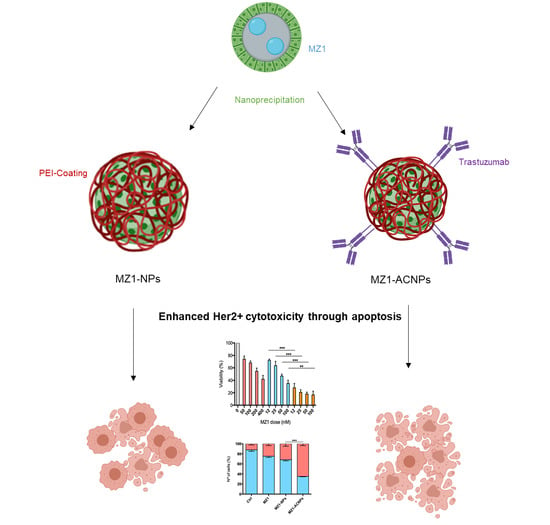
Controlled Delivery of BET-PROTACs: In Vitro Evaluation of MZ1-Loaded Polymeric Antibody Conjugated Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Preparation of Nanoparticles (NPs)
2.4. In Vitro Assays
3. Results
3.1. MZ1-Loaded Trastuzumbab Conjugated NPs (MZ1-ACNPs)
3.2. Cytotoxic Effect
3.3. Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
3.4. Cytotoxic Effect in HER2+, MZ1-Resistant Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chau, C.H.; Steeg, P.S.; Figg, W.D. Antibody–drug conjugates for cancer. Lancet 2019, 394, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, S.; Williams, M.; Kebble, B.; Dixit, R.; Tseng, L.; Yao, N.-S.; Tice, D.A.; Soria, J.-C. Antibody-drug conjugates: Future Directions in clinical and translational strategies to improve the therapeutic index. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5441–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolska-Washer, A.; Robak, T. Safety and Tolerability of Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Cancer. Drug Saf. 2019, 42, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohashi, K.; Maruvka, Y.E.; Michor, F.; Pao, W. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor–resistant disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Protacs: Chimeric Molecules That Target Proteins to the Skp1–Cullin–F Box Complex for Ubiquitination and Degradation PNAS. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/content/98/15/8554 (accessed on 3 June 2020).
- Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Xia, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.P.; Wei, W. PROTACs: A novel strategy for cancer therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, M.; Crews, C.M. PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs)—Past, present and future. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2019, 31, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, J.J.; Neklesa, T.K. Targeting nuclear receptors with PROTAC degraders. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 493, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanover, A. The unravelling of the ubiquitin system. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neklesa, T.; Snyder, L.B.; Willard, R.R.; Vitale, N.; Raina, K.; Pizzano, J.; Gordon, D.; Bookbinder, M.; Macaluso, J.; Dong, H.; et al. Abstract 5236: ARV-110: An androgen receptor PROTAC degrader for prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5236. [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan, J.J.; Qian, Y.; Gough, S.M.; Andreoli, M.; Bookbinder, M.; Cadelina, G.; Bradley, J.; Rousseau, E.; Willard, R.; Pizzano, J.; et al. Abstract P5-04-18: ARV-471, an Oral Estrogen Receptor PROTAC Degrader for Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Rao, Y. PROTACs as potential therapeutic agents for cancer drug resistance. Biochemistry 2019, 59, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hu, B.; Wang, M.; Xu, F.; Miao, B.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Hayes, D.F.; Chinnaswamy, K.; et al. Discovery of ERD-308 as a highly potent proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) degrader of estrogen receptor (ER). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1420–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, K.; Lu, J.; Qian, Y.; Altieri, M.; Gordon, D.; Rossi, A.M.K.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Dong, H.; Siu, K.; et al. PROTAC-induced BET protein degradation as a therapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7124–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winter, G.E.; Buckley, D.L.; Paulk, J.; Roberts, J.M.; Souza, A.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Bradner, J.E. Phthalimide conjugation as a strategy for in vivo target protein degradation. Science 2015, 348, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawar, A.; Gollavilli, P.N.; Wang, S.; Asangani, I.A. Resistance to BET Inhibitor leads to alternative therapeutic vulnerabilities in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2236–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, F.; Wei, Q.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, P.; Lu, T.; Chen, Y.; et al. Discovery of novel small molecule induced selective degradation of the bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) Bromodomain protein BRD4 and BRD2 with cellular potencies. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, M.S.; Testa, A.; Lucas, X.; Chan, K.H.; Chen, W.; Lamont, D.J.; Zengerle, M.; Ciulli, A. Structural basis of PROTAC cooperative recognition for selective protein degradation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, R.P.; Deangelo, S.L.; Buckley, D.; He, Z.; Donovan, K.A.; An, J.; Safaee, N.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Ponthier, C.M.; Ishoey, M.; et al. Plasticity in binding confers selectivity in ligand-induced protein degradation article. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Fiskus, W.; Qian, Y.; Rajapakshe, K.; Raina, K.; Coleman, K.G.; Crew, A.P.; Shen, A.; Saenz, D.T.; Mill, C.P.; et al. BET protein proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) exerts potent lethal activity against mantle cell lymphoma cells. Leukemia 2018, 32, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblejas-López, M.D.M.; Nieto-Jimenez, C.; Burgos, M.; Gómez-Juárez, M.; Montero, J.C.; Esparís-Ogando, A.; Pandiella, A.; Galán-Moya, E.M.; Ocaña, A. Activity of BET-Proteolysis targeting chimeric (PROTAC) Compounds in triple negative breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; He, M.