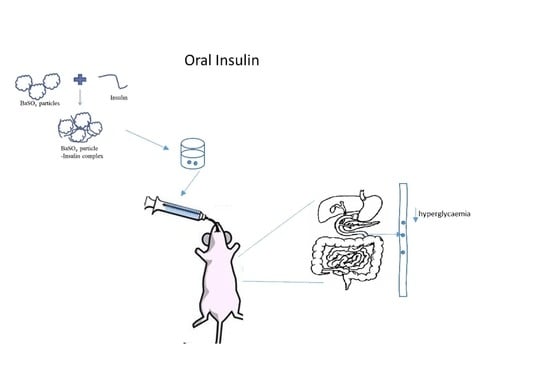
Insulin-Loaded Barium Salt Particles Facilitate Oral Delivery of Insulin in Diabetic Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.1.1. Reagents
2.1.2. Reagent Preparation
2.2. Synthesis of Empty and Insulin-Loaded Ba Salt Particles
2.2.1. Synthesis of Particles by Precipitation Reaction
2.2.2. Insulin Loading into Ba Salt Particles
2.3. Characterization and Morphological Screening of Ba Salt Particles
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.3.2. Elemental Analysis of Particles by Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
2.4. Particle Stability Assessment
2.5. Insulin Loading Efficiency of Ba Salt Particles
2.5.1. Insulin Loading Efficiency of Ba Salt Particles and Subsequent Release of Insulin from Particles at a Wide Range of pHs
2.5.2. Morphological Assessment of Empty and Insulin-Loaded Particles by FE-SEM
2.6. Assessment of Adhesion of Ba Salt Particles to Mucin
2.6.1. Spectrophotometric Analysis of Particle Adhesion to Mucin
2.6.2. Assessment of Particle Adhesion to Mucin Using FT-IR
2.7. Administration of Insulin-Loaded Particles to Diabetic Animals and Management of Hyperglycemia
2.7.1. Induction of Diabetes in Rats with Streptozotocin (STZ)
2.7.2. Effect of Orally Administrated Insulin-Loaded Particles on Hyperglycemia
2.7.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Characterization and Morphological Analysis of Synthesized Ba Salt Particles
3.1.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
3.1.2. Element Analysis of Ba Salt Particles by Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
3.2. Particle Stability Assessment
3.3. Insulin Loading of Ba Salt Particles
3.3.1. Insulin Loading Efficiency of Ba Salt Particles and Subsequent Release of Insulin from Particles at a Wide Range of pHs
3.3.2. Morphological Analysis of Ba Salt Particles by FE-SEM
3.4. Analysis of Effect of Insulin Loading into Particles by FE-SEM
3.4.1. Effect of Insulin Loading into Baso4 Particles: Changes in Morphology and Aggregation Pattern
3.4.2. Effect of Insulin Loading into Baso3 Particles: Change in Morphology and Aggregation Pattern
3.4.3. Effect of Insulin Loading into Baco3 Particles: Changes in Morphology and Aggregation Pattern
3.5. Assessment of Mucin Adhesion to Ba Salt Particle
3.5.1. Analysis of Mucin Adhesion to Ba Salt Particles Using FT-IR
3.5.2. Quantitation of Mucin Adhesion to Particles
3.6. Oral Administration of Insulin-Loaded Particles to Diabetic Rats and Effect on Blood Glucose Level
Effect of Orally Administrated Insulin on Hyperglycemia
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterization and Morphological Screening of Empty Ba Salt Particles
4.2. Particle Stability Assessment
4.3. Insulin Loading Efficiency of Ba Salt Particles and Subsequent Release of Insulin from Particles at Lower pHs
4.4. Morphological Analysis of Ba Salt Particle by FE-SEM
4.5. Assessment of Mucin Adhesion to Ba Salt Particles
4.6. Effect of Orally Administrated Nano-Insulin on Hyperglycemia
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zaman, R.; Islam, R.A.; Ibnat, N.; Othman, I.; Zaini., A.; Lee, C.Y.; Chowdhury, E.H. Current strategies in extending half-lives of therapeutic proteins. J. Control. Release 2019, 30, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curto, M.D.D.; Maroni, A.; Palugan, L.; Zema, L.; Gazzaniga, A.; Sangalli, M.E. Oral Delivery System for Two-pulse Colonic Release of Protein. Drugs and Protease Inhibitor/Absorption Enhancer Compounds. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 3251–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, R.; Othman, I.; Chowdhury, E.H. Carrier Mediated Systemic Delivery of Protein and Peptide Therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 6167–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiowitz, E.; Jacob, J.S.; Jong, Y.S.; Carino, G.P.; Chickering, D.E.; Chaturvedi, P.; Santos, C.A.; Vijayaraghvan, K.; Montgomery, S.; Bassett, M.; et al. Biologically erodable microspheres as potential oral drug delivery systems. Nature 1997, 386, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensign, L.M.; Cone, R.; Hanes, J. Oral drug delivery with polymeric nanoparticles: The gastrointestinal mucus barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.M.; Zhou, L.; Guo, X.D.; Jiang, W.; Ling, L.; Qian, Y.; Luo, K.Q.; Zhang, L.J. HP55-coated capsule containing PLGA/RS nanoparticles for oral delivery of insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 425, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zheng, J.M.; Xu, H.; Wei, G.; Hao, J.S. Bioadhesive polysaccharide in protein delivery system: Chitosan