Pharmaceutical Applications of Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions for Micro-/Nanoparticle Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions (SFEE)
2.1. Supercritical Fluid (SCF)
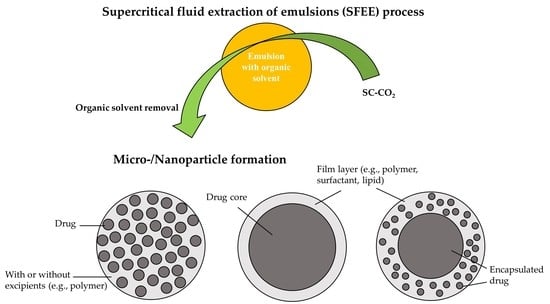
2.2. SFEE Process, Apparatus, and Its Extraction Mechanism
2.2.1. SFEE Process and Apparatus
2.2.2. Mechanism of SFEE
Drawbacks of Conventional Micro-/Nanoparticle Solidification Processes
Excellent Solvent Removal and Solidification Mechanism of SFEE
3. SFEE Application Cases
3.1. Drug Delivery System
3.1.1. Microencapsulation for Controlled Release
3.1.2. Nanoparticle for Improved Drug Delivery
3.1.3. Pulmonary Drug Delivery
3.1.4. Polymeric Gene Delivery
3.1.5. Tissue Engineering
3.1.6. Nanoparticles of Inorganic Materials
3.2. Solubilization via Nanoparticles of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs
3.3. Physicochemical Stabilization
3.4. Solidification of Liquid Drug
4. Expert Opinions and Perspectives
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EE | encapsulation efficiency |
| SFEE | supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions |
| SCF | supercritical fluid |
| GRAS | generally recognized as a safe |
| US-FDA | United States Food and Drug Administration |
| SC-CO2 | supercritical carbon dioxide |
| Tc | critical temperature |
| Pc | critical pressure |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide |
| RESS | rapid expansion of supercritical solutions |
| SAS | supercritical antisolvent |
| PGSS | particles from gas saturated solutions |
| SAA | supercritical assisted atomization |
| SA-SD | supercritical fluid-assisted spray-drying |
| W/O/W | water-in-oil-in-water emulsion |
| W/O/O | water-in-oil-in-oil emulsion |
| S/O/W | solid-in-oil-in-water emulsion |
| S/O/O | solid-in-oil-in-oil emulsion |
| O/W | oil-in-water emulsion |
| O/O | oil-in-oil emulsion |
| CPPs | critical process parameters |
| b-SFEE | batch-type SFEE process |
| c-SFEE | continuous SFEE |
| c-SFEE-PC | continuous SFEE with packed column |
| PSD | particle size distribution |
| DCM | dichloromethane |
| PLGA | poly(lactic/glycolic) acid |
| EA | ethyl acetate |
| SE | solvent evaporation |
| ppm | parts per million |
| GMP | good manufacturing practices |
| PLA | poly-lactic acid |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| h-IGF | human insulin-like growth factor |
| PCL | polycaprolactone |
| PVA | polyvinyl alcohol |
| SLN | solid lipid nanoparticles |
| pDNA | plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| SEM-EDX | scanning electron microscope/energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| BCS | biopharmaceutical classification system |
| QbD | quality by design |
| PGX | pressurized gas expanded |
| CQA | critical quality attribute |
| CMA | critical material attributes |
References
- Cocero, M.J.; Martín, Á.; Mattea, F.; Varona, S. Encapsulation and co-precipitation processes with supercritical fluids: Fundamentals and applications. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 47, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Huertas, C.E.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Polymer-based nanocapsules for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Singh, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Porwal, O.; Fuloria, N.K. Graphene-based nanomaterial system: A boon in the era of smart nanocarriers. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 245–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamarekh, K.S.; Gad, H.A.; Soliman, M.E.; Sammour, O.A. Towards the production of monodisperse gelatin nanoparticles by modified one step desolvation technique. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, N.I.; Nkanga, C.I.; Walker, R.B.; Noundou, X.S.; Krause, R.W.M. Encapsulation and physicochemical evaluation of efavirenz in liposomes. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundargi, R.C.; Babu, V.R.; Rangaswamy, V.; Patel, P.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Nano/micro technologies for delivering macromolecular therapeutics using poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) and its derivatives. J. Control. Release 2008, 125, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiio, T.M.; Park, S. Physical properties of nanoparticles do matter. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S. Fabrication of aerosol-based nanoparticles and their applications in biomedical fields. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.; Kim, K.B.; Yeo, Y.; Lee, W. Pharmacokinetic aspects of the clinically used proteasome inhibitor drugs and efforts toward nanoparticulate delivery systems. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Kim, S.; Park, K. Issues in long-term protein delivery using biodegradable microparticles. J. Control. Release 2010, 146, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyar, S.; Nafisi, S.; Mohseni, M.; Mehravi, B. Design and synthesis of potential nano-carrier for delivery of diphencyprone to hair follicle. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğar, N.; Akkın, S.; Nielsen, T.T.; Özçelebi, E.; Erdoğdu, B.; Nemutlu, E.; İskit, A.B.; Bilensoy, E. Development of oral aprepitant-loaded chitosan–polyethylene glycol-coated cyclodextrin nanocapsules: Formulation, characterization, and pharmacokinetic evaluation. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Kaminskas, L.M.; Marasini, N. Recent advances in nano/microparticle-based oral vaccines. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Shimoyama, Y. Supercritical extraction of emulsion in microfluidic slug-flow for production of nanoparticle suspension in aqueous solution. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 118, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjitha, V.; Rai, V.R. Selenium nanostructure: Progress towards green synthesis and functionalization for biomedicine. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Mazumder, B.; Sharma, P.P.; Ahmed, Y. Pharmacokinetics and hypoglycemic effect of gliclazide loaded in Isabgol husk mucilage microparticles. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.K.; Diep, D.B.; Tønnesen, H.H. Nanomedicine-based antimicrobial peptide delivery for bacterial infections: Recent advances and future prospects. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 377–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Kim, J.O. Recent progress in cancer immunotherapy approaches based on nanoparticle delivery devices. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.; Park, J.-S. Recent trends of self-emulsifying drug delivery system for enhancing the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 439–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwa, R.; Jeong, J.-H.; Yook, S. Development of immunotherapy and nanoparticles-based strategies for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, I.S.; Yoon, M.S.; Park, C.-W.; Hong, J.T.; Chung, Y.B.; Kim, J.-S.; Shin, D.H. Replacement techniques to reduce animal experiments in drug and nanoparticle development. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.; Merkle, H.P.; Gander, B. Microencapsulation by solvent extraction/evaporation: Reviewing the state of the art of microsphere preparation process technology. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Porta, G.; Reverchon, E. Nanostructured microspheres produced by supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 100, 1020–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, J.; Fusaro, F.; Casas, N.; Mazzotti, M.; Muhrer, G. Production of PLGA micro-and nanocomposites by supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions: I. Encapsulation of lysozyme. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 50, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Donnell, P.B.; McGinity, J.W. Preparation of microspheres by the solvent evaporation technique. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 28, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.A. The manufacturing techniques of various drug loaded biodegradable poly (lactide-co-glycolide)(PLGA) devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2475–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chang, S.; Du, G.; Li, Y.; Gong, J.; Yang, M.; Wei, Z. Encapsulation of azithromycin into polymeric microspheres by reduced pressure-solvent evaporation method. Int. J. pharm. 2012, 433, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godbee, J.; Scott, E.; Pattamunuch, P.; Chen, S.; Mathiowitz, E. Role of solvent/non-solvent ratio on microsphere formation using the solvent removal method. J. Microencapsul. 2004, 21, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-W.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-L.; Liu, Y.-Z. Effects of solvent evaporation rate on the properties of protein-loaded PLLA and PDLLA microspheres fabricated by emulsion-solvent evaporation process. J. Microencapsul. 2002, 19, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katou, H.; Wandrey, A.J.; Gander, B. Kinetics of solvent extraction/evaporation process for PLGA microparticle fabrication. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-I.; Anderson, K.W.; Mehta, R.C.; Deluca, P.P. Prediction of solvent removal profile and effect on properties for peptide-loaded PLGA microspheres prepared by solvent extraction/evaporation method. J. Control. Release 1995, 37, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavanetto, F.; Conti, B.; Genta, I.; Giunchedi, P. Solvent evaporation, solvent extraction and spray drying for polylactide microsphere preparation. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 84, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Ha, E.-S.; Kim, M.-S. Surface modification strategies for high-dose dry powder inhalers. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 635–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamatari, M.; Charisi, A.; Malamataris, S.; Kachrimanis, K.; Nikolakakis, I. Spray Drying for the Preparation of Nanoparticle-Based Drug Formulations as Dry Powders for Inhalation. Processes 2020, 8, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomasin, C.; Johansen, P.; Alder, R.; Bemsel, R.; Hottinger, G. A contribution to overcoming the problem of residual solvents in biodegradable microspheres prepared by coacervation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1996, 42, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Abuzar, S.M.; Hyun, S.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, M.-S.; Park, J.-S.; Hwang, S.-J. Enhancing the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs using supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knez, Z.; Weidner, E. Particles formation and particle design using supercritical fluids. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2003, 7, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fages, J.; Lochard, H.; Letourneau, J.-J.; Sauceau, M.; Rodier, E. Particle generation for pharmaceutical applications using supercritical fluid technology. Powder Technol. 2004, 141, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kankala, R.K.; Xu, P.-Y.; Chen, B.-Q.; Wang, S.-B.; Chen, A.-Z. Supercritical fluid (SCF)-assisted fabrication of carrier-free drugs: An eco-friendly welcome to Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, I.; Bettini, R. Are pharmaceutics really going supercritical? Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knez, Ž.; Škerget, M.; Hrnčič, M.K.; Čuček, D. Particle formation using sub-and supercritical fluids. In Supercritical Fluid Technology for Energy and Environmental Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 31–67. [Google Scholar]
- Della Porta, G.; Falco, N.; Reverchon, E. NSAID drugs release from injectable microspheres produced by supercritical fluid emulsion extraction. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1484–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, G.D.; Falco, N.; Reverchon, E. Continuous supercritical emulsions extraction: A new technology for biopolymer microparticles production. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cun, D.; Zhang, C.; Bera, H.; Yang, M. Particle engineering principles and technologies for pharmaceutical biologics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 140–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.T.; Santana, Á.L.; Meireles, M.A.A.; Petenate, A.J.; Silva, E.K.; Albarelli, J.Q.; Johner, J.C.; Gomes, M.T.M.; Torres, R.A.D.C.; Hatami, T. Recent Developments in Particle Formation with Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions Process for Encapsulation. In Supercritical Antisolvent Precipitation Process; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Gupta, R.B. Supercritical CO2-based formation of silica nanoparticles using water-in-oil microemulsions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrut, M.; Jung, J.; Leboeuf, F. Method for Obtaining Solid Particles from at least a Water Soluble Product. France Patent Application No. FR0106403A, 15 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Shekunov, B.Y.; Seitzinger, J.S. Method and Apparatus for Continuous Particle Production Using Supercritical Fluid. U.S. Patent Application No. US2004/0156911, 8 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Shekunov, B.Y.; Gibson, K.A. Supercritical Fluid Extraction Produced by In-Line Homogenization. U.S. Patent Application No. US2008/0260825, 22 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Della Porta, G.; Campardelli, R.; Falco, N.; Reverchon, E. PLGA microdevices for retinoids sustained release produced by supercritical emulsion extraction: Continuous versus batch operation layouts. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 4357–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, W.; Ma, G. A novel strategy for the preparation of porous microspheres and its application in peptide drug loading. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 478, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattea, F.; Martín, Á.; Schulz, C.; Jaeger, P.; Eggers, R.; Cocero, M.J. Behavior of an organic solvent drop during the supercritical extraction of emulsions. AIChE J. 2010, 56, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Huff, R.; Shekunov, B.Y. Drug encapsulation using supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, N.; Reverchon, E.; Della Porta, G. Injectable PLGA/hydrocortisone formulation produced by continuous supercritical emulsion extraction. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, N.; Reverchon, E.; Della Porta, G. Continuous supercritical emulsions extraction: Packed tower characterization and application to poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) + insulin microspheres production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 8616–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Porta, G.; Falco, N.; Giordano, E.; Reverchon, E. PLGA microspheres by supercritical emulsion extraction: A study on insulin release in myoblast culture. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 1831–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campardelli, R.; Reverchon, E.; Della Porta, G. Biopolymer particles for proteins and peptides sustained release produced by supercritical emulsion extraction. Procedia Eng. 2012, 42, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Della Porta, G.; Campardelli, R.; Cricchio, V.; Oliva, F.; Maffulli, N.; Reverchon, E. Injectable PLGA/hydroxyapatite/chitosan microcapsules produced by supercritical emulsion extraction technology: An in vitro study on teriparatide/gentamicin controlled release. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Porta, G.; Campardelli, R.; Reverchon, E. Monodisperse biopolymer nanoparticles by continuous supercritical emulsion extraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2013, 76, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, A.L.; Trivedi, V.; Mitchell, J.C. Preparation of polycaprolactone nanoparticles via supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of emulsions. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murakami, Y.; Shimoyama, Y. Production of nanosuspension functionalized by chitosan using supercritical fluid extraction of emulsion. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 128, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giufrida, W.M.; Cabral, V.F.; Cardoso-Filho, L.; dos Santos Conti, D.; de Campos, V.E.; da Rocha, S.R. Medroxyprogesterone-encapsulated poly (3-hydroxybutirate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) nanoparticles using supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 118, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Shekunov, B.Y.; Yim, D.; Cipolla, D.; Boyd, B.; Farr, S. Production of solid lipid nanoparticle suspensions using supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions (SFEE) for pulmonary delivery using the AERx system. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, A.S.; Ambati, B.K.; Kompella, U.B. Gene delivery nanoparticles fabricated by supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 387, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palazzo, I.; Lamparelli, E.P.; Ciardulli, M.C.; Scala, P.; Reverchon, E.; Forsyth, N.; Maffulli, N.; Santoro, A.; Della Porta, G. Supercritical emulsion extraction fabricated PLA/PLGA micro/nano carriers for growth factor delivery: Release profiles and cytotoxicity. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Porta, G.; Castaldo, F.; Scognamiglio, M.; Paciello, L.; Parascandola, P.; Reverchon, E. Bacteria microencapsulation in PLGA microdevices by supercritical emulsion extraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 63, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, I.; Raimondo, M.; Della Porta, G.; Guadagno, L.; Reverchon, E. Encapsulation of health-monitoring agent in poly-methyl-methacrylate microcapsules using supercritical emulsion extraction. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 90, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campardelli, R.; Della Porta, G.; Gomez, V.; Irusta, S.; Reverchon, E.; Santamaria, J. Encapsulation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in PLA microspheres using supercritical emulsion extraction to produce bactericidal nanocomposites. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, M.; Kluge, J.; Mazzotti, M.; Lattuada, M. Preparation of biocompatible magnetite–PLGA composite nanoparticles using supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2010, 54, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekunov, B.Y.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Seitzinger, J.; Huff, R. Nanoparticles of poorly water-soluble drugs prepared by supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, J.; Fusaro, F.; Mazzotti, M.; Muhrer, G. Production of PLGA micro-and nanocomposites by supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions: II. Encapsulation of Ketoprofen. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 50, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C.; Calvo, L. Supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions to nanoencapsulate vitamin E in polycaprolactone. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 119, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawar, I.A.; Ghosh, T.; Park, J.K.; Kuh, H.-J. Tumor spheroid-based microtumor models for preclinical evaluation of anticancer nanomedicines. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 735–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareeb, D.A.; Saleh, S.R.; Seadawy, M.G.; Nofal, M.S.; Abdulmalek, S.A.; Hassan, S.F.; Khedr, S.M.; AbdElwahab, M.G.; Sobhy, A.A.; Yassin, A.M. Nanoparticles of ZnO/Berberine complex contract COVID-19 and respiratory co-bacterial infection in addition to elimination of hydroxychloroquine toxicity. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 735–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.; Lee, S.-E.; Kim, D.-H.; Pyo, Y.-C.; Park, J.