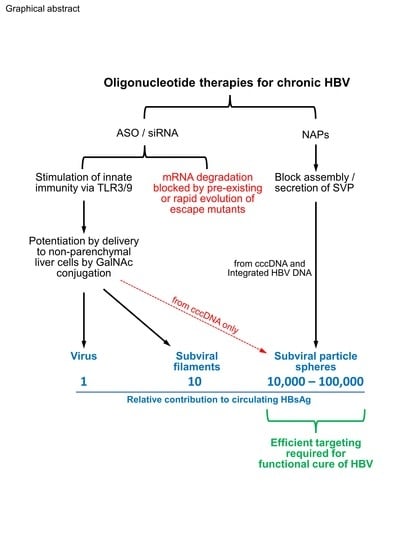
Oligonucleotide-Based Therapies for Chronic HBV Infection: A Primer on Biochemistry, Mechanisms and Antiviral Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Oligonucleotide Modifications and Effects on Structure and Function
3. Liver Immunoreactivity, Cellular Uptake of Oligonucleotides, Lnp and Galnac
4. Pharmacodynamics of the ASO/siRNA Response
5. Molecular Biology of HBV vs. Mechanistic Approaches of Oligonucleotide-Based Drugs
6. Animal Models Suitable for the Evaluation of ASO, siRNA and NAPs
7. NAP Effects In Vitro, In Vivo and Humans in HBV Infection
8. ASO/siRNA Effects In Vitro, In Vivo and in Humans in HBV Infection
9. Conclusions and Perspective
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crooke, S.T.; Baker, B.F.; Crooke, R.M.; Liang, X.H. Antisense technology: An overview and prospectus. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, T.A.; Koo, S.; Bennett, C.F.; Crooke, S.T.; Dean, N.M.; Baker, B.F. Efficient reduction of target RNAs by small interfering RNA and RNase H-dependent antisense agents. A comparative analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 7108–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, M.; Judge, A.; MacLachlan, I. siRNA and innate immunity. Oligonucleotides 2009, 19, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, A.M. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA and their immune effects. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 709–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, A.D.; Sood, V.; Shaw, J.R.; Fang, D.; McClintock, K.; MacLachlan, I. Sequence-dependent stimulation of the mammalian innate immune response by synthetic siRNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioud, M. Induction of inflammatory cytokines and interferon responses by double-stranded and single-stranded siRNAs is sequence-dependent and requires endosomal localization. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, V.; Guenthner-Biller, M.; Bourquin, C.; Ablasser, A.; Schlee, M.; Uematsu, S.; Noronha, A.; Manoharan, M.; Akira, S.; de Fougerolles, A.; et al. Sequence-specific potent induction of IFN-alpha by short interfering RNA in plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR7. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, V.; Barchet, W.; Schlee, M.; Hartmann, G. RNA recognition via TLR7 and TLR8. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2008, 183, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, M.R.; Jimenez, R.M.; Chaput, J.C. Analysis of aptamer discovery and technology. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooke, S.T.; Vickers, T.A.; Liang, X.H. Phosphorothioate modified oligonucleotide-protein interactions. Nucl. Acids Res. 2020, 48, 5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillant, A. Nucleic acid polymers: Broad spectrum antiviral activity, antiviral mechanisms and optimization for the treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis D infection. Antivir. Res. 2016, 133, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillant, A. REP 2139: Antiviral Mechanisms and Applications in Achieving Functional Control of HBV and HDV Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, A.; Juteau, J.M.; Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Lackman-Smith, C.; Ptak, R.; Jiang, S. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 fusion by blocking gp41 core formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.M.; Rojek, J.M.; Gundersen, A.; Stroher, U.; Juteau, J.M.; Vaillant, A.; Kunz, S. Inhibition of cellular entry of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus by amphipathic DNA polymers. Virology 2008, 372, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocisko, D.A.; Vaillant, A.; Lee, K.S.; Arnold, K.M.; Bertholet, N.; Race, R.E.; Olsen, E.A.; Juteau, J.M.; Caughey, B. Potent antiscrapie activities of degenerate phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamur, M.M.; Peri-Naor, R.; Mayer, R.; Vaillant, A. Interaction of nucleic acid polymers with the large and small forms of hepatitis delta antigen protein. Hepatology 2017, 66, 504A. [Google Scholar]
- Boulon, R.; Angelo, L.; Blanchet, M.; Vaillant, A.; Labonte, P. PH-dependent Interaction of NAPs with the HSP40 Chaperone DnaJB12. Hepatology 2021, 74, 512A. [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein, F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1970, 92, 4718–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, S.; Eckstein, F. Inhibition of deoxyribonucleases by phosphorothioate groups in oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucl. Acids Res. 1988, 16, 11691–11704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, F. Phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides: What is their origin and what is unique about them? Antisense Nucl. Acid Drug Dev. 2000, 10, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.P.; Reeves, K.K.; Snyder, E.; Farrell, J.; Powell, J.W.; Mohan, V.; Griffey, R.H. Hydration of single-stranded phosphodiester and phosphorothioate oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucl. Acids Res. 1996, 24, 3261–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaroszewski, J.W.; Clausen, V.; Cohen, J.S.; Dahl, O. NMR investigations of duplex stability of phosphorothioate and phosphorodithioate DNA analogues modified in both strands. Nucl. Acids Res. 1996, 24, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioud, M.; Furset, G.; Cekaite, L. Suppression of immunostimulatory siRNA-driven innate immune activation by 2’-modified RNAs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 361, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, A.D.; Bola, G.; Lee, A.C.; MacLachlan, I. Design of noninflammatory synthetic siRNA mediating potent gene silencing in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2006, 13, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidan, V.M.; Cohen, J.S.; Amariglio, N.; Hirsch-Lerner, D.; Barenholz, Y. Interaction of oligonucleotides with cationic lipids: The relationship between electrostatics, hydration and state of aggregation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1464, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, M.; Pallan, P.S. Insights from crystallographic studies into the structural and pairing properties of nucleic acid analogs and chemically modified DNA and RNA oligonucleotides. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2007, 36, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.B.; Seth, P.P. The Medicinal Chemistry of Therapeutic Oligonucleotides. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 9645–9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; De Hoyos, C.L.; Migawa, M.T.; Vickers, T.A.; Sun, H.; Low, A.; Bell, T.A., 3rd; Rahdar, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Hart, C.E.; et al. Chemical modification of PS-ASO therapeutics reduces cellular protein-binding and improves the therapeutic index. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Le, B.T.; Chakravarthy, M.; Kosbar, T.R.; Veedu, R.N. Systematic evaluation of 2’-Fluoro modified chimeric antisense oligonucleotide-mediated exon skipping in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monia, B.P.; Lesnik, E.A.; Gonzalez, C.; Lima, W.F.; McGee, D.; Guinosso, C.J.; Kawasaki, A.M.; Cook, P.D.; Freier, S.M. Evaluation of 2’-modified oligonucleotides containing 2’-deoxy gaps as antisense inhibitors of gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 14514–14522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Iyer, R.P.; Shaw, D.R.; Lisziewicz, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Roskey, A.; Agrawal, S. Hybrid oligonucleotides: Synthesis, biophysical properties, stability studies, and biological activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1996, 4, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, R.A.; Miraglia, L.J.; Cummins, L.L.; Owens, S.R.; Sasmor, H.; Dean, N.M. Characterization of a potent and specific class of antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor of human protein kinase C-alpha expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Assi, H.; Rangadurai, A.K.; Shi, H.; Liu, B.; Clay, M.C.; Erharter, K.; Kreutz, C.; Holley, C.L.; Al-Hashimi, H.M. 2’-O-Methylation can increase the abundance and lifetime of alternative RNA conformational states. Nucl. Acids Res. 2020, 48, 12365–12379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuschner, P.J.; Ameres, S.L.; Kueng, S.; Martinez, J. Cleavage of the siRNA passenger strand during RISC assembly in human cells. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Arora, A.; Wengel, J.; Maiti, S. Thermodynamic, counterion, and hydration effects for the incorporation of locked nucleic acid nucleotides into DNA duplexes. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 7347–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, V.; Nilsson, L. Insights into structure, dynamics and hydration of locked nucleic acid (LNA) strand-based duplexes from molecular dynamics simulations. Nucl. Acids Res. 2008, 36, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierzek, E.; Pasternak, A.; Pasternak, K.; Gdaniec, Z.; Yildirim, I.; Turner, D.H.; Kierzek, R. Contributions of stacking, preorganization, and hydrogen bonding to the thermodynamic stability of duplexes between RNA and 2’-O-methyl RNA with locked nucleic acids. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 4377–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, H.G.; Shim, I.; Stein, C.; Orum, H.; Hansen, H.F.; Koch, T. Electronic Structures of LNA Phosphorothioate Oligonucleotides. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2017, 8, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimo, T.; Tachibana, K.; Kawawaki, Y.; Watahiki, Y.; Ishigaki, T.; Nakatsuji, Y.; Hara, T.; Kawakami, J.; Obika, S. Enhancement of exon skipping activity by reduction in the secondary structure content of LNA-based splice-switching oligonucleotides. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 6850–6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, C.; Marino, J.P.; Le Grice, S.F. Examining Ty3 polypurine tract structure and function by nucleoside analog interference. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2773–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabon-Martinez, Y.V.; Xu, Y.; Villa, A.; Lundin, K.E.; Geny, S.; Nguyen, C.H.; Pedersen, E.B.; Jorgensen, P.T.; Wengel, J.; Nilsson, L.; et al. LNA effects on DNA binding and conformation: From single strand to duplex and triplex structures. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Gissberg, O.; Pabon-Martinez, Y.V.; Wengel, J.; Lundin, K.E.; Smith, C.I.E.; Zain, R.; Nilsson, L.; Villa, A. The ability of locked nucleic acid oligonucleotides to pre-structure the double helix: A molecular simulation and binding study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burel, S.A.; Hart, C.E.; Cauntay, P.; Hsiao, J.; Machemer, T.; Katz, M.; Watt, A.; Bui, H.H.; Younis, H.; Sabripour, M.; et al. Hepatotoxicity of high affinity gapmer antisense oligonucleotides is mediated by RNase H1 dependent promiscuous reduction of very long pre-mRNA transcripts. Nucl. Acids Res. 2016, 44, 2093–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuya, T.; Hori, S.; Watanabe, A.; Nakajima, M.; Gahara, Y.; Rokushima, M.; Yanagimoto, T.; Kugimiya, A. Ribonuclease H1-dependent hepatotoxicity caused by locked nucleic acid-modified gapmer antisense oligonucleotides. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas-Lopes, M.A.; Mafra, K.; David, B.A.; Carvalho-Gontijo, R.; Menezes, G.B. Differential Location and Distribution of Hepatic Immune Cells. Cells 2017, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure-Dupuy, S.; Vegna, S.; Aillot, L.; Dimier, L.; Esser, K.; Broxtermann, M.; Bonnin, M.; Bendriss-Vermare, N.; Rivoire, M.; Passot, G.; et al. Characterization of Pattern Recognition Receptor Expression and Functionality in Liver Primary Cells and Derived Cell Lines. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.; Schefczyk, S.; Trippler, M.; Treckmann, J.W.; Baba, H.A.; Gerken, G.; Schlaak, J.F.; Broering, R. Antiviral Toll-like Receptor Signaling in Non-Parenchymal Liver Cells Is Restricted to TLR3. Viruses 2022, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, F.I.; Orr, R.M.; Goddard, P.M.; Lacey, H.A.; Lancashire, H.; Judson, I.R.; Beck, T.; Bryan, B.; Cotter, F.E. Pharmacokinetics of G3139, a phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotide antisense to bcl-2, after intravenous administration or continuous subcutaneous infusion to mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 281, 420–427. [Google Scholar]
- Geary, R.S.; Yu, R.Z.; Watanabe, T.; Henry, S.P.; Hardee, G.E.; Chappell, A.; Matson, J.; Sasmor, H.; Cummins, L.; Levin, A.A. Pharmacokinetics of a tumor necrosis factor-alpha phosphorothioate 2’-O-(2-methoxyethyl) modified antisense oligonucleotide: Comparison across species. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.Z.; Kim, T.W.; Hong, A.; Watanabe, T.A.; Gaus, H.J.; Geary, R.S. Cross-species pharmacokinetic comparison from mouse to man of a second-generation antisense oligonucleotide, ISIS 301012, targeting human apolipoprotein B-100. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehl, I.; Seiffert, S.; Brikh, C.; Quinet, J.; Jamard, C.; Dorfler, N.; Lockridge, J.A.; Cova, L.; Vaillant, A. Nucleic Acid Polymers with Accelerated Plasma and Tissue Clearance for Chronic Hepatitis B Therapy. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijsterbosch, M.K.; Manoharan, M.; Rump, E.T.; De Vrueh, R.L.; van Veghel, R.; Tivel, K.L.; Biessen, E.A.; Bennett, C.F.; Cook, P.D.; van Berkel, T.J. In vivo fate of phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides: Predominant uptake by scavenger receptors on endothelial liver cells. Nucl. Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3290–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akinc, A.; Querbes, W.; De, S.; Qin, J.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Jayaprakash, K.N.; Jayaraman, M.; Rajeev, K.G.; Cantley, W.L.; Dorkin, J.R.; et al. Targeted delivery of RNAi therapeutics with endogenous and exogenous ligand-based mechanisms. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, B.; Keough, E.; Matter, A.; Leander, K.; Young, S.; Carlini, E.; Sachs, A.B.; Tao, W.; Abrams, M.; Howell, B.; et al. Biodistribution of small interfering RNA at the organ and cellular levels after lipid nanoparticle-mediated delivery. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2011, 59, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Love, K.T.; Dorkin, J.R.; Sirirungruang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Bogorad, R.L.; Yin, H.; Chen, Y.; Vegas, A.J.; et al. Lipopeptide nanoparticles for potent and selective siRNA delivery in rodents and nonhuman primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3955–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Qin, J.; Jiang, Y.; Duncan, R.G.; Brigham, B.; Fishman, S.; Nair, J.K.; Akinc, A.; Barros, S.A.; Kasperkovitz, P.V. Shielding of Lipid Nanoparticles for siRNA Delivery: Impact on Physicochemical Properties, Cytokine Induction, and Efficacy. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2014, 3, e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debacker, A.J.; Voutila, J.; Catley, M.; Blakey, D.; Habib, N. Delivery of Oligonucleotides to the Liver with GalNAc: From Research to Registered Therapeutic Drug. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, T.P.; Graham, M.J.; Yu, J.; Carty, R.; Low, A.; Chappell, A.; Schmidt, K.; Zhao, C.; Aghajan, M.; Murray, H.F.; et al. Targeted delivery of antisense oligonucleotides to hepatocytes using triantennary N-acetyl galactosamine improves potency 10-fold in mice. Nucl. Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8796–8807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janas, M.M.; Harbison, C.E.; Perry, V.K.; Carito, B.; Sutherland, J.E.; Vaishnaw, A.K.; Keirstead, N.D.; Warner, G. The Nonclinical Safety Profile of GalNAc-conjugated RNAi Therapeutics in Subacute Studies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2018, 46, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, T.; Adams, D.; Silva, A.; Lozeron, P.; Hawkins, P.N.; Mant, T.; Perez, J.; Chiesa, J.; Warrington, S.; Tranter, E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of RNAi therapy for transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Shulga-Morskaya, S.; Liebow, A.; Bettencourt, B.R.; Sutherland, J.E.; Hutabarat, R.M.; Clausen, V.A.; Karsten, V.; Cehelsky, J.; et al. Effect of an RNA interference drug on the synthesis of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) and the concentration of serum LDL cholesterol in healthy volunteers: A randomised, single-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.J.; Lee, R.G.; Brandt, T.A.; Tai, L.J.; Fu, W.; Peralta, R.; Yu, R.; Hurh, E.; Paz, E.; McEvoy, B.W.; et al. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Effects of ANGPTL3 Antisense Oligonucleotides. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.; White, S.; Borodovsky, A.; Bettencourt, B.R.; Strahs, A.; Clausen, V.; Wijngaard, P.; Horton, J.D.; Taubel, J.; Brooks, A.; et al. A Highly Durable RNAi Therapeutic Inhibitor of PCSK9. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebow, A.; Li, X.; Racie, T.; Hettinger, J.; Bettencourt, B.R.; Najafian, N.; Haslett, P.; Fitzgerald, K.; Holmes, R.P.; Erbe, D.; et al. An Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting Glycolate Oxidase Reduces Oxalate Production in Models of Primary Hyperoxaluria. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, T.S.; Karsten, V.; Chan, A.; Chiesa, J.; Boyce, M.; Bettencourt, B.R.; Hutabarat, R.; Nochur, S.; Vaishnaw, A.; Gollob, J. Clinical Proof of Concept for a Novel Hepatocyte-Targeting GalNAc-siRNA Conjugate. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardh, E.; Harper, P.; Balwani, M.; Stein, P.; Rees, D.; Bissell, D.M.; Desnick, R.; Parker, C.; Phillips, J.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; et al. Phase 1 Trial of an RNA Interference Therapy for Acute Intermittent Porphyria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Blomenkamp, K.; Peterson, R.M.; Subbotin, V.M.; Schwabe, C.; Hamilton, J.; Chu, Q.; Christianson, D.R.; Hegge, J.O.; Kolbe, J.; et al. Development of an RNAi therapeutic for alpha-1-antitrypsin liver disease. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e135348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viney, N.J.; Guo, S.; Tai, L.J.; Baker, B.F.; Aghajan, M.; Jung, S.W.; Yu, R.Z.; Booten, S.; Murray, H.; Machemer, T.; et al. Ligand conjugated antisense oligonucleotide for the treatment of transthyretin amyloidosis: Preclinical and phase 1 data. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, R.; Ramsden, D.; Agarwal, S.; Agarwal, S.; Aluri, K.; Arciprete, M.; Brown, C.; Castellanos-Rizaldos, E.; Charisse, K.; Chong, S.; et al. The Nonclinical Disposition and Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Properties of N-Acetylgalactosamine-Conjugated Small Interfering RNA Are Highly Predictable and Build Confidence in Translation to Human. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2022, 50, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardif, J.C.; Karwatowska-Prokopczuk, E.; Amour, E.S.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Shapiro, M.D.; Moriarty, P.M.; Baum, S.J.; Hurh, E.; Bartlett, V.J.; Kingsbury, J.; et al. Apolipoprotein C-III reduction in subjects with moderate hypertriglyceridaemia and at high cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosia, C.; Sgro, F.; Conti, L.; Baldassi, C.; Brusa, D.; Cavallo, F.; Cunto, F.D.; Turco, E.; Pagnani, A.; Zecchina, R. RNAs competing for microRNAs mutually influence their fluctuations in a highly non-linear microRNA-dependent manner in single cells. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, J.K.; Chow, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Leung, S.W. siRNA Versus miRNA as Therapeutics for Gene Silencing. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2015, 4, e252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seo, G.J.; Kincaid, R.P.; Phanaksri, T.; Burke, J.M.; Pare, J.M.; Cox, J.E.; Hsiang, T.Y.; Krug, R.M.; Sullivan, C.S. Reciprocal inhibition between intracellular antiviral signaling and the RNAi machinery in mammalian cells. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.R.; Gupta, S.; Qin, J.; Racie, T.; He, G.; Lentini, S.; Malone, R.; Yu, M.; Matsuda, S.; Shulga-Morskaya, S.; et al. Investigating the pharmacodynamic durability of GalNAc-siRNA conjugates. Nucl. Acids Res. 2020, 48, 11827–11844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levrero, M.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Belloni, L.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M. Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. HBV DNA Integration: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Viruses 2017, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandri, M.; Petersen, J. cccDNA Maintenance in Chronic Hepatitis B—Targeting the Matrix of Viral Replication. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3873–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, A. HBsAg, Subviral Particles, and Their Clearance in Establishing a Functional Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, 1351–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Jiang, D.; Luo, S.; Du, N.; Chen, W.; Deng, L.; Zeng, C. Whole genome characterization of hepatitis B virus quasispecies with massively parallel pyrosequencing. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.T.; Huang, S.Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Cai, X.H.; Guo, Y.F.; Wang, M.J.; Han, Y.; Yu, D.M.; Jiang, J.H.; et al. Characterization of Full-Length Genomes of Hepatitis B Virus Quasispecies in Sera of Patients at Different Phases of Infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2203–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Zhou, B.; Cai, D.; Zong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mercier, A.; Guo, H.; Hou, J.; Colonno, R.; et al. Rapid Turnover of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA Indicated by Monitoring Emergence and Reversion of Signature-Mutation in Treated Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Hepatology 2021, 73, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Maya, S.; Ploss, A. Animal Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection-Success, Challenges, and Future Directions. Viruses 2021, 13, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestas, J.; Hughes, C.C. Of mice and not men: Differences between mouse and human immunology. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschaler, J.; Schlorke, D.; Arnhold, J. Differences in innate immune response between man and mouse. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 34, 433–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Kirschning, C.J.; Hacker, H.; Redecke, V.; Hausmann, S.; Akira, S.; Wagner, H.; Lipford, G.B. Human TLR9 confers responsiveness to bacterial DNA via species-specific CpG motif recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9237–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, W.M.; Nicodemus, C.F.; Carter, W.A.; Horvath, J.C.; Strayer, D.R. Discordant biological and toxicological species responses to TLR3 activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavilanes, F.; Gonzalez-Ros, J.M.; Peterson, D.L. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen. Characterization of the lipid components and their association with the viral proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 7770–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoneweis, K.; Motter, N.; Roppert, P.L.; Lu, M.; Wang, B.; Roehl, I.; Glebe, D.; Yang, D.; Morrey, J.D.; Roggendorf, M.; et al. Activity of nucleic acid polymers in rodent models of HBV infection. Antivir. Res. 2018, 149, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.A.; Krull, D.L.; Brown, H.R.; de Serres, M. Morphologic characterization of PhoenixBio (uPA+/+/SCID) humanized liver chimeric mouse model. Drug Metab. Lett. 2010, 4, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, C.I.; Werner, M.; Paul, A.; Gerken, G.; Schlaak, J.F.; Vaillant, A.; Broering, R. Nucleic acid-based polymers effective against hepatitis B Virus infection in patients don’t harbor immunostimulatory properties in primary isolated liver cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchet, M.; Sinnathamby, V.; Vaillant, A.; Labonte, P. Inhibition of HBsAg secretion by nucleic acid polymers in HepG2.2.15cells. Antivir. Res. 2019, 164, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulon, R.; Blanchet, M.; Lemasson, M.; Vaillant, A.; Labonte, P. Characterization of the antiviral effects of REP 2139 on the HBV lifecycle in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2020, 183, 104853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.; Agarwal, K.; Yuen, M.F.; Jucov, A.; Schwabe, C.; Le, K.; Wang, S.; Westland, C.; Steel, K.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and antiviral activity of the S-antigen Transport Inhibiting Oligonucleotide Polymers (STOPS) drug candidate ALG-010133 in subjects with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, S871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, A. Editorial: In vitro mechanistic evaluation of nucleic acid polymers: A cautionary tale. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2022, 28, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.C.; Nie, Y.; Ren, S.; Tilani, N.; De Costa, T.S.; Pamdey, R.K.; Hong, J.; Smith, D.B.; Symons, J.A.; Beigelman, L.; et al. Mechanism of action of hepatitis B virus S antigen transport-inhibiting oligonucleotide polymer, STOPS, molecules. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2021, 27, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordeen, F.; Scougall, C.A.; Grosse, A.; Qiao, Q.; Ajilian, B.B.; Reaiche-Miller, G.; Finnie, J.; Werner, M.; Broering, R.; Schlaak, J.F.; et al. Therapeutic Antiviral Effect of the Nucleic Acid Polymer REP 2055 against Persistent Duck Hepatitis B Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordeen, F.; Vaillant, A.; Jilbert, A.R. Nucleic acid polymers inhibit duck hepatitis B virus infection in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5291–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordeen, F.; Vaillant, A.; Jilbert, A.R. Nucleic acid polymers prevent the establishment of duck hepatitis B virus infection in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5299–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinet, J.; Jamard, C.; Burtin, M.; Lemasson, M.; Guerret, S.; Sureau, C.; Vaillant, A.; Cova, L. Nucleic acid polymer REP 2139 and nucleos(T)ide analogues act synergistically against chronic hepadnaviral infection in vivo in Pekin ducks. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2127–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahtab, M.; Bazinet, M.; Vaillant, A. Safety and Efficacy of Nucleic Acid Polymers in Monotherapy and Combined with Immunotherapy in Treatment-Naive Bangladeshi Patients with HBeAg+ Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazinet, M.; Pantea, V.; Placinta, G.; Moscalu, I.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Iarovoi, L.; Smesnoi, V.; Musteata, T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of 48 Weeks REP 2139 or REP 2165, Tenofovir Disoproxil, and Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2a in Patients With Chronic HBV Infection Naive to Nucleos(t)ide Therapy. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2180–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazinet, M.; Anderson, M.; Pantea, V.; Placinta, G.; Moscalu, I.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Iarovoi, L.; Smesnoi, V.; et al. Analysis of HBsAg Immunocomplexes and cccDNA Activity During and Persisting After NAP-Based Therapy. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 5, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazinet, M.; Anderson, M.; Pantea, V.; Placinta, G.; Moscalu, I.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Iarovoi, L.; Smesnoi, V.; et al. HBsAg isoform dynamics during NAP-based therapy of HBeAg-negative chronic HBV and HBV/HDV infection. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazinet, M.; Pantea, V.