Stilbene Content and Expression of Stilbene Synthase Genes in Korean Pine Pinus koraiensis Siebold & Zucc
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Stilbene Identification and Quantification by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS
2.3. Isolation, Cloning, and Sequencing of PkSTS Genes of P. koraiensis
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
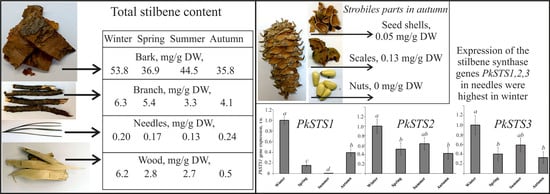
3.1. Stilbene Identification and Quantification
3.2. Expression Analysis of PkSTS Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komarova, T.A.; Sibirina, L.A.; Lee, D.K.; Kang, H.S. The Restoration Process after Fire in the Broadleaved-Dark Coniferous-Korean Pine Forest of the South Sikhote-Alin Mountains. For. Sci. Technol. 2007, 3, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.-Z.; Löfgren, K.-G. A Theory of Red Pine (Pinus koraiensis) Management for Both Timber and Commercial Seeds. For. Sci. 2000, 46, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zou, P.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, J.; Regenstein, J.M.; Yang, X. Isolation, Purification, Structure and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharide from Pinecones of Pinus koraiensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suprun, A.R.; Dubrovina, A.S.; Tyunin, A.P.; Kiselev, K.V. Profile of Stilbenes and Other Phenolics in Fanagoria White and Red Russian Wines. Metabolites 2021, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovina, A.S.; Kiselev, K.V. Regulation of Stilbene Biosynthesis in Plants. Planta 2017, 246, 597–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidlin, L.; Poutaraud, A.; Claudel, P.; Mestre, P.; Prado, E.; Santos-Rosa, M.; Wiedemann-Merdinoglu, S.; Karst, F.; Merdinoglu, D.; Hugueney, P. A Stress-Inducible Resveratrol O-Methyltransferase Involved in the Biosynthesis of Pterostilbene in Grapevine. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, I.M.; Park, M.R.; Chun, J.C.; Yun, S.J. Resveratrol Accumulation and Resveratrol Synthase Gene Expression in Response to Abiotic Stresses and Hormones in Peanut Plants. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, V.S. Localized Production of Phytoalexins by Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) Kernels in Response to Invasion by Aspergillus Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beňová, B.; Adam, M.; Onderková, K.; Královský, J.; Krajíček, M. Analysis of Selected Stilbenes in Polygonum Cuspidatum by HPLC Coupled with CoulArray Detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 2404–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokaya, M.B.; Maršík, P.; Münzbergová, Z. Active Constituents in Rheum Acuminatum and Rheum Australe (Polygonaceae) Roots: A Variation between Cultivated and Naturally Growing Plants. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 41, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Liu, C.; Chang, E.; Ji, J.; Yao, X.; Yue, J.; Bartish, I.V.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.; Shi, S. High Temperature and UV-C Treatments Affect Stilbenoid Accumulation and Related Gene Expression Levels in Gnetum parvifolium. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 25, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boue, S.M.; Shih, B.Y.; Burow, M.E.; Eggleston, G.; Lingle, S.; Pan, Y.B.; Daigle, K.; Bhatnagar, D. Postharvest Accumulation of Resveratrol and Piceatannol in Sugarcane with Enhanced Antioxidant Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8412–8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.M.; Yu, C.; Toma, R.B.; Cho, S.Y.; Reiboldt, W.; Lee, J.; van Breemen, R.B. Resveratrol in Raw and Baked Blueberries and Bilberries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5867–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimando, A.M.; Pan, Z.; Polashock, J.J.; Dayan, F.E.; Mizuno, C.S.; Snook, M.E.; Liu, C.-J.; Baerson, S.R. In Planta Production of the Highly Potent Resveratrol Analogue Pterostilbene via Stilbene Synthase and O-Methyltransferase Co-Expression. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2012, 10, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Ju, D.-T.; Chang, C.-F.; Muralidhar Reddy, P.; Velmurugan, B.K. A Review on the Effects of Current Chemotherapy Drugs and Natural Agents in Treating Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Biomedicine 2017, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbulova, A.; Colucci, G.; Apone, F. New Trends in Cosmetics: By-Products of Plant Origin and Their Potential Use as Cosmetic Active Ingredients. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naboulsi, I.; Aboulmouhajir, A.; Kouisni, L.; Bekkaoui, F.; Yasri, A. Plants Extracts and Secondary Metabolites, Their Extraction Methods and Use in Agriculture for Controlling Crop Stresses and Improving Productivity: A Review. Acad. J. Med. Plants 2018, 6, 223–240. [Google Scholar]
