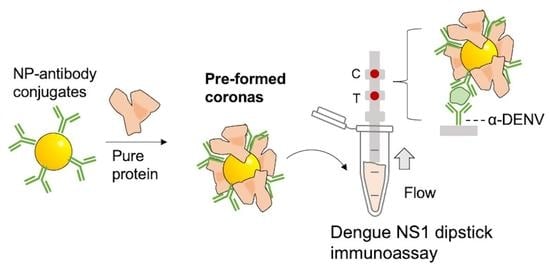
The Influence of Preforming Protein Coronas on the Performance of Dengue NS1 Immunoassays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gold NP Synthesis
2.2. Immunoprobe (NP–Ab Conjugate) Preparation
2.3. Running Immunoassays
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. LOD KD Analysis
2.6. Protein Corona Formation and Analysis
2.6.1. Protein Corona Formation
2.6.2. Protein Corona Detachment from AuNP
2.6.3. Tryptic Digestion of the Detached Protein for Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.7. MS Data Analysis with Proteome Discoverer 2.4
3. Results
3.1. Synthesizing NP–Antibody Conjugates
3.2. Protein Corona Characterization
3.3. Effect of Preformed Coronas of Pure Proteins
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hristov, D.; Rijal, H.; Jose, G.-M.; Hamad, K. Developing a Paper-Based Antigen Assay to Differentiate Between Coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2 Spike Variants. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7825–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Puig Guixé, H.; Bosch, I.; Gehrke, L.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Challenges of the nano-bio interface in lateral flow and dipstick immunoassays. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraca, F.; Boselli, L.; Castagnola, V.; Dawson, K.A. Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticle Cellular Uptake: Influence of Transient Bionano Interactions. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 3800–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, P.C.; Lin, S.; Parak, W.J.; Davis, T.P.; Caruso, F. A Decade of the Protein Corona. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11773–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Cedervall, T.; Berggård, T.; Flanagan, M.B.; Lynch, I.; Elia, G.; Dawson, K. The Evolution of the Protein Corona around Nanoparticles: A Test Study. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7503–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, S.; Schöttler, S.; Kotman, N.; Baier, G.; Musyanovych, A.; Kuharev, J.; Landfester, K.; Schild, H.; Jahn, O.; Tenzer, S.; et al. Protein Corona of Nanoparticles: Distinct Proteins Regulate the Cellular Uptake. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, L.; Warrington, J.; Rogan, J.; Rothwell, D.G.; Brady, G.; Dive, C.; Kostarelos, K.; Hadjidemetriou, M. The biomolecule corona of lipid nanoparticles contains circulating cell-free DNA. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaguera, C.; Guerra-Rebollo, M.; Lázaro, M.Á.; Cascante, A.; Rubio, N.; Blanco, J.; Borrós, S. In Vivo Retargeting of Poly(beta aminoester) (OM-PBAE) Nanoparticles is Influenced by Protein Corona. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Rao, L.; Yu, G.; Cook, T.R.; Chen, X.; Huang, F. Supramolecular cancer nanotheranostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 2839–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, B.; Zhou, J.; Lu, H.; Zhang, H.; Huang, F.; Wang, H. Controlling Intracellular Enzymatic Self-Assembly of Peptide by Host–Guest Complexation for Programming Cancer Cell Death. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 7588–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Puig, H.; Bosch, I.; Carre-Camps, M.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Effect of the protein corona on antibody-antigen binding in nanoparticle sandwich immunoassays. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hristov, D.; Pimentel, A.J.; Ujialele, G.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. The immunoprobe aggregation state is central to dipstick immunoassay performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34620–34629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehnal, D.; Bittrich, S.; Deshpande, M.; Svobodová, R.; Berka, K.; Bazgier, V.; Velankar, S.; Burley, S.K.; Koča, J.; Rose, A.S. Mol* Viewer: Modern web app for 3D visualization and analysis of large biomolecular structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W431–W437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borhani, D.W.; Rogers, D.P.; Engler, J.A.; Brouillette, C.G. Crystal structure of truncated human apolipoprotein A-I suggests a lipid-bound conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12291–12296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugio, S.; Kashima, A.; Mochizuki, S.; Noda, M.; Kobayashi, K. Crystal structure of human serum albumin at 2.5 Å resolution. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1999, 12, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monath, T.P. Dengue: The risk to developed and developing countries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2395–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dengue. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dengue/index.html (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Watanabe, S.; Tan, K.H.; Rathore, A.P.S.; Rozen-Gagnon, K.; Shuai, W.; Ruedl, C.; Vasudevan, S.G. The Magnitude of Dengue Virus NS1 Protein Secretion Is Strain Dependent and Does Not Correlate with Severe Pathologies in the Mouse Infection Model. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5508–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Quijada, C.; Gomez-Marquez, J.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Repurposing old antibodies for new diseases by exploiting cross reactivity and multicolored nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 6626–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.O.; de Puig, H.; Yen, C.-w.; Bosch, I.; Gómez-Márquez, J.; Clavet, C.; Hamad-Schifferli, K.; Gehrke, L. A Comparison of Nanoparticle-Antibody Conjugation Strategies in Sandwich Immunoassays. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2017, 38, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Quijada, C.; de Puig Guixé, H.; Sanchez-Purra, M.; Yelleswarapu, C.; Evans, J.; Celli, J.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Protease degradation of protein coronas and its impact on cancer cells and drug payload release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14588–14596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkey, C.D.; Olsen, J.B.; Song, F.; Liu, R.; Guo, H.; Olsen, D.W.H.; Cohen, Y.; Emili, A.; Chan, W.C.W. Protein Corona Fingerprinting Predicts the Cellular Interaction of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2439–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Buhler, E.; Boué, F.; Carn, F. How does the size of gold nanoparticles depend on citrate to gold ratio in Turkevich synthesis? Final answer to a debated question. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 492, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Brown, K.A.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Changes in Oligonucleotide Conformation on Nanoparticle Surfaces by Modification with Mercaptohexanol. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1925–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelov, B.; Angelova, A. Nanoscale clustering of the neurotrophin receptor TrkB revealed by super-resolution STED microscopy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 9797–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanali, G.; di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Marino, M.; Fasano, M.; Ascenzi, P. Human serum albumin: From bench to bedside. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 209–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, M.; Curry, S.; Terreno, E.; Galliano, M.; Fanali, G.; Narciso, P.; Notari, S.; Ascenzi, P. The extraordinary ligand binding properties of human serum albumin. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Carter, D.C. Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature 1992, 358, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahley, R.W.; Innerarity, T.L.; Rall, S.C.; Weisgraber, K.H. Plasma lipoproteins: Apolipoprotein structure and function. J. Lipid Res. 1984, 25, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, D.P.; de Dreu, A.; Hofstraat, S.R.J.; Kluza, E.; Zwolsman, R.; Deckers, J.; Anbergen, T.; de Bruin, K.; Trines, M.M.; Nugraha, E.G.; et al. Nanoengineering Apolipoprotein A1-Based Immunotherapeutics. Adv. Ther. 2021, 4, 2100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Tanimura, M.; Luo, C.C.; Datta, S.; Chan, L. The apolipoprotein multigene family: Biosynthesis, structure, structure-function relationships, and evolution. J. Lipid Res. 1988, 29, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G.J.; Puntes, V. Time Evolution of the Nanoparticle Protein Corona. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cifuentes-Rius, A.; de Puig Guixé, H.; Kah, J.C.Y.; Borros, S.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Optimizing the properties of the protein corona surrounding nanoparticles for payload release. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10066–10074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciaurriz, P.; Bravo, E.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Effect of architecture on the activity of glucose oxidase/horseradish peroxidase/carbon nanoparticle conjugates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 414, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Abundance | Protein | % Abundance |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Albumin | 52.1% |
| 2 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | 7.5% |
| 3 | Apolipoprotein A-I | 3.9% |
| 4 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 | 3.8% |
| 5 | Immunoglobulin gamma-1 heavy chain | 3.8% |
| 6 | Methylguanosine phosphate-specific 5′-nucleotidase | 2.8% |
| 7 | Immunoglobulin kappa constant | 2.5% |
| 8 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 | 2.0% |
| 9 | Serotransferrin | 1.7% |
| 10 | Carabin | 1.4% |
| 11 | Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin | 1.3% |
| 12 | Glial fibrillary acidic protein | 0.9% |
| 13 | Haptoglobin | 0.9% |
| 14 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | 0.8% |
| 15 | Complement C3 | 0.6% |
| 16 | Transthyretin | 0.6% |
| 17 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant alpha 1 | 0.6% |
| 18 | Apolipoprotein A-II | 0.6% |
| 19 | Hemopexin | 0.5% |
| 20 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 2 | 0.5% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rijal, H.; Goggin, L.; Muriph, R.; Evans, J.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. The Influence of Preforming Protein Coronas on the Performance of Dengue NS1 Immunoassays. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112439
Rijal H, Goggin L, Muriph R, Evans J, Hamad-Schifferli K. The Influence of Preforming Protein Coronas on the Performance of Dengue NS1 Immunoassays. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(11):2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112439
Chicago/Turabian StyleRijal, Hom, Laura Goggin, Rachel Muriph, Jason Evans, and Kimberly Hamad-Schifferli. 2022. "The Influence of Preforming Protein Coronas on the Performance of Dengue NS1 Immunoassays" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 11: 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112439
APA StyleRijal, H., Goggin, L., Muriph, R., Evans, J., & Hamad-Schifferli, K. (2022). The Influence of Preforming Protein Coronas on the Performance of Dengue NS1 Immunoassays. Pharmaceutics, 14(11), 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112439