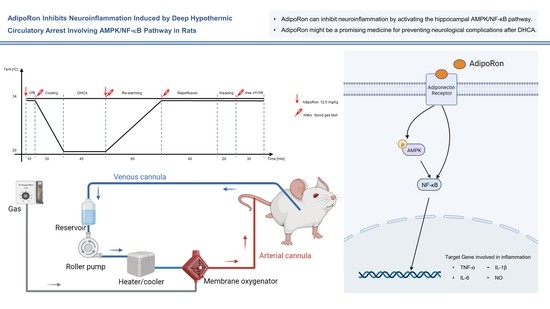
AdipoRon Inhibits Neuroinflammation Induced by Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest Involving the AMPK/NF-κB Pathway in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Cardiac Surgery with CPB/DHCA
2.3. Proteomic Analysis of Hippocampus Based on Tandem Mass Tags (TMT)
2.4. Drug Treatment
2.5. Blood Gas Analysis
2.6. BV2 Cell Culture
2.7. Immunostaining of Hippocampus
2.8. Western Blots
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.10. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.11. Nitric Oxide Production Measurement
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Adiponectin Receptor 1 Protein Was Upregulated after DHCA
3.2. Effects of AdipoRon on Physiological Parameters during CPB with DHCA
3.3. AdipoRon Has an Anti-Inflammatory Effect in Rats
3.4. AdipoRon Inhibited Neuroinflammation Following DHCA Involving AMPK Phosphorylation and NF-κB Downregulation
3.5. AdipoRon Attenuates Neuroinflammation in BV2 Cells
3.6. AdipoRon Inhibits Neuroinflammation in BV2 Cells via Activating AMPK Protein and Downregulating NF-κB Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vuylsteke, A.; Sharples, L.; Charman, G.; Kneeshaw, J.; Tsui, S.; Dunning, J.; Wheaton, E.; Klein, A.; Arrowsmith, J.; Hall, R.; et al. Circulatory arrest versus cerebral perfusion during pulmonary endarterectomy surgery (PEACOG): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Du, S.; Chen, S.; Zheng, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Zheng, S. The role of deep hypothermic circulatory arrest in surgery for renal or adrenal tumor with vena cava thrombus: A single-institution experience. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Le, S.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Wu, J.; Song, Y.; Xie, F.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Incidence, Risk Factors and Outcomes of Postoperative Headache After Stanford Type a Acute Aortic Dissection Surgery. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 781137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centola, L.; Kanamitsu, H.; Kinouchi, K.; Fuji, Y.; Ito, H.; Maeda, K.; Beckman, R.; Ma, X.; Hanley, F.L.; Riemer, R.K. Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest Activates Neural Precursor Cells in the Neonatal Brain. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 110, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroudis, C.D.; Karlsson, M.; Ko, T.; Hefti, M.; Gentile, J.I.; Morgan, R.W.; Plyler, R.; Mensah-Brown, K.G.; Boorady, T.W.; Melchior, R.W.; et al. Cerebral mitochondrial dysfunction associated with deep hypothermic circulatory arrest in neonatal swine. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2018, 54, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, S. Severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome in patients following Total aortic arch replacement with deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 14, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Stone, G.W.; Holmes, D.R.; Gersh, B. Reperfusion injury, microvascular dysfunction, and cardioprotection: The “dark side” of reperfusion. Circulation 2009, 120, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engels, M.; Bilgic, E.; Pinto, A.; Vasquez, E.; Wollschläger, L.; Steinbrenner, H.; Kellermann, K.; Akhyari, P.; Lichtenberg, A.; Boeken, U. A cardiopulmonary bypass with deep hypothermic circulatory arrest rat model for the investigation of the systemic inflammation response and induced organ damage. J. Inflamm. 2014, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jungwirth, B.; Mackensen, G.B.; Blobner, M.; Neff, F.; Reichart, B.; Kochs, E.F.; Nollert, G. Neurologic outcome after cardiopulmonary bypass with deep hypothermic circulatory arrest in rats: Description of a new model. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006, 131, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Liu, L.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Y. Risk factors of cerebral complications after Stanford type A aortic dissection undergoing arch surgery. Asian J. Surg. 2022, 45, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada-Iwabu, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Honma, T.; Hamagami, K.; Matsuda, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tanabe, H.; Kimura-Someya, T.; Shirouzu, M.; et al. A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Nature 2013, 503, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, W.L.; Scherer, P.E. Cell Biology. Ronning after the adiponectin receptors. Science 2013, 342, 1460–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenke, A.; Yazdanyar, M.; Miyahara, S.; Chekhoeva, A.; Immohr, M.B.; Kistner, J.; Boeken, U.; Lichtenberg, A.; Akhyari, P. AdipoRon Attenuates Inflammation and Impairment of Cardiac Function Associated With Cardiopulmonary Bypass-Induced Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e018097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, E.; Daniele, A.; Salzillo, A.; Ragone, A.; Naviglio, S.; Sapio, L. AdipoRon and Other Adiponectin Receptor Agonists as Potential Candidates in Cancer Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragone, A.; Salzillo, A.; Spina, A.; Naviglio, S.; Sapio, L. Integrating Gemcitabine-Based Therapy With AdipoRon Enhances Growth Inhibition in Human PDAC Cell Lines. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 837503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramzan, A.A.; Bitler, B.G.; Hicks, D.; Barner, K.; Qamar, L.; Behbakht, K.; Powell, T.; Jansson, T.; Wilson, H. Adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon induces apoptotic cell death and suppresses proliferation in human ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 461, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapio, L.; Nigro, E.; Ragone, A.; Salzillo, A.; Illiano, M.; Spina, A.; Polito, R.; Daniele, A.; Naviglio, S. AdipoRon Affects Cell Cycle Progression and Inhibits Proliferation in Human Osteosarcoma Cells. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 7262479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, R.C.; Jian, M.; Ma, O.K.; Bunting, M.; Kwan, J.S.; Zhou, G.J.; Senthilkumar, K.; Iyaswamy, A.; Chan, P.K.; Li, M.; et al. Chronic oral administration of adipoRon reverses cognitive impairments and ameliorates neuropathology in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5669–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, T.; Ueta, T.; Honjo, M.; Aihara, M. The Neuroprotective Effect of the Adiponectin Receptor Agonist AdipoRon on Glutamate-Induced Cell Death in Rat Primary Retinal Ganglion Cells. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 35, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Xiang, H.; Li, A.; Lin, W.; Huang, Z.; Guo, J.; Wang, P.; Chi, Y.; Xiang, K.; Xu, Y.; et al. Activating Adiponectin Signaling with Exogenous AdipoRon Reduces Myelin Lipid Accumulation and Suppresses Macrophage Recruitment after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2019, 36, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Sun, Z.; Liang, F.; Xu, W.; Lu, J.; Shi, L.; Shao, A.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J. AdipoRon Attenuates Neuroinflammation After Intracerebral Hemorrhage Through AdipoR1-AMPK Pathway. Neuroscience 2019, 412, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, C.; Bucci, I.; Napolitano, G. The Role of the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor-kappa B in Thyroid Autoimmunity and Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Yan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.; Ji, B. A novel target to reduce microglial inflammation and neuronal damage after deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 159, 2431–2444.e2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraj, S.; Torok, N.; Dasu, M.R.; Samols, D.; Jialal, I. Adiponectin decreases C-reactive protein synthesis and secretion from endothelial cells: Evidence for an adipose tissue-vascular loop. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Li, P.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Leak, R.K.; Chen, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J. Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics reveal novel mechanism of injury expansion after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2012, 43, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Chu, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, Z.; Chen, N. Neuroinflammatory In Vitro Cell Culture Models and the Potential Applications for Neurological Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 671734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, F.A.; MacKintosh, C.; Hardie, D.G. AMP-activated protein kinase: A cellular energy sensor that comes in 12 flavours. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2987–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, G.; You, Y.; Li, H.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, M.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, H.; Xu, Q.L.; Dai, L.; Wang, P.; et al. Discovery of AdipoRon analogues as novel AMPK activators without inhibiting mitochondrial complex I. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 200, 112466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Lin, W. The Function of NF-Kappa B During Epilepsy, a Potential Therapeutic Target. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 851394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, S.; Ertel, A.; Engel, K.M.; Simon, J.C.; Saalbach, A. Overexpression of S100A9 in obesity impairs macrophage differentiation via TLR4-NFkB-signaling worsening inflammation and wound healing. Theranostics 2022, 12, 1659–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Sun, Y. Safflower Yellow B Protects Brain against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury through AMPK/NF-kB Pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2019, 2019, 7219740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, D.; Shi, Y.; Gong, Z.; Xia, T.; Ren, H.; He, D.; Yang, J.; Han, Y.; Zeng, C. AdipoRon, an adiponectin receptor agonist, protects contrast-induced nephropathy by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via activation of the AMPK pathway. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2020, 24, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Muraguchi, M.; et al. Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NF-kappaB signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. Circulation 2000, 102, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.; Karin, M. Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 693–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Soldano, S.; Contini, P.; Sulli, A.; Seriolo, B.; Montagna, P.; Brizzolara, R. Intracellular NF-kB-decrease and IKBα increase in human macrophages following CTLA4-Ig treatment. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2013, 31, 943–946. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushworth, S.A.; Zaitseva, L.; Murray, M.Y.; Shah, N.M.; Bowles, K.M.; MacEwan, D.J. The high Nrf2 expression in human acute myeloid leukemia is driven by NF-κB and underlies its chemo-resistance. Blood 2012, 120, 5188–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Lei, Y.Q.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, Z.C.; Cao, H. Triptolide improves neurobehavioral functions, inflammation, and oxidative stress in rats under deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. Aging 2021, 13, 3031–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaha, M.M.; Helal, M.G.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Said, E.; Salem, H.A. Diacerein versus adipoRon as adiponectin modulators in experimentally-induced end-stage type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 90, 103806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatorski, H.; Salaga, M.; Zielińska, M.; Majchrzak, K.; Binienda, A.; Kordek, R.; Małecka-Panas, E.; Fichna, J. AdipoRon, an Orally Active, Synthetic Agonist of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 Receptors Has Gastroprotective Effect in Experimentally Induced Gastric Ulcers in Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, S.; Cazareth, J.; Zarif, H.; Guyon, A.; Heurteaux, C.; Chabry, J.; Petit-Paitel, A. Globular Adiponectin Limits Microglia Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype through an AdipoR1/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, R.; Lau, W.B.; Yuan, Y.X.; Liang, B.; Li, R.; Gao, E.H.; Koch, W.J.; Ma, X.L.; et al. AdipoRon, the first orally active adiponectin receptor activator, attenuates postischemic myocardial apoptosis through both AMPK-mediated and AMPK-independent signalings. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E275–E282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.G.; Liu, C.L.; Yan, H.J. AdipoRon improves cognitive dysfunction of Alzheimer’s disease and rescues impaired neural stem cell proliferation through AdipoR1/AMPK pathway. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 327, 113249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, K.P.; Huang, J.S.; Wang, Z.C.; Hong, Z.N. Resveratrol attenuates neuroinflammation after deep hypothermia with circulatory arrest in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 155, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lei, Y.Q.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, Z.C.; Cao, H. Beneficial effects of chlorogenic acid treatment on neuroinflammation after deep hypothermic circulatory arrest may be mediated through CYLD/NF-κB signaling. Brain Res. 2021, 1767, 147572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, W.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, J.; Liu, G.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, S.; Ji, B. AdipoRon Inhibits Neuroinflammation Induced by Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest Involving the AMPK/NF-κB Pathway in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112467
Yan W, Gao S, Zhang Q, Qi J, Liu G, Teng Y, Wang J, Yan S, Ji B. AdipoRon Inhibits Neuroinflammation Induced by Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest Involving the AMPK/NF-κB Pathway in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(11):2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112467
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Weidong, Sizhe Gao, Qiaoni Zhang, Jiachen Qi, Gang Liu, Yuan Teng, Jian Wang, Shujie Yan, and Bingyang Ji. 2022. "AdipoRon Inhibits Neuroinflammation Induced by Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest Involving the AMPK/NF-κB Pathway in Rats" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 11: 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112467
APA StyleYan, W., Gao, S., Zhang, Q., Qi, J., Liu, G., Teng, Y., Wang, J., Yan, S., & Ji, B. (2022). AdipoRon Inhibits Neuroinflammation Induced by Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest Involving the AMPK/NF-κB Pathway in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 14(11), 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112467