Uncertainty in Visual Generative AI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- How can GAI uncertainty be quantified?
- How should GAI uncertainty be evaluated?
- What text-to-image and image-to-text model combination performs best?
2. Background
2.1. Image Retrieval and Visual GAI
2.1.1. Image-to-Text Generation
2.1.2. Text-to-Image Generation
2.2. Image Quality Assessment
- Single stimulus (Likert rating of a single image);
- Double stimulus (Likert rating of two images presented one after another);
- Forced choice (images are compared and the best one is selected);
- Similarity judgment (given two images, the difference in quality between them is quantified).
2.3. Text Evaluation Methods
3. Methodology
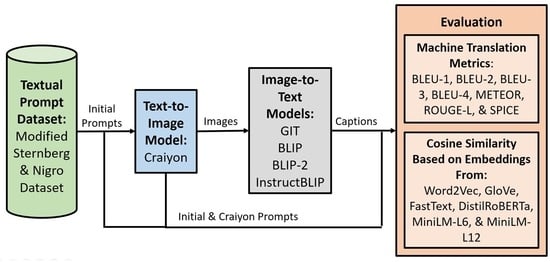
3.1. Textual Prompts: Modified Sternberg and Nigro Dataset
3.2. Text-to-Image Model: Craiyon
3.3. Image-to-Text Models: GIT, BLIP, BLIP-2, and InstructBLIP
3.4. Textual Evaluation Metrics
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Machine Translation Results
4.2. Cosine Similarity Results
4.3. Major Results
- Machine translation methods yielded consistently low scores in comparison to the cosine similarity scores;
- For the cosine similarity metrics, the Craiyon prompts yielded higher scores than the initial prompts when comparing them with the generated captions;
- Vector space models (Word2Vec, GLoVe, and FastText) were most generous with their similarity scores compared to pre-trained language models;
- Image-to-text models minimally affected the similarity scores.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OpenAI Introducing ChatGPT. 2022. Available online: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Google. Generative AI Examples. 2023. Available online: https://cloud.google.com/use-cases/generative-ai (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Baidoo-Anu, D.; Ansah, L.O. Education in the era of generative artificial intelligence (AI): Understanding the potential benefits of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. J. AI 2023, 7, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, J.M.; Thompson, K.; Corrin, L. Mapping out a research agenda for generative artificial intelligence in tertiary education. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2023, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesko, B.; Topol, E.J. The imperative for regulatory oversight of large language models (or generative AI) in healthcare. NPJ Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godwin, R.C.; Melvin, R.L. The role of quality metrics in the evolution of AI in healthcare and implications for generative AI. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 2893–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oniani, D.; Hilsman, J.; Peng, Y.; Poropatich, R.K.; Pamplin, J.C.; Legault, G.L.; Wang, Y. From military to healthcare: Adopting and expanding ethical principles for generative artificial intelligence. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.02448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Lin, H.; Li, M.; Ma, S.; Avdeev, M.; Shi, S. Generative artificial intelligence and its applications in materials science: Current situation and future perspectives. J. Mater. 2023, 9, 798–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regenwetter, L.; Nobari, A.H.; Ahmed, F. Deep generative models in engineering design: A review. J. Mech. Design. 2022, 144, 071704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI Introducing ChatGPT Plus. 2023. Available online: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt-plus (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Microsoft. Bing Chat. 2023. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/edge/features/bing-chat (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Pichai, S. An Important Next Step on Our AI Journey. 2023. Available online: https://blog.google/technology/ai/bard-google-ai-search-updates/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Combs, K.; Bihl, T.J.; Ganapathy, S. Utilization of Generative AI for the Characterization and Identification of Visual Unknowns. Nat. Lang. Process. J. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmer, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. OpenAI White Paper. 2018. Available online: https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/openai-assets/research-covers/language-unsupervised/language_understanding_paper.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. In Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2020), Virtual, 6–12 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI. GPT-4 Technical Report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774v4. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, E.; Ghahramani, Z. LaMDA: Our Breakthrough Conversation Technology. 