Binary Mixtures of Some Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients with Fatty Alcohols—The Criteria of Successful Eutectic Formation and Dissolution Improvement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Thermal Analysis and Melt Crystallization
2.3. Characterization of Melt Crystallized API/Fatty Alcohol Mixtures
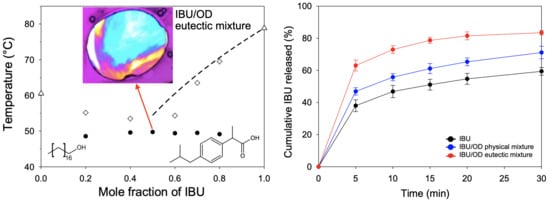
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Melting Behaviors of API/Fatty Alcohol Mixtures
3.2. Crystallization Behaviors of IBU/Fatty Alcohol Mixtures
3.3. In Vitro Release Behaviors of IBU/Fatty Alcohol Mixtures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawabata, Y.; Wada, K.; Nakatani, M.; Yamada, S.; Onoue, S. Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: Basic approaches and practical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: Basic science and product development. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florence, A.T.; Attwood, D. Physicochemical Principles of Pharmacy: In Manufature, Formulation and Clinical Use, 6th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 351–375. [Google Scholar]
- He, X. Integration of physical, chemical, mechanical, and biopharmaceutical properties in solid oral dosage form development. In Developing Solid Oral Dosage Forms, 1st ed.; Qiu, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, G.G.Z., Liu, L., Porter, W.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 409–441. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, B.J.; Bergström, C.A.S.; Vinarov, Z.; Kuentz, M.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P.; Brandl, M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Shrestha, N.; Préat, V.; et al. Successful oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs both depends on the intraluminal behavior of drugs and of appropriate advanced drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jermain, S.V.; Brough, C.; Williams, R.O., III. Amorphous solid dispersions and nanocrystal technologies for poorly water-soluble drug delivery—An update. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, W.; Motherwell, W.D.S.; Trask, A.V. Pharmaceutical cocrystals: An emerging approach to physical property enhancement. MRS Bull. 2006, 31, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kipp, J.E. The role of solid nanoparticle technology in the parenteral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 284, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesisoglou, F.; Panmai, S.; Wu, Y. Nanosizing—Oral formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shegokar, R.; Müller, R.H. Nanocrystals: Industrially feasible multifunctional formulation technology for poorly soluble actives. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 399, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.-W.; Kang, Z.; Jin, Y.S.; Kim, I.W. Dissolution enhancement of sorafenib tosylate by co-milling with tetradecanol post-extracted using supercritical carbon dioxide. Pharmazie 2020, 75, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- De Waard, H.; Hinrichs, W.L.J.; Frijlink, H.W. A novel bottom-up process to produce drug nanocrystals: Controlled crystallization during freeze-drying. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuvada, S.; Nangia, A. Eutectics as improved pharmaceutical materials: Design, properties and characterization. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 906–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuner, C.; Dressman, J. Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, D.; Wang, W.; Schmitt, E.A.; Qiu, Y.; Krill, S.L.; Fort, J.J. Properties of rapidly dissolving eutectic mixtures of poly(ethylene glycol) and fenofibrate: The eutectic microstructure. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callister, W.D., Jr.; Rethwisch, D.G. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 9th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 297–355. [Google Scholar]
- Sathisaran, I.; Dalvi, S.V. Engineering cocrystals of poorly water-soluble drugs to enhance dissolution in aqueous medium. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Obi, N. Studies on absorption of eutectic mixture. I. A comparison of the behavior of eutectic mixture of sulfathiazole and that of ordinary sulfathiazone in man. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1961, 9, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, A.H.; Gibaldi, M.; Kanig, J.L. Increasing dissolution rates and gastrointestinal absorption of drugs via solid solutions and eutectic mixtures. III. Experimental evaluations of griseofulvin–succinic acid solid solution. J. Pharm. Sci. 1966, 55, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, W.L.; Niazi, S. Differential thermal analysis and X-ray diffraction studies of griseofulvin-succinic acid solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 1973, 62, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, D.; Wang, W.; Schmitt, E.A.; Long, M.A. Prediction of poly(ethylene glycol)-drug eutectic compositions using an index based on the van’t Hoff equation. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vippagunta, S.R.; Wang, Z.; Hornung, S.; Krill, S.L. Factors affecting the formation of eutectic solid dispersions and their dissolution behavior. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: Pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6288–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noweck, K.; Grafahrend, W. Fatty alcohols. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; Volume 14, pp. 117–141. [Google Scholar]
- Galichet, L.Y. Myristyl alcohol. In Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 6th ed.; Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E., Eds.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. 456–457. [Google Scholar]
- Guest, R.T. Stearyl alcohol. In Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 6th ed.; Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E., Eds.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. 700–701. [Google Scholar]
- Code of Federal Regulations Title 21: Food and Drugs. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?SID=c1b0922b68214656303fe9df50bdf10d&mc=true&node=se21.3.172_1864&rgn=div8 (accessed on 22 October 2020).
