Simultaneous Physico-Mechanical and In Vivo Assessment towards Factual Skin Performance Profile of Topical Polymeric Film-Forming Systems
Abstract
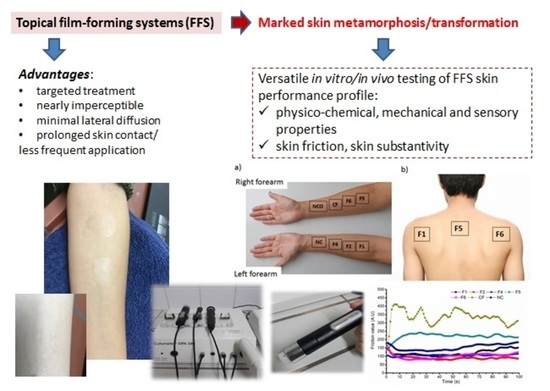
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polymeric FFS
2.3. Screening of Physico-Chemical, Mechanical and Sensory Properties
2.3.1. Drying Time
2.3.2. Sensory Properties
2.3.3. Film Thickness
2.3.4. Spreadability
2.3.5. Flexibility/Mechanical Resistance
2.3.6. pH Value of the FFS
2.4. In Vivo Skin Performance Studies
2.4.1. Subjects
2.4.2. Study Protocols
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preformulation Study
3.2. Physico-Mechanical and Sensory Profiling
3.3. In Vivo Skin Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frederiksen, K.; Guy, R.H.; Petersson, K. Formulation considerations in the design of topical, polymeric film-forming systems for sustained drug delivery to the skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 91, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Yu, X.; Shao, W.; Guo, P.; Cao, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xu, Y. Co-delivery of terbinafine hydrochloride and urea with an in situ film-forming system for nail targeting treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurdo Schroeder, I.; Franke, P.; Schaefer, U.F.; Lehr, C.M. Development and characterization of film forming polymeric solutions for skin drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asasutjarit, R.; Sookdee, P.; Veeranondha, S.; Fuongfuchat, A.; Itharat, A. Application of film-forming solution as a transdermal delivery system of piperine-rich herbal mixture extract for anti-inflammation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodratti, A.; Alexandridis, P. Amphiphilic block copolymers in drug delivery: Advances in formulation structure and performance. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 1085–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, C.G.M.; Selmin, F.; Franze, S.; Musazzi, U.M.; Quaroni, G.M.G.; Casiraghi, A.; Cilurzo, F. A glimpse in critical attributes to design cutaneous film forming systems based on ammonium methacrylate. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunter, D.J.; Daniels, R. In vitro skin permeation and penetration of nonivamide from novel film-forming emulsions. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2013, 26, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunter, D.J.; Rottke, M.; Daniels, R. Oil in oil emulsions with enhanced substantivity for the treatment of chronic skin diseases. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottke, M.; Lunter, D.J.; Daniels, R. In vitro studies on release and skin permeation of nonivamide from oil-in-oil-emulsions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunter, D.J.; Daniels, R. New film forming emulsions containing Eudragit NE and/or RS 30D for sustained dermal delivery of nonivamide. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, H.O.; Ghorab, M.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Makram, T.S.; Ghoneim, A.M. Rapid pain relief using transdermal film forming polymeric solution of ketorolac. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilurzo, F.; Selmin, F.; Gennari, C.G.M.; Montanari, L.; Minghetti, P. Application of methyl methacrylate copolymers to the development of transdermal or loco-regional drug delivery systems. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvie-Cook, H.; Frederiksen, K.; Petersson, K.; Guy, R.H.; Gordeev, S. Characterization of topical film-forming systems using Atomic force microscopy and Raman microspectroscopy. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). CHMP/QWP/708282/2018 Draft Guideline on Quality and Equivalence of Topical Products. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). 2018. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/quality-equivalence-topical-products (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Sanchez-Ballester, N.M.; Bataille, B.; Benabbas, R.; Alonso, B.; Soulairol, I. Development of alginate esters as novel multifunctional excipients for direct compression. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederiksen, K.; Guy, R.H.; Petersson, K. The potential of polymeric film-forming systems as sustained delivery platforms for topical drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surber, C.; Knie, U. Metamorphosis of Vehicles: Mechanisms and Opportunities. In pH of the Skin: Issues and Challenges; Surber, C., Abels, C., Maibach, H., Eds.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, A.; Padula, C.; Nicoli, S.; Pescina, S.; Santi, P. The role of vehicle metamorphosis on triamcinolone acetonide delivery to the skin from microemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danby, S.G.; Draelos, Z.D.; Gold, L.F.S.; Cha, A.; Vlahos, B.; Aikman, L.; Sanders, P.; Wu-Linhares, D.; Cork, M.J. Vehicles for atopic dermatitis therapies: More than just a placebo. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2020, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, M.O.; Maia Campos, P.M.B.G. Application of biophysical and skin imaging techniques to evaluate the film-forming effect of cosmetic formulations. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2019, 41, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.K.; Butarbutar, M.; Sriwidodo, S.; Wathoni, N. Film-forming sprays for topical drug delivery. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 2909–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). 2813:2014; Paints and Varnishes—Determination of gloss value at 20°, 60°, and 85°. 4th ed. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–23.