2021. Available online: https://blog.google/technology/ai/lamda/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Pichai, S. Google I/O 2022: Advancing Knowledge and Computing. 2022. Available online: https://blog.google/technology/developers/io-2022-keynote/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Narang, S.; Chowdhery, A. Pathways Language Model (PaLM): Scaling to 540 Billion Parameters for Breakthrough Performance. 2022. Available online: https://ai.googleblog.com/2022/04/pathways-language-model-palm-scaling-to.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Chowdhery, A.; Narang, S.; Devlin, J.; Bosma, M.; Mishra, G.; Roberts, A.; Barham, P.; Chung, H.W.; Sutton, C.; Gehrmann, S.; et al. PaLM: Scaling language modeling with pathways. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2023, 24, 1–113. Available online: https://jmlr.org/papers/volume24/22-1144/22-1144.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Google. PaLM 2 Technical Report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.10403. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahramani, Z. Introducing PaLM 2. 2023. Available online: https://blog.google/technology/ai/google-palm-2-ai-large-language-model/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Meta, A.I. Introducing LLaMA: A Foundational, 65-Billion-Parameter Large Language Model. 2023. Available online: https://ai.facebook.com/blog/large-language-model-llama-meta-ai/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.-A.; Lacroix, T.; Roziere, B.; Goyal, N.; Hambro, E.; Azhar, F.; et al. LLaMA: Open and efficient foundation language model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13971. [Google Scholar]
- Inflection, A.I. Inflection-1. 2023. Available online: https://inflection.ai/assets/Inflection-1.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Nichol, A.; Dhariwal, P.; Ramesh, A.; Shyam, P.; Mishkin, P.; McGrew, B.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, M. GLIDE: Toward photorealistic image generation and editing with text-guided diffusion models. In Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022; Available online: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v162/nichol22a/nichol22a.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- OpenAI. DALL-E: Creating Images from Text. 2021. Available online: https://openai.com/research/dall-e (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; Available online: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/radford21a/radford21a.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- OpenAI. DALL-E 2. 2022. Available online: https://openai.com/dall-e-2 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Ramesh, A.; Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A.; Chu, C.; Chen, M. Hierarchical text-conditional image generation with CLIP latents. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.06125. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI. DALL-E 3. 2023. Available online: https://openai.com/dall-e-3 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Betker, J.; Goh, G.; Jing, L.; Brooks, T.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Ouyang, L.; Zhuang, J.; Lee, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Improving Image Generation with Better Captions. 2023. Available online: https://cdn.openai.com/papers/dall-e-3.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Dayma, B.; Patril, S.; Cuenca, P.; Saifullah, K.; Ahraham, T.; Le Khac, P.; Melas, L.; Ghosh, R. DALL-E Mini. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/borisdayma/dalle-mini (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Dayma, B.; Patril, S.; Cuenca, P.; Saifullah, K.; Abraham, T.; Le Khac, P.; Melas, L.; Ghosh, R. DALL-E Mini Explained. Available online: https://wandb.ai/dalle-mini/dalle-mini/reports/DALL-E-Mini-Explained--Vmlldzo4NjIxODA (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Dayma, B.; Cuenca, P. DALL-E Mini—Generative Images from Any Text Prompt. Available online: https://wandb.ai/dalle-mini/dalle-mini/reports/DALL-E-mini-Generate-images-from-any-text-prompt--VmlldzoyMDE4NDAy (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Midjourney. 2022. Available online: https://www.midjourney.com/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- StabilityAI Stable Difussion Launch Announcement. 2022. Available online: https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-announcement (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Essert, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–23 June 2022; Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2022/html/Rombach_High-Resolution_Image_Synthesis_With_Latent_Diffusion_Models_CVPR_2022_paper.