nanoparticles improve the intestinal absorption of insulin in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 249, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Lim, T.M.; Lim, L.Y. Pharmacological activity of peroral chitosan- insulin nanoparticles in diabetic rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 293, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Sande, M.; Teijeiro-Osorio, D.; Remuñán-López, C.; Alonso, M.J. Glucomannan, a promising polysaccharide for biopharmaceutical purposes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des Rieux, A.; Fievez, V.; Garinot, M.; Schneider, Y.J.; Préat, V. Nanoparticles as potential oral delivery systems of proteins and vaccines: A mechanistic approach. J. Control. Release 2006, 116, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; Harpe, V. Digestive system structure and function. In Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; p. 570. [Google Scholar]
- Banga, A.K. Oral Delivery of Peptide and Protein Drugs. In Therapeutic Peptides and Proteins Formulation, Processing, and Delivery Systems, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FA, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Park Drive, UK, 2006; pp. 229–250. [Google Scholar]
- Krauland, A.H.; Guggi, D.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Oral insulin delivery: The potential of thiolated chitosan-insulin tablets on nondiabetic rats. J. Control. Release 2004, 95, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molero, J.E.; Aleck, K.; Sinha, M.K.; Brownscheidle, C.M.; Shapiro, L.J.; Sperling, M.A. Orally administered liposome entrapped insulin in diabetic animals. Horm. Res. 1982, 16, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanov, A.V.; Kononenko, N.I.; Lishko, V.K.; Shevchenko, A.V. Effect of liposomally entrapped insulin administered per os on the blood sugar level in normal and experimentally diabetic rats. Ukr. Biokhim. Zh. 1980, 52, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halberg, I.; Lyby, K.; Wassermann, K.; Heise, T.; Zijlstra, E.; Plum-Mörschel, L. Efficacy and safety of oral basal insulin versus subcutaneous insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes: A randomised, double-blind, phase 2 trial. Lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 18, 30372–30373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Advances in oral peptide therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 19, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.M.; Lautz, M.; Moore, L.M.; Williams, P.E.; Reddy, P.; Cherrington, A.D. Enterically delivered insulin tregopil exhibits rapid absorption characteristics and a pharmacodynamic effect similar to human insulin in conscious dogs. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbit, E.; Kidron, M. Oral insulin delivery in a physiologic context: Review. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geho, W.B.; Rosenberg, L.N.; Schwartz, S.L.; Lau, J.R.; Gana, T.J. A single-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial of oral hepatic-directed vesicle insulin add-on to oral antidiabetic treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.; Othman, I.; Zain, A.Z.M. Controlled release of insulin in blood from strontium-substituted carbonate apatite complexes. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Busaidi, H.; Karim, M.E.; Abidin, S.; Tha, K.K.; Chowdhury, E.H. Magnesium Fluoride Forms Unique Protein Corona for Efficient Delivery of Doxorubicin into Breast Cancer Cells. Toxics 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakhtiar, A.; Kamaruzman, N.I.; Othman, I.; Zaini, A.; Chowdhury, E.H. Intracellular Delivery of p53 Gene and MAPK siRNA into Breast Cancer Cells utilizing Barium Salt Nanoparticles. J. Breast Cancer Res. Adv. 2017, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sifontes, Á.B.; Cañizales, E.; Toro-Mendoza, J.; Ávila, E.; Hernández, P.; Blas, A.; Delgado, G.; Gutiérrez, B.; Díaz, Y.; Cruz-Barrios, E. Obtaining Highly Crystalline Barium Sulphate Nanoparticles via Chemical Precipitation and Quenching in Absence of Polymer Stabilizers. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Vimalathithan, R.M.; Ponnusamy, V. Synthesis and characterization of BaSO4 nano-particles using micro emulsion technique. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 1, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, X.; Zhang, F.; Sha, F.; Zhao, J.; Shiab, H.; Zhang, J. Controllable synthesis of nanostructured BaSO4 and BaSO3 crystals on the basis of DMSO oxidation chemistry. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infrared Spectroscopy (IR). Studylab. Available online: https://studylib.net/doc/10832883/infrared-spectroscopy-ir- (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Sreedhar, B.; Vani, C.S.; Devi, D.K.; Rao, M.B.; Rambabu, C. Shape Controlled Synthesis of Barium Carbonate Microclusters and Nanocrystallites using Natural Polysachharide—Gum Acacia. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 2, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wu, J.G.; Soloway, R.D.; Martini, D.K.; Xu, N.; Xu, G-X. Influence of water on the Infrared Spectra of Mucin. Mikrochim. Acta 1988, 1, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, E.; Heinemann, L.; Plum-Mörschel, L. Oral Insulin Reloaded: A Structured Approach. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kontermann, R.E. Half-life extended biotherapeutics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deangelis, P.L. Heparosan Polymers and Methods of Making and Using Same for the Enhancement of Therapeutics, the Board of Regents of the University of Oklahoma. U.S. Patent 9,603,945, 28 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhru, S.H.; Furtado, S.; Morello, A.P.; Mathiowitz, E. Oral delivery of proteins by biodegradable nanoparticles. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gesenberg, C.; Zheng, W. Oral Formulations for Preclinical Studies: Principle, Design, and Development Considerations (Chapter 17). In Developing Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Pharmaceutical Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; Qiu, Y., Zhang, G.G.Z., Chen, Y., Mantri, R.V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 455–495. [Google Scholar]
- Koziolek, M.; Grimm, M.; Becker, D.; Iordanov, V.; Zou, H.; Shimizu, J.; Wanke, C.; Garbacz, G.; Weitschies, W. Investigation of pH and Temperature Profiles in the GI Tract of Fasted Human Subjects Using the Intellicap® System. JPDDR 2015, 104, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, K.; Sugiyama, M.; Mukai, T. Adhesion Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria on Intestinal Mucin. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaje, K.; Lin, K.J.; Wey, S.P.; Lin, C.K.; Yeh, T.H.; Nguyen, H.N.; Hsu, C.W.; Yen, T.C.; Juang, J.H.; Sung, H.W. Biodistribution, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of insulin analogues in a rat model: Oral delivery using pH-Responsive nanoparticles vs. subcutaneous injection. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6849–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















| Salt B | Ba Salt Particles |
|---|---|
| Salt A(1M BaCl2, 5 µL) | |
| 1M Na2SO4 (2 µL) | BaSO4 |
| 1M Na2SO3 (2 µL) | BaSO3 |
| 1M Na2CO3(2 µL) | BaCO3 |
| 20× concentrated Ba particle formulations prepared for in vivo use | |
| 1M Na2CO3(40 µL) | BaCO3 |
| Salt B | Ba salt particles |
| Salt A (1M BaCl2 100 µL) | |
| 1M Na2SO4 (40 µL) | BaSO4 |
| 1M Na2SO3 (40 µL) | BaSO3 |
| Salt B | Insulin | Salt A(1 M BaCl2 5 µL) |
|---|---|---|
| 1M Na2SO4 (2 µL) | FITC-Insulin(2 mg/mL,1–25 µL)/Insulin Aspart (1–5 IU/kg) | BaSO4 |
| 1M Na2SO3 (2 µL) | FITC-Insulin(2 mg/mL,1–25 µL)/Insulin Aspart (1–5 IU/kg) | BaSO3 |
| 1M Na2CO3(2 µL) | FITC-Insulin(2 mg/mL,1–25 µL)/Insulin Aspart (1–5 IU/kg) | BaCO3 |
| 20× concentrated Ba particle formulations loaded with Insulin Aspart prepared for in vivo use | ||
| Salt B | Insulin | Salt (1 M BaCl2 100 µL) |
| 1M Na2SO4 (40 µL) | Insulin Aspart (100 IU/kg) | BaSO4 |
| 1M Na2SO3 (40 µL) | Insulin Aspart (100 IU/kg) | BaSO3 |
| 1M Na2CO3(40 µL) | Insulin Aspart (100 IU/kg) | BaCO3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaman, R.; Karim, M.E.; Othman, I.; Zaini, A.; Chowdhury, E.H. Insulin-Loaded Barium Salt Particles Facilitate Oral Delivery of Insulin in Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080710
Zaman R, Karim ME, Othman I, Zaini A, Chowdhury EH. Insulin-Loaded Barium Salt Particles Facilitate Oral Delivery of Insulin in Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(8):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080710
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaman, Rahela, Md. Emranul Karim, Iekhsan Othman, Anuar Zaini, and Ezharul Hoque Chowdhury. 2020. "Insulin-Loaded Barium Salt Particles Facilitate Oral Delivery of Insulin in Diabetic Rats" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 8: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080710
APA StyleZaman, R., Karim, M. E., Othman, I., Zaini, A., & Chowdhury, E. H. (2020). Insulin-Loaded Barium Salt Particles Facilitate Oral Delivery of Insulin in Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceutics, 12(8), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080710