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). D3359-17; Standard Test Methods for Measuring Adhesion by Tape Test. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). D523-14; Standard Test Method for Specular Gloss. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). D1005-95; Standard Test Method for Measurement of Dry-Film Thickness of Organic Coatings Using Micrometers. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Siepmann, J.; Faham, A.; Clas, S.D.; Boyd, B.J.; Jannin, V.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Zhao, H.; Lecommandoux, S.; Evans, J.C.; Allen, C.; et al. Lipids and polymers in pharmaceutical technology: Lifelong companions. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 558, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqil, M.; Ali, A.; Sultana, Y.; Najmi, A.K. Fabrication and evaluation of polymeric films for transdermal delivery of pinacidil. Pharmazie 2004, 59, 631–635. [Google Scholar]
- Zayed, G.M.; Rasoul, S.A.E.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Saddik, M.S.; Alshora, D.H. In vitro and in vivo characterization of domperidone-loaded fast dissolving buccal films. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidberger, M.; Nikolic, I.; Pantelic, I.; Lunter, D. Optimization of Rheological Behaviour and Skin Penetration of Thermogelling Emulsions with Enhanced Substantivity for Potential Application in Treatment of Chronic Skin Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatelain, E.; Gabard, B.; Surber, C. Skin penetration and sun protection factor of five UV filters: Effect of the vehicle. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 2003, 16, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodduturi, S.; Manek, R.V.; Kolling, W.M.; Stodghill, S.P.; Repka, M.A. Water vapor sorption of hot-melt extruded hydroxypropyl cellulose films: Effect on physico-mechanical properties, release characteristics, and stability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 3047–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, S.H.; Shen, C.J.; Shen, C.F.; Cheng, C.M. Role of pH Value in Clinically Relevant Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- KlucelTM Hydroxypropylcellulose. Physical and Chemical Properties. 2012. Available online: https://www.ashland.com/search?chemistry=Cellulosics (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Ghoshal, S.; Denner, P.; Stapf, S.; Mattea, C. Study of the Formation of Poly(vinyl alcohol) Films. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 1913–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Yokota, M.; Maibach, H.I. In vitro human skin model to evaluate water permeability and determine wound dressings’ occlusivity. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2007, 26, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monica, L.L.; Jordi, G.; Francisco, F.C. In situ bioadhesive film-forming system for topical delivery of mometasone furoate: Characterization and biopharmaceutical properties. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, E.; Picard, C.; Savary, G. Complementary approaches to understand the spreading behavior on skin of O/W emulsions containing different emollients. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 193, 111132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, E.; Picard, C.; Savary, G. Spreading behavior of cosmetic emulsions: Impact of oil phase. Biotribology 2018, 16, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pailler-Mattei, C.; Nicoli, S.; Pirot, F.; Vargiolu, R.; Zahouani, H. A new approach to describe the skin surface physical properties in vivo. Colloids Surf. B 2009, 68, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojumdar, E.H.; Pham, Q.D.; Topgaard, D.; Sparr, E. Skin hydration: Interplay between molecular dynamics, structure and water uptake in the stratum corneum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Function | Constituents | (%, w/w) |