-S. Recent advances of nanotechnology for the delivery of anticancer drugs for breast cancer treatment. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansook, P.; Maw, P.D.; Soe, H.M.S.H.; Chuangchunsong, R.; Saiborisuth, K.; Payonitikarn, N.; Autthateinchai, R.; Pruksakorn, P. Development of amphotericin B nanosuspensions for fungal keratitis therapy: Effect of self-assembled γ-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, H.S.; Mun, Y.-H.; Koh, S.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, S.M.; Kang, N.-W.; Lee, M.Y.; Cho, C.-W.; Kim, D.-D. An overview of chondrosarcoma with a focus on nanoscale therapeutics. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Rahman, L.; Kim, S.-H.; Cao, J.; Arjuna, A.; Lallo, S.; Jhun, B.H.; Yoo, J.-W. Recent advances of nanocellulose in drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhadi, E.; Nassirli, H.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. An updated review on therapeutic effects of nanoparticle-based formulations of saffron components (safranal, crocin, and crocetin). J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shan, X.; Luo, C.; He, Z. Emerging nanoparticulate drug delivery systems of metformin. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavijeh, M.S.; Maghsoudpour, A.; Khayat, M.; Rad, I.; Hatamie, S. Distribution of “molybdenum disulfide/cobalt ferrite” nanocomposite in animal model of breast cancer, following injection via differential infusion flow rates. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannon-Peppas, L.; Blanchette, J.O. Nanoparticle and targeted systems for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Ha, E.-S.; Kim, M.-S. Physicochemical analysis techniques specialized in surface characterization of inhalable dry powders. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 519–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, N.; Cipolla, D.; Park, H.; Zhou, Q.T. Physical stability of dry powder inhaler formulations. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.; Yousaf, S.; Najlah, M.; Ahmed, W.; Elhissi, A. Proliposome powder or tablets for generating inhalable liposomes using a medical nebulizer. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-J. Recent progresses in the development of hyaluronic acid-based nanosystems for tumor-targeted drug delivery and cancer imaging. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Cho, W.; Cha, K.-H.; Park, J.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, H.J.; Hwang, S.-J. Enhanced dissolution of megestrol acetate microcrystals prepared by antisolvent precipitation process using hydrophilic additives. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 396, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, E.-S.; Lee, S.-K.; Choi, D.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Hwang, S.-J.; Kim, M.-S. Application of diethylene glycol monoethyl ether in solubilization of poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Jin, S.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, H.J.; Song, H.-S.; Neubert, R.H.; Hwang, S.-J. Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of amorphous atorvastatin calcium nanoparticles using supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.W.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.; Woo, J.-S.; Hwang, S.-J. Preparation and characterization of simvastatin/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex using supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 66, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lee, S.-E.; Pyo, Y.-C.; Tran, P.; Park, J.-S. Solubility enhancement and application of cyclodextrins in local drug delivery. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweed, N.M.; Fayez, A.M.; El-Emam, S.Z.; Dawoud, M.H. Response surface optimization of self nano-emulsifying drug delivery system of rosuvastatin calcium for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadpara, N.P.; Thumar, R.V.; Kalola, V.N.; Patel, P.B. Quality by design (QBD): A complete review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2012, 17, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, V.; Thakur, S.; Patil, A.; Shukla, A. Quality by design (QbD) approaches in current pharmaceutical set-up. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 737–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuk, D.-H.; Ha, E.-S.; Ha, D.-H.; Sim, W.-Y.; Lee, S.-K.; Jeong, J.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Baek, I.-h.; Park, H.; Choi, D.H. Development of a resveratrol nanosuspension using the antisolvent precipitation method without solvent removal, based on a quality by design (QbD) approach. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beg, S.; Hasnain, M.S.; Rahman, M.; Swain, S. Introduction to Quality by Design (QbD): Fundamentals, Principles, and Applications. In Pharmaceutical Quality by Design; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Than, Y.M.; Titapiwatanakun, V. Statistical design of experiment-based formulation development and optimization of 3D printed oral controlled release drug delivery with multi target product profile. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Choi, D.H. Quality by design approach to the development of transdermal patch systems and regulatory perspective. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 669–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, D.H.; Park, H.; Ha, E.-S.; Kim, H.-H.; Jang, S.W.; Kim, M.-S. Optimization of bilayer tablet manufacturing process for fixed dose combination of sustained release high-dose drug and immediate release low-dose drug based on quality by design (QbD). Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 605, 120838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, G. Supercritical fluids: Technology and application to food processing. J. Food Eng. 2005, 67, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahena, F.; Zaidul, I.; Jinap, S.; Karim, A.; Abbas, K.; Norulaini, N.; Omar, A. Application of supercritical CO2 in lipid extraction–A review. J. Food Eng. 2009, 95, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Rao, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liao, X. Supercritical carbon dioxide applications in food processing. Food Eng. Rev. 2021, 13, 570–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.W. Modern supercritical fluid technology for food applications. Ann. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.; Mendiola, J.A.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E. Supercritical fluid extraction: Recent advances and applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2495–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rochfort, S.; Isbel, A.; Ezernieks, V.; Elkins, A.; Vincent, D.; Deseo, M.A.; Spangenberg, G.C. Utilisation of design of experiments approach to optimise supercritical fluid extraction of medicinal cannabis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.K.; Mandal, S.C.; Mandal, V.; Beg, S.; Singh, B. QbD as an emerging paradigm in extraction technology for developing optimized bioactives. Pharma Times 2014, 46, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Kamboj, S.; Khurana, R.; Singh, G.; Rana, V. Physicochemical and functional performance of pectin extracted by QbD approach from Tamarindus indica L. pulp. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, I.; Afzal, M.; Quazi, A.M.; Beg, S. Emergence of quality by design in extraction technology for bioactive compounds. In Pharmaceutical Quality by Design; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 379–397. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, T.; Uhlenbrock, L.; Strube, J. Distinct and Quantitative Validation for Predictive Process Modelling in Steam Distillation of Caraway Fruits and Lavender Flower Following a Quality-By-Design (QbD) Approach. Processes 2020, 8, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Abert-Vian, M.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Strube, J.; Uhlenbrock, L.; Gunjevic, V.; Cravotto, G. Green extraction of natural products. Origins, current status, and future challenges. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yver, A.L.; Bonnaillie, L.M.; Yee, W.; McAloon, A.; Tomasula, P.M. Fractionation of whey protein isolate with supercritical carbon dioxide—Process modeling and cost estimation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 240–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weidner, E. High pressure micronization for food applications. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 47, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temelli, F. Perspectives on the use of supercritical particle formation technologies for food ingredients. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 134, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klettenhammer, S.; Ferrentino, G.; Morozova, K.; Scampicchio, M. Novel Technologies Based on Supercritical Fluids for the Encapsulation of Food Grade Bioactive Compounds. Foods 2020, 9, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Couto, R.; Seifried, B.; Moquin, P.; Delgado, L.; Temelli, F. Characterization of oat beta-glucan and coenzyme Q10-loaded beta-glucan powders generated by the pressurized gas-expanded liquid (PGX) technology. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, R.; Seifried, B.; Moquin, P.; Temelli, F. Coenzyme Q10 solubility in supercritical CO2 using a dynamic system. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 24, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Nguyen, H.; Wismer, W.; Temelli, F. Development of an orange-flavoured functional beverage formulated with beta-glucan and coenzyme Q10-impregnated beta-glucan. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.; Seifried, B.; Yépez, B.; Moquin, P.; Temelli, F. Adsorptive precipitation of co-enzyme Q10 on PGX-processed β-glucan powder. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 141, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badens, E.; Masmoudi, Y.; Mouahid, A.; Crampon, C. Current situation and perspectives in drug formulation by using supercritical fluid technology. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 134, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Method | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent evaporation (SE) |