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Saharia, C.; William, C.; Saxena, S.; Li, L.; Whang, J.; Denton, E.; Ghasemipour, S.K.S.; Ayan, B.K.; Mahdavi, S.S.; Lopes, R.G.; et al. Photorealistic text-to-image diffusion models with deep language understanding. In Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2022), New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2022/hash/ec795aeadae0b7d230fa35cbaf04c041-Abstract-Conference.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Yu, J.; Xu, Y.; Koh, J.Y.; Luong, T.; Baid, G.; Wang, Z.; Vasudevan, V.; Ku, A.; Yang, Y.; Ayan, B.K.; et al. Scaling autoregressive models for content-rich text-to-image generation. Trans. Mach. Learn. Res. 2022. Available online: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=AFDcYJKhND (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Alba, D. OpenAI Chatbot Spits out Biased Musings, Despite Guardrails. Bloomberg. 2022. Available online: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/newsletters/2022-12-08/chatgpt-open-ai-s-chatbot-is-spitting-out-biased-sexist-results (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Wolf, Z.B. AI Can Be Racist, Sexist and Creepy. What Should We Do about It? CNN Politics: What Matters. 2023. Available online: https://www.cnn.com/2023/03/18/politics/ai-chatgpt-racist-what-matters/index.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Weidinger, L.; Mellor, J.; Rauh, M.; Griffin, C.; Uesato, J.; Huang, P.; Cheng, M.; Glaese, M.; Balle, B.; Kasirzadeh, A.; et al. Ethical and social risks of harm from language models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.04359. [Google Scholar]
- CNN Journalist Says He Had a Creepy Encounter with New Tech that Left Him Unable to Sleep. 2023. Available online: https://www.cnn.com/videos/business/2023/02/17/bing-chatgpt-chatbot-artificial-intelligence-ctn-vpx-new.cnn (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Daws, R. Medical Chatbot Using OpenAI’s GPT-3 Told a Fake Patient to Kill Themselves. 2020. Available online: https://www.artificialintelligence-news.com/2020/10/28/medical-chatbot-openai-gpt3-patient-kill-themselves/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Chen, C.; Fu, J.; Lyu, L. A pathway towards responsible AI generated content. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 19–25 August 2023; Available online: https://www.ijcai.org/proceedings/2023/0803.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Luccioni, A.S.; Akiki, C.; Mitchell, M.; Jernite, Y. Stable bias: Analyzing societal representations in diffusion models. In Proceedings of the 37th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2023), New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–16 December 2023; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2023/file/b01153e7112b347d8ed54f317840d8af-Paper-Datasets_and_Benchmarks.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Bird, C.; Ungless, E.L.; Kasirzadeh, A. Typology of risks of generative text-to-image models. In Proceedings of the 2023 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–10 August 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, N.; Hirota, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nakashima, Y. Uncurated image-text datasets: Shedding light on demographic bias. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2023/papers/Garcia_Uncurated_Image-Text_Datasets_Shedding_Light_on_Demographic_Bias_CVPR_2023_paper.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Torralba, A.; Fergus, R.; Freeman, W.T. 80 Million tiny images: A large dataset for non-parametric object and scene recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 1958–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, V.U.; Birhane, A. Large datasets: A pyrrhic win for computer vision? arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.16923. [Google Scholar]
- Shuhmann, C.; Beaumont, R.; Vencu, R.; Gordon, C.; Wightman, R.; Cherti, M.; Coombes, T.; Katta, A.; Mullis, C.; Wortsman, M.; et al. LAION-5B: An open large-scale dataset for training next generation image-text models. In Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2022), New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2022/file/a1859debfb3b59d094f3504d5ebb6c25-Paper-Datasets_and_Benchmarks.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Desai, K.; Kaul, G.; Aysola, Z.; Johnson, J. RedCaps: Web-curated image-text data created by the people, for the people. In Proceedings of the 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2021), Virtual, 6–12 December 2021; Available online: https://datasets-benchmarks-proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2021/file/e00da03b685a0dd18fb6a08af0923de0-Paper-round1.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Sharma, P.; Ding, N.; Goodman, S.; Soricut, R. Conceptual captions: A cleaned, hypernymed, image alt-text dataset for automatic image captioning. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birhane, A.; Prabhu, V.U.; Kahembwe, E. Multimodal datasets: Misogyny, pornography, and malignant stereotypes. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.01963. [Google Scholar]