- O’Neil, M.J.; Heckelman, P.E.; Koch, C.B.; Roman, K.J. The Merck Index, 14th ed.; Merck & Co.: Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 574–575. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, I.N. Physical Chemistry, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 351–394. [Google Scholar]
- Évora, A.O.L.; Castro, R.A.E.; Maria, T.M.R.; Silva, M.R.; ter Horst, J.H.; Canotilho, J.; Eusébio, M.E.S. Co-crystals of diflunisal and isomeric pyridinecarboxamides—A thermodynamics and crystal engineering contribution. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 4749–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fedors, R.F. A method for estimating both the solubility parameters and molar volumes of liquids. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1974, 14, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, A.F.M. CRC Handbook of Solubility Parameters and Other Cohesion Parameters, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1991; pp. 527–582. [Google Scholar]
- Ponnammal, P.; Kanaujia, P.; Yani, Y.; Ng, W.K.; Tan, R.B.H. Orally disintegrating tablets containing melt extruded amorphous solid dispersion of tacrolimus for dissolution enhancement. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sepassi, K.; Yalkowsky, S.H. Solubility prediction in octanol: A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2006, 7, E184–E191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChemSpider. Available online: http://www.chemspider.com (accessed on 22 October 2020).
- Gribble, C.D.; Hall, A.J. A Practical Introduction to Optical Mineralogy, 1st ed.; George Allen & Unwin: London, UK, 1985; pp. 180–201. [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 3rd ed.; Pearson: Harlow, Essex, UK, 2014; pp. 309–449. [Google Scholar]
- McConnell, J.F. 2-(4-Isobuthylphenyl) propionic acid. C13H18O2 ibuprofen or prufen. Cryst. Struct. Commun. 1974, 3, 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, H.; Khomane, K.S.; Bansal, A.K. Implication of microstructure on the mechanical behaviour of an aspirin–paracetamol eutectic mixture. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 8471–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, S.; Jang, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, I.W. Binary Mixtures of Some Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients with Fatty Alcohols—The Criteria of Successful Eutectic Formation and Dissolution Improvement. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111098
Jin S, Jang J, Lee S, Kim IW. Binary Mixtures of Some Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients with Fatty Alcohols—The Criteria of Successful Eutectic Formation and Dissolution Improvement. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(11):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111098
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Songhee, Jisun Jang, Soyeon Lee, and Il Won Kim. 2020. "Binary Mixtures of Some Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients with Fatty Alcohols—The Criteria of Successful Eutectic Formation and Dissolution Improvement" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 11: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111098
APA StyleJin, S., Jang, J., Lee, S., & Kim, I. W. (2020). Binary Mixtures of Some Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients with Fatty Alcohols—The Criteria of Successful Eutectic Formation and Dissolution Improvement. Pharmaceutics, 12(11), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111098