A Superhydrophobic Surface on a Superalloy Substrate with Properties of High Mechanical Strength and Self-Cleaning of Carbon Deposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Superalloy Surfaces
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Microscopic Morphology of a Single Groove
3.2. Wettability of the Surface with Groove Arrays
3.3. Effect of Laser Processing on Surface Mechanical Strength
3.4. Stability and Durability of the Superhydrophobic Superalloy Surface
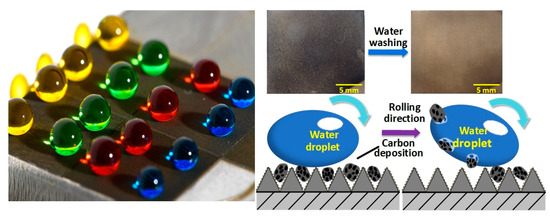
3.5. Self-Cleaning of Carbon Deposition
3.5.1. Self-Cleaning of Artificial Carbon Black
3.5.2. Self-Cleaning of High-Temperature Carbon Deposition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Y.; Sathasivam, S.; Song, J.; Crick, C.R.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P. Robust self-cleaning surfaces that function when exposed to either air or oil. Science 2015, 347, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, F.; D’Acunzi, M.; Sharifi-Aghili, A.; Saal, A.; Gao, N.; Kaltbeitzel, A.; Sloot, T.; Berger, R.; Butt, H.; Vollmer, D. When and how self-cleaning of superhydrophobic surfaces works. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaw9727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutzius, T.M.; Jung, S.; Maitra, T.; Graeber, G.; Köhme, M.; Poulikakos, D. Spontaneous droplet trampolining on rigid superhydrophobic surfaces. Nature 2015, 527, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljkovic, N.; Preston, D.J.; Enright, R.; Wang, E.N. Electrostatic charging of jumping droplets. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Yan, D.; Chen, Y.; Song, J. Self-driven oil/water separator with super-high separation rate. Nano Energy 2024, 119, 109066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latthe, S.S.; Sutar, R.S.; Shinde, T.B.; Pawar, S.B.; Khot, T.M.; Bhosale, A.K.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Xing, R.; Mao, L.; Liu, S. Superhydrophobic leaf mesh decorated with SiO2 nanoparticle–polystyrene nanocomposite for oil–water separation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudu, B.K.; Kumar, A. Robust and durable superhydrophobic steel and copper meshes for separation of oil-water emulsions. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 133, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Banerjee, D.; Marin Quintero, J.S.; Fishlock, S.J.; McLaughlin, J.; Waghmare, P.R.; Roy, S.S. Polarity dependent electrowetting for directional transport of water through patterned superhydrophobic laser induced graphene fibers. Carbon 2021, 182, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cho, H.; Hwang, W. Simple fabrication method of flexible and translucent high-aspect ratio superhydrophobic polymer tube using a repeatable replication and nondestructive detachment process. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; de Ruiter, J.; Varanasi, K.K. Photothermal trap utilizing solar illumination for ice mitigation. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat0127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreder, M.J.; Alvarenga, J.; Kim, P.; Aizenberg, J. Design of anti-icing surfaces: Smooth, textured or slippery? Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobina Sam, E.; Kobina Sam, D.; Lv, X.; Liu, B.; Xiao, X.; Gong, S.; Yu, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, J. Recent development in the fabrication of self-healing superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Hu, W.; Liu, L. Volcano-like hierarchical superhydrophobic surface synthesized via facile one-step secondary anodic oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 540, 148337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Manoucheri, I.; Moradian, R.; Pourabbas, B. One-step chemical vapor deposition and modification of silica nanoparticles at the lowest possible temperature and superhydrophobic surface fabrication. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durret, J.; Szkutnik, P.D.; Frolet, N.; Labau, S.; Gourgon, C. Superhydrophobic polymeric films with hierarchical structures produced by nanoimprint (nil) and plasma roughening. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmanin, T.; de Givenchy, E.T.; Amigoni, S.; Guittard, F. Superhydrophobic surfaces by electrochemical processes. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1378–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasitha, T.P.; Philip, J. Optimal condition for fabricating mechanically durable superhydrophobic titanium surface by rapid breakdown anodization: Self cleaning and bouncing characteristics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 585, 152628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Han, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y. Laser-induced graphene superhydrophobic surface transition from pinning to rolling for multiple applications. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2200096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajab, F.H.; Liu, Z.; Li, L. Long term superhydrophobic and hybrid superhydrophobic/superhydrophilic surfaces produced by laser surface micro/nano surface structuring. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.S.; Dewanda, F.; Lee, M.S.; Sekita, H.; Sumiyoshi, T. Formation of superhydrophobic soda-lime glass surface using femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 265, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Tieu, A.K.; Wan, S.; Zhu, H.; Pham, S.T.; Johnston, B. Surface characteristics and wettability of superhydrophobic silanized inorganic glass coating surfaces textured with a picosecond laser. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 537, 147808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Modin, E.B.; Sayfutdinova, A.R.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Vasiliev, A.L.; Emelyanenko, A.M. Combination of functional nanoengineering and nanosecond laser texturing for design of superhydrophobic aluminum alloy with exceptional mechanical and chemical properties. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10113–10123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagdheesh, R.; García-Ballesteros, J.J.; Ocaña, J.L. One-step fabrication of near superhydrophobic aluminum surface by nanosecond laser ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 374, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, J.D.; Sarkar, D.K.; Perron, J.; Audibert-Hayet, A.; Melot, D. Nano-micro structured superhydrophobic zinc coating on steel for prevention of corrosion and ice adhesion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 447, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trdan, U.; Hočevar, M.; Gregorčič, P. Transition from superhydrophilic to superhydrophobic state of laser textured stainless steel surface and its effect on corrosion resistance. Corros. Sci. 2017, 123, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnedenkov, S.V.; Sinebryukhov, S.L.; Egorkin, V.S.; Mashtalyar, D.V.; Emelyanenko, A.M.; Boinovich, L.B. Electrochemical properties of the superhydrophobic coatings on metals and alloys. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 3075–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanithakumari, S.C.; Kumar, C.A.; Thinaharan, C.; Kishor, G.R.; George, R.P.; Kaul, R.; Bindra, K.S.; Philip, J. Laser patterned titanium surfaces with superior antibiofouling, superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning and durability: Role of line spacing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 418, 127257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, A.M.; Modestov, A.D.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Shiryaev, A.A.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Dvoretskaya, O.V.; Ganne, A.A. Corrosion behavior of superhydrophobic aluminum alloy in concentrated potassium halide solutions: When the specific anion effect is manifested. Corros. Sci. 2016, 112, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Pan, W.; Wang, K.; Chen, F.; Sun, Y. Fabrication of micro-reentrant structures by liquid/gas interface shape-regulated electrochemical deposition. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2020, 159, 103637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Shin, H.S.; Chu, C.N. Fabrication of micro-pin array with high aspect ratio on stainless steel using nanosecond laser beam machining. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 264, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.F.; An, W.R.; Ju, Y.W.; Antonov, S.; Bi, Z.N.; Li, W.; Wu, J.T. Evaluation of microstructural degradation and its corresponding creep property in integral cast turbine rotor made of K424 alloy. Mater. Charact. 2019, 158, 109946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Le, A.T. A review on deposit formation in the injector of diesel engines running on biodiesel. Energy Sources Part A 2019, 41, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolakopoulos, P.G. Simulation of deposits effect on cylinder liner and influence on new and worn compression ring of a turbocharged di engine. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2021, 106, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavchov, R.I.; Mosbach, S.; Kraft, M.; Pearson, R.; Filip, S.V. An adsorption-precipitation model for the formation of injector external deposits in internal combustion engines. Appl. Energy 2018, 228, 1423–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Lu, X.; Shu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, W.; Yao, J.; Niu, Z.; Xie, Y. Robust, superhydrophobic aluminum fins with excellent mechanical durability and self-cleaning ability. Micromachines 2023, 14, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Xi, C.; Yu, H. Fabrication of self-cleaning superhydrophobic surface on stainless steel by nanosecond laser. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 115002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Xu, S.; Jiang, X.; Chen, J.; Yuan, X. A simple way to achieve self-cleaning surfaces with unique antifouling property. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 9072432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.L.; Ruan, M.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Hu, L.Y.; Ma, F.M.; Yu, Z.L.; Feng, W. Fabrication of anisotropic PTFE superhydrophobic surfaces using laser microprocessing and their self-cleaning and anti-icing behavior. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 535, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.; Aravindan, S.; Sarathi, R.; Rao, P.V. Fabrication of self-cleaning superhydrophobic silicone rubber insulator through laser texturing. Surf. Eng. 2021, 37, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Huo, L.; Liu, J.; Bai, Z. High-efficient laser-based bionic surface structuring for enhanced surface functionalization and self-cleaning effect. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 37, 102691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milles, S.; Soldera, M.; Kuntze, T.; Lasagni, A.F. Characterization of self-cleaning properties on superhydrophobic aluminum surfaces fabricated by direct laser writing and direct laser interference patterning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 525, 146518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Song, J. Super-fast fog collector based on self-driven jet of mini fog droplets. Small 2023, 19, 2301745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Song, J.; Sun, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Z. Rapid fabrication of large-area, corrosion-resistant superhydrophobic Mg alloy surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4404–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, Y.; Deng, X.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P. High-efficiency bubble transportation in an aqueous environment on a serial wedge-shaped wettability pattern. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 13567–13576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.; Xu, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Song, J. Solid-like slippery coating with highly comprehensive performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| No. | Substrate | Laser | CA | Contaminant | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1A99 Al alloy | Femtosecond laser | 152° | Dust (20~40μm) | Su et al. [35] |
| 2 | 304 SS | Fiber nanosecond laser | 152 ± 1.3° | Iron powder (98~106 μm) | Wan et al. [36] |
| 3 | 304 SS | Femtosecond laser | ~150° | Sponge particles | Yao et al. [37] |
| 4 | PTFE | CO2 laser | 168.36° | Dust | Zhan et al. [38] |
| 5 | Silicone rubber | Nd:YAG nanosecond laser | 159 ± 1° | Dust | Patil et al. [39] |
| 6 | SS 304 L | UV laser | ~154° | Dust | Wang et al. [40] |
| 7 | Al 2024 | Nanosecond laser + picosecond laser | 161 ± 2° | MnO2 (1 μm, 100 μm), PA (~100 μm) | Milles et al. [41] |
| C | Cr | Co | W | Mo | Al | Ti | Fe | Nb | V | Si | Mn | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.14–0.2 | 8.5–10.5 | 12.0–15.0 | 1.0–1.8 | 2.7–3.4 | 5.0–5.7 | 4.2–4.7 | 2.0 | 0.5–1.0 | 0.5–1.0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | Bal. |
| 1700 mm/s | 1300 mm/s | 900 mm/s | 500 mm/s | 100 mm/s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d/μm | CA/° | d/μm | CA/° | d/μm | CA/° | d/μm | CA/° | d/μm | CA/° | |
| h/μm | RA‖/° | h/μm | RA‖/° | h/μm | RA‖/° | h/μm | RA‖/° | h/μm | RA‖/° | |
| L/μm | RA⊥/° | L/μm | RA⊥/° | L/μm | RA⊥/° | L/μm | RA⊥/° | L/μm | RA⊥/° | |
| 30 W | 87.02 ± 2.28 | 149.3 ± 2.1 | 91.25 ± 3.20 | 146.1 ± 3.7 | 98.08 ± 2.24 | 158.3 ± 2.3 | 105.40 ± 4.44 | 160.2 ± 1.6 | 116.65 ± 3.35 | 151.4 ± 1.9 |
| 5.72 ± 0.38 | None | 6.93 ± 0.46 | None | 8.87 ± 0.91 | None | 12.57 ± 1.31 | 5.2 ± 0.8 | 76.06 ± 3.95 | 10.4 ± 0.9 | |
| 85 | None | 90 | None | 95 | None | 100 | 7.9 ± 0.8 | 115 | 16.9 ± 0.9 | |
| 15 W | 73.37 ± 2.13 | 125.1 ± 4.6 | 77.42 ± 1.59 | 127.0 ± 5.0 | 85.08 ± 3.27 | 142.6 ± 2.2 | 90.67 ± 3.05 | 164.5 ± 0.9 | 98.80 ± 5.06 | 161.9 ± 2.2 |
| 3.80 ± 0.15 | None | 4.68 ± 0.22 | None | 6.19 ± 0.52 | None | 10.32 ± 0.64 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 42.78 ± 2.04 | 4.8 ± 0.9 | |
| 70 | None | 75 | None | 85 | None | 90 | 4.4 ± 0.7 | 95 | 5.8 ± 0.7 | |
| 1.5 W | 54.31 ± 2.82 | 102.0 ± 4.9 | 54.27 ± 1.77 | 106.3 ± 2.4 | 54.30 ± 2.41 | 108.2 ± 1.5 | 55.75 ± 1.41 | 111.0 ± 5.9 | 50.38 ± 1.18 | 157.1 ± 1.7 |
| 3.14 ± 0.17 | None | 3.87 ± 0.17 | None | 5.07 ± 0.35 | None | 5.92 ± 0.40 | None | 15.24 ± 1.23 | 15.0 ± 0.8 | |
| 50 | None | 50 | None | 50 | None | 50 | None | 50 | 16.6 ± 1.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Song, J. A Superhydrophobic Surface on a Superalloy Substrate with Properties of High Mechanical Strength and Self-Cleaning of Carbon Deposition. Materials 2024, 17, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020508
Zhang B, Chen Y, Song J. A Superhydrophobic Surface on a Superalloy Substrate with Properties of High Mechanical Strength and Self-Cleaning of Carbon Deposition. Materials. 2024; 17(2):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020508
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bingzhen, Yang Chen, and Jinlong Song. 2024. "A Superhydrophobic Surface on a Superalloy Substrate with Properties of High Mechanical Strength and Self-Cleaning of Carbon Deposition" Materials 17, no. 2: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020508
APA StyleZhang, B., Chen, Y., & Song, J. (2024). A Superhydrophobic Surface on a Superalloy Substrate with Properties of High Mechanical Strength and Self-Cleaning of Carbon Deposition. Materials, 17(2), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020508