Chang, L.; Yu, X. Trampoline inspired stretchable triboelectric nanogenerators as tactile sensors for epidermal electronic. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.; Tian, J.; Sun, G.; Zou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Shi, B.; Fan, Y.; Fan, Y.; et al. Self-powered pulse sensor for antidiastole of cardiovascular disease. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, A.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered electrostatic actuation systems for manipulating the movement of both microfluid and solid objects by using triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 27, 606408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Huang, X.; Xu, L.; Lai, Y.-C.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H. Triboelectric nanogenerators enabled sensing and actuation for robotics. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.; Wang, Z.L. A single-electrode based triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered tracking system. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6594–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhu, W.; Gu, G.; Jiang, T.; Xu, L.; Chen, B.; Han, C.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.L. Integrative square-grid triboelectric nanogenerator as a vibrational energy harvester and impulsive force sensor. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Y. Fingerprint-inspired electronic skin based on triboelectric nanogenerator for fine texture recognition. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Sun, X.; Diao, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Qin, C.; Liang, E.; Mao, Y. Triboelectric touch-free screen sensor for noncontact gesture recognizing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Ren, C.; Shi, X.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; et al. Contribution of ferromagnetic medium to the output of triboelectric nanogenerators derived from Maxwell’s Equations. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Pu, X.; Du, X.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; et al. Screen-printed washable electronic textiles as self-powered touch gesture tribo-sensors for intelligent human-machine interaction. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5190–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Yan, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, X. Stretchable and shape-adaptable triboelectric nanogenerator based on biocompatible liquid electrolyte for biomechanical energy harvesting and wearable human-machine interaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, A.; Alluri, N.R.; Saravanakumar, B.; Selvarajan, S.; Kim, S.-J. Human interactive triboelectric nanogenerator as a self-powered smart seat. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 12, 9692–9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, H. Self-powered electronic skin based on the triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, H.; Bao, R.; Zhong, L.W. Skin-inspired highly stretchable and conformable matrix networks for multifunctional sensing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Dong, K.; Shen, S.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, X.; Ye, C.; Wang, Z.L. Fully fabric-based triboelectric nanogenerators as self-powered human-machine interactive keyboards. Nanomicro. Lett. 2021, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, T.; Qsbc, D.; Zzbc, D.; Thbc, D.; Zsbc, D.; Clbc, D. Hybridized wearable patch as a multi-parameter and multi-functional human-machine interface. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, M.; Hetian, Y.; Sun, L. Triboelectric self-powered wearable flexible patch as 3D motion control interface for robotic manipulator. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11561–11571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical study of contact-mode triboelectric nanogenerators as an effective power source. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Shi, Q.; He, T.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Ma, Y.; Kwong, D.L.; Lee, C. Wearable triboelectric/aluminum nitride nano-energy-nano-system with self-sustainable photonic modulation and continuous force sensing. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, P.; Zhao, T.; Luan, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. A Robust and Wearable Triboelectric Tactile Patch as Intelligent Human-Machine Interface. Materials 2021, 14, 6366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216366
Hu Z, Wang J, Wang Y, Wang C, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Xu P, Zhao T, Luan Y, Liu C, et al. A Robust and Wearable Triboelectric Tactile Patch as Intelligent Human-Machine Interface. Materials. 2021; 14(21):6366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216366
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zhiyuan, Junpeng Wang, Yan Wang, Chuan Wang, Yawei Wang, Ziyi Zhang, Peng Xu, Tiancong Zhao, Yu Luan, Chang Liu, and et al. 2021. "A Robust and Wearable Triboelectric Tactile Patch as Intelligent Human-Machine Interface" Materials 14, no. 21: 6366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216366
APA StyleHu, Z., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Wang, C., Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., Xu, P., Zhao, T., Luan, Y., Liu, C., Qiao, L., Shu, M., Mi, J., Pan, X., & Xu, M. (2021). A Robust and Wearable Triboelectric Tactile Patch as Intelligent Human-Machine Interface. Materials, 14(21), 6366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216366