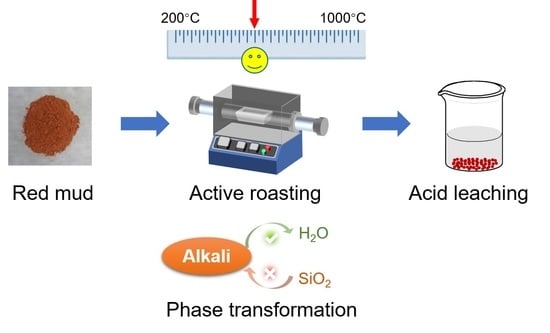
An Eco-Friendly Acid Leaching Strategy for Dealkalization of Red Mud by Controlling Phase Transformation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Red Mud
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Phase Transformation Behavior of Red Mud
3.2. The Diluted Acid Leaching of Red Mud
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borra, C.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Recovery of Rare Earths and Other Valuable Metals From Bauxite Residue (Red Mud): A Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.; Hassani, A.; Azami, O. Thermo-mechanical properties of alkali-activated slag-Red mud concrete. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, P.; Xue, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, W. Red mud derived facile hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchical porous α-Fe2O3 microspheres as efficient adsorbents for removal of Congo red. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2020, 140, 109379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Li, G.; Luo, J.; Ye, Q.; Liu, M.; Peng, Z.; Jiang, T. Enrichment of Sc2O3 and TiO2 from bauxite ore residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayes, W.; Jarvis, A.; Burke, I.; Walton, M.; Feigl, V.; Klebercz, O.; Gruiz, K. Dispersal and attenuation of trace contaminants downstream of the Ajka bauxite residue (red mud) depository failure, Hungary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5147–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, C.; Yun, T.Y.; Krishnan, V.; Puma, G.L. Application of modified red mud in environmentally-benign applications: A review paper. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 25, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukiza, E.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, N. Preparation and characterization of a red mud-based road base material: Strength formation mechanism and leaching characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 220, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Kim, M.; Li, D.; Kim, H.; Huang, C. The removal of phosphate by thermally treated red mud from water: The effect of surface chemistry on phosphate immobilization. Chemosphere. 2020, 247, 125867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, R.; Liberato, C.; Montini, M.; Gallo, J.; Cincotto, M.; Pileggi, R. Evaluation of transition from fluid to elastic solid of cementitious pastes with bauxite residue using oscillation rheometric and isothermal calorimetry. Appl. Rheol. 2013, 23, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, R.; Bernardo, H.; Maciel, M.; Pileggi, R.; Cincotto, M. Using isothermal calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetry and FTIR to monitor the hydration reaction of Portland cements associated with red mud as a supplementary material. J Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 1877–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, F.; Ye, Y.; Guo, Y.; Hartley, W.; Xue, S. Effect of amendments on the leaching behavior of alkaline anions and metal ions in bauxite residue. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 85, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, H.; Mayes, W.; Rogerson, M.; Stewart, D.; Burked, I. Alkaline residues and the environment: A review of impacts, management practices and opportunities. J. Cleaner. Prod. 2016, 112, 3571–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choe, G.; Kang, S.; Kang, H. Mechanical Properties of Concrete Containing Liquefied Red Mud Subjected to Uniaxial Compression Loads. Materials. 2020, 13, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mymrin, V.; Guidolin, M.; Klitzke, W.; Alekseev, K.; Guidolin, R.; Avanci, M.; Pawlowsky, U.; Winter, E.; Catai, R. Environmentally clean ceramics from printed circuit board sludge, red mud of bauxite treatment and steel slag. J. Cleaner Prod. 2017, 164, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y. Preparation of road base material by utilizing electrolytic manganese residue based on Si-Al structure: Mechanical properties and Mn2+ stabilization/solidification characterization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Analysis and comparison of asphalt mixes containing waste fillers using a novel ranking Methodology. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Ren, H.; Huang, X.; Li, M.; Tang, Y.; Guo, F. Low cost red mud modified graphitic carbon nitride for the removal of organic pollutants in wastewater by the synergistic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 237, 116477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Lyu, G.; Guo, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Recovery of alkali and alumina from bauxite residue (red mud) and complete reuse of the treated residue. J. Cleaner. Prod. 2018, 188, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Wen, Z.; Huang, J.; Lin, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Lan, M.; Li, H.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Technical and Product Evaluation of Industrial Solid Waste(GB/T 32326-2015); China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- GräFe, M.; Power, G.; Klauber, C. Bauxite Residue Issues: III. Alkalinity and Associated Chemistry. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Sun, R.; Cao, Y. Neutralization of red mud using bio-acid generated by hydrothermal carbonization of waste biomass for potential soil application. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 271, 122525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiao, X.; Meng, K.; Chu, B.; Wang, C.; Chu, P. Multiple flocculant prepared with dealkalized red mud and fly ash: Properties and characterization. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, J.; Xue, S. Alkalinity neutralization and structure upgrade of bauxite residue waste via synergistic pyrolysis with biomass. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 93, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T. Approaches to improve alumina extraction based on the phase transformation mechanism of recovering alkali and extracting alumina by the calcification-carbonization method. Hydrometallurgy. 