Neural Stem Cell Spreading on Lipid Based Artificial Cell Surfaces, Characterized by Combined X-ray and Neutron Reflectometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results
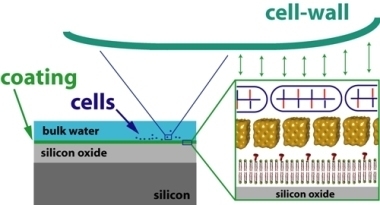
2.1. Coating structure and arrangement
| Neutron sld [10−6 Å−2] [f] | X-ray sld [10−6 Å−2] [f] | Thickness [Å] | hydration [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lipid heads | 1.78 | 13.8 | 11 | 54 (lower) / 63 (upper) |
| lipid chains | −0.2 | 8 | 18 | 17 |
| hydrated region | 6.36 [a] / 3.9 [b] | 9.45 | 26 | 100 |
| streptavidin | 1.2 | 10.5 | 38 | 0 |
| AK-cyclo[RGDfC] | 1.2 | 10.2 [b] | 30 | 12 |


2.2. Stem cell growth experiments


3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Howe, A.K.; Aplin, A.E.; Juliano, R.L. Anchorage-dependent ERK signaling––mechanisms and consequences. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002, 12, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marko, K.; Ligeti, M.; Mezo, G.; Mihala, N.; Kutnyanszky, E.; Kiss, E.; Hudecz, F.; Madarasz, E. A novel synthetic peptide polymer with cyclic RGD motifs supports serum-free attachment of anchorage-dependent cells. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votavova, H.; Hudecz, F.; Kajtar, J.; Szekerke, M.; Sponar, J.; Blaha, K. Conformation of Branched Polypeptides Based On Poly(L-Lysine)––Circular-Dichroism Study. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 1980, 45, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezo, G.; Hudecz, F.; Kajtar, J.; Szekerke, M. Synthesis and Chiroptical Properties of Model Peptides Suitable for The Immunological Characterization of Branched Polypeptides With The General Formula Poly[Lys (Xi-Dl-Alam)]. Acta Chim. Hung. 1990, 127, 803–812. [Google Scholar]
- Szokan, G.; Mezo, G.; Hudecz, F.; Majer, Z.; Schon, I.; Nyeki, O.; Szirtes, T.; Dolling, R. Racemization Analyses of Peptides and Amino-Acid Derivatives by Chromatography With Pre-Column Derivatization. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1989, 12, 2855–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Aumailley, M.; Gurrath, M.; Muller, G.; Calvete, J.; Timpl, R.; Kessler, H. Arg-Gly-Asp Constrained Within Cyclic Pentapeptides––Strong and Selective Inhibitors of Cell-Adhesion To Vitronectin and Laminin Fragment-P1. FEBS Lett. 1991, 291, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaff, M.; Tangemann, K.; Muller, B.; Gurrath, M.; Muller, G.; Kessler, H.; Timpl, R.; Engel, J. Selective Recognition of Cyclic Rgd Peptides of Nmr Defined Conformation by Alpha-Ii-Beta-3, Alpha-V-Beta-3, And Alpha-5-Beta-1 Integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20233–20238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anton, E.S.; Kreidberg, J.A.; Rakic, P. Distinct functions of alpha(3) and alpha(v) integrin receptors in neuronal migration and laminar organization of the cerebral cortex. Neuron 1999, 22, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, E.; Gullberg, D.; Balzac, F.; Altruda, F.; Silengo, L.; Tarone, G. Alpha(V) Integrin Subunit Is Predominantly Located in Nervous-Tissue and Skeletal-Muscle During Mouse Development. Dev. Dyn. 1994, 201, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marko, K.; Gocza, E.; Apati, A.; Kohidi, T.; Madarasz, E. Synthetic adhesive peptide conjugate supports xeno-free culturing of embryonic and neural stem cells. Eur. Cell. Mater. 2010, 20, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Ananthanarayanan, B.; Little, L.; Schaffer, D.V.; Healy, K.E.; Tirrell, M. Neural stem cell adhesion and proliferation on phospholipid bilayers functionalized with RGD peptides. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8706–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thid, D.; Holm, K.; Eriksson, P.S.; Ekeroth, J.; Kasemo, B.; Gold, J. Supported phospholipid bilayers as a platform for neural progenitor cell culture. