Study of Gliding Arc Plasma Treatment for Bamboo-Culm Surface Modification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material
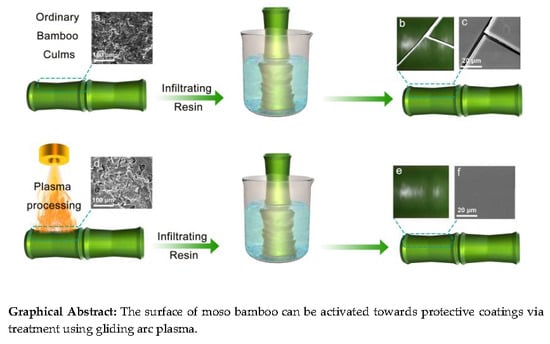
2.2. Plasma Treatment of Outer- and Inner-Layer of Bamboo Culms
2.3. Resin Soaking after Plasma Treatment
2.4. Characterizations
2.4.1. Contact Angle Measurements and Surface Energy Calculation
2.4.2. Surface Microstructure Observation
2.4.3. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Investigation
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Effect of Plasma Treatment on the Surface Characteristics of Bamboo Culm
3.1.1. Effect of Gliding Arc Plasma Treatment of Bamboo Culm on Contact Angles and Surface Energy of Outer-Layer Surface
3.1.2. The Effect of Gliding Arc Plasma Modification on Inner-Layer Surface Properties
3.2. Effect of Plasma Treatment on Surface Microstructure of Bamboo Culm
3.2.1. Effect of Gliding Arc Plasma Treatment on the Microstructure of Outer-Layer Surface
3.2.2. Effect of Gliding Arc Plasma Treatment on the Microstructure of Inner-Layer Surface
3.3. XPS Study of the Surface Functional Groups of Bamboo Culm Following Gliding Arc Plasma Treatment
3.3.1. The Outer-Layer Surface
3.3.2. The Inner-Layer Surface
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.S.; Jiang, S.X.; Tang, Y.Y. Industrial utilization on bamboo. In International Network for Bamboo and Rattan; People’s Republc: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liese, W. Bamboo and Rattan in the World. J. Bamboo Rattan 2003, 2, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liese, W.; Tang, T.K.H. Bamboo: The Plant and Its Uses; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.S.; Zheng, T.; Li, N.; Wang, P.; Abulikemu, G. Modification of bamboo-based activated carbon using microwave radiation and its effects on the adsorption of methylene blue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3309–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Jiang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Hui, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z. Effect of surface modification of bamboo cellulose fibers on mechanical properties of cellulose/epoxy composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 51, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, D.; Bose, S.K.; Hossain, M.M. Physical and mechanical properties of urea formaldehyde-bonded particleboard made from bamboo waste. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2011, 31, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wei, X.; Smith, L.M.; Wang, G.; Chen, F. Evaluation of Uniformity of Bamboo Bundle Veneer and Bamboo Bundle Laminated Veneer Lumber (BLVL). Forests 2019, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liese, W.; Kumar, S. Bamboo Preservation Compendium; Centre for Indian Bamboo Resource and Technology: Vansda, India, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liese, W.; Shanmughavel, P.; Peddappaiah, R.S.; Liese, W. Research on bamboo. Wood Sci. Technol. 1987, 21, 189–209. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, P.J.; Satya, S.; Pant, K.K.; Naik, S.N.; Kardam, V. Chemical characterization and decay resistance analysis of smoke treated bamboo species. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2016, 74, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umphauk, S. CCA wood preservative absorption of bamboo culms by soaking method. In Proceedings of the Kasetsart University Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 30 January 2 February 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, F.; Bao, B. Field tests for mold resistance with BHT and BTA added to bamboo preservatives. J. Zhejiang A F Univ. 2013, 30, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.S. Bamboo Preservation by Sap Displacement; International Network for Bamboo and Rattan: New Delhi, India, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.T. The effect of high-temperature drying on the antisplitting properties of makino bamboo culm (Phyllostachys makinoi Hay.). Wood Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Cui, H.W.; Du, G.B. Surface wettability, surface free energy, and surface adhesion of microwave plasma-treated Pinus yunnanensis wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.; Wakatani, M. Plasma Physics: Basic Theory with Fusion Applications; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Tang, L.J.; Zheng, F.; Xue, G.; Du, G.B.; Zhang, W.D.; Lv, C.L.; Yong, Q.; Zhang, R.; Tang, B.J. Oxygen plasma-treated enzymatic hydrolysis lignin as a natural binder for manufacturing biocomposites. Holzforschung 2011, 65, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, R.; Sauerbier, P.; Ohms, G.; Viöl, W.; Militz, H. Wood Protection through Plasma Powder Deposition-An Alternative Coating Process. Forests 2019, 10, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramidis, G.; Militz, H.; Avar, I.; Viöl, W.; Wolkenhauer, A. Improved absorption characteristics of thermally modified beech veneer produced by plasma treatment. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2012, 70, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Evans, P. Etching of wood surfaces by glow discharge plasma. Wood Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jing, G.; Yu, D.; Wang, S. Effects on surface properties of natural bamboo fibers treated with atmospheric pressure argon plasma. Surf. Interface Anal. Int. J. Devot. Dev. Appl. Tech. Anal. Surf. Interfaces Thin Films 2006, 38, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X. Surface modification of poplar veneer by means of radio frequency oxygen plasma (RF-OP) to improve interfacial adhesion with urea-formaldehyde resin. Holzforschung 2015, 69, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, X. Development of an industrial applicable dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma treatment for improving bondability of poplar veneer. Holzforschung 2016, 70, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, X. Effect of plasma processing rate on poplar veneer surface and its application in plywood. BioResources 2015, 11, 1571–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Tang, L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, X. Influence of atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment on the surface properties of wheat straw. BioResources 2014, 10, 1024–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlica, R.; Shih, K.-Y.; Hnatiuc, B.; Locke, B.R. Hydrogen generation by pulsed gliding arc discharge plasma with sprays of alcohol solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 9466–9470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indarto, A.; Yang, D.R.; Choi, J.-W.; Lee, H.; Song, H.K. Gliding arc plasma processing of CO2 conversion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czernichowski, A. Gliding arc: Applications to engineering and environment control. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, F.; Hussain, T.; Nazir, A.; Iqbal, K. Improving dimensional stability of cotton knits through resin finishing. J. Eng. Fibers Fabrics 2014, 9, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militz, H.; Schaffert, S.; Peters, B.C.; Fitzgerald, C.J. Termite resistance of DMDHEU-treated wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.; Wepner, F.; Xie, Y.; Militz, H. Wood protection with dimethyloldihydroxy-ethyleneurea and its derivatives. Development of commercial wood preservatives. Efficacy, environmental, and health issues. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 2008, 356–371. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Gao, H.; Sun, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, X. Impact of DMDHEU resin treatment on the mechanical properties of poplar. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2014, 22, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, R.; Minato, K.; Norimoto, M. Chemical modification of wood by non-formaldehyde cross-linking reagents. 2. Moisture adsorption and creep properties. Wood Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, C.J.; Chaudhury, M.K.; Good, R.J. Interfacial Lifshitz-van der Waals and polar interactions in macroscopic systems. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesel, A.; Mozetic, M.; Zalar, A. XPS characterization of PTFE after treatment with RF oxygen and nitrogen plasma. Surf. Interface Anal. Int. J. Devot. Dev. Appl. Tech. Anal. Surf. Interfaces Thin Films 2008, 40, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, Y.; Han, S.; Kim, K.J. Improvement of hydrophobic properties of polymer surfaces by plasma source ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 4763–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, I.; Demirkir, C. Activation of spruce wood surfaces by plasma treatment after long terms of natural surface inactivation. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2010, 30, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altgen, D.; Avramidis, G.; Viöl, W.; Mai, C. The effect of air plasma treatment at atmospheric pressure on thermally modified wood surfaces. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Layers of Bamboo Culm | Evoluted Groups |
|---|---|
| Outer-layer | O-CO-N, -NO2−,-NO3−, C-O-C, C-O-H |
| Inner-layer | O-CO-OH, C-O-C = O |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Du, G. Study of Gliding Arc Plasma Treatment for Bamboo-Culm Surface Modification. Forests 2019, 10, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10121086
Li B, Li J, Zhou X, Zhang J, Li T, Du G. Study of Gliding Arc Plasma Treatment for Bamboo-Culm Surface Modification. Forests. 2019; 10(12):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10121086
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bin, Jinxing Li, Xiaojian Zhou, Jun Zhang, Taohong Li, and Guanben Du. 2019. "Study of Gliding Arc Plasma Treatment for Bamboo-Culm Surface Modification" Forests 10, no. 12: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10121086
APA StyleLi, B., Li, J., Zhou, X., Zhang, J., Li, T., & Du, G. (2019). Study of Gliding Arc Plasma Treatment for Bamboo-Culm Surface Modification. Forests, 10(12), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10121086