Effect of Oxygen Plasma Pre-Treatment on the Surface Properties of Si-Modified Cotton Membranes for Oil/Water Separations
Abstract
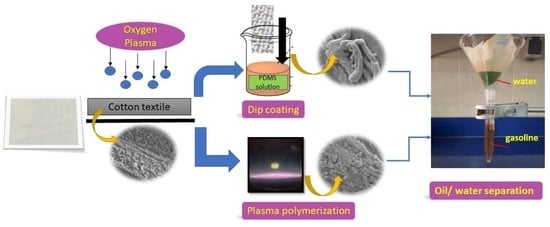
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dip-Coating
2.3. Plasma Polymerization
2.4. O2 Plasma Pre-Treatment
2.5. Structural and Morphological Characterization
2.6. Laundry Test
2.7. Separation Efficiency
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sam, E.K.; Liu, J.; Lv, X. Surface Engineering Materials of Superhydrophobic Sponges for Oil/Water Separation: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 2353–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.; Rezaei, N.; Hamedi, H.; Zendehboudi, S.; Duan, X. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic membranes for oil-water separation application: A comprehensive review. Mater. Des. 2021, 204, 109599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellopollath, K.; Gore, P.M.; Kandasubramanian, B. Foamed materials for oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2021, 5, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.L.D. Cotton fabrics modified for use in oil/water separation: A perspective review. Cellulose 2021, 28, 4575–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Cui, P.; Jiang, W. A review on oil/water mixture separation material. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 14546–14568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Dunderdale, G.J.; England, M.W.; Hozumi, A. Oil/water separation techniques: A review of recent progresses and future directions. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2017, 5, 16025–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, U.; Faizan, M.; Sajid, M. Multifunctional membranes with super-wetting characteristics for oil-water separation and removal of hazardous environmental pollutants from water: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 285, 102276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Gao, S.W.; Cai, J.S.; He, C.L.; Mao, J.J.; Zhu, T.X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J.Y.; Meng, K.; Zhang, K.Q.; et al. Recent progress in fabrication and applications of superhydrophobic coating on cellulose-based substrates. Materials 2016, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nthunya, L.N.; Gutierrez, L.; Derese, S.; Nxumalo, E.N.; Verliefde, A.R.; Mamba, B.B.; Mhlanga, S.D. A review of nanoparticle-enhanced membrane distillation membranes: Membrane synthesis and applications in water treatment. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 2757–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padaki, M.; Murali, R.S.; Abdullah, M.S.; Misdan, N.; Moslehyani, A.; Kassim, M.A.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F. Membrane technology enhancement in oil-water separation. A Review. Desalination 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, C.; Kim, Y. Purification of oily seawater/wastewater using superhydrophobic nano-silica coated mesh and sponge. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 40, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Kang, M.; Huang, C.; Fu, G. Fabrication of highly durable and robust superhydrophobic-superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes based on a fluorine-free system for efficient oil/water separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 570, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, H.R.; Park, J.; Yi, J.; Hwang, W. Robust and continuous oil/water separation with superhydrophobic glass microfiber membrane by vertical polymerization under harsh conditions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Seeger, S. Polyester materials with superwetting silicone nanofilaments for oil/water separation and selective oil absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4699–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J. Facial preparation of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic textiles by depositing nano-SiO2 for oil–water separation. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Jiang, P.; Ke, Q.; Cheng, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic polydimethylsiloxane-coated cotton for oil-water separation process: An evidence of the relationship between its loading capacity and oil absorption ability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Heo, J.H.; Jeon, S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kang, H.W. Bio-inspired hollow PDMS sponge for enhanced oil–water separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, Y.D. High-performance, recyclable and superhydrophobic oil absorbents consisting of cotton with a polydimethylsiloxane shell. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Dong, J.