- Reinisalo, M.; Kårlund, A.; Koskela, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Karjalainen, R.O. Polyphenol Stilbenes: Molecular Mechanisms of Defence against Oxidative Stress and Aging-Related Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 340520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, J.; Poutaraud, A.; Hugueney, P. Metabolism and Roles of Stilbenes in Plants. Plant Sci. 2009, 177, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Delaunois, B.; Conreux, A.; Donnez, D.; Nuzzo, V.; Cordelier, S.; Clément, C.; Courot, E. Biosynthesis, Metabolism, Molecular Engineering, and Biological Functions of Stilbene Phytoalexins in Plants. BioFactors 2010, 36, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibutani, S.; Samejima, M.; Doi, S. Effects of Stilbenes from Bark of Picea glehnii (Sieb. et Zucc) and Their Related Compounds against Feeding Behaviour of Reticulitermes speratus (Kolbe). J. Wood Sci. 2004, 50, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, K.V.; Ogneva, Z.V.; Suprun, A.R.; Grigorchuk, V.P.; Dubrovina, A.S. Action of Ultraviolet-C Radiation and p-Coumaric Acid on Stilbene Accumulation and Expression of Stilbene Biosynthesis-Related Genes in the Grapevine Vitis amurensis Rupr. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, K.; Melliou, E.; Alizoti, P.; Magiatis, P. Identification of Black Pine (Pinus nigra Arn.) Heartwood as a Rich Source of Bioactive Stilbenes by QNMR. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-S.; Han, J.Y.; Choi, Y.E. Enhanced Accumulation of Pinosylvin Stilbenes and Related Gene Expression in Pinus Strobus after Infection of Pine Wood Nematode. Tree Physiol. 2021, 41, 1972–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromova, A.; Tyukavkina, N.; Lutskii, V.; Kalabin, G.; Kushnarev, D. Hydroxystilbenes of the Inner Bark of Pinus sibirica. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1975, 11, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.-J.; Bae, Y.-S. Stilbenoids of Korean Pine (Pinus koraiensis) Inner Bark*. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2009, 37, 474–479. [Google Scholar]
- Jyske, T.; Brännström, H.; Halmemies, E.; Laakso, T.; Kilpeläinen, P.; Hyvönen, J.; Kärkkäinen, K.; Saranpää, P. Stilbenoids of Norway Spruce Bark: Does the Variability Caused by Raw-Material Processing Offset the Biological Variability? Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, R.B. Effects of Exposure to High Ozone Concentrations on Stilbenes in Sitka Spruce (Picea sitchensis(Bong.) Carr.) Bark and on Its Lignification Response to Infection with Heterobasidion annosum(Fr.) Bref. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1996, 48, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harju, A.; Venalainen, M. Stilbenes as constitutive and induced protection compounds in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). In Proceedings of the Fourth International Workshop on the Genetics of Host-Parasite Interactions in Forestry: Disease and Insect Resistance in Forest Trees; Sniezko, R.A., Yanchuk, A.D., Kliejunas, J.T., Palmieri, K.M., Alexander, J.M., Frankel, S.J., Eds.; Gen. Tech. Rep. PSW-GTR-240; Pacific Southwest Research Station, Forest Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture: Albany, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 240, pp. 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mulat, D.G.; Latva-Mäenpää, H.; Koskela, H.; Saranpää, P.; Wähälä, K. Rapid Chemical Characterisation of Stilbenes in the Root Bark of Norway Spruce by Off-Line HPLC/DAD-NMR. Phytochem. Anal. 2014, 25, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suprun, A.R.; Dubrovina, A.S.; Aleynova, O.A.; Kiselev, K.V. The Bark of the Spruce Picea Jezoensis Is a Rich Source of Stilbenes. Metabolites 2021, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pérez, M.-E.; Royer, M.; Herbette, G.; Desjardins, Y.; Pouliot, R.; Stevanovic, T. Picea Mariana Bark: A New Source of Trans-Resveratrol and Other Bioactive Polyphenols. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyunin, A.P.; Nityagovsky, N.N.; Grigorchuk, V.P.; Kiselev, K.V. Stilbene Content and Expression of Stilbene Synthase Genes in Cell Cultures of Vitis amurensis Treated with Cinnamic and Caffeic Acids. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2018, 65, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.; Luca, V.D. Mesocarp Localization of a Bi-Functional Resveratrol/Hydroxycinnamic Acid Glucosyltransferase of Concord Grape (Vitis labrusca). Plant J. 2007, 49, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, K.V.; Grigorchuk, V.P.; Ogneva, Z.V.; Suprun, A.R.; Dubrovina, A.S. Stilbene Biosynthesis in the Needles of Spruce Picea jezoensis. Phytochemistry 2016, 131, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, M.; Jeandet, P.; Bessis, R.; Joubert, J.M. Induction of Phytoalexin (Resveratrol) Synthesis in Grapevine Leaves Treated with Aluminum Chloride (AlCl3). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 1979–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerbacher, A.; Ralph, S.G.; Bohlmann, J.; Fenning, T.M.; Gershenzon, J.; Schmidt, A. Biosynthesis of the Major Tetrahydroxystilbenes in Spruce, Astringin and Isorhapontin, Proceeds via Resveratrol and Is Enhanced by Fungal Infection. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, R.L.; Keeling, C.I.; Yuen, M.M.S.; Raymond, A.; Taylor, G.A.; Vandervalk, B.P.; Mohamadi, H.; Paulino, D.; Chiu, R.; Jackman, S.D.; et al. Improved White Spruce (Picea glauca) Genome Assemblies and Annotation of Large Gene Families of Conifer Terpenoid and Phenolic Defense Metabolism. Plant J. 2015, 83, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, K.V.; Aleynova, O.A.; Tyunin, A.P. Expression of the R2R3 MYB Transcription Factors in Vitis amurensis Rupr. Plants and Cell Cultures with Different Resveratrol Content. Russ. J. Genet. 2017, 53, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehlert, R.; Schöppner, A.; Kindl, H. Stilbene Synthase from Seedlings of Pinus sylvestris: Purification and Induction in Response to Fungal Infection. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1990, 3, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovina, A.S.; Kiselev, K.V.; Khristenko, V.S. Expression of Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase (CDPK) Genes under Abiotic Stress Conditions in Wild-Growing Grapevine Vitis amurensis. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, K.V.; Dubrovina, A.S.; Shumakova, O.A.; Karetin, Y.A.; Manyakhin, A.Y. Structure and Expression Profiling of a Novel Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase Gene, CDPK3a, in Leaves, Stems, Grapes, and Cell Cultures of Wild-Growing Grapevine Vitis amurensis Rupr. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovina, A.S.; Aleynova, O.A.; Kiselev, K.V. Influence of Overexpression of the True and False Alternative Transcripts of Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase CPK9 and CPK3a Genes on the Growth, Stress Tolerance, and Resveratrol Content in Vitis amurensis Cell Cultures. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, K.V.; Dubrovina, A.S. A New Method for Analyzing Gene Expression Based on Frequency Analysis of RT-PCR Products Obtained with Degenerate Primers. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2010, 32, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, K.V.; Shumakova, O.A.; Manyakhin, A.Y.; Mazeika, A.N. Influence of Calcium Influx Induced by the Calcium Ionophore, A23187, on Resveratrol Content and the Expression of CDPK and STS Genes in the Cell Cultures of Vitis amurensis. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 68, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodan, A.; Kuroda, H.; Sakai, F. A Stilbene Synthase from Japanese Red Pine (Pinus densiflora): Implications for Phytoalexin Accumulation and down-Regulation of Flavonoid Biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3335–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patyra, A.; Dudek, M.K.; Kiss, A.K. LC-DAD–ESI-MS/MS and NMR Analysis of Conifer Wood Specialized Metabolites. Cells 2022, 11, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaston, J.; Richard, T.; Cluzet, S.; Palos Pinto, A.; Dufour, M.-C.; Corio-Costet, M.-F.; Mérillon, J.-M. Pinus Pinaster Knot: A Source of Polyphenols against Plasmopara viticola. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8884–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.H.; Kertesz, M. Conformational Information from Vibrational Spectra of Styrene, Trans-Stilbene, and Cis-Stilbene. J. Phys. Chem. A 1997, 101, 3823–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karashima, S.; Miao, X.; Kanayama, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nishitani, J.; Kavka, N.; Mitric, R.; Suzuki, T. Ultrafast Ring Closure Reaction of Gaseous Cis-Stilbene from S1(Ππ*). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 3283–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliegmann, J.; Schröder, G.; Schanz, S.; Britsch, L.; Schröder, J. Molecular Analysis of Chalcone and Dihydropinosylvin Synthase from Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris), and Differential Regulation of These and Related Enzyme Activities in Stressed Plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 18, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiber, S.; Schröder, G.; Schröder, J. Molecular and Enzymatic Characterization of Two Stilbene Synthases from Eastern White Pine (Pinus strobus). A Single Arg/His Difference Determines the Activity and the PH Dependence of the Enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1995, 361, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.