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2008, 84A, 940–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezo, G.; de Oliveira, E.; Krikorian, D.; Feijlbrief, M.; Jakab, A.; Tsikaris, V.; Sakarellos, C.; Welling-Wester, S.; Andreu, D.; Hudecz, F. Synthesis and comparison of antibody recognition of conjugates containing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D epitope VII. Bioconjugate Chem. 2003, 14, 1260–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manea, M.; Mezo, G.; Hudecz, F.; Przybylski, M. Polypeptide conjugates comprising a beta-amyloid plaque-specific epitope as new vaccine structures against Alzheimer's disease. Biopolymers 2004, 76, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, M.R.; Reich, C.; Gast, A.P.; Radler, J.O.; Nickel, B. Structure and dynamics of crystalline protein layers bound to supported lipid bilayers. Langmuir 2007, 23, 6263–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellana, E.T.; Cremer, P.S. Solid supported lipid bilayers: From biophysical studies to sensor design. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2006, 61, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiss, S.; Kastl, K.; Janshoff, A.; Steinem, C. Formation of irreversibly bound annexin Al protein domains on POPC/POPS solid supported membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wacklin, H.; Bain, C.D. Changes in molecular composition and packing during lipid membrane reconstitution from phospholipid-surfactant micelles. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.E.; Majewski, J.; Watkins, E.B.; Mulder, D.J.; Gog, T.; Kuhl, T.L. Probing the local order of single phospholipid membranes using grazing incidence x-ray diffraction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 058103–058107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, E.B.; Miller, C.E.; Mulder, D.J.; Kuhl, T.L.; Majewski, J. Structure and Orientational Texture of Self-Organizing Lipid Bilayers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 238101:1–238101:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.L.; Howland, M.C.; Szmodis, A.W.; Li, Q.J.; Daemen, L.L.; Parikh, A.N.; Majewski, J. Early Stages of Oxidative Stress-Induced Membrane Permeabilization: A Neutron Reflectometry Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3631–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.T.; Fukuto, M.; Yang, L. In situ x-ray reflectivity studies on the formation of substrate-supported phospholipid bilayers and monolayers. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 77, 031909:1–031909:7. [Google Scholar]
- Hochrein, M.B.; Reich, C.; Krause, B.; Radler, J.O.; Nickel, B. Structure and mobility of lipid membranes on a thermoplastic substrate. Langmuir 2006, 22, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackmann, E. Supported membranes: Scientific and practical applications. Science 1996, 271, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, I.; Li, M.; Horswell, S.L.; Szymanski, G.; Lipkowski, J.; Majewski, J.; Satija, S. Electric field-driven transformations of a supported model biological membrane––An electrochemical and neutron reflectivity study. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 1763–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, P.K.; Loh, K.P.; Wohland, T.; Nesladek, M.; Van Hove, E. Supported Lipid Bilayer on Nanocrystalline Diamond: Dual Optical and Field-Effect Sensor for Membrane Disruption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, V.; Sirenko, O.; Schafer, R.J.; Groves, J.T. Lipid mobility and molecular binding in fluid lipid membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2826–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, A.N. Membrane-substrate interface: Phospholipid bilayers at chemically and topographically structured surfaces. Biointerphases 2008, 3, FA22–FA32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.; Lee, S.E.; Jung, H.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kawai, T.; Suh, K.Y. Soft lithographic patterning of supported lipid bilayers onto a surface and inside microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, J.T.; Ulman, N.; Boxer, S.G. Micropatterning fluid lipid bilayers on solid supports. Science 1997, 275, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovis, J.S.; Boxer, S.G. Patterning barriers to lateral diffusion in supported lipid bilayer membranes by blotting and stamping. Langmuir 2000, 16, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.H.; Parikh, A.N.; Groves, J.T. Direct patterning of membrane-derivatized colloids using in-situ UV-ozone photolithography. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, M.; Neumann, J.; Wixforth, A.; Radler, J.O.; Schneider, M.F. Dynamic patterns in a supported lipid bilayer driven by standing surface acoustic waves. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3050–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Tang, C.S.; Rossetti, F.F.; Textor, M.; Keller, B.; Voros, J.; Reimhult, E. Formation of supported lipid bilayers on indium tin oxide for dynamically- patterned membrane-functionalized microelectrode arrays. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, A.E.; Ngassam, V.; Dang, P.; Sanii, B.; Wu, H.W.; Yee, C.K.; Yeh, Y.; Parikh, A.N. Cell Attachment Behavior on Solid and Fluid Substrates Exhibiting Spatial Patterns of Physical Properties. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6992–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.L.; Hickey, J.; Jablin, M.S.; Trujillo, A.; Freyer, J.P.; Majewski, J. Mouse Fibroblast Cell Adhesion Studied by Neutron Reflectometry. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencer, J.; Mills, T.; Anghel, V.; Krueger, S.; Epand, R.M.; Katsaras, J. Detection of submicron-sized raft-like domains in membranes by small-angle neutron scattering. Eur. Phys. J. E 2005, 18, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A. Co-refinement of multiple-contrast neutron/X-ray reflectivity data using MOTOFIT. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2006, 39, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Spinke, J.; Bayerl, T.; Sackmann, E.; Knoll, W. Streptavidin binding to biotinylated lipid layers on solid supports: A neutron reflection and surface plasmon optical study. Biophys. J. 1992, 63, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traub, W. Crystal Structure of Biotin. Nature 1956, 178, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, P.C.; Ohlendorf, D.H.; Wendoloski, J.J.; Salemme, F.R. Structural Origins of High-Affinity Biotin Binding To Streptavidin. Science 1989, 243, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salunke, D.M.; Vijayan, M. X-Ray Studies On Crystalline Complexes Involving Amino-Acids and Peptides.11. Crystal-Structure of The Amino-Acid Vitamin Complex Lysine Pantothenate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 798, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, C.; Hochrein, M.B.; Krause, B.; Nickel, B. A microfluidic setup for studies of solid-liquid interfaces using x-ray reflectivity and fluorescence microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2005, 76, 095103:1–095103:7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlett, K.; Madarasz, E. Retinoic acid induced neural differentiation in a neuroectodermal cell line immortalized by p53 deficiency. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 47, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Huth, M.; Hertrich, S.; Mezo, G.; Madarasz, E.; Nickel, B. Neural Stem Cell Spreading on Lipid Based Artificial Cell Surfaces, Characterized by Combined X-ray and Neutron Reflectometry. Materials 2010, 3, 4994-5006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3114994
Huth M, Hertrich S, Mezo G, Madarasz E, Nickel B. Neural Stem Cell Spreading on Lipid Based Artificial Cell Surfaces, Characterized by Combined X-ray and Neutron Reflectometry. Materials. 2010; 3(11):4994-5006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3114994
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuth, Martin, Samira Hertrich, Gabor Mezo, Emilia Madarasz, and Bert Nickel. 2010. "Neural Stem Cell Spreading on Lipid Based Artificial Cell Surfaces, Characterized by Combined X-ray and Neutron Reflectometry" Materials 3, no. 11: 4994-5006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3114994
APA StyleHuth, M., Hertrich, S., Mezo, G., Madarasz, E., & Nickel, B. (2010). Neural Stem Cell Spreading on Lipid Based Artificial Cell Surfaces, Characterized by Combined X-ray and Neutron Reflectometry. Materials, 3(11), 4994-5006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3114994