A Novel Piggyback Strategy for mRNA Delivery Exploiting Adenovirus Entry Biology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
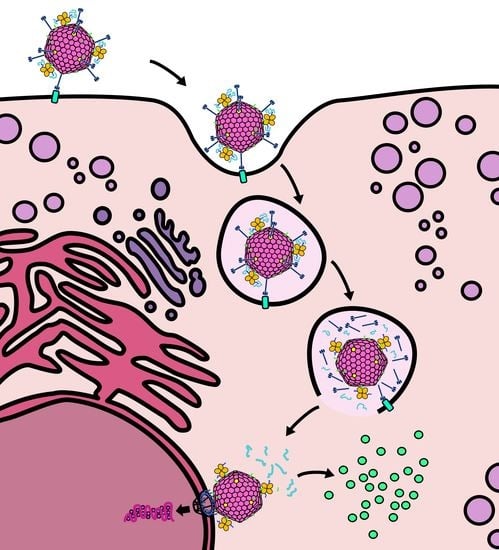
2.1. Design of a Novel Strategy for “Piggyback” Delivery of mRNA
2.2. Assessment of Adenovirus-Polylysine-Mediated mRNA Delivery
2.3. Polylysine-Mediated mRNA Conjugation Alters Adenovirus Tropism
2.4. Adenovirus-Polylysine Co-Delivery of Two mRNAs
2.5. In Vivo Delivery of mRNA via Adenovirus-Polylysine Strategy
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Production of Retargeted Adenovirus
4.2. Preparation and Validation of Biotinylated Adenovirus
4.3. Construction of AdPK4-STAVpLys-mRNA Complexes
4.4. In Vitro Evaluation of Gene Transfer by AdPK4-STAVpLys-mRNA Complexes
4.5. In Vivo Evaluation of Gene Transfer by AdPK4-STAVpLys-mRNA Complexes
4.6. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaudhary, N.; Weissman, D.; Whitehead, K.A. mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases: Principles, delivery and clinical translation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 817–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.; Gao, M.; Li, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.Q.; Xu, X. Next-Generation Vaccines: Nanoparticle-Mediated DNA and mRNA Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2001812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.J.; Atai, N.A.; Cacciottolo, M.; Nice, J.; Salehi, A.; Guo, C.; Sedgwick, A.; Kanagavelu, S.; Gould, S.J. Exosome-mediated mRNA delivery in vivo is safe and can be used to induce SARS-CoV-2 immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, A.J.; Jiang, A.Y.; Zhang, P.; Wooster, R.; Anderson, D.G. The clinical progress of mRNA vaccines and immunotherapies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, M.D.J.; Rose, L.M.; Russell, R.A.; Bowman, L.A.H.; Graham, C.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Doores, K.J.; Malim, M.H.; Draper, S.J.; Howarth, M.; et al. Modular capsid decoration boosts adenovirus vaccine-induced humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2022; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, N.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Ahmed, S.N.; Dey, S.K. Efficacy, Immunogenicity and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 714170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.J.; Greig, J.A.; Michalson, K.T.; Lian, S.; Martino, R.A.; Meggersee, R.; Turner, K.B.; Nambiar, K.; Dyer, C.; Hinderer, C.; et al. Intranasal gene therapy to prevent infection by SARS-CoV-2 variants. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Satapathy, S.R.; Dutta, T. Delivery Strategies for mRNA Vaccines. Pharm. Med. 2022, 36, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E.; Zatloukal, K.; Cotten, M.; Kirlappos, H.; Mechtler, K.; Curiel, D.T.; Birnstiel, M.L. Coupling of adenovirus to transferrin-polylysine/DNA complexes greatly enhances receptor-mediated gene delivery and expression of transfected genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 6099–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curiel, D.T.; Wagner, E.; Cotten, M.; Birnstiel, M.L.; Agarwal, S.; Li, C.M.; Loechel, S.; Hu, P.C. High-efficiency gene transfer mediated by adenovirus coupled to DNA-polylysine complexes. Hum. Gene Ther. 1992, 3, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wagner, E.; Cotten, M.; Agarwal, S.; Harris, C.; Rømer, M.; Miller, L.; Hu, P.C.; Curiel, D. Direct in vivo gene transfer to airway epithelium employing adenovirus-polylysine-DNA complexes. Hum. Gene Ther. 1993, 4, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircheis, R.; Schüller, S.; Brunner, S.; Ogris, M.; Heider, K.H.; Zauner, W.; Wagner, E. Polycation-based DNA complexes for tumor-targeted gene delivery in vivo. J. Gene Med. 1999, 1, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S.; Kämpgen, E.; Wagner, E.; Pirkhammer, D.; Trcka, J.; Korschan, H.; Lindemann, A.; Dorffner, R.; Kittler, H.; Kasteliz, F.; et al. Immunotherapy of metastatic malignant melanoma by a vaccine consisting of autologous interleukin 2-transfected cancer cells: Outcome of a phase I study. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Zintchenko, A.; Ogris, M.; Wagner, E. A dimethylmaleic acid-melittin-polylysine conjugate with reduced toxicity, pH-triggered endosomolytic activity and enhanced gene transfer potential. J. Gene Med. 2007, 9, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E.; Ogris, M.; Zauner, W. Polylysine-based transfection systems utilizing receptor-mediated delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 30, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson-Ryan, I.