-Y.; Lee, J.K.; Choi, O.; Kim, C.Y.; Jang, J.-H.; Hwang, B.Y.; Hong, Y.-S. Biosynthesis of Methylated Resveratrol Analogs through the Construction of an Artificial Biosynthetic Pathway in E. coli. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimoda, K.; Kubota, N.; Uesugi, D.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hamada, H.; Hamada, H. Glycosylation of Stilbene Compounds by Cultured Plant Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piao, S.; Chen, L.; Kang, N.; Qiu, F. Simultaneous Determination of Five Characteristic Stilbene Glycosides in Root Bark of Morus albus L. (Cortex mori) Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. 2011, 22, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyunin, A.P.; Suprun, A.R.; Nityagovsky, N.N.; Manyakhin, A.Y.; Karetin, Y.A.; Dubrovina, A.S.; Kiselev, K.V. The Effect of Explant Origin and Collection Season on Stilbene Biosynthesis in Cell Cultures of Vitis amurensis Rupr. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2019, 136, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valletta, A.; Iozia, L.M.; Leonelli, F. Impact of Environmental Factors on Stilbene Biosynthesis. Plants 2021, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Bark Season/Stilbene Compound | Bark Collected in Winter, mg/g DW | Bark Collected in Spring, mg/g DW | Bark Collected in Summer, mg/g DW | Bark Collected in Autumn, mg/g DW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-astringin (1) * | ||||
| t-piceid (2) | ||||
| cis-piceid (3) | ||||
| t-isorhapontin (4) | ||||
| t-pinostilbenoside (5) | ||||
| t-resveratrol (6) | ||||
| t-pinostilben (7) | ||||
| Total |
| Needles Season/Stilbene Compound | Needles Collected in Winter, mg/g DW | Needles Collected in Spring, mg/g DW | Needles Collected in Summer, mg/g DW | Needles Collected in Autumn, mg/g DW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-astringin (1) * | ||||
| t-piceid (2) | ||||
| cis-piceid (3) | ||||
| t-isorhapontin (4) | ||||
| t-pinostilbenoside (5) | ||||
| t-resveratrol (6) | ||||
| t-pinostilben (7) | ||||
| Total |
| Branch Season/Stilbene Compound | Branch Collected in Winter, mg/g DW | Branch Collected in Spring, mg/g DW | Branch Collected in Summer, mg/g DW | Branch Collected in Autumn, mg/g DW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-astringin (1) * | ||||
| t-piceid (2) | ||||
| cis-piceid (3) | ||||
| t-isorhapontin (4) | ||||
| t-pinostilbenoside (5) | ||||
| t-resveratrol (6) | ||||
| t-pinostilben (7) | ||||
| Total |
| Wood Season/Stilbene Compound | Wood Collected in Winter, mg/g DW | Wood Collected in Spring, mg/g DW | Wood Collected in Summer, mg/g DW | Wood Collected in Autumn, mg/g DW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-astringin (1) * | ||||
| t-piceid (2) | ||||
| cis-piceid (3) | ||||
| t-isorhapontin (4) | ||||
| t-pinostilbenoside (5) | ||||
| t-resveratrol (6) | ||||
| t-pinostilben (7) | ||||
| Total |
| Strobiles Parts/Stilbene | Scales, mg/g DW | Seed Shells, mg/g DW | Nuts, mg/g DW |
|---|---|---|---|
| t-astringin (1) * | 0.017 ± 0.003 a | 0.007 ± 0.001 b | 0 |
| t-piceid (2) | 0.036 ± 0.009 a | 0.035 ± 0.014 a | 0 |
| cis-piceid (3) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| t-isorhapontin (4) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| t-pinostilbenoside (5) | 0.051 ± 0.014 a | 0.008 ± 0.005 b | 0 |
| t-resveratrol (6) | 0.004 ± 0.002 | 0 | 0 |
| t-pinostilben (7) | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 0.127 ± 0.031 a | 0.050 ± 0.013 b | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suprun, A.R.; Dubrovina, A.S.; Grigorchuk, V.P.; Kiselev, K.V. Stilbene Content and Expression of Stilbene Synthase Genes in Korean Pine Pinus koraiensis Siebold & Zucc. Forests 2023, 14, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14061239
Suprun AR, Dubrovina AS, Grigorchuk VP, Kiselev KV. Stilbene Content and Expression of Stilbene Synthase Genes in Korean Pine Pinus koraiensis Siebold & Zucc. Forests. 2023; 14(6):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14061239
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuprun, Andrey R., Alexandra S. Dubrovina, Valeria P. Grigorchuk, and Konstantin V. Kiselev. 2023. "Stilbene Content and Expression of Stilbene Synthase Genes in Korean Pine Pinus koraiensis Siebold & Zucc" Forests 14, no. 6: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14061239
APA StyleSuprun, A. R., Dubrovina, A. S., Grigorchuk, V. P., & Kiselev, K. V. (2023). Stilbene Content and Expression of Stilbene Synthase Genes in Korean Pine Pinus koraiensis Siebold & Zucc. Forests, 14(6), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14061239