2019, 189, 105123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Liu, F.; Khoso, S.; Zeng, H.; Sun, W.; Tang, H.; Wang, L. Staged leaching behavior of red mud during dealkalization with mild acid. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 196, 105123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Dhawan, N. Investigation of carbothermic microwave reduction followed by acid leaching for recovery of iron and aluminum values from Indian red mud. Miner. Eng. 2020, 159, 106653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Bal, R.; Dey, R. Heterogeneous recyclable copper oxide supported on activated red mud as an efficient and stable catalyst for the one pot hydroxylation of benzene to phenol. Mol. Catal. 2020, 499, 111310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Wang, N.; Liu, S. Radiological restrictions of using red mud as building material additive. Waste Manage Res. 2012, 30, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, W.; Guan, X. An active dealkalization of red mud with roasting and water leaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Huang, M.; Jia, D.; Zhang, N. Effects of cooling method on removal of sodium from active roasting red mud based on water leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, D.; Niu, S.; Yan, B.; Shi, Q.; Lu, C.; Crittenden, J. Insights into modified red mud for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx: Activation mechanism of targeted leaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Xie, Q.; Zou, X.; Qing, C.; Frost, R. Kinetic study of goethite dehydration and the effect of aluminium substitution on the dehydrate. Thermochim. Acta. 2012, 545, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scrivener, K.; Füllmann, T.; Gallucci, E.; Walenta, G. Quantitative study of Portland cement hydration by X-ray diffraction/Rietveld analysis and independent methods. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Z. CuO catalysts supported on activated red mud for efficient catalytic carbon monoxide oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Abudouwufu, T.; Yusufu, T.; He, J.; Sidike, A. Photoluminescence properties and energy transfer of a single-phased white-emitting NaAlSiO4: Ce3+, Sm3+ phosphor. J. Rare Earths. 2017, 35, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.; Rosa, W.; Ferrer, M.M.; Cunha, T.R.; Moreno, Z.M.; Sambrano, J.; Martínez, J.; Pizani, P.; Alonso, J.; Hernandes, A.; et al. Spin-phonon coupling in uniaxial anisotropic spin-glass based on Fe2TiO5 pseudobrookite. J. Alloys. Compd. 2019, 799, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivenko, P.; Guziy, S. Aluminosilicate coatings with enhanced heat- and corrosion resistance. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 73, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Lyu, F.; Hu, G.; Tang, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R. Dealkalization of Bauxite Residue through Acid Neutralization and Its Revegetation Potential. JOM 2019, 72, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, K.; Kurtoglu, S.; Uzun, A.; Soyer-Uzun, S. Consequences of Simple Acid-Pretreatments on Geopolymerization and Thermal Stability of Red Mud-Based Geopolymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 7156–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Couperthwaite, S.; Santini, T.; Pepper, R. Experimental and geochemical modelling investigations on the weathering behaviour of bauxite residue: Effect of pH. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 5, 103509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Sample | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Na2O | CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw red mud | 30.34 | 23.59 | 15.00 | 6.62 | 12.44 | 2.03 |
| Sample | pH of Leachate | Mass Loss/wt.% |
|---|---|---|
| RM-800-A0.1 | 7 | 21.08 |
| RM-800-A0.25 | 5 | 34.67 |
| RM-800-A0.5 | 1 | 36.18 |
| RM-800-A1 | 1 | 37.97 |
| Sample | Fe | Al | Si | Na | Ti | Ca | Mass Loss/% | Dealkalization Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw RM | 30.34 | 23.59 | 15.00 | 12.44 | 6.62 | 2.03 | ||
| RM-500A | 33.00 | 27.38 | 11.52 | 1.02 | 6.72 | 0.31 | 12.73 | 92.8 |
| RM-800A0.1 | 35.69 | 24.34 | 6.08 | 2.78 | 7.91 | 1.01 | 21.08 | 82.4 |
| Ref. | Method | Dealkalization Rate/% | Acid Concentration | Leachate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gong et al., 2020 | Acid leaching | 97.6 | Acidic | |
| Kaya et al., 2018 | Acid leaching | 95.7 | 6 M | Acidic |
| Zeng et al., 2020 | Acid leaching | 94.16 | 1.84 M | |
| Gupta et al., 2019 | Acid leaching | 31.9 | 1 M | Neutral |
| Liu et al., 2017 | Water leaching | >90 | Three stages of water leaching | |
| Zhu et al., 2015 | Water leaching | 82 | Four stages of water leaching | Neutral |
| This work | Diluted acid leaching | 92.8 | 0.1 M | Neutral |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Lei, T.; Wang, B.; Ma, S.; Lin, Y.; Lu, X.; Ye, Z. An Eco-Friendly Acid Leaching Strategy for Dealkalization of Red Mud by Controlling Phase Transformation. Materials 2022, 15, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020580
Wu J, Lei T, Wang B, Ma S, Lin Y, Lu X, Ye Z. An Eco-Friendly Acid Leaching Strategy for Dealkalization of Red Mud by Controlling Phase Transformation. Materials. 2022; 15(2):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020580
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jiaming, Tianyu Lei, Beibei Wang, Shuwei Ma, Yulong Lin, Xiaolei Lu, and Zhengmao Ye. 2022. "An Eco-Friendly Acid Leaching Strategy for Dealkalization of Red Mud by Controlling Phase Transformation" Materials 15, no. 2: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020580
APA StyleWu, J., Lei, T., Wang, B., Ma, S., Lin, Y., Lu, X., & Ye, Z. (2022). An Eco-Friendly Acid Leaching Strategy for Dealkalization of Red Mud by Controlling Phase Transformation. Materials, 15(2), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020580