Design of a Transdermal Sustained Release Formulation Based on Water-Soluble Ointment Incorporating Tulobuterol Nanoparticles
Abstract
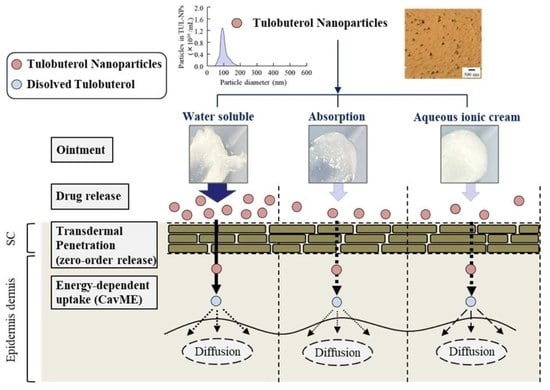
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Preparation of Ointments Incorporating TUL-NPs
2.4. Measurement of TUL Particles
2.5. Drug Solubility of TUL Ointments
2.6. Viscosity of the Ointments
2.7. Stability of the TUL Ointments
2.8. Drug Release from TUL Ointments
2.9. In Vitro Transdermal Penetration of Ointments Incorporating TUL
2.10. Measurement of TUL by HPLC Method
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Ointments Incorporating TUL-NPs
3.2. Drug Release of TUL in WS/TUL, AB/TUL, and AC/TUL Ointments with and without l-Menthol
3.3. Transdermal Delivery of TUL in WS/TUL, AB/TUL, and AC/TUL Ointments with and without l-Menthol
3.4. Effect of Energy-Dependent Endocytosis on Transdermal Pathway of TUL-NPs in Men-WS/TUL-NP Ointment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, S.I.; Kim, B.H. Bioequivalence assessment of tulobuterol transdermal delivery system in healthy subjects. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 56, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Song, C.; Baik, S.; Kim, D.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Device-assisted transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, P.D.; El-Tamimy, M.; Keah, H.H.; Boyd, B.J. Tocopheryl phosphate mixture (TPM) as a novel lipid-based transdermal drug delivery carrier: Formulation and evaluation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mofidfar, M.; O’Farrell, L.; Prausnitz, M.R. Pharmaceutical jewelry: Earring patch for transdermal delivery of contraceptive hormone. J. Control. Release 2019, 301, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwah, H.; Garg, T.; Goyal, A.K.; Rath, G. Permeation enhancer strategies in transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, T.; Kondo, R.; Miyazaki, J.; Fukumokto, K.; Torigoe, H. Clinical evaluation of a transdermal therapeutic system of the beta2-agonist tulobuterol in patients with mild or moderate persistent bronchial asthma. Arzneimittelforschung 2004, 54, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsunuma, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Nagao, M.; Akasawa, A.; Nomura, I.; Yamaoka, A.; Kondo, H.; Masuda, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Terada, A.; et al. Effects of transdermal tulobuterol in pediatric asthma patients on long-term leukotriene receptor antagonist therapy: Results of a randomized, open-label, multicenter clinical trial in japanease children aged 4–12 years. Allergol. Int. 2013, 62, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murakami, Y.; Sekijima, H.; Fujisawa, Y.; Ooi, K. Adjustment of Conditions for Combining Oxybutynin Transdermal Patch with Heparinoid Cream in Mice by Analyzing Blood Concentrations of Oxybutynin Hydrochloride. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McConville, J. Special Focus Issue: Transdermal, Topical and Folicular Drug Delivery Systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.C.; DeLouise, L.A. Nanoparticle-Enabled Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems for Enhanced Dose Control and Tissue Targeting. Molecules 2016, 21, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pegoraro, C.; MacNeil, S.; Battaglia, G. Transdermal drug delivery: From micro to nano. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, D.; Attari, Z.; Reddy, M.S.; Damodaram, A.; Koteshwara, K.B.G. Solid lipid nanoparticles of irbesartan: Preparation, characterization, optimization and pharmacokinetic studies. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 53, e15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montenegro, L.; Lai, F.; Offera, A.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Micicchè, L.; Maccioni, A.M.; Valenti, D.; Fadda, A.M. From nanoemulsions to nanostructured lipid carriers: A relevant development in dermal delivery of drugs and cosmetics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ogata, F.; Deguchi, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Sasaki, H.; Kawasaki, N.; Nagai, N. Energy-Dependent Endocytosis Is Responsible for Skin Penetration of Formulations Based on a Combination of Indomethacin Nanoparticles and l-Menthol in Rat and Göttingen Minipig. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, N.; Ogata, F.; Yamaguchi, M.; Fukuoka, Y.; Otake, H.; Nakazawa, Y.; Kawasaki, N. Combination with l-Menthol Enhances Transdermal Penetration of Indomethacin Solid Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagai, N.; Ogata, F.; Otake, H.; Nakazawa, Y.; Kawasaki, N. Design of a transdermal formulation containing raloxifene nanoparticles for osteoporosis treatment. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 5215–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otake, H.; Goto, R.; Ogata, F.; Isaka, T.; Kawasaki, N.; Kobayakawa, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Nagai, N. Fixed-Combination Eye Drops Based on Fluorometholone Nanoparticles and Bromfenac/Levofloxacin Solution Improve Drug Corneal Penetration. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 5343–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, N.; Ogata, F.; Otake, H.; Nakazawa, Y.; Kawasaki, N. Energy-dependent endocytosis is responsible for drug transcorneal penetration following the instillation of ophthalmic formulations containing indomethacin nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, N.; Ito, Y.; Okamoto, N.; Shimomura, Y. A nanoparticle formulation reduces the corneal toxicity of indomethacin eye drops and enhances its corneal permeability. Toxicology 2014, 319, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, N.; Iwamae, A.; Tanimoto, S.; Yoshioka, C.; Ito, Y. Pharmacokinetics and Antiinflammatory Effect of a Novel Gel System Containing Ketoprofen Solid Nanoparticles. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mäger, I.; Langel, K.; Lehto, T.; Eiríksdóttir, E.; Langel, U. The role of endocytosis on the uptake kinetics of luciferin-conjugated cell-penetrating peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malomouzh, A.I.; Mukhitov, A.R.; Proskurina, S.E.; Vyskocil, F.; Nikolsky, E.E. The effect of dynasore, a blocker of dynamin-dependent endocytosis, on spontaneous quantal and non-quantal release of acetylcholine in murine neuromuscular junctions. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2014, 459, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.L.; Oh, C.; Ahn, S.H.; Choi, J.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Choi, I.S.; Song, C.S.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y. Inhibition of endocytosis of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus by rottlerin and its potential prophylactic administration in piglets. Antivir. Res. 2021, 195, 105191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wen, J.; Sharma, M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Topical Drug Delivery: Mechanisms, Dosage Form Perspectives, and Translational Status. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 3203–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.A.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Ibrahim, F.; Samy, A.M.; Fetoh, E.; Nutan, M.T. In vitro release, rheological, and stability studies of mefenamic acid coprecipitates in topical formulations. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2011, 16, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, M.; Otake, H.; Nakazawa, Y.; Okamoto, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Sasaki, H.; Nagai, N. Balance of Drug Residence and Diffusion in Lacrimal Fluid Determine Ocular Bioavailability in In Situ Gels Incorporating Tranilast Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, N.; Isaka, T.; Deguchi, S.; Minami, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Otake, H.; Okamoto, N.; Nakazawa, Y. In Situ Gelling Systems Using Pluronic F127 Enhance Corneal Permeability of Indomethacin Nanocrystals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, A.; Salatin, S.; Jafari, S.; Mahmoudian, M.; Jelvehgari, M. The Factors Determining the Skin Penetration and Cellular Uptake of Nanocarriers: New Hope for Clinical Development. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 4315–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, N.; Ito, Y. Therapeutic effects of gel ointments containing tranilast nanoparticles on paw edema in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaplun-Frischoff, Y.; Touitou, E. Testosterone skin permeation enhancement by menthol through formation of eutectic with drug and interaction with skin lipids. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunta, J.R.; Goskonda, V.R.; Brotherton, H.O.; Khan, M.A.; Reddy, I.K. Effect of menthol and related terpenes on the percutaneous absorption of propranolol across excised hairless mouse skin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Kim, J.; Herrera, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Kabanov, A.V.; Sahay, G. Brief update on endocytosis of nanomedicines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimeno-Benito, I.; Giusti, A.; Dekkers, S.; Haase, A.; Janer, G. A review to support the derivation of a worst-case dermal penetration value for nanoparticles. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 119, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderem, A.; Underhill, D.M. Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 593–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, L.; Sun, J.; Zhai, Y.; He, Z. The endocytosis and intracellular fate of nanomedicines: Implication for rational design. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rappoport, J. Focusing on clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Biochem. J. 2008, 412, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Byrne, J.D.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. More effective nanomedicines through particle design. Small 2011, 7, 1919–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Lykotrafitis, G.; Bao, G.; Suresh, S. Size-Dependent Endocytosis of Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2008, 21, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Ointment | Content (%w/w) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS/TUL | Men-WS/TUL | AB/TUL | Men-AB/TUL | AC/TUL | Men-AC/TUL | |
