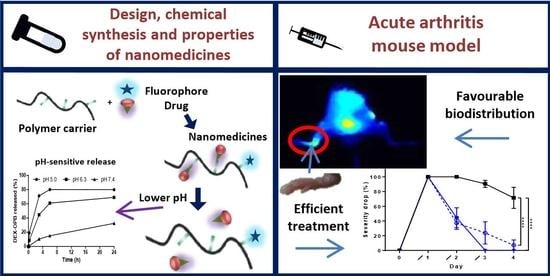
Polymer Nanomedicines with Ph-Sensitive Release of Dexamethasone for the Localized Treatment of Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Monomers
2.3. Synthesis of Trithiocarbonate Chain Transfer Agent (CTA)
2.4. Synthesis of HPMA Linear Copolymer Precursor
2.5. Synthesis of the Copolymer Conjugate with The Fluorescent Dye (LC-Cy5.5)
2.6. Synthesis of Copolymer Conjugate with the Derivate of Dexamethasone (LC-DEX-OPB or LC-Cy5.5-DEX-OPB)
2.7. Characterization of the Polymer Carriers and the Conjugates
2.8. In Vitro Drug Release
2.9. In Vivo Animal Model—Adjuvant-Induced Acute Arthritis (AIA)
2.10. Clinical Assessment of Arthritis
2.11. In Vivo and Ex Vivo Biodistribution of Fluorescently Labeled Polymer Conjugates
2.12. In Vivo Therapeutic Effect of DEX-OPB Polymer Conjugate
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design and Synthesis of Anti-Inflammatory Polymer-Based Therapeutics
3.1.1. Synthesis of Linear Copolymer Precursors and Carriers
3.1.2. Synthesis of Copolymer Conjugates with a Fluorescent Dye and Derivate of Dexamethasone
3.1.3. In Vitro Dexamethasone Release
3.2. In Vivo Study
3.2.1. In Vivo Biodistribution of Polymer Conjugates
3.2.2. Ex Vivo Biodistribution
3.2.3. In Vivo—Anti-Inflammatory Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Gabalawy, H.; Guenther, L.C.; Bernsein, C.N. Epidemiology of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases: Incidence, Prevalence, Natural History, and Comorbidities. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 2010, 85, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, W.; De Angelis, R.; Lamanna, G.; Cervini, C. The clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Radiol. 1998, 27, S18–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zou, H.; Chen, G.; Huang, G. Synthesis and Biological Activities of Chemical Drugs for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Top. Curr. Chem. 2019, 377, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Sriwastawa, B.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Bannerjee, S.K. Drug delivery systems: An updated review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, S.; Tang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, L. Nanomedicine-advantages for their use in rheumatoid arthritis theranostics. J. Control. Release 2019, 316, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, J.-Y.; Kang, W.C.; Kang, Y.J.; Khang, D. Suppression of human arthritis synovial fibroblasts inflammation using dexamethasone-carbon nanotubes via increasing caveolin-dependent endocytosis and recovering mitochondrial membrane potential. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5761–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, R.; Song, G.; Fu, X.; Song, R.; Li, L.; Pu, W.; Gao, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, Q.; He, F.; et al. Reactive oxygen species-responsive dexamethasone-loaded nanoparticles for targeted treatment of rheumatoid arthritis via suppressing the iRhom2/TNF-α/BAFF signaling pathway. Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Quan, L.; Cui, L.; Goldring, S.R.; Wang, D. Development of macromolecular prodrug for rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1205–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopecek, J.; Kopečková, P. HPMA copolymers: Origins, early developments, present, and future. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 122–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koziolová, E.; Goel, S.; Chytil, P.; Janoušková, O.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W.; Etrych, T. A tumor-targeted polymer theranostics platform for positron emission tomography and fluorescence imaging. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10906–10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Crielaard, B.J.; Dusad, A.; Lele, S.M.; Rijcken, C.J.F.; Metselaar, J.M.; Kostková, H.; Etrych, T.; Ulbrich, K.; et al. Nanomedicines for inflammatory arthritis: Head-to-head comparison of glucocorticoid-containing polymers, micelles, and liposomes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldie, I.; Nachemson, A. Synovial pH in rheumatoid knee-joints. I. The effect of synovectomy. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1969, 40, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dusad, A.; Ren, K.; Purdue, P.E.; Goldring, S.R.; Wang, D. The Evaluation of the Therapeutic Efficacy and Side Effects of a Macromolecular Dexamethasone Prodrug in the Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Li, F.; Zhao, G.; Chhonker, Y.S.; Averill, C.; Galdamez, J.; Purdue, P.E.; Wang, X.; Fehringer, E.V.; Garvin, K.L.; et al. Pharmacokinetic and Biodistribution Studies of HPMA Copolymer Conjugates in an Aseptic Implant Loosening Mouse Model. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1418–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, L.; Yuan, F.; Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Alnouti, Y.; Wang, D. Pharmacokinetic and Biodistribution Studies of N-(2-Hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide Copolymer-Dexamethasone Conjugates in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis Rat Model. