Skin Barrier Function in Infants: Update and Outlook
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Skin Structure and Function
2.1. Epidermis
2.2. Dermal-Epidermal Junction
2.3. Dermis
3. Infant Skin Maturation
3.1. Structure and Composition
3.2. Function
3.2.1. Cell Turnover
3.2.2. Hydration and Water-holding Capacity
3.2.3. Immunological Barrier
3.2.4. pH
3.2.5. Photoprotection
3.2.6. Sebaceous Activity
3.2.7. Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL)
4. Percutaneous Absorption in Infants
4.1. Surface Area
4.2. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
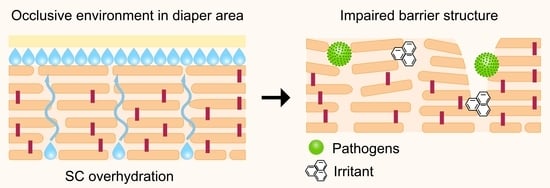
4.3. Use of Diapers
5. Appropriate Care of the Diaper Area
6. Skin Cleansing of the Diaper Area
6.1. Baby Wipes
6.2. Formulation of Baby Wipes
6.2.1. Water
6.2.2. Preservatives
6.2.3. Surfactants
6.2.4. Emollients
6.2.5. pH Buffering Compounds
6.3. Post-Cleansing Barrier-Repair Creams
7. Safety Concerns of Repeated Exposure to Baby Wipes
7.1. Diaper Dermatitis (DD)
7.2. Atopic Dermatitis (AD)
8. Challenges and Opportunities
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- West, D.P.; Worobec, S.; Solomon, L.M. Pharmacology and toxicology of infant skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1981, 76, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stamatas, G.N.; Nikolovski, J.; Mack, M.C.; Kollias, N. Infant skin physiology and development during the first years of life: A review of recent findings based on in vivo studies. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 33, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, N.; Hadgraft, J.; Rutter, N. Skin permeability in the newborn. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1987, 88, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiou, Y.B.; Blume-Peytavi, U. Stratum corneum maturation. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2004, 17, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammarlund, K.; Sedin, G. Transepidermal water loss in newborn infants: III. Relation to gestational age. Acta Paediatr. 1979, 68, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harpin, V.; Rutter, N. Barrier properties of the newborn infant’s skin. J. Pediatr. 1983, 102, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, D.P.; Halket, J.M.; Harvey, D.R.; Hadgraft, J.; Solomon, L.M.; Harper, J.I. Percutaneous absorption in preterm infants. Fetal Neonatal Investig. Rep. 1987, 4, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggett, P.G.; Cooper, L.V.; Ellis, S.H.; McAinsh, J. Percutaneous absorption of chlorhexidine in neonatal cord care. Arch. Dis. Child. 1981, 56, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aitken, J.; Williams, F.L. A systematic review of thyroid dysfunction in preterm neonates exposed to topical iodine. Arch. Dis. Child. 2014, 99, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpin, V.; Rutter, N. Percutaneous alcohol absorption and skin necrosis in a preterm infant. Arch. Dis. Child. 1982, 57, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormack, J.J.; Boisits, E.K.; Fisher, L.B. An in vitro comparison of the permeability of adult versus neonatal skin. In Neonatal Skin: Structure and Function; Maibach, H.I., Boisits, E.K., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 149–166. [Google Scholar]
- Fairley, J.A.; Rasmussen, J.E. Comparison of stratum corneum thickness in children and adults. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1983, 8, 652–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolovski, J.; Stamatas, G.N.; Kollias, N.; Wiegand, B.C. Barrier function and water-holding and transport properties of infant stratum corneum are different from adult and continue to develop through the first year of life. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, F.; Martella, A.; Bertoni, L.; Seidenari, S. Skin barrier, hydration, and pH of the skin of infants under 2 years of age. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2001, 18, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schade, H.; Marchionini, A. Der säuremantel der haut (nach gaskettenmessungen). Klin. Wochenschr. 1928, 7, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, R.K.; Bush, R.D.; Ruebusch, N.A. Corneocytes Undergo Systematic Changes in Element Concentrations Across the Human Inner Stratum Corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmid-Wendtner, M.H.; Korting, H.C. The pH of the Skin Surface and Its Impact on the Barrier Function. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 19, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothman, S. pH of sweat and skin surface. In Physiology and Biochemistry of the Skin; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1954; pp. 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lemper, M.; De Paepe, K.; Rogiers, V.; Adam, R. Baby Care Products. In Handbook of Cosmetic Science and Technology, 3rd ed.; Barel, A.O., Paye, M., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Informa Healthcare: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 613–621. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, J.; Eady, R.; Pope, F. Anatomy and organization of human skin. In Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 3.2–3.80. [Google Scholar]