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Ak, F.; Dodson, L.; Colonna, M.; Powell, M.; Mutch, D.; Spitzer, D.; Hansen, T.; et al. Incorporation of porcine adenovirus 4 fiber protein enhances infectivity of adenovirus vector on dendritic cells: Implications for immune-mediated cancer therapy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnykh, V.N.; Mikheeva, G.V.; Douglas, J.T.; Curiel, D.T. Generation of recombinant adenovirus vectors with modified fibers for altering viral tropism. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6839–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousova, N.; Krendelchtchikova, V.; Curiel, D.T.; Krasnykh, V. Modulation of adenovirus vector tropism via incorporation of polypeptide ligands into the fiber protein. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8621–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hemminki, A.; Siegal, G.P.; Barnes, M.N.; Dmitriev, I.; Krasnykh, V.; Liu, B.; Curiel, D.T.; Alvarez, R.D. Adenoviruses with an RGD-4C modification of the fiber knob elicit a neutralizing antibody response but continue to allow enhanced gene delivery. Gynecol. Oncol. 2005, 96, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Kaliberov, S.; Zhang, J.; Muz, B.; Azab, A.K.; Sohn, R.E.; Kaliberova, L.; Du, Y.; Curiel, D.T.; Arbeit, J.M. The myeloid-binding peptide adenoviral vector enables multi-organ vascular endothelial gene targeting. Lab. Investig. A J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2014, 94, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaliberov, S.A.; Kaliberova, L.N.; Hong Lu, Z.; Preuss, M.A.; Barnes, J.A.; Stockard, C.R.; Grizzle, W.E.; Arbeit, J.M.; Curiel, D.T. Retargeting of gene expression using endothelium specific hexon modified adenoviral vector. Virology 2013, 447, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zauner, W.; Kichler, A.; Schmidt, W.; Mechtler, K.; Wagner, E. Glycerol and polylysine synergize in their ability to rupture vesicular membranes: A mechanism for increased transferrin-polylysine-mediated gene transfer. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 232, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauner, W.; Kichler, A.; Schmidt, W.; Sinski, A.; Wagner, E. Glycerol enhancement of ligand-polylysine/DNA transfection. Bio.Tech. 1996, 20, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmuth, A.M.; Oberli, M.A.; Jaklenec, A.; Langer, R.; Blankschtein, D. mRNA vaccine delivery using lipid nanoparticles. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, M.L.; Persano, F.; Persano, S. Advances in Lipid Nanoparticles for mRNA-Based Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 589959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassett, K.J.; Benenato, K.E.; Jacquinet, E.; Lee, A.; Woods, A.; Yuzhakov, O.; Himansu, S.; Deterling, J.; Geilich, B.M.; Ketova, T.; et al. Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticles for Intramuscular Administration of mRNA Vaccines. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Lagniton, P.N.P.; Liu, Y.; Xu, R.H. mRNA vaccines for COVID-19: What, why and how. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1446–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, J.W.; Gaiha, G.D.; Traverso, G. Oral Biologic Delivery: Advances Toward Oral Subunit, DNA, and mRNA Vaccines and the Potential for Mass Vaccination During Pandemics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 61, 517–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devoldere, J.; Peynshaert, K.; Dewitte, H.; Vanhove, C.; De Groef, L.; Moons, L.; Özcan, S.Y.; Dalkara, D.; De Smedt, S.C.; Remaut, K. Non-viral delivery of chemically modified mRNA to the retina: Subretinal versus intravitreal administration. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2019, 307, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.; Karl, C.E.; Halfmann, P.J.; Kawaoka, Y.; Winkler, E.S.; Keeler, S.P.; Holtzman, M.J.; Yu, J.; Diamond, M.S. Nasally delivered interferon-λ protects mice against infection by SARS-CoV-2 variants including Omicron. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, H.; Du, X.; Wang, J. Mucosal vaccine delivery: A focus on the breakthrough of specific barriers. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 9, 3456–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesin, B.; Lopez, J.; Noirat, A.; Authié, P.; Fert, I.; Le Chevalier, F.; Moncoq, F.; Nemirov, K.; Blanc, C.; Planchais, C.; et al. An intranasal lentiviral booster reinforces the waning mRNA vaccine-induced SARS-CoV-2 immunity that it targets to lung mucosa. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2022, 9, 2984–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.O.; Kafai, N.M.; Dmitriev, I.P.; Fox, J.M.; Smith, B.K.; Harvey, I.B.; Chen, R.E.; Winkler, E.S.; Wessel, A.W.; Case, J.B.; et al. A Single-Dose Intranasal ChAd Vaccine Protects Upper and Lower Respiratory Tracts against SARS-CoV-2. Cell 2020, 183, 169–184.e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.O.; Feldmann, F.; Zhao, H.; Curiel, D.T.; Okumura, A.; Tang-Huau, T.L.; Case, J.B.; Meade-White, K.; Callison, J.; Chen, R.E.; et al. A single intranasal dose of chimpanzee adenovirus-vectored vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.B.; Cao, J.W.; Wang, J.K.; Lin, H.Z.; Gao, D.Y.; Qian, G.Y.; Park, Y.D.; Chen, Z.F.; Wang, Q. SpyTag/SpyCatcher molecular cyclization confers protein stability and resilience to aggregation. New Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Zhang, W.B. SpyTag-SpyCatcher Chemistry for Protein Bioconjugation In Vitro and Protein Topology Engineering In Vivo. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2033, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Chang, Y.; Luo, H. SpyTag/SpyCatcher cyclization enhances the thermostability and organic solvent tolerance of L-phenylalanine aldolase. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.K.; Rijal, P.; Rahikainen, R.; Keeble, A.H.; Schimanski, L.; Hussain, S.; Harvey, R.; Hayes, J.W.P.; Edwards, J.C.; McLean, R.K.; et al. A COVID-19 vaccine candidate using SpyCatcher multimerization of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor-binding domain induces potent neutralising antibody responses. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Li, J.; Dmitriev, I.P.; Kashentseva, E.A.; Curiel, D.T. Efficient Genome Editing Achieved via Plug-and-Play Adenovirus Piggyback Transport of Cas9/gRNA Complex on Viral Capsid Surface. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 10443–10455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uil, T.G.; Seki, T.; Dmitriev, I.; Kashentseva, E.; Douglas, J.T.; Rots, M.G.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Curiel, D.T. Generation of an adenoviral vector containing an addition of a heterologous ligand to the serotype 3 fiber knob. Cancer Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Lu, Z.H.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Tremblay, J.M.; St Croix, B.; Seaman, S.; Gonzalez-Pastor, R.; Kashentseva, E.A.; Dmitriev, I.P.; Curiel, D.T. Advanced genetic engineering to achieve in vivo targeting of adenovirus utilizing camelid single domain antibody. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2021, 334, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, J.A.; Hennessey, J.P., Jr. Evaluation of accuracy and precision of adenovirus absorptivity at 260 nm under conditions of complete DNA disruption. Virology 2002, 295, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotten, M.; Baker, A.; Birnstiel, M.L.; Zatloukal, K.; Wagner, E. Preparation of adenovirus-polylysine-DNA complexes. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2001, 12.3.1–12.3.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Dmitriev, I.P.; Brough, D.E.; Kashentseva, E.A.; Li, J.; Curiel, D.T. A New Gorilla Adenoviral Vector with Natural Lung Tropism Avoids Liver Toxicity and Is Amenable to Capsid Engineering and Vector Retargeting. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00265-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.; Rice-Boucher, P.J.; Collins, L.T.; Wagner, E.; Aulisa, L.; Hughes, J.; Curiel, D.T. A Novel Piggyback Strategy for mRNA Delivery Exploiting Adenovirus Entry Biology. Viruses 2022, 14, 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102169
Lee M, Rice-Boucher PJ, Collins LT, Wagner E, Aulisa L, Hughes J, Curiel DT. A Novel Piggyback Strategy for mRNA Delivery Exploiting Adenovirus Entry Biology. Viruses. 2022; 14(10):2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102169
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Myungeun, Paul J. Rice-Boucher, Logan Thrasher Collins, Ernst Wagner, Lorenzo Aulisa, Jeffrey Hughes, and David T. Curiel. 2022. "A Novel Piggyback Strategy for mRNA Delivery Exploiting Adenovirus Entry Biology" Viruses 14, no. 10: 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102169
APA StyleLee, M., Rice-Boucher, P. J., Collins, L. T., Wagner, E., Aulisa, L., Hughes, J., & Curiel, D. T. (2022). A Novel Piggyback Strategy for mRNA Delivery Exploiting Adenovirus Entry Biology. Viruses, 14(10), 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102169