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seymour, L.W.; Duncan, R.; Strohalm, J.; Kopeček, J. Effect of molecular weight (Mw) of N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide copolymers on body distribution and rate of excretion after subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, and intravenous administration to rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1987, 21, 1341–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chytil, P.; Etrych, T.; Kříž, J.; Subr, V.; Ulbrich, K. N-(2-Hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide-based polymer conjugates with pH-controlled activation of doxorubicin for cell-specific or passive tumour targeting. Synthesis by RAFT polymerisation and physicochemical characterisation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 41, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitake, K.; Satoh, K.; Kamigaito, M.; Okamoto, Y. Stereogradient Polymers Formed by Controlled/Living Radical Polymerization of Bulky Methacrylate Monomers. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1991–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrier, S.; Takolpuckdee, P.; Mars, C.A. Reversible Addition−Fragmentation Chain Transfer Polymerization: End Group Modification for Functionalized Polymers and Chain Transfer Agent Recovery. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 2033–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziolová, E.; Kostka, L.; Kotrchová, L.; Šubr, V.; Konefal, R.; Nottelet, B.; Etrych, T. N-(2-Hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide-Based Linear, Diblock, and Starlike Polymer Drug Carriers: Advanced Process for Their Simple Production. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 4003–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakovicová, H.; Etrych, T.; Ulbrich, K. HPMA-based polymer conjugates with drug combination. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 37, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzezinski, M.R.; Abraham, T.L.; Stone, C.L.; Dean, R.A.; Bosron, W.F. Purification and characterization of a human liver cocaine carboxylesterase that catalyzes the production of benzoylecgonine and the formation of cocaethylene from alcohol and cocaine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 48, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.J.; Husson, Z.M.A.; Hu, D.-E.; Callejo, G.; Brindle, K.M.; Smith, E.S.J. Increased hyperpolarized [1-(13) C] lactate production in a model of joint inflammation is not accompanied by tissue acidosis as assessed using hyperpolarized (13) C-labelled bicarbonate. NMR Biomed. 2018, 31, e3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clavel, G.; Marchiol-Fournigault, C.; Renault, G.; Boissier, M.-C.; Fradelizi, D.; Bessis, N. Ultrasound and Doppler micro-imaging in a model of rheumatoid arthritis in mice. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, D.D.; Latham, K.A.; Rosloniec, E.F. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathy, S.S.; Masocha, W. Gait analysis of C57BL/6 mice with complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis using the CatWalk system. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samtani, M.N.; Jusko, W.J. Comparison of dexamethasone pharmacokinetics in female rats after intravenous and intramuscular administration. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2005, 26, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gross, S.; Gammon, S.T.; Moss, B.L.; Rauch, D.; Harding, J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Ratner, L.; Piwnica-Worms, D. Bioluminescence imaging of myeloperoxidase activity in vivo. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheraiet, Z.; Hessainia, S.; Ouarna, S.; Berredjem, M.; Aouf, N.-E. A simple and eco-sustainable method for the O-Boc protection/deprotection of various phenolic structures under water-mediated/catalyst-free conditions. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2013, 6, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.-M.; Quan, L.-D.; Tian, J.; Alnouti, Y.; Fu, K.; Thiele, G.M.; Wang, D. Synthesis and evaluation of a well-defined HPMA copolymer-dexamethasone conjugate for effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2910–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bachmann, K. Drug Metabolism in Pharmacology: Principles and Practice; Hacker, M., Messer, W., Bachmann, K., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 131–173. [Google Scholar]