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Albrecht, J.; Schmid, P.; Le Gal, F.; Gordien, E.; Krawczyk, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of REP 2139 and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus co-infection (REP 301 and REP 301-LTF): A non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pantea, V.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Anderson, M.; Gersch, J.; Holzmayer, V.; Elsner, C.; Krawczyk, A.; et al. Persistent control of HBV and HDV infection following REP 2139-Ca and pegIFN therapy in chronic HBV/HDV co-infection. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 5, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourliere, M.; Bazinet, M.; Ali, S.B.; Lecompte, L.; Vaillant, A. Subcutaneous administration of REP 2139-Mg in the compassionate treatment of cirrhotic HBV/HDV co-infection. AASLD 2021, 2021, LP-14. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, X.M.; Li, G.Q.; Jin, Y.Y.; Zhuang, M.; Li, D. Combination of small interfering RNAs mediates greater suppression on hepatitis B virus cccDNA in HepG2.2.15 cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 3849–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xiang, W.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W.; Lu, D. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus (HBV) by LNA-mediated nuclear interference with HBV DNA transcription. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Cheng, T.; Cai, Y.J.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, T.; Xia, D.Z.; Li, R.Y.; Yang, L.W.; Wang, Y.B.; et al. RNA Interference inhibits hepatitis B virus of different genotypes in vitro and in vivo. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkey, J.L.; Chiari, E.F.; Isom, H.C. Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific short hairpin RNA is capable of reducing the formation of HBV covalently closed circular (CCC) DNA but has no effect on established CCC DNA in vitro. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.L.; Huang, L.R.; Huang, C.C.; Lai, H.L.; Liu, C.J.; Huang, Y.T.; Hsu, Y.W.; Lu, C.Y.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, P.J. RNA interference-mediated control of hepatitis B virus and emergence of resistant mutant. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanbakht, H.; Mueller, H.; Walther, J.; Zhou, X.; Lopez, A.; Pattupara, T.; Blaising, J.; Pedersen, L.; Albaek, N.; Jackerott, M.; et al. Liver-Targeted Anti-HBV Single-Stranded Oligonucleotides with Locked Nucleic Acid Potently Reduce HBV Gene Expression In Vivo. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2018, 11, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Rozema, D.B.; Hossbach, M.; John, M.; Hamilton, H.L.; Chu, Q.; Hegge, J.O.; Klein, J.J.; Wakefield, D.H.; Oropeza, C.E.; et al. Hepatocyte-targeted RNAi therapeutics for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrissey, D.V.; Lockridge, J.A.; Shaw, L.; Blanchard, K.; Jensen, K.; Breen, W.; Hartsough, K.; Machemer, L.; Radka, S.; Jadhav, V.; et al. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, E.P.; Dhillon, A.P.; Ardzinski, A.; Bidirici-Ertekin, L.; Cobarrubias, K.D.; Cuconati, A.; Kondratowicz, A.S.; Kwak, K.; Li, A.H.L.; Miller, A.; et al. ARB-1740, a RNA Interference Therapeutic for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, M.K.; Janas, M.M.; Jiang, Y.; Barry, J.D.; Davis, W.; Agarwal, S.; Berman, D.; Brown, C.R.; Castoreno, A.; LeBlanc, S.; et al. From bench to bedside: Improving the clinical safety of GalNAc-siRNA conjugates using seed-pairing destabilization. Nucl. Acids Res. 2022, 50, 6656–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koser, M.; Craig, K.P.; Cyr, W.A.; Wang, W.; Brown, B.D.; Abrams, M. Preclinical Characterization of Galxc™ RNAi Therapeutics Targeting Different Regions of the HBV Genome. Hepatology 2018, 68, 267A. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeev, K.G.; Nair, J.K.; Jayaraman, M.; Charisse, K.; Taneja, N.; O’Shea, J.; Willoughby, J.L.; Yucius, K.; Nguyen, T.; Shulga-Morskaya, S.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific delivery of siRNAs conjugated to novel non-nucleosidic trivalent N-acetylgalactosamine elicits robust gene silencing in vivo. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, P.E.; Mueller, C.; Cossette, T.L.; Golant, A.; Tang, Q.; Beattie, S.G.; Brantly, M.; Campbell-Thompson, M.; Blomenkamp, K.S.; Teckman, J.H.; et al. In vivo post-transcriptional gene silencing of alpha-1 antitrypsin by adeno-associated virus vectors expressing siRNA. Lab. Investig. 2007, 87, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Grefhorst, A.; Anderson, N.N.; Racie, T.S.; Bramlage, B.; Akinc, A.; Butler, D.; Charisse, K.; Dorkin, R.; Fan, Y.; et al. Therapeutic RNAi targeting PCSK9 acutely lowers plasma cholesterol in rodents and LDL cholesterol in nonhuman primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11915–11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.Z.; Lemonidis, K.M.; Graham, M.J.; Matson, J.E.; Crooke, R.M.; Tribble, D.L.; Wedel, M.K.; Levin, A.A.; Geary, R.S. Cross-species comparison of in vivo PK/PD relationships for second-generation antisense oligonucleotides targeting apolipoprotein B-100. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.J.; Lee, R.G.; Bell, T.A., 3rd; Fu, W.; Mullick, A.E.; Alexander, V.J.; Singleton, W.; Viney, N.; Geary, R.; Su, J.; et al. Antisense oligonucleotide inhibition of apolipoprotein C-III reduces plasma triglycerides in rodents, nonhuman primates, and humans. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.M. TKM-HBV RNAi Therapeutic for Chronic HBV Infeciton. In Proceedings of the DIA/FDA Oligonucleotide-Based Therapeutics Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 9 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hean, J.; Crowther, C.; Ely, A.; Ul Islam, R.; Barichievy, S.; Bloom, K.; Weinberg, M.S.; van Otterlo, W.A.; de Koning, C.B.; Salazar, F.; et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in vivo using lipoplexes containing altritol-modified antiviral siRNAs. Artif. DNA PNA XNA 2010, 1, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, S.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; Lin, Y.; Xia, Y.; Sun, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Poly(I:C) treatment leads to interferon-dependent clearance of hepatitis B virus in a hydrodynamic injection mouse model. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10421–10431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, J.; Wang, Y.; Dixon, R.; Bowden, S.; Qiao, M.; Einck, L.; Locarnini, S. The use of ampligen alone and in combination with ganciclovir and coumermycin A1 for the treatment of ducks congenitally-infected with duck hepatitis B virus. Antivir. Res. 1993, 21, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Pei, R.; Xu, Y.; Yang, D.; Roggendorf, M.; Lu, M. RNAi induces innate immunity through multiple cellular signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Gane, E.; Cheng, C.; Sievert, W.; Roberts, S.K.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Denning, J.; Symonds, W.; et al. HBcrAg, HBV-RNA declines in A Phase 2a Study Evaluating the Multi-dose Activity of ARB-1467 in HBeAg-Positive and Negative Virally Suppressed Subjects with Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2017, 66, 22A. [Google Scholar]
- Eley, T.; Russ, R.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Gane, E.J.; Roberts, S.K.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Symonds, W.; Mendez, P. Pharmacokinetics and exploratory exposure-response of siRNAs administered monthly as ARB-001467 (ARB-1467) in a Phase 2a study in HBeAg positive and negative virally suppressed subjects with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2017, 66, 23A. [Google Scholar]
- Schluep, T.; Lickliter, J.; Hamilton, J.; Lewis, D.L.; Lai, C.L.; Lau, J.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Gish, R.G.; Given, B.D. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of ARC-520 Injection, an RNA Interference-Based Therapeutic for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection, in Healthy Volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2017, 6, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Yuen, M.F.; Chan, H.L.; Gish, R.G.; Locarnini, S.A.; Chavez, D.; Ferrari, C.; Given, B.D.; Hamilton, J.; Kanner, S.B.; et al. RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a source of HBsAg. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan0241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Schiefke, I.; Yoon, J.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Heo, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lik Yuen Chan, H.; Yoon, K.T.; Klinker, H.; Manns, M.; et al. RNA Interference Therapy With ARC-520 Results in Prolonged Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Response in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Hepatology 2020, 72, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Locarnini, S.; Lim, T.H.; Strasser, S.I.; Sievert, W.; Cheng, W.; Thompson, A.J.; Given, B.D.; Schluep, T.; Hamilton, J.; et al. Combination treatments including the small-interfering RNA JNJ-3989 induce rapid and sometimes prolonged viral responses in patients with CHB. J. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.; Lim, Y.S.; Cloutier, D.; Shen, L.; Cathcart, A.; Ding, X.; Pang, P.; Huang, S.; Yuen, M.F. Safety and antiviral activity of VIR-2218, an X-targeting RNAi therapeutic, in participants with chronic hepatitis B infection: Week 48 follow-up results. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S287. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, M.F. HBV RNAi Inhibitor RG6346 in Phase 1b-2a Trial was Safe, Well Tolerated, and Resulted in Subatantial and Durable Reductions in Serum HBsAg Levels. Presented at the AASLD 2020 Late Breakong Oral Presentation, Online, 11–16 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, M.F.; Berliba, E.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Holmes, J.; Leerapun, A.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Strasser, S.; Jucov, A.; Gane, E.; Thi, E.P.; et al. Long-term suppression maintained after cessation of AB-729 treatment and comparable on-treatment response observed in HBeAg+ subjects. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, S876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Lim, Y.S.; Cloutier, D.; Shen, L.; Arizpe, A.; Pang, P.; Tay, C.; Thanawala, V.; Gupta, S.V.; Cathcart, A.; et al. Preliminary on-treatment data from a phase 2 study evaluating VIR-2218 in combination with pegylated interferon alfa-2a in participants with chronic hepatitis B infection. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S738. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, M.F.; Wong, D.K.; Schluep, T.; Lai, C.L.; Ferrari, C.; Locarnini, S.; Lo, R.C.; Gish, R.G.; Hamilton, J.; Wooddell, C.I.; et al. Long-term serological, virological and histological responses to RNA inhibition by ARC-520 in Chinese chronic hepatitis B patients on entecavir treatment. Gut 2021, 71, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganchua, S.C.; Paratala, B.; Iott, C.; Yuen, M.F.; Gane, E.; Eley, T.; Sims, K.; Gray, K.; Antoniello, D.; Lam, A.M.; et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B surface antigen by RNA interference therapeutic AB-729 is associated with increased cytokine signatures in HBV DNA+ chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, S850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganchua, S.C.; Paratala, B.; Iott, C.; Gane, E.; Yuen, M.F.; Eley, T.; Sims, K.; Gray, K.; Antoniello, D.; Lam, A.M.; et al. Reduction of hepatitis B surface antigen mediated by RNA interference therapeutic AB-729 in chronic hepatitis B patients is associated with T cell activation and a decline in exhausted CD8 T cells. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, S851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Heo, J.; Kumada, H.; Suzuki, F.; Suzuki, Y.; Xie, Q.; Jia, J.; Karino, Y.; Hou, J.; Chayama, K.; et al. Phase IIa, randomised, double-blind study of GSK3389404 in patients with chronic hepatitis B on stable nucleos(t)ide therapy. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gane, E.; Yuen, M.F.; Kim, D.J.; Chan, H.L.; Surujbally, B.; Pavlovic, V.; Das, S.; Triyatni, M.; Kazma, R.; Grippo, J.F.; et al. Clinical Study of Single Stranded Oligonucleotide RO7062931 in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1795–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillant, A. Targeting Subviral Particles: A Critical Step in Achieving HBV Functional Cure but Where Are We with Current Agents in Clinical Development? Viruses 2022, 14, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Heo, J.; Jang, J.W.; Yoon, J.H.; Kweon, Y.O.; Park, S.J.; Tami, Y.; You, S.; Yates, P.; Tao, Y.; et al. Safety, tolerability and antiviral activity of the antisense oligonucleotide bepirovirsen in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A phase 2 randomized controlled trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastelein, J.J.; Wedel, M.K.; Baker, B.F.; Su, J.; Bradley, J.D.; Yu, R.Z.; Chuang, E.; Graham, M.J.; Crooke, R.M. Potent reduction of apolipoprotein B and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol by short-term administration of an antisense inhibitor of apolipoprotein B. Circulation 2006, 114, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, E.J.; Guo, S.; Benson, M.D.; Booten, S.; Freier, S.; Hughes, S.G.; Kim, T.W.; Jesse Kwoh, T.; Matson, J.; Norris, D.; et al. Suppressing transthyretin production in mice, monkeys and humans using 2nd-Generation antisense oligonucleotides. Amyloid 2016, 23, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Singh, J.; Smith, S.; Jordan, W.; Remingler, K.; Joshi, S.; Ermler, M.; Delahaye, J.; Taylor, A.; Chakraborty, S.; et al. Treatment with GSK3228836 Leads to HBsAg Reduction and Induction of Interferon Gamma Related Proteins and Chemokines in a Phase 2a, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S455. [Google Scholar]
- Gane, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Visvanathan, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Nguyen, A.H.; Wallin, J.J.; Chen, D.Y.; McDonald, C.; Arora, P.; Tan, S.K.; et al. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of the Oral TLR8 Agonist Selgantolimod in Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayithan, N.; Ghosh, A.; Dwivedi, A.; Wallin, J.J.; Tan, S.K.; Chen, D.; Kottilil, S.; Poonia, B. Oral Selective TLR8 Agonist Selgantolimod Induces Multiple Immune Cell Responses in Humans. Viruses 2021, 13, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, M.; Judge, A.; Ambegia, E.; Choi, C.; Yaworski, E.; Palmer, L.; McClintock, K.; MacLachlan, I. Misinterpreting the therapeutic effects of small interfering RNA caused by immune stimulation. Hum. Gene Ther. 2008, 19, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Model | SVP Production | Genetic Diversity (Pre-Existing ASO/Sirna Escape Mutants) | Rapid Turnover of cccDNA (Evolution of ASO/RNAi Escape Mutants) | TLR9 Activity (CpG DNA) | TLR3 Reactivity (dsRNA/RNAi) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | LDL-based (SVP are spherical) | Present | Present | Present (KCs) | Present (LSECs, KCs) |
| Transgenic mice | LDL metabolism opposite to humans (SVP are octahedral) | None | Present but turnover unknown | Yes but human and rodent CpG sequences differ | Stronger vs. primate |
| AAV/HDI-mice | LDL metabolism opposite to humans (SVP are octahedral) | None | Present but turnover unknown | Yes but human and rodent CpG sequences differ | Stronger vs. primate |
| Scid-Hu mice | SVP production is attenuated (altered lipid metabolism) | Present (limited due to short term infection) | Yes | Yes but human and rodent CpG sequences differ | Stronger vs. primate |
| Ducks | LDL metabolism similar to humans | Present (limited due to short term infection) | Yes | Yes but via altered reactivity by TLR15 | Similar to primate |
| Woodchucks | LDL metabolism opposite to humans | Present (chronic infection) | Yes | Yes but human and rodent CpG sequences differ | Similar to primate |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaillant, A. Oligonucleotide-Based Therapies for Chronic HBV Infection: A Primer on Biochemistry, Mechanisms and Antiviral Effects. Viruses 2022, 14, 2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092052
Vaillant A. Oligonucleotide-Based Therapies for Chronic HBV Infection: A Primer on Biochemistry, Mechanisms and Antiviral Effects. Viruses. 2022; 14(9):2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092052
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaillant, Andrew. 2022. "Oligonucleotide-Based Therapies for Chronic HBV Infection: A Primer on Biochemistry, Mechanisms and Antiviral Effects" Viruses 14, no. 9: 2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092052
APA StyleVaillant, A. (2022). Oligonucleotide-Based Therapies for Chronic HBV Infection: A Primer on Biochemistry, Mechanisms and Antiviral Effects. Viruses, 14(9), 2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092052