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Tong, Y.; Rao, Y. PROTACs: Great opportunities for academia and industry. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, H.; Sun, X.; Rao, Y. PROTAC technology: Opportunities and challenges. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, R.A.; Fawell, S.; Floc’h, N.; Flemington, V.; McKerrecher, D.; Smith, P.D. Challenges and opportunities in cancer drug resistance. Chem. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, F.; Yang, F.; Jiang, X.; Sun, H.; Feng, F.; Xue, J.; Liu, W. Targeted degradation of anaplastic lymphoma kinase by gold nanoparticle-based multi-headed proteolysis targeting chimeras. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, F.; Scott, C.J. Antibody-targeted nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Immunotherapy 2011, 3, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, M.C.; Scott, C.J. Antibody Conjugated nanoparticles as a novel form of antibody drug conjugate chemotherapy. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2018, 30, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, A.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; Fajardo, M.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Otero, A.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; López-Solera, I.; Rodríguez, A.M. Hybrid scorpionate/cyclopentadienyl magnesium and zinc complexes: Synthesis, coordination chemistry, and ring-opening polymerization studies on cyclic esters. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 2859–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Moreno, C.; Garcés, A.; Sánchez-Barba, L.F.; Fajardo, M.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Otero, A.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Antiñolo, A.; Broomfield, L.; López-Solera, M.I.; et al. Discrete heteroscorpionate lithium and zinc alkyl complexes. synthesis, structural studies, and ROP of cyclic esters. Organometallics 2008, 27, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niza, E.; Noblejas-López, M.D.M.; Bravo, I.; Nieto-Jiménez, C.; Castro-Osma, J.A.; Canales-Vázquez, J.; Lara-Sanchez, A.; Galán Moya, E.M.; Burgos, M.; Ocaña, A.; et al. Trastuzumab-Targeted biodegradable nanoparticles for enhanced delivery of dasatinib in HER2+ metastasic breast cancer. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamaly, N.; Yameen, B.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Degradable controlled-release polymers and polymeric nanoparticles: Mechanisms of controlling drug release. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2602–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambertini, M.; Vaz-Luis, I. Is HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer still an incurable disease? Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 471–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, C.; Hughes, S.J.; Testa, A.; Chen, W.; Lamont, D.J.; Rocha, S.; Alessi, D.R.; Romeo, R.; Ciulli, A. Homo-PROTACs: Bivalent small-molecule dimerizers of the VHL E3 ubiquitin ligase to induce self-degradation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, S.; Fu, L. Small-molecule PROTACs: An emerging and promising approach for the development of targeted therapy drugs. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, K.; Li, D.; Shi, C.; Ma, X.; Rong, G.; Kang, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, B. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as the delivery carrier for drug. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| NPs-Formulation | Average Size (nm) | PdI | Z-Potencial (mV) | EE 1 (%) | LE 2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MZ1-NPs | 124.9 ± 3.3 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | +46.3 ± 0.9 | 55.7 | 6.3 |
| MZ1-ACNPs | 114 ± 2.3 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | +31.8 ± 0.5 | 13.9 | 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cimas, F.J.; Niza, E.; Juan, A.; Noblejas-López, M.d.M.; Bravo, I.; Lara-Sanchez, A.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; Ocaña, A. Controlled Delivery of BET-PROTACs: In Vitro Evaluation of MZ1-Loaded Polymeric Antibody Conjugated Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100986
Cimas FJ, Niza E, Juan A, Noblejas-López MdM, Bravo I, Lara-Sanchez A, Alonso-Moreno C, Ocaña A. Controlled Delivery of BET-PROTACs: In Vitro Evaluation of MZ1-Loaded Polymeric Antibody Conjugated Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(10):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100986
Chicago/Turabian StyleCimas, Francisco J., Enrique Niza, Alberto Juan, María del Mar Noblejas-López, Iván Bravo, Agustín Lara-Sanchez, Carlos Alonso-Moreno, and Alberto Ocaña. 2020. "Controlled Delivery of BET-PROTACs: In Vitro Evaluation of MZ1-Loaded Polymeric Antibody Conjugated Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 10: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100986
APA StyleCimas, F. J., Niza, E., Juan, A., Noblejas-López, M. d. M., Bravo, I., Lara-Sanchez, A., Alonso-Moreno, C., & Ocaña, A. (2020). Controlled Delivery of BET-PROTACs: In Vitro Evaluation of MZ1-Loaded Polymeric Antibody Conjugated Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics, 12(10), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100986