|
| |
| Solvent extraction |
|
|
|
| Spray drying (SD) |
|
|
|
| Coacervation |
|
|
|
| Purpose | Drug | Carrier | Emulsification Method | Emulsion Type | Type of SFEE | Summary | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug delivery system | Microencapsulation for controlled release: for hydrophobic drugs | ||||||
| Indomethacin Ketoprofen | PLGA Eudragit RS | High-speed dispersator for microparticle High-pressure homogenizer for nanoparticle | O(EA)/W | b-SFEE c-SFEE |
| [54] | |
| Piroxicam | PLGA | High-speed stirrer | O(EA)/W | b-SFEE |
| [24] | |
| Piroxicam Diclofenac Na | PLGA | High-speed stirrer Sonication+ high-speed stirrer | O(EA)/W W/O(EA)/W | b-SFEE |
| [43] | |
| NA | PLGA | High-speed stirrer Sonication+ high-speed stirrer | O(EA)/W W/O(EA)/W | c-SFEE-PC |
| [44] | |
| Hydrocortisone | PLGA | Sonication+ high-speed Stirrer High-speed stirrer | W/O(EA)/W S/O(EA)/W | c-SFEE-PC |
| [55] | |
| Microencapsulation for controlled release: for hydrophilic drugs | |||||||
| Lysozyme | PLGA | Homogenizer | W/O(EA)/W S/O(EA)/W In situ S/O(EA)/W | b-SFEE |
| [25] | |
| Insulin | PLGA | Sonication+ high-speed homogenizer | W/O(EA)/W | c-SFEE-PC |
| [56,57] | |
| Bovine serum albumin (BSA) h-IGF | PLGA, PLA | Sonication+ high-speed Stirrer | W/O(EA)/W | c-SFEE-PC |
| [58] | |
| Microencapsulation for controlled release: for the combination of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs | |||||||
| Teriparatide and Gentamicin | PLGA/ Hydroxyapatite/ Chitosan | Sonication+ high-speed Stirrer | O(EA)/W W/O(EA)/W | c-SFEE-PC |
| [59] | |
| NA | PLA, PCL, PLGA | Stirring and ultrasonication | O(Acetone)/W | c-SFEE-PC |
| [60] | |
| NA | Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Vortex mixing | O(Acetone)/W | b-SFEE |
| [61] | |
| NA | PVA | Microfluidic system | O(EA)/W | b-SFEE |
| [15] | |
| Ibuprofen | PVA/Chitosan | Microfluidic system | O(EA)/W | b-SFEE |
| [62] | |
| Medroxy-progesterone acetate | PHBV | Ultrasonication | O(DCM)/W | b-SFEE |
| [63] | |
| Pulmonary drug delivery | |||||||
| Indomethacin Ketoprofen | Solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN) | High-pressure homogenization | O(Chloroform)/W | c-SFEE |
| [64] | |
| Polymeric gene delivery | |||||||
| pFlt23K, pEGFP | PLGA | Sonication | W/O(EA)/W | b-SFEE |
| [65] | |
| Tissue engineering | |||||||
| Growth factor | PLGA/PLA | Ultrasonication and high-speed stirring | W/O(EA)/W | c-SFEE-PC |
| [66] | |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | PLGA | Ultrasonication and high-speed stirring | S/W/O(EA)/W | b-SFEE |
| [67] | |
| Diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A | Poly-methyl-methacrylate (PMMA) | Ultrasonication and high-speed homogenizer | O/O(EA)/W | c-SFEE-PC |
| [68] | |
| Nanoparticles of inorganic materials | |||||||
| TiO2 Nanoparticle | PLA | Sonication and high-speed stirring | S/W(EtOH)/O(EA)/W S/O(EA)/W | c-SFEE-PC |
| [69] | |
| Fe3O4 magnetite | PLGA | Sonicated under magnetic stirring | S/O(DCM)/W | c-SFEE |
| [70] | |
| Solubilization of poorly water-soluble drugs | Cholesterol acetate, Griseofulvin, Megestrol acetate | NA | High-pressure homogenization | O(EA, Toluene, DCM)/W | c-SFEE |
| [71] |
| Physicochemical stabilization | Ketoprofen | PLGA | Hgh-pressure homogenization | O(EA)/W | b-SFEE |
| [72] |
| Solidification of liquid drug | Vitamin E | Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Vortex mixing | O(Acetone+)/W | b-SFEE |
| [73] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, S.; Ha, E.-S.; Kim, M.-S.; Hwang, S.-J. Pharmaceutical Applications of Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions for Micro-/Nanoparticle Formation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111928
Park H, Kim J-S, Kim S, Ha E-S, Kim M-S, Hwang S-J. Pharmaceutical Applications of Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions for Micro-/Nanoparticle Formation. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(11):1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111928
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Heejun, Jeong-Soo Kim, Sebin Kim, Eun-Sol Ha, Min-Soo Kim, and Sung-Joo Hwang. 2021. "Pharmaceutical Applications of Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions for Micro-/Nanoparticle Formation" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 11: 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111928
APA StylePark, H., Kim, J. -S., Kim, S., Ha, E. -S., Kim, M. -S., & Hwang, S. -J. (2021). Pharmaceutical Applications of Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Emulsions for Micro-/Nanoparticle Formation. Pharmaceutics, 13(11), 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111928