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. Co-solvent induced self-roughness superhydrophobic coatings with self-healing property for versatile oil-water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 459, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, N.; Miao, X.; Yang, X.; Long, M.; Deng, W.; Zhou, Q.; Deng, W. An alternative fabrication of underoil superhydrophobic or underwater superoleophobic stainless steel meshes for oil-water separation: Originating from one-step vapor deposition of polydimethylsiloxane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 204, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Men, X.; Zhang, Z. A rapid, facile and practical fabrication of robust PDMS@starch coatings for oil-water separation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 99, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, H.N.; Vo, P.P.; Hayashi, K.; Kinashi, K.; Sakai, W.; Tsutsumi, N. Recycled PET as a PDMS-Functionalized electrospun fibrous membrane for oil-water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, L.; Khatibi, A.; Basuvalingam, S.B.; Caschera, D.; Shokri, B. Fabrication of a Flexible Si-cotton Filter Membrane for Efficient Hot Oil/Hot Water Separation. Fibers Polym. 2021, 23, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, L.; Khatibi, A.; Shokri, B. Hydrophobic and oleophilic cotton fabrics for efficient oil-water separation through low-pressure plasma polymerization. Iran. J. Phys. Res. 2020, 19, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Yuen, C.W.M.; Kan, C.W.; Cheuk, K.K.L.; Daoud, W.A.; Lam, P.L.; Tsoi, W.Y.I. Influence of atmospheric pressure plasma treatment on various fibrous materials: Performance properties and surface adhesion analysis. Vacuum 2010, 84, 1466–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, B.; Breedveld, V.; Hess, D.W. Fabrication of “roll-off” and “sticky” superhydrophobic cellulose surfaces-via plasma processing. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4785–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, I.B.; Ladhari, N. Hydrophobic behavior of cotton fabric activated with air atmospheric-pressure plasma. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 111, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugavelayutham, G.; Anupriyanka, T.; Bhagyashree, P.; Premasudha, P. Plasma Surface Modification of Cotton Fabric by Using Low Pressure Plasma. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2021, 49, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montarsolo, A.; Periolatto, M.; Zerbola, M.; Mossotti, R.; Ferrero, F. Hydrophobic sol-gel finishing for textiles: Improvement by plasma pre-treatment. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.L.; Kan, C.W.; Yuen, C.W. Effect of oxygen plasma pretreatment and titanium dioxide overlay coating on flame retardant finished cotton fabrics. BioResources 2011, 6, 1454–1474. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, J.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J.; Raji, Y.O.; Gbadamosi, A.O.; el Badawy, T.H.; Said, K.A.M. An overview of superhydrophobic ceramic membrane surface modification for oil-water separation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 643–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caschera, D.; Mezzi, A.; Cerri, L.; de Caro, T.; Riccucci, C.; Ingo, G.M.; Padeletti, G.; Biasiucci, M.; Gigli, G.; Cortese, B. Effects of plasma treatments for improving extreme wettability behavior of cotton fabrics. Cellulose 2014, 21, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth-Wehrenalp, G. Inorganic Polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2192–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevington, P. Data Reduction and Error Analysis; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 56–91. Available online: http://www.spy-hill.net/~myers/201/notes/textalk.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2022).
- Yang, J.; Yin, L.; Tang, H.; Song, H.; Gao, X.; Liang, K.; Li, C. Polyelectrolyte-fluorosurfactant complex-based meshes with superhydrophilicity and superoleophobicity for oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 268, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, S. Nonflammable and Magnetic Sponge Decorated with Polydimethylsiloxane Brush for Multitasking and Highly Efficient Oil–Water Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefnagels, H.F.; Wu, D.; de With, G.; Ming, W. Biomimetic superhydrophobic and highly oleophobic cotton textiles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 13158–13163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Long, X.; du, J.; Sun, C.; fu, S.; Xu, C. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of cotton treated with the TBCC/H2O2/NaHCO3 system. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhu, P. Flame retardancy and thermal behavior of cotton fabrics based on a novel phosphorus-containing siloxane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 479, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Jo, K.I.; Kim, E.; Park, J.H.; Ko, J.W.; Lee, J.H. Preparation of polydimethylsiloxane-modified waterborne polyurethane coatings for marine applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakroub, G.; Duguet, T.; Esvan, J.; Lacaze-Dufaure, C.; Roualdes, S.; Rouessac, V. Comparative study of bulk and surface compositions of plasma polymerized organosilicon thin films. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 25, 101256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakida, T.; Takeda, K.; Tanaka, I.; Takagishi, T. Free Radicals in Cellulose Fibers Treated with Low Temperature Plasma. Text. Res. J. 2014, 59, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaideki, K.; Jayakumar, S.; Thilagavathi, G.; Rajendran, R. A study on the antimicrobial efficacy of RF oxygen plasma and neem extract treated cotton fabrics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 7323–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, F.; Liu, W. The Influence of Plasma Treatment on the Tribological Properties of Hybrid PTFE/Cotton Fabric/Phenolic Composites. Polym. Compos. 2009, 30, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, D.; Bujanda, A.; Demaree, J.D.; Hirvonen, J.K.; Kosik, W.; Jensen, R.; Mcknight, S. Surface modification of polyamide fibers and films using atmospheric plasmas. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 4384–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Luo, W.; Cui, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Jian, T.; Li, X.; Yan, Q.; Liu, H.; Ouyang, C.; et al. Sequence-Defined Peptoids with –OH and –COOH Groups As Binders to Reduce Cracks of Si Nanoparticles of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caschera, D.; Cortese, B.; Mezzi, A.; Brucale, M.; Ingo, G.M.; Gigli, G.; Padeletti, G. Ultra hydrophobic/superhydrophilic modified cotton textiles through functionalized diamond-like carbon coatings for self-cleaning applications. Langmuir 2013, 29, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.C.; Hong, Y.C.; Cho, S.G.; Ji, Y.Y.; Han, C.S.; Uhm, H.S. Surface modification of polyimide films, filter papers, and cotton clothes by HMDSO/toluene plasma at low pressure and its wettability. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, 1223–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźnicka, M. Synthesis and Properties of Telechelic Polysiloxane and Polyether Homo- and Co-Polymers; Universität Rostock: Rostock, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groza, A.; Surmeian, A. Characterization of the Oxides Present in a Polydimethylsiloxane Layer Obtained by Polymerisation of Its Liquid Precursor in Corona Discharge. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 204296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljević, J.; Gorjanc, M.; Jerman, I.; Tomšič, B.; Modic, M.; Mozetič, M.; Orel, B.; Simončič, B. Influence of oxygen plasma pre-treatment on the water repellency of cotton fibers coated with perfluoroalkyl-functionalized polysilsesquioxane. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamà, I.E.; D’Amone, S.; Arcadio, V.; Caschera, D.; Toro, R.G.; Gigli, G.; Cortese, B. Underwater Wenzel and Cassie oleophobic behaviour. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 3854–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caschera, D.; Toro, R.G.; Federici, F.; Riccucci, C.; Ingo, G.M.; Gigli, G.; Cortese, B. Flame retardant properties of plasma pre-treated/diamond-like carbon (DLC) coated cotton fabrics. Cellulose 2015, 22, 2797–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, M.M.; Ducker, R.E.; MacDonald, J.C.; Lambert, C.R.; McGimpsey, W.G. Super-hydrophobic, highly adhesive, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Xanthopoulos, N.; Reymond, F.; Rossier, J.S.; Girault, H.H. Polymer microchips bonded by O2-plasma activation. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, C.; Shao, J.; Li, Y. Fabrication of superhydrophobic cotton fabrics through wrapping silica with plasma-induced grafting polymerization. Text. Res. J. 2017, 89, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashti, M.P.; Alimohammadi, F.; Shamei, A. Preparation of water-repellent cellulose fibers using a polycarboxylic acid/hydrophobic silica nanocomposite coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 3208–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, B.; Caschera, D.; Federici, F.; Ingo, G.M.; Gigli, G. Superhydrophobic fabrics for oil-water separation through a diamond like carbon (DLC) coating. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2014, 2, 6781–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, J.; Ge, M.; Cao, C.; Deng, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, K.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Lai, Y. Robust Flower-Like TiO2@Cotton Fabrics with Special Wettability for Effective Self-Cleaning and Versatile Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ge, L.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Li, F. Layered double hydroxide functionalized textile for effective oil/water separation and selective oil adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Mohammadi, S. Synthesis of a novel hydrogel nanocomposite coated on cotton fabric for water-oil separation. Water Air. Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidulych, M.; Shelemin, A.; Hanuš, J.; Khalakhan, I.; Krakovsky, I.; Kočová, P.; Mašková, H.; Kratochvíl, J.; Pleskunov, P.; Štěrba, J.; et al. Superwettable antibacterial textiles for versatile oil/water separation. Plasma Process. Polym. 2019, 16, 1900003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, J.K. Fabrication of zirconia based durable superhydrophobic-superoleophilic fabrics using non fluorinated materials for oil-water separation and water purification. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 103632–103640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.Y.; Guan, C.S.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.D.; Zeng, J.B. Cellulose nanocrystal coated cotton fabric with superhydrophobicity for efficient oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Guo, S. Calcium ions enhanced mussel-inspired underwater superoleophobic coating with superior mechanical stability and hot water repellence for efficient oil/water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 503, 144180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, C.; Hu, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Xia, T.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. Reusable, salt-tolerant and superhydrophilic cellulose hydrogel-coated mesh for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Lu, X.; Ren, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wan, M.; Jiang, L. Underwater Self-Cleaning PEDOT-PSS Hydrogel Mesh for Effective Separation of Corrosive and Hot Oil/Water Mixtures. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 1, 1400099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Tian, D.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication of a durable coral-like superhydrophilic MgO coating on stainless steel mesh for efficient oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 248, 117144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanthong, P.; Reubroycharoen, P.; Kongparakul, S.; Samart, C.; Wang, Z.; Hao, X.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Fabrication and evaluation of nanocellulose sponge for oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Water Contact Angle (°) | Sliding Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|
| Pristine cotton | 0 | - |
| Si-Cot_Dip | 137 ± 3 | 50 ± 2 |
| Si-Cot_Dip/O2 | 145 ± 3 | 30 ± 2 |
| Si-Cot_Plasma | 134 ± 3 | 25 ± 2 |
| Si-Cot_Plasma/O2 | 144 ± 3 | 15 ± 2 |
| Material | Method | Type of Oils | SE of Room Temperature Mixture | Number of Cycles | SE of High Temperature Mixture | Number of Cycles | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDMS | Plasma polymerization | Gasoline Hexadecane | 90 | 30 | 90 | 30 (Hot oil/Hot water) | This work |
| PDMS | Dip coating | Gasoline Hexadecane | 95 | 30 | 95 | 30 (Hot oil/Hot water) | This work |
| DLC | Coating by plasma | Pump oil | 100 | 1 | - | - | [58] |
| Acrylamide and acrylonitrile | Graft copolymerization | Crude Olive Diesel | 95–99 | 1 | - | - | [61] |
| HMDSO | Plasma polymer | Oil Hexane | 99 | 1 | - | - | [62] |
| HDTMS and SA | Dip coating | Hexadecane Diesel | 100 | 1 | - | - | [63] |
| HDTS | Dip coating | chloroform | 98 | 10 | - | - | [64] |
| PDMS | Vapor deposition | Hexane | 99 | 1 | - | - | [20] |
| PDA-Ca complex | Dip coating | Gasoline | - | - | 97 | 80 (Hot water) | [65] |
| LiCl/DMAc | Dip coating | hexane | 98.5 | 60 | - | - | [66] |
| PEDOT-PSS hydrogel | Chemical polymerization | Diesel | - | - | 99 | 50 (Hot water) | [67] |
| Mg (NO3)2 | Dip coating | Diesel | 10 | 96 | - | - | [68] |
| Stearoyl | Dip coating | octan | 10 | 100 | - | - | [69] |
| PDMS-Fe3O4@MF | Co-deposition | toluene | 30 | 99.9 | - | - | [36] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghorbani, L.; Caschera, D.; Shokri, B. Effect of Oxygen Plasma Pre-Treatment on the Surface Properties of Si-Modified Cotton Membranes for Oil/Water Separations. Materials 2022, 15, 8551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238551
Ghorbani L, Caschera D, Shokri B. Effect of Oxygen Plasma Pre-Treatment on the Surface Properties of Si-Modified Cotton Membranes for Oil/Water Separations. Materials. 2022; 15(23):8551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238551
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhorbani, Leila, Daniela Caschera, and Babak Shokri. 2022. "Effect of Oxygen Plasma Pre-Treatment on the Surface Properties of Si-Modified Cotton Membranes for Oil/Water Separations" Materials 15, no. 23: 8551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238551
APA StyleGhorbani, L., Caschera, D., & Shokri, B. (2022). Effect of Oxygen Plasma Pre-Treatment on the Surface Properties of Si-Modified Cotton Membranes for Oil/Water Separations. Materials, 15(23), 8551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238551