- Fabbrizzi, S.; Papadopoulos, S.; Ntoutsi, E.; Kompatsiaris, I. A survey on bias in visual datasets. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 223, 103552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottile, Z. What to Know about Lensa, the AI Portrait App All over Social Media. CNN Style. 2023. Available online: https://www.cnn.com/style/article/lensa-ai-app-art-explainer-trnd/index.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Heikkila, M. The Viral AI Avatar App Lensa Undressed Me—Without My Consent. 2022. Available online: https://www.technologyreview.com/2022/12/12/1064751/the-viral-ai-avatar-app-lensa-undressed-me-without-my-consent/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Buell, S. An MIT Student Asked AI to Make Her Headshot More ‘Professional’. It Gave Her Lighter Skin and Blue Eyes. The Boston Globe. 2023. Available online: https://www.bostonglobe.com/2023/07/19/business/an-mit-student-asked-ai-make-her-headshot-more-professional-it-gave-her-lighter-skin-blue-eyes/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Hacker, P.; Engel, A.; Mauer, M. Regulating ChatGPT and other large generative AI models. In Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–15 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, U.; Lee, J.; An, C.; Lee, H.; Park, S.; Baek, R.; Choi, H. A review of multi-modal learning from the text-guided visual processing viewpoint. Sensors 2022, 22, 6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraheem, S.S.; Le, T.; Nguyen, T.V. Image synthesis: A review of methods, datasets, evaluation metrics, and future outlook. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 10813–10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elasri, M.; Elharrouss, O.; Al-Maadeed, S.; Tairi, H. Image generation: A review. Neural Process. Lett. 2022, 54, 4609–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, M. Image-text retrieval: A survey on recent research and development. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vienna, Austria, 23–29 July 2022; Available online: https://www.ijcai.org/proceedings/2022/0759.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Bithel, S.; Bedathur, S. Evaluating Cross-modal generative models using retrieval task. In Proceedings of the 46th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Taipei, Taiwan, 23–27 July 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borji, A. How good are deep models in understanding the generated images? arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.10760. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Deng, L. Deep learning for image-to-text generation: A technical overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żelaszczyk, M.; Mańdziuk, J. Cross-modal text and visual generation: A systematic review. Part 1—Image to text. Inf. Fusion. 2023, 93, 302–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, K.; Bihl, T.J.; Ganapathy, S. Integration of computer vision and semantics for characterizing unknowns. In Proceedings of the 56th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Bourdev, L.; Girshick, R.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Dollar, P. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference Proceedings, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.; Johnson, J.; Krishna, R.; Li, F. A hierarchical approach for generating descriptive image paragraphs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2017/html/Krause_A_Hierarchical_Approach_CVPR_2017_paper.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Bernardi, R.; Cakici, R.; Elliott, D.; Erdem, A.; Erdem, E.; Ikizler-Cinbis, N.; Keller, F.; Muscat, A.; Plank, B. Automatic description generation from images: A survey of models, datasets, and evaluation measures. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2016, 55, 409–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, L.; Lin, K.; Gan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, L. GIT: A generative image-to-text transformer for vision and language. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.14100. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Xiong, C.; Hoi, S. Bootstrapping language-image pre-training for unified vision-language understanding and generation. In Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022; Available online: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v162/li22n.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Alayrax, J.; Donahue, J.; Luc, P.; Miech, A.; Barr, I.; Hasson, Y.; Lenc, K.; Mensch, A.; Millican, K.; Reyolds, M.; et al. Flamingo: A visual language model for few-shot learning. In Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2022), New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2022/hash/960a172bc7fbf0177ccccbb411a7d800-Abstract-Conference.