- Visscher, M.O. Update on the use of topical agents in neonates. Newborn Infant. Nurs. Rev. 2009, 9, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K.; Mukherjee, S.; Chandar, P. Stratum corneum fatty acids: Their critical role in preserving barrier integrity during cleansing. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, P.M. Epidermal lipids, barrier function, and desquamation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1983, 80, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, P.W.; van den Bergh, B. The physical, chemical and functional properties of lipids in the skin and other biological barriers. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1998, 91, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R. Thematic review series: Skin lipids. The role of epidermal lipids in cutaneous permeability barrier homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 2531–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Candi, E.; Schmidt, R.; Melino, G. The cornified envelope: A model of cell death in the skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. 2005, 6, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oranges, T.; Dini, V.; Romanelli, M. Skin physiology of the neonate and infant: Clinical implications. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rawlings, A.V.; Matts, P.J. Stratum corneum moisturization at the molecular level: An update in relation to the dry skin cycle. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burgeson, R.E.; Christiano, A.M. The dermal-epidermal junction. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluhr, J.W.; Darlenski, R.; Taieb, A.; Hachem, J.P.; Baudouin, C.; Msika, P.; De Belilovsky, C.; Berardesca, E. Functional skin adaptation in infancy—Almost complete but not fully competent. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeger, P.H.; Schreiner, V.; Klaassen, I.A.; Enzmann, C.C.; Friedrichs, K.; Bleck, O. Epidermal barrier lipids in human vernix caseosa: Corresponding ceramide pattern in vernix and fetal skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 146, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haubrich, K.A. Role of vernix caseosa in the neonate: Potential application in the adult population. Am. Assoc. Crit.-Care Nurses Clin. Issues 2003, 14, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, M.I.B.; Wickett, R.R.; Visscher, M.O.; Pickens, W.L.; Hoath, S.B. Characterization of Vernix Caseosa as a Natural Biofilm: Comparison to Standard Oil-Based Ointments. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2000, 17, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.; Downe, S.; Gomez, L. Skin care in the well term newborn: Two systematic reviews. Birth 2005, 32, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Pregnancy, Childbirth, Postpartum, and Newborn Care: A Guide for Essential Practice; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatas, G.N.; Nikolovski, J.; Luedtke, M.A.; Kollias, N.; Wiegand, B.C. Infant skin microstructure assessed in vivo differs from adult skin in organization and at the cellular level. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2010, 27, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitellaro-Zuccarello, L.; Cappelletti, S.; Dal Pozzo Rossi, V.; Sari-Gorla, M. Stereological analysis of collagen and elastic fibers in the normal human dermis: Variability with age, sex, and body region. Anat. Rec. 1994, 238, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, R.A. Pediatric Dermatology, 4th ed.; Schachner, L.A., Hansen, R.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, C. Newborn skin care. In Cosmetic Dermatology; Baran, R., Maibach, H., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 1994; pp. 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Hardman, M.J.; Byrne, C. Skin structural development. In Neonatal Skin: Structure and Function, 2nd ed.; Hoath, S.B., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeger, P.H.; Enzmann, C.C. Skin physiology of the neonate and young infant: A prospective study of functional skin parameters during early infancy. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2002, 19, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, D.; Matts, P.J.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. Variation of Stratum Corneum Biophysical and Molecular Properties with Anatomic Site. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, D.; Marks, R. The Determination of Regional and Age Variations in the Rate of Desquamation: A Comparison of Four Techniques. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1980, 74, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machado, M.