- Laizure, S.C.; Herring, V.; Hu, Z.; Witbrodt, K.; Parker, R.B. The role of human carboxylesterases in drug metabolism: Have we overlooked their importance? Pharmacotherapy 2013, 33, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etrych, T.; Subr, V.; Strohalm, J.; Sírová, M.; Ríhová, B.; Ulbrich, K. HPMA copolymer-doxorubicin conjugates: The effects of molecular weight and architecture on biodistribution and in vivo activity. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.N.; Chimatadar, S.A.; Nandibewoor, S.T. Interaction between a potent corticosteroid drug-dexamethasone with bovine serum albumin and human serum albumin: A fluorescence quenching and fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy study. J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 2010, 100, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexis, F.; Pridgen, E.; Molnar, L.K.; Farokhzad, O.C. Factors affecting the clearance and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2008, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchettini, P.; Stuart, O.A.; Mohamed, F.; Yoo, D.; Sugarbaker, P.H. Docetaxel: Pharmacokinetics and tissue levels after intraperitoneal and intravenous administration in a rat model. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2002, 49, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Temsamani, J.; Tang, J.Y. Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and stability of oligodeoxynucleotide phosphorothioates in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7595–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harivardhan Reddy, L.; Sharma, R.K.; Chuttani, K.; Mishra, A.K.; Murthy, R.S.R. Influence of administration route on tumor uptake and biodistribution of etoposide loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in Dalton’s lymphoma tumor bearing mice. J. Control. Release 2005, 105, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Li, J.-J.; Guo, N.-H.; Chang, D.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-T.; Lin, W.-J.; Chi, K.-H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Liu, R.-S.; et al. Evaluation of the Biological Behavior of a Gold Nanocore-Encapsulated Human Serum Albumin Nanoparticle (Au@HSANP) in a CT-26 Tumor/Ascites Mouse Model after Intravenous/Intraperitoneal Administration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, B.D.; Adeyemo, A.; O’Leary, M.E.; Bottaro, A. Animal models of rheumatoid pain: Experimental systems and insights. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, Y.H.; Tiemann, K.M.; Hunstad, D.A.; Elsabahy, M.; Wooley, K.L. Polymeric nanoparticles in development for treatment of pulmonary infectious diseases. Wires Nanomed. Nanobi. 2016, 8, 842–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Owens, D.E., III; Peppas, N.A. Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 307, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, M.M.; Fries, L.F. The role of complement in inflammation and phagocytosis. Immunol. Today 1991, 12, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, G.; Brindle, S.D.; Greengard, P. The route of absorption of intraperitoneally administered compounds. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1971, 178, 562–564. [Google Scholar]
- Claassen, V. Intraperitoneal Drug Administration. In Neglected Factors in Pharmacology and Neuroscience Research; Huston, J.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 12, pp. 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Ahmet, A.; Ward, L.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Mandelcorn, E.D.; Leigh, R.; Brown, J.P.; Cohen, A.; Kim, H. A practical guide to the monitoring and management of the complications of systemic corticosteroid therapy. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Copolymer | Mwa (kg/mol) | Đa (-) | Mon:CTA:Ini Ratio | Hydrazides (mol %) | RHc (nm) | FTTcd (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-TTc | 33 | 1.05 | 500:2:1 | - | 4.0 | 0.98 |
| LC | 33 | 1.05 | - | - | 4.0 | - |
| LC-NHNH2 | 37 | 1.11 | - | 6.0 | 4.5 | - |
| Sample | Mwa (kg/mol) | Đa (-) | Cy 5.5 b (wt %) | DEX-OPB c (wt %) | RHd (nm) | PDId |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-DEX-OPB | 39 | 1.1 | - | 5.2 | 5.0 | 0.3 |
| LC-Cy5.5 | 37 * | 1.1 * | 1.75 | - | 4.5 * | 0.3 * |
| LC-Cy5.5-DEX-OPB | 37 * | 1.1 * | 1.00 | 6.0 | 4.5 * | 0.3 * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Libánská, A.; Randárová, E.; Lager, F.; Renault, G.; Scherman, D.; Etrych, T. Polymer Nanomedicines with Ph-Sensitive Release of Dexamethasone for the Localized Treatment of Inflammation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080700
Libánská A, Randárová E, Lager F, Renault G, Scherman D, Etrych T. Polymer Nanomedicines with Ph-Sensitive Release of Dexamethasone for the Localized Treatment of Inflammation. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(8):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080700
Chicago/Turabian StyleLibánská, Alena, Eva Randárová, Franck Lager, Gilles Renault, Daniel Scherman, and Tomáš Etrych. 2020. "Polymer Nanomedicines with Ph-Sensitive Release of Dexamethasone for the Localized Treatment of Inflammation" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 8: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080700
APA StyleLibánská, A., Randárová, E., Lager, F., Renault, G., Scherman, D., & Etrych, T. (2020). Polymer Nanomedicines with Ph-Sensitive Release of Dexamethasone for the Localized Treatment of Inflammation. Pharmaceutics, 12(8), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080700