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. BLIP-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.12597. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Tiong, A.M.H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Fung, P.; Hoi, S. InstructBLIP: Toward general-purpose vision-language model with instruction tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.08485. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Yoon, S.; Fuentes, A.; Park, D.S. A comprehensive survey of image augmentation technics for deep learning. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 137, 109347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, G.; Min, X. Perceptual image quality assessment: A survey. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 63, 211301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D.M. Seven challenges in image quality assessment: Past, present, and future research. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 905685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantiuk, R.K.; Tomaszewska, A.; Mantiuk, R. Comparison of four subjective methods for image quality assessment. Comput. Graph. Forum. 2012, 31, 2478–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatolo, F.A.; Gimino, M.G.C.A.; Cogotti, E. TeTIm-Eval: A novel curated evaluation data set for comparing text-to-image models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.07839. [Google Scholar]
- Salimans, T.; Goodfellow, I.; Wojciech, Z.C.V.; Radford, A.; Chen, X. Improved techniques for training GANs. In Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2016), Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2016/hash/8a3363abe792db2d8761d6403605aeb7-Abstract.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Sun, W.; Min, X.; Liu, X.; Zhai, G.; Lin, W. AGIQA-3K: An open database for AI-generated image quality assessment. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.04717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrmann, S.; Clark, E.; Thibault, S. Repairing the cracked foundation: A survey of obstacles in evaluation practices for generated text. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2023, 77, 103–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessel, J.; Holtzman, A.; Forbes, M.; Le Bras, R.; Choi, Y. CLIPscore: A reference-free evaluation metric for image captioning. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 7–11 November 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papineni, K.; Roukoas, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W. Bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Denver, CO, USA, 7–12 July 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C. Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Text Summarization Branches Out Workshop, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; Available online: https://aclanthology.org/W04-1013 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Banerjee, S.; Lavie, A. METEOR: An automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Summarization, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 29 June 2005; Available online: https://aclanthology.org/W05-0909 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Snover, M.; Door, B.; Schwartz, R.; Micciulla, L.; Makhoul, J. A study of translation edit rate with targeted human annotation. In Proceedings of the 7th Conference of the Association for Machine Translation in the Americas: Technical Papers, Cambridge, MA, USA, 8–12 August 2006; Available online: https://aclanthology.org/2006.amta-papers.25 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Snover, M.; Madnani, N.; Dorr, B.; Schwartz, R. TERp system description. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation and MetricsMATR, Uppsala, Sweden, 15–16 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vedantam, R.; Zitnick, C.L.; Parikh, D. CIDEr: Consensus-based image description evaluation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2015/html/Vedantam_CIDEr_Consensus-Based_Image_2015_CVPR_paper.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Anderson, P.; Fernando, B.; Johnson, M.; Gould, S. SPICE: Semantic propositional image caption evaluation. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Kishore, V.; Wu, F.; Weinberger, K.Q.; Artzi, Y. BERTScore: Evaluating text generation with BERT. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 26 April–1 May 2020; Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.09675 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 5–8 December 2013; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2013/file/9aa42b31882ec039965f3c4923ce901b-Paper.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Mikolov, T.; Yih, W.; Zweig, G. Linguistic regularities in continuous space word representations. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–14 June 2013; Available online: https://aclanthology.org/N13-1090.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Gunther, F.; Rinaldi, L.; Marelli, M. Vector-space models of semantic representation from a cognitive perspective: A discussion of common misconceptions. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2019, 14, 1006–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmirazadi, O.; Lugowski, A.; Younge, K. Text similarity in vector space models: A comparative study. In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Pasadena, CA, USA, 13–15 December 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojanowski, P.; Grave, E.; Joulin, A.; Mikolov, T. Enriching word vectors with subword information. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2017, 5, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Nulty, P.; Lillis, D. A comparative study on word embeddings in deep learning for text classification. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 18–20 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.E.; Neumann, M.; Iyyer, M.; Gardner, M.; Clark, C.; Lee, K.; Zettlemoyer, L. Deep contextualized word representations. In Proceedings of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technology, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.05365 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Le, Q.V. XLnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2019/hash/dc6a7e655d7e5840e66733e9ee67cc69-Abstract.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Combs, K.; Lu, H.; Bihl, T.J. Transfer learning and analogical inference: A critical comparison of algorithms, methods, and applications. Algorithms 2023, 16, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Settlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Chen, M.; Goodman, S.; Gimpel, K.; Sharma, P.; Soricut, R. ALBERT: A lite BERT for self-supervised learning of language representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 26 April–1 May 2020; Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: Smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, R.G.; Krawczyk, D.C.; Holyoak, K.J.; Hummel, J.E.; Chow, T.W.; Miller, B.L.; Knowlton, B.J. A neurocomputational model of analogical reasoning and its breakdown in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2004, 16, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wei, F.; Dong, L.; Bao, H.; Yang, N.; Zhou, M. MiniLM: Deep self-attention distillation for task-agnostic compression of pre-trained transformers. In Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2020), Virtual, 6–12 December 2020; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2020/hash/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Abstract.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Sternberg, R.J.; Nigro, G. Developmental patterns in the solution of verbal analogies. Child Dev. 1980, 51, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, K.; Bihl, T.J. A preliminary look at generative AI for the creation of abstract verbal-to-visual analogies. In Proceedings of the 57th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2024; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10125/106520 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Reviriego, P.; Merino-Gomez, E. Text to image generation: Leaving no language behind. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.09333. [Google Scholar]
- O’Meara, J.; Murphy, C. Aberrant AI creations: Co-creating surrealist body horror using the DALL-E Mini text-to-image generator. Converg. Int. J. Res. New Media Technol. 2023, 29, 1070–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fang, H.; Lin, T.; Vedantam, R.; Gupta, S.; Dollar, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO captions: Data collection and evaluation server. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.00325. [Google Scholar]






| Type | Model Family | Model Name | Release Date | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language models | OpenAI Generative Pre-Trained (GPT) | GPT-1 | June2018 | [14,15] |
| GPT-2 | November 2019 | [16] | ||
| GPT-3 | May 2020 | [17] | ||
| GPT-3.5 | March 2022 | [1] | ||
| GPT-4 | March 2023 | [10,18] | ||
| Google Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMDA) | LaMDA | May 2021 | [19] | |
| LaMDA 2 | May 2022 | [20] | ||
| Google Pathways Language Model (PaLM) | PaLM | March 2023 | [21,22] | |
| PaLM 2 | May 2023 | [23,24] | ||
| Meta Large Language Model Meta AI (LLaMA) | LLaMA | February 2023 | [25,26] | |
| Inflection | Inflection-1 | June 2023 | [27] | |
| Image generator models | OpenAI GLIDE | GLIDE | December 2021 | [28] |
| OpenAI DALL-E | DALL-E | February 2021 | [29,30] | |
| DALL-E 2 | April 2022 | [31,32] | ||