|---|---|---|
| Polymer or combination of polymers | Eudragit® RS | 8.5–19.0 |
| Eudragit® NE 30 D | 5.0–10.0 | |
| Klucel® GF | 2.5–5.0 | |
| Eudragit® RS/Klucel® GF | 4/1 | |
| Plasticizer/penetration enhancer | TEC 1 | 20 * |
| TBC 2 | 20 * | |
| Propylene glycol | 20 * | |
| Glycerol | 20 * | |
| MCT 3 | 20 * | |
| Polysorbate 80 | 0.3–3 | |
| Solvent or mixture of solvents | Propylene glycol/EtOH 4/water 5 | 1–5/73.4–92.4/1.3–12.7 |
| EtOH/water | 73.4–86.0/3.3–8.2 | |
| Isopropyl alcohol/water | 73.0–87.5/3.3–12.7 | |
| EtOH/water/ethyl acetate | 74.0/10.6/1 |
| Excipients | Composition (%, w/w) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | |
| Eudragit® RS PO | 8.5 | 10.0 | 17.5 | − | − | 4.0 |
| Eudragit® NE 30 D | − | − | − | − | 6.0 | − |
| Klucel® GF | − | − | − | 3.5 | − | 1.0 |
| TEC 1 | − | 2.0 | − | − | − | − |
| MCT 2 | − | − | − | 0.7 | − | − |
| Propylene glycol | 1.0 | − | 3.5 | − | − | 0.5 |
| EtOH 3 | 86.7 | 84.7 | 73.4 | 95.8 | − | 92.9 |
| Isopropyl alcohol | − | − | − | − | 85.0 | − |
| Polysorbate 80 | 1.0 | − | − | − | − | 0.3 |
| Water 4 up to | 100 | 100 | 100 | − | 100 | 100 |
| Formulation | Drying Time of the Film (32.0 ± 0.1 °C) (min) | Drying Time of the Film (25 ± 2 °C) (min) | Film Surface (mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 6.6 ± 0.4 a | 24.0 ± 0.6 e | 223.0 ± 21.2 d |
| F2 | 4.6 ± 0.1 b | 32.0 ± 2.5 f | 121.0 ± 2.0 d |
| F3 | 5.3 ± 0.2 c | 22.0 ± 2.0 e | 79.0 ± 1.5 g |
| F4 | 13.5 ± 0.9 d | 40.0 ± 0.6 d | 24.0 ± 1.2 d |
| F5 | 6.3 ± 0.6 a | 48.0 ± 1.5 d | 72.0 ± 5.2 g |
| F6 | 4.6 ± 0.4 b | 32.0 ± 2.0 f | 83.0 ± 1.5 g |
| Formulation | Folding Endurance Value | Film Thickness (mm) | pH Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 112.0 ± 2.9 a | 0.007 ± 0.002 f | 6.9 ± 0.1 g |
| F2 | 54.0 ± 3.2 b | 0.021 ± 0.001 d | 6.1 ± 0.1 d |
| F3 | 95.0 ± 1.5 c | 0.096 ± 0.002 d | 6.7 ± 0.1 e |
| F4 | 78.0 ± 1.5 c | 0.046 ± 0.001 d | 8.3 ± 0.1 d |
| F5 | 56.0 ± 3.5 b | 0.011 ± 0.002 d | 7.5 ± 0.1 d |
| F6 | 105.0 ± 9.0 e | 0.033 ± 0.003 f | 6.6 ± 0.1 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Timotijević, M.D.; Ilić, T.; Savić, S.; Pantelić, I. Simultaneous Physico-Mechanical and In Vivo Assessment towards Factual Skin Performance Profile of Topical Polymeric Film-Forming Systems. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020223
Timotijević MD, Ilić T, Savić S, Pantelić I. Simultaneous Physico-Mechanical and In Vivo Assessment towards Factual Skin Performance Profile of Topical Polymeric Film-Forming Systems. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(2):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020223
Chicago/Turabian StyleTimotijević, Mirjana D., Tanja Ilić, Snežana Savić, and Ivana Pantelić. 2022. "Simultaneous Physico-Mechanical and In Vivo Assessment towards Factual Skin Performance Profile of Topical Polymeric Film-Forming Systems" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 2: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020223
APA StyleTimotijević, M. D., Ilić, T., Savić, S., & Pantelić, I. (2022). Simultaneous Physico-Mechanical and In Vivo Assessment towards Factual Skin Performance Profile of Topical Polymeric Film-Forming Systems. Pharmaceutics, 14(2), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020223