Iron Elution from Iron and Steel Slag Using Bacterial Complex Identified from the Seawater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Primary Screening to Isolate the Bacterial Strains for Iron Elution by Luminol Reaction
2.3. Identification of Bacterial Strains by PCR and Sequencing
2.4. Measurements of Iron Elution Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-AES)
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopies (SEM) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Measurements
2.6. Iron Elution Capacity of Bacteria in the Seawater
2.7. Screening of Bacterial Strains for the Synthesis of Biofilm on ISS
2.8. Phenol-Sulfuric Acid Method to Quantify the Amount of Biofilm
2.9. Iron Elution Capacity of Bacteria with Biofilm in the Seawater
3. Results
3.1. Primary Screening to Isolate the Bacterial Strains for Iron Elution by Luminol Reaction
3.2. Identification of Bacterial Strains by 16S rRNA Sequencing
3.3. Chemical Analyses of CSMS after Treatment of TO1
3.4. Iron Elution from CMSM Using TO1 in the Seawater
3.5. Screening of Bacterial Strains for the Synthesis of Biofilm on ISS
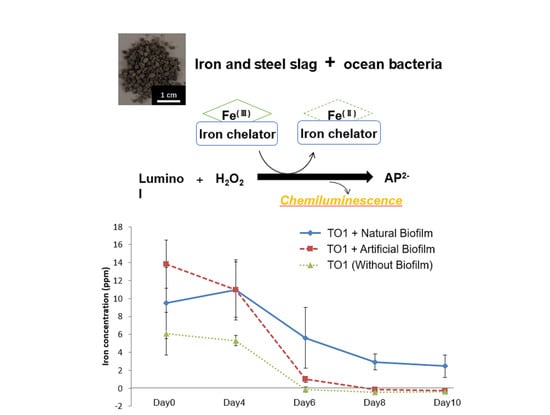
3.6. Iron Elution from CMSM Using TO1 with Biofilms in the Seawater
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, K.R.; Gopakumar, A.; Chetri, J.K. Critical review of applications of iron and steel slags for carbon sequestration and environmental remediation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristelo, N.; Coelho, J.; Miranda, T.; Palomo, Á.; Fernández-Jiménez, A. Alkali activated composites—An innovative concept using iron and steel slag as both precursor and aggregate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 103, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.; Hartwell, T.; Jones, N.; Byrne, C. Sustainable steelmaking: Recycling steelmill byproducts-Some practical developments and outstanding issues. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2004, 31, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakase, K.; Matsui, A.; Kikuchi, N.; Miki, Y. Effect of slag composition on phosphorus separation from steelmaking slag by reduction. Tetsu-Hagane J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2016, 102, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, M.; Fukushima, M.; Kiso, E.; Kato, T.; Shibuya, M.; Horiya, S.; Nishida, A.; Otsuka, K.; Komai, T. Application of iron humates to barren ground in a coastal area for restoring seaweed beds. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2010, 43, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliavini, M.; Rombolà, A.D. Iron deficiency and chlorosis in orchard and vineyard ecosystems. Eur. J. Agron. 2001, 15, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Higuchi, K.; Yoshida, M.; Tadano, T. Comparison of iron availability in leaves of barley and rice. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2005, 51, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, T.J. On the Phytoplankton of the South-West Atlantic and Bellingshausen Sea, 1929–1931; Cambridge at the Univ. Press: Cambridge, UK, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.H.; Fitzwater, S.E. Iron deficiency limits phytoplankton growth in the north-east pacific subarctic. Nature 1988, 331, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coale, K.H.; Johnson, K.S.; Fitzwater, S.E.; Gordon, R.M.; Tanner, S.; Chavez, F.P.; Ferioli, L.; Sakamoto, C.; Rogers, P.; Millero, F.; et al. A massive phytoplankton bloom induced by an ecosystem-scale iron fertilization experiment in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Nature 1996, 383, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, S.; Quéguiner, B.; Armand, L.; Belviso, S.; Bombled, B.; Bopp, L.; Bowie, A.; Brunet, C.; Brussaard, C.; Carlotti, F.; et al. Effect of natural iron fertilization on carbon sequestration in the Southern Ocean. Nature 2007, 446, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashima, A.; Ishikawa, T.; Takeuchi, D.; Iwao, T.; Maegawa, M. Effects of removing Diadema on barren ground in Haidaura Bay, Mie Prefecture. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 2014, 80, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Yamamoto, M. Influence of seawater temperature and organic matter on iron elution from a mixture of steelmaking slag and composts. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivertsen, K. Geographic and environmental factors affecting the distribution of kelp beds and barren grounds and changes in biota associated with kelp reduction at sites along the Norwegian coast. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1997, 54, 2872–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Hamasuna, N.; Fukushima, M.; Okita, S.; Horiya, S.; Kiso, E.; Shibuya, M.; Sadakata, M. Recovery from barren ground by supplying slug and humic substances. J. Jpn. Inst. Energy 2006, 85, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, Y.; Kuma, K.; Kudo, I.; Matsunaga, K. Iron requirement of the brown macroalgae Laminaria japonica, Undaria pinnatifida (Phaeophyta) and the crustose coralline alga Lithophyllum yessoense (Rhodophyta), and their competition in the northern Japan Sea. Phycologia 1995, 34, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Minami, K.; Liu, D. Characteristics of organic matter mixed with steelmaking slag for accelerating iron elution in seaweed bed restoration. Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu 2017, 43, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, M.; Kiso, E. The present situation and the prospects of the marine utilization of converter slag. J. Adv. Mar. Sci. Technol. Soc. 2011, 17, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Horii, K.; Tsutsumi, N.; Kitano, Y.; Kato, T. Processing and reusing technologies for steelmaking slag. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 2012, 394, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, H.I.; Funari, V.; Mayes, W.M.; Rogerson, M.; Prior, T.J. Recovery of Al, Cr and V from steel slag by bioleaching: Batch and column experiments. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 222, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Qian, C.X. The influence of microbial agent on the mineralization rate of steel slag. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langdahl, B.R.; Ingvorsen, K. Temperature characteristics of bacterial iron solubilisation and 14C assimilation in naturally exposed sulfide ore material at Citronen Fjord, North Greenland (83° N). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1997, 23, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, T.; Ito, K.; Wakai, S.; Tsurumaru, H.; Ohkuma, M.; Harayama, S. Iron corrosion induced by nonhydrogenotrophic nitrate-reducing Prolixibacter sp. strain MIC1-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlan, R.M. Biofilms: Microbial life on surfaces. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laspidou, C.S.; Rittmann, B.E. A unified theory for extracellular polymeric substances, soluble microbial products, and active and inert biomass. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korber, D.R.; James, G.A.; Costerton, J.W. Evaluation of fleroxacin activity against established Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorokin, D. Sulfitobacterpontiacus gen. nov., sp. nov.—A New Heterotrophic Bacterium from the Black Sea, specialized on Sulfite Oxidation. Microbiology 1995, 64, 295. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, J.M.; Mayer, F.; Moran, M.A.; Hodson, R.E.; Whitman, W.B. Sagittula stellata gen. nov., sp. nov., a lignin-transforming bacterium from a coastal environment. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horii, K.; Tsutsumi, N.; Kato, T.; Kitano, Y.; Sugahara, K. Overview of iron/steel slag application and development of new utilization technologies. Nippon Steel Sumitomo Met. Tech. Rep. 2015, 109, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Templeton, A.S. Geomicrobiology of iron in extreme environments. Elements 2011, 7, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Román, M.; Fernández-Remolar, D.; Amils, R.; Sánchez-Navas, A.; Schmid, T.; Martin-Uriz, P.S.; Rodríguez, N.; McKenzie, J.A.; Vasconcelos, C. Microbial mediated formation of Fe-carbonate minerals under extreme acidic conditions. Sci. Rep. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emmerich, M.; Bhansali, A.; Lösekann-Behrens, T.; Schröder, C.; Kappler, A.; Behrens, S. Abundance, distribution, and activity of Fe(II)-oxidizing and Fe(III)-reducing microorganisms in hypersaline sediments of Lake Kasin, Southern Russia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4386–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stintzi, A.; Evans, K.; Meyer, J.M.; Poole, K. Quorum-sensing and siderophore biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: LasR/lasI mutants exhibit reduced pyoverdine biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 166, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomason, M.K.; Voichek, M.; Dar, D.; Addis, V.; Fitzgerald, D.; Gottesman, S.; Sorek, R.; Greenberga, E.P. A rhli 5’ UTR-derived sRNA regulates RhlR-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. MBio 2019, 10, e02253-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewenza, S.; Sokol, P.A. Regulation of ornibactin biosynthesis and N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone production by cepR in Burkholderia cepacia. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okazaki, M.; Sakuda, S.; Ozaki, N.; Kogure, T.; Nagasawa, H. Structural and functional diversity of acidic polysaccharides from various species of coocolithophorid algae. Thalass. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2004, 20, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Alnnasouri, M.; Dagot, C.; Pons, M.N. Comparison of four methods to assess biofilm development. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, D.; Wiedmann, M.; McLandsborough, L.A. Microtiter plate assay for assessment of Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2950–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yan, Z.; Xu, J. Quantitative variation of biofilms among strains in natural populations of Candida albicans. Microbiology 2003, 149, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flemming, H.C.; Neu, T.R.; Wozniak, D.J. The EPS matrix: The “House of Biofilm Cells”. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 7945–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokare, C.R.; Chakraborty, S.; Khopade, A.N.; Mahadik, K.R. Biofilm: Importance and applications. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 159–168. [Google Scholar]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsukidate, H.; Otake, S.; Kato, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Kitatsuji, M.; Yoshimura, E.; Suzuki, M. Iron Elution from Iron and Steel Slag Using Bacterial Complex Identified from the Seawater. Materials 2021, 14, 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061477
Tsukidate H, Otake S, Kato Y, Yoshimura K, Kitatsuji M, Yoshimura E, Suzuki M. Iron Elution from Iron and Steel Slag Using Bacterial Complex Identified from the Seawater. Materials. 2021; 14(6):1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061477
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsukidate, Hidenori, Seika Otake, Yugo Kato, Ko Yoshimura, Masafumi Kitatsuji, Etsuro Yoshimura, and Michio Suzuki. 2021. "Iron Elution from Iron and Steel Slag Using Bacterial Complex Identified from the Seawater" Materials 14, no. 6: 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061477
APA StyleTsukidate, H., Otake, S., Kato, Y., Yoshimura, K., Kitatsuji, M., Yoshimura, E., & Suzuki, M. (2021). Iron Elution from Iron and Steel Slag Using Bacterial Complex Identified from the Seawater. Materials, 14(6), 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061477