| TUL | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| MC | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| HPβCD | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| PEG 4000 | 43.8 | 43.8 | - | - | - | - |
| PEG 400 | 43.8 | 43.8 | - | - | - | |
| Cetyl alcohol | 0.4 | 0.4 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 15 | 15 |
| Mineral oil | - | - | 56 | 56 | - | - |
| White wax | - | - | 12 | 12 | - | - |
| Sodium tetraborate | - | - | 0.5 | 0.5 | - | - |
| Propylene glycol | - | - | - | - | 10 | 10 |
| Beeswax | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2 |
| l-menthol | - | 2 | - | 2 | - | 2 |
| Distilled water ad. | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Ointment | Mean Particle Size (μm) | Solubility (μM) | Viscosity (mPa∙s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS/TUL | WS/TUL-MP | 28.0 ± 0.31 | 139 ± 7.9 | 1476 ± 83 |
| WS/TUL-NP | 0.113 ± 0.0038 | 192 ± 9.3 *,# | 710 ± 47 *,# | |
| Men-WS/TUL-MP | 27.5 ± 0.29 | 139 ± 8.5 | 1466 ± 86 | |
| Men-WS/TUL-NP | 0.113 ± 0.0033 | 193 ± 9.0 *,# | 747 ± 45 *,# | |
| AB/TUL | AB/TUL-MP | 28.3 ± 0.32 | 112 ± 6.9 | 79.6 ± 7.8 |
| AB/TUL-NP | 0.119 ± 0.0038 | 189 ± 9.2 *,# | 76.3 ± 7.9 | |
| Men-AB/TUL-MP | 27.7 ± 0.29 | 113 ± 8.1 | 77.5 ± 7.9 | |
| Men-AB/TUL-NP | 0.116 ± 0.0035 | 185 ± 8.8 *,# | 70.2 ± 8.4 | |
| AC/TUL | AC/TUL-MP | 29.2 ± 0.36 | 116 ± 6.8 | 599 ± 37 |
| AC/TUL-NP | 0.110 ± 0.0039 | 186 ± 7.9 *,# | 597 ± 35 | |
| Men-AC/TUL-MP | 28.1 ± 0.28 | 120 ± 7.0 | 606 ± 39 | |
| Men-AC/TUL-NP | 0.112 ± 0.0036 | 188 ± 9.1 *,# | 605 ± 38 | |
| Ointment | Jc (×10−2 μmol/cm2/h) | Kp (×10−3 cm/h) | Km | τ (h) | D (×10−3 cm2/h) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS/TUL | WS/TUL-MP | 0.09 ± 0.01 # | 0.13 ± 0.01 # | 0.01 ± 0.01 # | 0.09 ± 0.03 # | 0.25 ± 0.17 # |
| WS/TUL-NP | 0.10 ± 0.02 # | 0.14 ± 0.02 # | 0.01 ± 0.01 # | 1.17 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 # | |
| Men-WS/TUL-MP | 0.62 ± 0.10 * | 0.85 ± 0.14 * | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 1.01 ± 0.07 | 0.83 ± 0.05 * | |
| Men-WS/TUL-NP | 2.79 ± 0.49 *,# | 3.82 ± 0.68 *,# | 0.36 ± 0.07 *,# | 1.13 ± 0.02 | 0.74 ± 0.02 * | |
| AB/TUL | AB/TUL-MP | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.10 ± 0.07 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.43 | 3.70 ± 2.11 |
| AB/TUL-NP | 0.11 ± 0.08 | 0.16 ± 0.11 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.14 | 3.65 ± 2.08 | |
| Men-AB/TUL-MP | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.15 | 5.86 ± 3.15 | |
| Men-AB/TUL-NP | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.05 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.39 ± 0.18 | 9.36 ± 4.62 | |
| AC/TUL | AC/TUL-MP | 0.12 ± 0.06 | 0.16 ± 0.09 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.08 # | 3.66 ± 1.59 # |
| AC/TUL-NP | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.28 ± 0.19 # | 2.24 ± 1.58 # | |
| Men-AC/TUL-MP | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 * | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.83 ± 0.29 * | 13.49 ± 5.54 *, | |
| Men-AC/TUL-NP | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 * | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.75 ± 0.14 * | 11.19 ± 5.15 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagai, N.; Ogata, F.; Deguchi, S.; Fushiki, A.; Daimyo, S.; Otake, H.; Kawasaki, N. Design of a Transdermal Sustained Release Formulation Based on Water-Soluble Ointment Incorporating Tulobuterol Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112431
Nagai N, Ogata F, Deguchi S, Fushiki A, Daimyo S, Otake H, Kawasaki N. Design of a Transdermal Sustained Release Formulation Based on Water-Soluble Ointment Incorporating Tulobuterol Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(11):2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112431
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagai, Noriaki, Fumihiko Ogata, Saori Deguchi, Aoi Fushiki, Saki Daimyo, Hiroko Otake, and Naohito Kawasaki. 2022. "Design of a Transdermal Sustained Release Formulation Based on Water-Soluble Ointment Incorporating Tulobuterol Nanoparticles" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 11: 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112431
APA StyleNagai, N., Ogata, F., Deguchi, S., Fushiki, A., Daimyo, S., Otake, H., & Kawasaki, N. (2022). Design of a Transdermal Sustained Release Formulation Based on Water-Soluble Ointment Incorporating Tulobuterol Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics, 14(11), 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112431