| DALL-E 3 | October 2023 | [33,34] | ||
| Craiyon 1 | Craiyon 1 | July 2021 | [35,36,37] | |
| Midjourney | Midjourney | February 2022 | [38] | |
| Stability AI | Stable Diffusion | August 2022 | [39,40] | |
| Imagen | May 2022 | [41] | ||
| Parti | June 2022 | [42] |
| Model | Open-Source | Cost Structure | Tier/Image/Version | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DALL-E 2 | No | Pay-per-image | 1024 × 1024 | 0.02 USD/image |
| 512 × 512 | 0.018 USD/image | |||
| 256 × 256 | 0.016 USD/image | |||
| DALL-E 3 (Quality: HD) | No | Pay-per-image | 1024 × 1792 1792 × 1024 | 0.12 USD/image 0.12 USD/image |
| No | Pay-per-image | 1024 × 1024 | 0.08 USD/image | |
| DALL-E 3 (Quality: Standard) | No | Pay-per-image | 1024 × 1792 1792 × 1024 | 0.08 USD/image 0.08 USD/image |
| No | Pay-per-image | 1024 × 1024 | 0.04 USD/image | |
| Craiyon | Yes | Free; Subscription | Free | N/A |
| Supporter | 6 USD/mo or 60 USD/yr | |||
| Professional | 24 USD/mo or 240 USD/yr | |||
| Stable Diffusion 1 | Yes | Free; Pay-per-image | Free | N/A |
| Stable Diffusion XL 1.0 | 0.016 USD/image | |||
| Stable Diffusion XL 0.9 | 0.016 USD/image | |||
| Stable Diffusion XL 0.8 | 0.005 USD/image | |||
| Stable Diffusion 2.1 2 | 0.002 USD/image | |||
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 2 | 0.002 USD/image | |||
| Midjourney | No | Subscription | Basic | 10 USD/mo or 96 USD/yr |
| Standard | 30 USD/mo or 288 USD/yr | |||
| Pro | 60 USD/mo or 576 USD/yr | |||
| Mega | 120 USD/mo or 1152 USD/yr |
| Metric | Description | Citation |
|---|---|---|
| Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU) | Focused on n-gram precision between reference and candidate | [89] |
| Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation (ROUGE) | Based on the syntactic overlap, or word alignment, between references and candidates | [90] |
| Metric for Evaluation of Translation with Explicit Ordering (METEOR) | Measures based on unigram precision and recall | [91] |
| Translation Edit Rate (TER) | Calculated based on the number of operations needed to transform a candidate into a reference | [92] |
| TER-Plus (TERp) | Extension of TER that also factors in partial matches and word order | [93] |
| Consensus-based Image Description Evaluation (CIDEr) | Leverages term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) as weights when comparing matching candidate and reference n-grams | [94] |
| Semantic Propositional Image Caption Evaluation (SPICE) | Determines similarity by focusing on comparing the semantically rich content of references and candidates | [95] |
| Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers Score (BERTScore) | Utilizes BERT embeddings to compare the similarity | [96] |
| Initial Prompt | Craiyon Prompt |
|---|---|
| Different | Sorry unable to determine the nature of the image |
| Worst | Invalid caption |
| New | Undefined |
| Defraud | Warning explicit content detected |
| Model | BLEU-1 | BLEU-2 | BLEU-3 | BLEU-4 | ROUGE | METEOR | SPICE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIT | 19.4% | 4.4% | 1.2% | 0.4% | 23.6% | 9.9% | 7.1% |
| BLIP | 15.1% | 3.4% | 0.8% | 0.2% | 20.3% | 9.3% | 6.6% |
| BLIP-2 | 20% | 4.4% | 1.4% | 0.4% | 24.3% | 10.1% | 7.2% |
| InstructBLIP | 19.4% | 4.5% | 1.4% | 0.5% | 23.5% | 10% | 7.3% |
| Average | 18.5% | 4.2% | 1.2% | 0.4% | 22.9% | 9.8% | 7.2% |
| Model | Word2Vec | GloVe | FastText | DistilRoBERTa | MiniLM-L12 | MiniLM-L6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIT | 32.2% | 40% | 47.7% | 22.3% | 24.7% | 25.3% |
| BLIP | 31.7% | 39.5% | 50.2 | 18.3% | 20.3% | 20.4% |
| BLIP-2 | 32.4% | 40.1% | 48.1% | 21.3% | 23.3% | 24% |
| InstructBLIP | 32.5% | 40.3% | 49.8% | 21.8% | 24% | 24.5% |
| Average | 32.2% | 40% | 49% | 20.9% | 23.1% | 23.6% |
| Model | Word2Vec | GloVe | FastText | DistilRoBERTa | MiniLM-L12 | MiniLM-L6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIT | 41.7% | 72.1% | 78.1% | 28.2% | 27.1% | 28.1% |
| BLIP | 42.5% | 73.8% | 79.2% | 25.5% | 24.3% | 25.3% |
| BLIP-2 | 42.3% | 73.2% | 79.4% | 27.6% | 26.5% | 27.5% |
| InstructBLIP | 43.8% | 72.1% | 78.4% | 28.7% | 27.4% | 28.6% |
| Average | 42.6% | 72.8% | 78.8% | 27.5% | 26.3% | 27.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Combs, K.; Moyer, A.; Bihl, T.J. Uncertainty in Visual Generative AI. Algorithms 2024, 17, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17040136
Combs K, Moyer A, Bihl TJ. Uncertainty in Visual Generative AI. Algorithms. 2024; 17(4):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17040136
Chicago/Turabian StyleCombs, Kara, Adam Moyer, and Trevor J. Bihl. 2024. "Uncertainty in Visual Generative AI" Algorithms 17, no. 4: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17040136
APA StyleCombs, K., Moyer, A., & Bihl, T. J. (2024). Uncertainty in Visual Generative AI. Algorithms, 17(4), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17040136