Vitamin E-Loaded PLA- and PLGA-Based Core-Shell Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Structure Optimization and Controlled Drug Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of TP-Loaded PLA/PLGA NPs
2.3. Characterization Methods
2.4. Determination of the Solubility Properties of TP Drug
2.5. Critical Micelle Concentration (cmc) Studies
2.6. In Vitro Release Study
3. Results
3.1. Effect of the Component Concentrations on the Core-Shell Structure
3.2. Structural Characterization of the TP-Loaded PLA and PLGA Core-Shell NPs
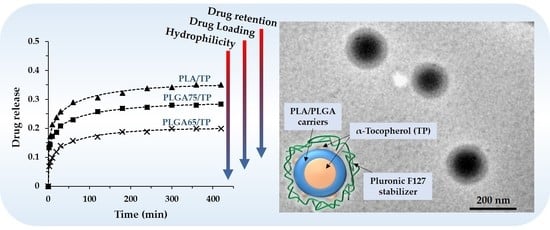
3.3. In Vitro Drug Release Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancan, F.; Papakostas, D.; Hadam, S.; Hackbarth, S.; Delair, T.; Primard, C.; Verrier, B.; Sterry, W.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A. Investigation of Polylactic Acid (PLA) Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems for Local Dermatotherapy. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanphai, P.; Vesper, A.R.; Bariyanga, J.; Bérubé, G.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Review on the delivery of steroids by carrier proteins. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 161, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janovák, L.; Turcsányi, Á.; Bozó, É.; Deák, Á.; Mérai, L.; Sebők, D.; Juhász, Á.; Csapó, E.; Abdelghafour, M.M.; Farkas, E.; et al. Preparation of novel tissue acidosis-responsive chitosan drug nanoparticles: Characterization and in vitro release properties of Ca2+ channel blocker nimodipine drug molecules. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarmento, B.; Ferreira, D.; Veiga, F.; Ribeiro, A. Characterization of insulin-loaded alginate nanoparticles produced by ionotropic pre-gelation through DSC and FTIR studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 66, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csapó, E.; Szokolai, H.; Juhász, Á.; Varga, N.; Janovák, L.; Dékány, I. Cross-linked and hydrophobized hyaluronic acid-based controlled drug release systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lassalle, V.; Ferreira, M.L. PLA Nano- and Microparticles for Drug Delivery: An Overview of the Methods of Preparation. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.J.; Gu, Y.C.; Gou, M.L.; Dai, M.; Li, X.Y.; Kan, B.; Yang, J.L.; Song, Q.F.; Wei, Y.Q.; Qian, Z.Y. Preparation of Biodegradable Polycaprolactone/Poly(ethylene glycol)/Polycaprolactone (PCEC) Nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhuo, R. Synthesis and drug release behavior of poly(trimethylene carbonate)–poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(trimethylene carbonate) nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, J.B.; Schmidt, C.E. Characterization of protein release from photocrosslinkable hyaluronic acid-polyethylene glycol hydrogel tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Xin, H.; Ren, Q.; Gu, J.; Zhu, L.; Du, F.; Feng, C.; Xie, Y.; Sha, X.; Fang, X. Nanoparticles of 2-deoxy-d-glucose functionalized poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(trimethylene carbonate) for dual-targeted drug delivery in glioma treatment. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, N.; Hornok, V.; Janovák, L.; Dékány, I.; Csapó, E. The effect of synthesis conditions and tunable hydrophilicity on the drug encapsulation capability of PLA and PLGA nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 176, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiss, É.; Gyulai, G.; Pénzes, C.B.; Idei, M.; Horváti, K.; Bacsa, B.; Bősze, S. Tuneable surface modification of PLGA nanoparticles carrying new antitubercular drug candidate. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 458, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duse, L.; Agel, M.R.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Schäfer, J.; Selo, M.A.; Ehrhardt, C.; Bakowsky, U. Photodynamic Therapy of Ovarian Carcinoma Cells with Curcumin-Loaded Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, I.; Li, S.; Martinez, M.B.; Vert, M. Protein release from physically crosslinked hydrogels of the PLA/PEO/PLA triblock copolymer-type. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y. Preparation and drug release behaviors of nimodipine-loaded poly(caprolactone)–poly(ethylene oxide)–polylactide amphiphilic copolymer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhem, N.; Danhier, F.; Préat, V. Vitamin E-based nanomedicines for anti-cancer drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 182, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigoneanu, I.G.; Astete, C.E.; Sabliov, C.M. Nanoparticles with entrapped α-tocopherol: Synthesis, characterization, and controlled release. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 105606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, S.; Simon, L.; Astete, C.E.; Alayoubi, A.; Sylvester, P.W.; Nazzal, S.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Kaddoumi, A.; Sabliov, C.M. Cellular uptake, antioxidant and antiproliferative activity of entrapped α-tocopherol and γ-tocotrienol in poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) and chitosan covered PLGA nanoparticles (PLGA-Chi). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 445, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astete, C.E.; Dolliver, D.; Whaley, M.; Khachatryan, L.; Sabliov, C.M. Antioxidant Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) Acid Nanoparticles Made with α-Tocopherol–Ascorbic Acid Surfactant. