Hollow Palladium Nanoparticles Facilitated Biodegradation of an Azo Dye by Electrically Active Biofilms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation of as-Synthesized Pd Nanoparticles
2.2. Evaluation of as-Developed EABs
2.3. Biodegradation of MO
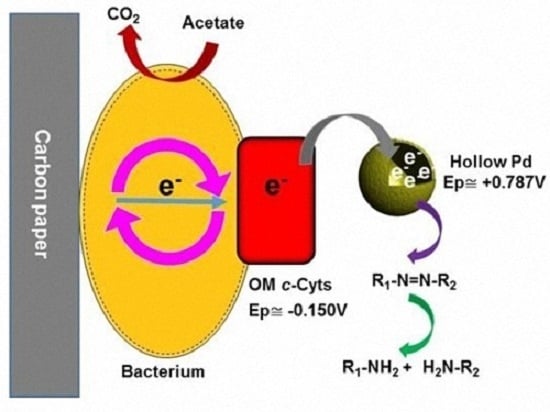
2.4. Possible Dye Degradation Mechanism
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Material
3.2. Catalyst Synthesis
3.3. Electrically Active Biofilm Formation
3.4. Characterization of Catalyst
3.5. Degradation of Methyl Orange
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalathil, S.; Lee, J.; Cho, M.H. Granular activated carbon based microbial fuel cell for simultaneous decolorization of real dye wastewater and electricity generation. New Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalathil, S.; Lee, J.; Cho, M.H. Efficient decolorization of real dye wastewater and bioelectricity generation using a novel single chamber biocathode-microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 119, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, Q. Peroxidase mediated decolorization and remediation of wastewater containing industrial dyes: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Singh, P.; Iyenger, L. Bacterial decolorization and degredation of azo dyes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 59, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Chang, J.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Singh, H.P.; Sharma, R.K. Metal nanoparticles with high catalytic activity in degradation of methyl orange: An electron relay effect. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 335, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaez, M.; Nolan, N.T.; Pillai, S.C.; Seery, M.K.; Falaras, P.; Kontos, A.G.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; Hamilton, J.W.J.; Byrne, J.A.; O’Shea, K.; et al. A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 125, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, I.; Jha, H.; Liu, N.; Schmuki, P. A review of photocatalysis using self-organized TiO2 nanotubes and other ordered oxide nanostructures. Small 2012, 8, 3073–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpan, U.G.; Hameed, B.H. Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2 based photocaalysts: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Rasul, M.G.; Martens, W.N.; Brown, R.; Hashib, M.A. Advances in heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of phenols and dyes wastewater: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 215, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khin, M.M.; Nair, A.S.; Babu, V.J.; Murugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on nanomaterials for environmental remediation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8075–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh Chaudhuri, R.; Paria, S. Visible light induced photocatalytic activity of sulfur doped hollow TiO2 nanoparticles, synthesized via a novel route. Dalt. Trans. 2014, 43, 5526–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mall, I.D. Mechanism of dye degradation during electrochemical treatment. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 15229–15240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Lei, L. Biodegradation of reactive blue 13 in a two stage anaerobic/aerobic fluidized beds system with a Pseudomonas sp. isolate. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigé, A.; Motte, B.; Borloo, J.; Buysschaert, G.; Devreese, B.; van Beeumen, J.J. Bacterial decolorization of textile dyes is an extracellular process requiring a multicomponent electron transfer pathway. Microb. Biotechnol. 2008, 1, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalathil, S.; Nguyen, V.H.; Shim, J.-J.; Khan, M.M.; Lee, J.; Cho, M.H. Enhanced performance of a microbial fuel cell using CNT/MnO2 nanocomposite as a bioanode material. J. Nanosci. Technol. 2013, 13, 7712–7716. [Google Scholar]
- Kalathil, S.; Lee, J.; Cho, M.H. Gold nanoparticles produced in situ mediate bioelectricity and hydrogen production in a microbial fuel cell by quantized capacitance charging. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalathil, S.; Lee, J.; Cho, M.H. Electrochemically active biofilm-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles in water. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1482–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalathil, S.; Khan, M.M.; Lee, J.; Cho, M.H. A simple biogenic route to rapid synthesis of Au@TiO2 nanocomposites by electrochemically active biofilms. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalathil, S.; Khan, M.M.; Ansari, S.A.; Lee, J.; Cho, M.H. Band gap narrowing of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanocrystals by electrochemically active biofilms and their visible light activity. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6323–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; Narayanan, R.; El-Sayed, M.A. Enhancing colloidal metallic nanocatalysis: Sharp edges and corners for solid nanoparticles and cage effect for hollow ones. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; O’Neil, D.; El-Sayed, M.A. Hollow and solid metallic nanoparticles in sensing and in nanocatalysis. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; Saira, F.; El-Sayed, M.A. Experimental evidence for the nanocage effect in catalysis with hollow nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3764–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh Chaudhuri, R.; Paria, S. Core/shell nanoparticles: Classes, properties, synthesis Mechanisms, characterization, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2373–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shi, J. Hollow-structured mesoporous materials: Chemical synthesis, functionalization and application. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3176–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan, M.; Gunawardhana, N.; Yoshio, M.; Nakashima, K. WO3 hollow nanospheres for high-lithium storage capacity and good cyclability. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Zhang, Y.; Voit, W.; Rao, K.V.; Muhammed, M. Synthesis and characterization of surfactant-coated superparamagnetic monodispersed iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 225, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.-T.; Gao, G.-H.; Wang, T.; Zhao, B.; Fu, X.-Z.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.-P. Electro-oxidation of formaldehyde and methanol over hollow porous palladium nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic activity. Catal. Commun. 2015, 58, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, H.; Nevin, K.P.; Jia, H.; Lowy, D.A.; Lovley, D.R.; Tender, L.M. Cyclic voltammetry of biofilms of wild type and mutant Geobacter sulfurreducens on fuel cell anodes indicates possible roles of OmcB, OmcZ, type IV pili, and protons in extracellular electron transfer. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.I. On the importance of identifying, characterizing, and predicting fundamental phenomena towards microbial electrochemistry applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvankar, N.S.; Mester, T.; Tuominen, M.T.; Lovley, D.R. Supercapacitors based on c-type cytochromes using conductive nanostructured networks of living bacteria. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.D.; Abdulateif, H.; Ismail, I.M.; Sabir, S.; Khan, M.Z. Bioelectricity generation and bioremediation of an azo-dye in a microbial fuel cell coupled activated sludge process. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, R.Y.; Malvankar, N.S.; Tuominen, M.T.; Lovley, D.R. Conductivity of individual Geobacter pili. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 8354–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, N.R.; Wang, Z.L.; Pal, T. Redox catalytic properties of palladium nanoparticles: Surfactant and electron donor-acceptor effects. Langmuir 2000, 16, 2457–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, F.; Rahunen, N.; Varcoe, J.R.; Avignone-Rossa, C.; Thumser, A.E.; Slade, R.C.T. A role for microbial palladium nanoparticles in extracellular electron transfer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, A.; Kalathil, S.; Deng, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Nakamura, R.; Nealson, K.H. Cell-secreted flavins bound to membrane cytochromes dictate electron transfer reactions to surfaces with diverse charge and pH. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.-P.; Zhang, H.-M.; Hu, J.-S.; Guo, Y.-G.; Wan, L.-J.; Bai, C.-L. Pt hollow Nanospheres: Facile synthesis and enhanced electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1540–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, K.-J.; Choi, M.-J.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, K.-Y.; Kim, I.S. Effect of different substrates on the performance, bacterial diversity, and bacterial viability in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3518–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguera, G.; McCarthy, K.D.; Mehta, T.; Nicoll, J.S.; Tuominen, M.T.; Lovley, D.R. Extracellular electron transfer via microbial nanowires. Nature 2005, 435, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalathil, S.; Chaudhuri, R.G. Hollow Palladium Nanoparticles Facilitated Biodegradation of an Azo Dye by Electrically Active Biofilms. Materials 2016, 9, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080653
Kalathil S, Chaudhuri RG. Hollow Palladium Nanoparticles Facilitated Biodegradation of an Azo Dye by Electrically Active Biofilms. Materials. 2016; 9(8):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080653
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalathil, Shafeer, and Rajib Ghosh Chaudhuri. 2016. "Hollow Palladium Nanoparticles Facilitated Biodegradation of an Azo Dye by Electrically Active Biofilms" Materials 9, no. 8: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080653
APA StyleKalathil, S., & Chaudhuri, R. G. (2016). Hollow Palladium Nanoparticles Facilitated Biodegradation of an Azo Dye by Electrically Active Biofilms. Materials, 9(8), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080653