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 9313–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugeshu, A.; Astete, C.; Leonardi, C.; Morgan, T.; Sabliov, C.M. Chitosan/PLGA particles for controlled release of α-tocopherol in the GI tract via oral administration. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1513–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, L.C.; Stout, R.W.; Sabliov, C. Bioavailability of Orally Delivered Alpha-Tocopherol by Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic) Acid (PLGA) Nanoparticles and Chitosan Covered PLGA Nanoparticles in F344 Rats. Nanobiomedicine 2016, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkő, M.; Varga, N.; Sebők, D.; Bohus, G.; Juhász, Á.; Dékány, I. Bovine serum albumin-sodium alkyl sulfates bioconjugates as drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 130, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. A simple equation for the description of solute release. III. Coupling of diffusion and relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.E.S.R.; Freitas, R.F.S.; Sousa, R.G. Synthesis, Characterization, and Study of PLGA Copolymer in Vitro Degradation. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 6, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che Man, Y.B.; Ammawath, W.; Mirghani, M.E.S. Determining α-tocopherol in refined bleached and deodorized palm olein by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyulai, G.; Magyar, A.; Rohonczy, J.; Orosz, J.; Yamasaki, M.; Bosze, S.; Kiss, E. Preparation and characterization of cationic Pluronic for surface modification and functionalization of polymeric drug delivery nanoparticles. Express Polym. Lett. 2016, 10, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouchemal, K.; Agnely, F.; Koffi, A.; Ponchel, G. A concise analysis of the effect of temperature and propanediol-1, 2 on Pluronic F127 micellization using isothermal titration microcalorimetry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Acetone Phase | Aqueous Phase | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | cPLA (mg·mL−1) | cTP (mg·mL−1) | cPLUR (mg·mL−1) | dDLS ± SD 1 (nm) | PI ± SD | EE% | DL% |
| PLA concentration dependence | 1.25 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 120 ± 33 | 0.120 ± 0.043 | – | – |
| 2.5 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 156 + 28 | 0.039 ± 0.012 | – | – | |
| 5.0 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 179 ± 35 | 0.082 ± 0.049 | – | – | |
| 10.0 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 201 ± 38 | 0.095 ± 0.026 | 69.11 | 14.73 | |
| TP concentration dependence | 10.0 | 0 | 0.1 | 188 ± 37 | 0.092 ± 0.059 | – | – |
| 10.0 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 189 ± 34 | 0.048 ± 0.028 | 91.28 | 4.36 | |
| 10.0 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 192 ± 30 | 0.062 ± 0.032 | 75.61 | 7.02 | |
| 10.0 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 201 ± 38 | 0.095 ± 0.026 | 69.11 | 14.73 | |
| 10.0 | 5.0 | 0.1 | 252 ± 53 | 0.073 ± 0.033 | 66.15 | 24.85 | |
| PLUR concentration dependence | 10.0 | 2.5 | 0 | 179 ± 40 | 0.315 ± 0.040 | 72.19 | 15.29 |
| 10.0 | 2.5 | 0.05 | 178 ± 21 | 0.304 ± 0.095 | 98.34 | 19.73 | |
| 10.0 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 201 ± 38 | 0.095 ± 0.026 | 69.11 | 14.73 | |
| 10.0 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 206 ± 36 | 0.089 ± 0.065 | 57.94 | 12.65 | |
| 10.0 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 212 ± 36 | 0.066 ± 0.029 | 40.75 | 9.24 | |
| Peppas–Sahlin Formulation | k1 (min–m) | k2 (min–2m) | m | R2 |
| PLA/TP NPs | 0.1371 | −0.01346 | 0.260 | 0.9974 |
| PLGA75/TP NPs | 0.1165 | −0.01189 | 0.248 | 0.9986 |
| PLGA65/TP NPs | 0.0572 | −0.00412 | 0.317 | 0.9974 |
| TP | 0.0304 | −0.00124 | 0.366 | 0.9978 |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas Formulation | km (min–n) | n | R2 | |
| PLA/TP NPs | 0.1339 | 0.182 | 0.9898 | |
| PLGA75/TP NPs | 0.1120 | 0.175 | 0.9982 | |
| PLGA65/TP NPs | 0.0592 | 0.223 | 0.9904 | |
| TP | 0.0310 | 0.311 | 0.9977 | |
| Weibull Formulation | a | b | R2 | |
| PLA/TP NPs | 6.52 | 0.178 | 0.9896 | |
| PLGA75/TP NPs | 7.85 | 0.166 | 0.9819 | |
| PLGA65/TP NPs | 15.45 | 0.220 | 0.9898 | |
| TP | 28.19 | 0.285 | 0.9945 | |
| First Order Formulation | k (min–1) | R2 | ||
| PLA/TP NPs | 0.0094 | 0.9792 | ||
| PLGA75/TP NPs | 0.0113 | 0.9532 | ||
| PLGA65/TP NPs | 0.0130 | 0.9514 | ||
| TP | 0.0079 | 0.9856 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varga, N.; Turcsányi, Á.; Hornok, V.; Csapó, E. Vitamin E-Loaded PLA- and PLGA-Based Core-Shell Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Structure Optimization and Controlled Drug Release. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11070357
Varga N, Turcsányi Á, Hornok V, Csapó E. Vitamin E-Loaded PLA- and PLGA-Based Core-Shell Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Structure Optimization and Controlled Drug Release. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(7):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11070357
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarga, Norbert, Árpád Turcsányi, Viktória Hornok, and Edit Csapó. 2019. "Vitamin E-Loaded PLA- and PLGA-Based Core-Shell Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Structure Optimization and Controlled Drug Release" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 7: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11070357
APA StyleVarga, N., Turcsányi, Á., Hornok, V., & Csapó, E. (2019). Vitamin E-Loaded PLA- and PLGA-Based Core-Shell Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Structure Optimization and Controlled Drug Release. Pharmaceutics, 11(7), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11070357