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. Assessment of the variation of skin barrier function with anatomic site, age, gender and ethnicity. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2010, 32, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.; Salgado, T.M.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. The relationship between transepidermal water loss and skin permeability. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 384, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogiers, V. EEMCO Guidance for the Assessment of Transepidermal Water Loss in Cosmetic Sciences. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 2001, 14, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, M.O.; Chatterjee, R.; Munson, K.A.; Pickens, W.L.; Hoath, S.B. Changes in diapered and nondiapered infant skin over the first month of life. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2000, 17, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijo, S.; Tagami, H. Dry skin of newborn infants: Functional analysis of the stratum corneum. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1991, 8, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, K.; Dowd, S.; Stamatas, G.; Nikolovski, J. Survey of bacterial diversity on infant skin over the first year of life. In Journal of Investigative Dermatology; Nature Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. AB3. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatas, G.N.; Tierney, N.K. Update on infant skin with special focus on dryness and the impact of moisturizers. In Treatment of Dry Skin Syndrome; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 295–310. [Google Scholar]
- Wanke, I.; Steffen, H.; Christ, C.; Krismer, B.; Götz, F.; Peschel, A.; Schaller, M.; Schittek, B. Skin commensals amplify the innate immune response to pathogens by activation of distinct signaling pathways. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parra, J.L.; Paye, M. EEMCO Guidance for the in vivo Assessment of Skin Surface pH. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 2003, 16, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrendt, H.; Green, M. Skin pH Pattern in the Newborn Infant. AMA J. Dis. Child. 1958, 95, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yosipovitch, G.; Maayan-Metzger, A.; Merlob, P.; Sirota, L. Skin barrier properties in different body areas in neonates. Pediatrics 2000, 106, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, R. Skin care of the diaper area. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2008, 25, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludriksone, L.; Bartels, N.G.; Kanti, V.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Kottner, J. Skin barrier function in infancy: A systematic review. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deraison, C.; Bonnart, C.; Lopez, F.; Besson, C.; Robinson, R.; Jayakumar, A.; Wagberg, F.; Brattsand, M.; Hachem, J.P.; Leonardsson, G. LEKTI fragments specifically inhibit KLK5, KLK7, and KLK14 and control desquamation through a pH-dependent interaction. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 3607–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hachem, J.P.; Man, M.Q.; Crumrine, D.; Uchida, Y.; Brown, B.E.; Rogiers, V.; Roseeuw, D.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M. Sustained serine proteases activity by prolonged increase in pH leads to degradation of lipid processing enzymes and profound alterations of barrier function and stratum corneum integrity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matousek, J.L.; Campbell, K.L. A comparative review of cutaneous pH. Vet. Dermatol. 2002, 13, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, T.; Holleran, W.M.; Grayson, S.; Gao, W.N.; Man, M.Q.; Kriehuber, E.; Behne, M.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M. Barrier recovery is impeded at neutral pH, independent of ionic effects: Implications for extracellular lipid processing. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1998, 290, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, G.K.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M. Lamellar Body Secretory Response to Barrier Disruption. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 98, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouwstra, J.; Dubbelaar, F.; Gooris, G.; Ponec, M. The lipid organisation in the skin barrier. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2000, 208, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Holleran, W.M.; Takagi, Y.; Imokawa, G.; Jackson, S.; Lee, J.M.; Elias, P.M. β-Glucocerebrosidase activity in murine epidermis: Characterization and localization in relation to differentiation. J. Lipid Res. 1992, 33, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M.C.; Tierney, N.K.; Ruvolo, E.; Stamatas, G.N.; Martin, K.M.; Kollias, N. Development of Solar UVR-Related Pigmentation Begins as Early as the First Summer of Life. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2335–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moise, A.F.; Harrison, S.L.; Gies, H.P. Solar ultraviolet radiation exposure of infants and small children. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 1999, 15, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.S.; Hawk, J.L.M.; Honig, P.; Giam, Y.C.; Hoath, S.; Mack, M.C.; Stamatas, G.N. New Insights About Infant and Toddler Skin: Implications for Sun Protection. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Fimmel, S.; Ortmann, J.; Turnbull, J.R.; Boschnakow, A.; Pochi, P. Sebaceous glands. In Neonatal Skin: Structure and Function, 2nd ed.; Hoath, S.B., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 59–87. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, C.A.; Taylor, J.; Cunliffe, W.J. Sebum excretion rates in mothers and neonates. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 142, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agache, P.; Blanc, D.; Barrand, C.; Laurent, R. Sebum levels during the first year of life. Br. J. Dermatol. 1980, 103, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasastry, P.; Downing, D.T.; Pochi, P.E.; Strauss, J.S. Chemical Composition of Human Skin Surface Lipids from Birth to Puberty. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1970, 54, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J.C.; Hartman, D.G.; Garofalo, M.J.; Basehoar, A.; Raynor, B.; Ashbrenner, E.; Akin, F.J. Comparison of closed chamber and open chamber evaporimetry. Skin Res. Technol. 2009, 15, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardesca, E.; Loden, M.; Serup, J.; Masson, P.; Rodrigues, L.M. The revised EEMCO guidance for the in vivo measurement of water in the skin. Skin Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhof, R.E.; De Jesus, M.E.P.; Xiao, P.; Ciortea, L.I.; Berg, E.P. Closed-chamber transepidermal water loss measurement: Microclimate, calibration and performance. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 31, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Charro, M.B.; Guy, R.H. Effective use of transdermal drug delivery in children. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 73, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AvRuskin, T.W.; Greenfield, E.; Prasad, V.; Greig, F.; Juan, C.S. Decreased T3 and T4 levels following topical application of povidone-iodine in premature neonates. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 7, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, M.; Carson, D.; Hetherton, A.M.; Symth, P.; Leslie, H. Hypothyroidism secondary to topical iodine treatment in infants with spina bifida. Acta Paediatr. 1994, 83, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoath, S.B.; Maibach, H.I. Neonatal Skin: Structure and Function; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bernauer, U.; Bodin, L.; Chaudhry, Q.; Coenraads, P.J.; Dusinska, M.; Ezendam, J.; Gaffet, E.; Galli, C.L.; Granum, B.; Panteri, E.; et al. The SCCS Notes of Guidance for the testing of cosmetic ingredients and their safety evaluation, 11th revision, 30–31 March 2021, SCCS/1628/21. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 127, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Reflection Paper: Formulations of Choice for the Paediatric Population. EMEA/CHMP/PEG/194810/2005. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/reflection-paper-formulations-choice-paediatric-population_en.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- West, D.P.; Heath, C.; Cameron Haley, A.; Mahoney, A.; Micali, G. Principles of Paediatric Dermatological Therapy. In Harper’s Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Renwick, A. Toxicokinetics in infants and children in relation to the ADI and TDI. Food Addit. Contam. 1998, 15, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorne, J. Impact of inter-individual differences in drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics on safety evaluation. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 18, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorne, J.; Walton, K.; Renwick, A. Human variability in xenobiotic metabolism and pathway-related uncertainty factors for chemical risk assessment: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klunk, C.; Domingues, E.; Wiss, K. An update on diaper dermatitis. Clin. Dermatol. 2014, 32, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, D.; Gennery, A.; Cant, A. The neonate. In Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 66–114. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, N.; Rutter, N. Development of the epidermis in the newborn. Neonatology 1986, 49, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton, D.J. Understanding irritant napkin dermatitis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruseler-van Embden, J.G.H.; Van Lieshout, L.M.C.; Smits, S.A.; Van Kessel, I.; Laman, J.D. Potato tuber proteins efficiently inhibit human faecal proteolytic activity: Implications for treatment of peri-anal dermatitis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 34, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, R.W.; Buckingham, K.W.; Stewart, R.L. Etiologic Factors in Diaper Dermatitis: The Role of Urine. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1986, 3, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, P.H.; Bucher, A.P.; Saeed, I.; Lee, P.C.; Davis, J.A.; Maibach, H.I. Faecal enzymes: In vivo human skin irritation. Contact Dermat. 1994, 30, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonezawa, K.; Haruna, M.; Shiraishi, M.; Matsuzaki, M.; Sanada, H. Relationship between skin barrier function in early neonates and diaper dermatitis during the first month of life: A prospective observational study. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014, 31, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, R.W.; Milligan, M.C.; Sarbaugh, F.C. Association of skin wetness and pH with diaper dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1994, 11, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, L. Clinical correlates with diaper dermatitis. Pediatrician 1987, 14, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Bouyer, G.; Toga, M.; Lebreton, R.; Stolley, P.; Lockhart, J. Outbreak of accidental hexachlorophene poisoning in France. Lancet 1982, 319, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concannon, P.; Gisoldi, E.; Phillips, S.; Grossman, R. Diaper dermatitis: A therapeutic dilemma—Results of a double-blind placebo controlled trial of miconazole nitrate 0.25%. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2001, 18, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelmetti, C. Skin cleansing in children. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2001, 15, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlin, C.C.; Frieden, I.J.; Eichenfield, L.F. Clinical approaches to skin cleansing of the diaper area: Practice and challenges. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavender, T.; Furber, C.; Campbell, M.; Victor, S.; Roberts, I.; Bedwell, C.; Cork, M.J. Effect on skin hydration of using baby wipes to clean the napkin area of newborn babies: Assessor-blinded randomised controlled equivalence trial. BMC Pediatr. 2012, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procter & Gamble. Data on File; Procter & Gamble Company: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Technavio. Wet Tissue and Wipe Market by Application, Distribution Channel, Technology, and Geography-Forecast & Analysis 2021–2025. Available online: https://www.technavio.com/report/wet-tissue-and-wipe-market-industry-analysis (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Vongsa, R.; Rodriguez, K.; Koenig, D.; Cunningham, C. Benefits of using an appropriately formulated wipe to clean diapered skin of preterm infants. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2019, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, K.J.; Cunningham, C.; Foxenberg, R.; Hoffman, D.; Vongsa, R. The science behind wet wipes for infant skin: Ingredient review, safety, and efficacy. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2020, 37, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehretsmann, C.; Schaefer, P.; Adam, R. Cutaneous tolerance of baby wipes by infants with atopic dermatitis, and comparison of the mildness of baby wipe and water in infant skin. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2001, 15, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odio, M.; Streicher-Scott, J.; Hansen, R.C. Disposable baby wipes: Efficacy and skin mildness. Dermatol. Nurs. 2001, 13, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, R.; Schnetz, B.; Mathey, P.; Pericoi, M.; de Prost, Y. Clinical demonstration of skin mildness and suitability for sensitive infant skin of a new baby wipe. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2009, 26, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, M.; Odio, M.; Taylor, T.; White, T.; Sargent, S.; Sluder, L.; Smith, L.; Flower, T.; Mason, B.; Rider, M.; et al. Skin care in the NICU patient: Effects of wipes versus cloth and water on stratum corneum integrity. Neonatology 2009, 96, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Bartels, N.; Massoudy, L.; Scheufele, R.; Dietz, E.; Proquitté, H.; Wauer, R.; Bertin, C.; Serrano, J.; Blume-Peytavi, U. Standardized diaper care regimen: A prospective, randomized pilot study on skin barrier function and epidermal IL-1α in newborns. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2012, 29, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume-Peytavi, U.; Lavender, T.; Jenerowicz, D.; Ryumina, I.; Stalder, J.F.; Torrelo, A.; Cork, M.J. Recommendations from a European roundtable meeting on best practice healthy infant skin care. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2016, 33, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Medicines Agency. Annex to the European Commission Guideline on ‘Excipients in the Labelling and Package Leaflet of Medicinal Products for Human Use’ (SANTE-2017-11668). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/annexeuropean-%20commission-guidelineexcipients-%20labelling-package-leafletmedicinal-%20products-human (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Blume-Peytavi, U.; Hauser, M.; Lunnemann, L.; Stamatas, G.N.; Kottner, J.; Garcia Bartels, N. Prevention of diaper dermatitis in infants—A literature review. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014, 31, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippke, F.; Schreiner, V.; Schwanitz, H.J. The acidic milieu of the horny layer. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 3, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, P.; Gliksberg, A.; Cohen, M.; Tzafrir, I.; Ziklo, N. Why are wet wipes so difficult to preserve? Understanding the intrinsic causes. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on the Quality of Water for Pharmaceutical Use. EMA/CHMP/CVMP/QWP/496873/2018. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-quality-water-pharmaceutical-use_en.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- US Food and Drug Administration. Water for Pharmaceutical Use. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/inspections-compliance-enforcement-and-criminal-investigations/inspection-technical-guides/water-pharmacuetical-use (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- United States Pharmacopeia. USP 43-NF 38. In Chapter <1231> Water for Pharmaceutical Purposes; United States Pharmacopeia: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- The European Pharmacopoeia. Monograph 0008. In Purified Water; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hamann, C.R.; Sahni, S.; Zug, K.A. Methylisothiazolinone: Still on Leave-on Products, but No Longer on Baby Wipes. Dermatitis 2019, 30, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varvaresou, A.; Papageorgiou, S.; Tsirivas, E.; Protopapa, E.; Kintziou, H.; Kefala, V.; Demetzos, C. Self-preserving cosmetics. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 31, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Treat, J.; Chaney, K.; Brod, B. Potential allergens in disposable diaper wipes, topical diaper preparations, and disposable diapers: Under-recognized etiology of pediatric perineal dermatitis. Dermatitis 2016, 27, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirwas, M.J.; Hamann, D.; Warshaw, E.M.; Maibach, H.I.; Taylor, J.S.; Sasseville, D.; DeKoven, J.G.; Fransway, A.F.; Mathias, C.G.T.; Zug, K.A.; et al. Epidemic of isothiazolinone allergy in North America: Prevalence data from the North American contact dermatitis group, 2013–2014. Dermatitis 2017, 28, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.W.; Nakrani, R. Six children with allergic contact dermatitis to methylisothiazolinone in wet wipes (baby wipes). Pediatrics 2014, 133, e434–e438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cahill, J.L.; Toholka, R.W.; Nixon, R.L. Methylisothiazolinone in baby wipes: A rising star among causes of contact dermatitis. Med. J. Aust. 2014, 200, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanedo-Tardana, M.P.; Zug, K.A. Methylisothiazolinone. Dermatitis 2013, 24, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárány, E.; Lindberg, M.; Lodén, M. Unexpected skin barrier influence from nonionic emulsifiers. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 195, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K.; Moore, D.J.; Subramanyan, K.; Misra, M.; Meyer, F. Cleansing without compromise: The impact of cleansers on the skin barrier and the technology of mild cleansing. Dermatol. Ther. 2004, 17, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.; Mundschau, S.; Seidling, J.; Wenzel, S. Baby care. In The Chemistry and Manufacture of Cosmetics, 2nd ed.; Schlossman, M., Ed.; Allured: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 1063–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, C.T.; Seidling, J.R.; Kroll, L.M.; Mundschau, S.A. Stable Emulsion for Prevention of Skin Irritation and Articles Using Same. EP2866784B1, 21 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, A.A. Non-Wovens with High Interfacial Pore Size and Method of Making Same. EP2193230B1, 29 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Draelos, Z.D. The science behind skin care: Cleansers. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, F.A. Annual review of cosmetic ingredient safety assessments: 2007–2010. Int. J. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 73S–127S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton, D.J. A review of the pathophysiology, prevention and treatment of irritant diaper dermatitis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2004, 20, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinfeld, N. Diaper Dermatitis: A Review and Brief Survey of Eruptions of the Diaper Area. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2005, 6, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Bartels, N.; Lunnemann, L.; Stroux, A.; Kottner, J.; Serrano, J.; Blume-Peytavi, U. Effect of diaper cream and wet wipes on skin barrier properties in infants: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014, 31, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, J.; McCall, E.; Kent, B. Clinical effectiveness of barrier preparations in the prevention and treatment of nappy dermatitis in infants and preschool children of nappy age. Int. J. Evid.-Based Healthc. 2008, 6, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, W.; Gloor, M. Effect of topically applied dexpanthenol on epidermal barrier function and stratum corneum hydration. Arzneimittelforschung 2000, 50, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wananukul, S.; Limpongsanuruk, W.; Singalavanija, S.; Wisuthsarewong, W. Comparison of dexpanthenol and zinc oxide ointment with ointment base in the treatment of irritant diaper dermatitis from diarrhea: A multicenter study. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2006, 89, 1654–1658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolff, H.H.; Kieser, M. Hamamelis in children with skin disorders and skin injuries: Results of an observational study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2007, 166, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiko, Y.; Tomikawa, M.; Shimizu, M. Enzymatic conversion of pantothenylalcohol to pantothenic acid. J. Vitam. 1969, 15, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slyshenkov, V.S.; Rakowska, M.; Moiseenok, A.G.; Wojtczak, L. Pantothenic acid and its derivatives protect Ehrlich ascites tumor cells against lipid peroxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E.; Nissen, H.P. Dexpanthenol enhances skin barrier repair and reduces inflammation after sodium lauryl sulphate-induced irritation. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2002, 13, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telofski, L.S.; Morello, A.P.; Mack Correa, M.C.; Stamatas, G.N. The Infant Skin Barrier: Can We Preserve, Protect, and Enhance the Barrier? Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 198789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, D. The aetiology and management of irritant diaper dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2001, 15, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, C.C.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Frieden, I.J. Diaper Dermatitis: Clinical Characteristics and Differential Diagnosis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014, 31, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamatas, G.N.; Tierney, N.K. Diaper Dermatitis: Etiology, Manifestations, Prevention, and Management. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalat, S.; Wall, D.; Goodyear, H. Diaper Dermatitis-Frequency and Contributory Factors in Hospital Attending Children. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2007, 24, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatas, G.N.; Zerweck, C.; Grove, G.; Martin, K.M. Documentation of Impaired Epidermal Barrier in Mild and Moderate Diaper Dermatitis In Vivo Using Noninvasive Methods. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2011, 28, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenfield, L.F.; Bogen, M.L. Absorption and efficacy of miconazole nitrate 0.25% ointment in infants with diaper dermatitis. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 2007, 6, 522–526. [Google Scholar]
- Felter, S.P.; Carr, A.N.; Zhu, T.; Kirsch, T.; Niu, G. Safety evaluation for ingredients used in baby care products: Consideration of diaper rash. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 90, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckers, I.A.G.; McLean, S.; Linssen, S.; Mommers, M.; van Schayck, C.P.; Sheikh, A. Investigating International Time Trends in the Incidence and Prevalence of Atopic Eczema 1990-2010: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanifin, J.M.; Rajka, G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1980, 92, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Linde, Y.W. Dry skin in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. Suppl. 1992, 177, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, J.; Maibach, H. The correlation between transepidermal water loss and percutaneous absorption: An overview. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turpeinen, M.; Salo, O.; Leisti, S. Effect of percutaneous absorption of hydrocortisone on adrenocortical responsiveness in infants with severe skin disease. Br. J. Dermatol. 1986, 115, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpeinen, M. Influence of age and severity of dermatitis on the percutaneous absorption of hydrocortisone in children. Br. J. Dermatol. 1988, 118, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, H.; Lloyd, K.; Williams, H.; Arkwright, P.D.; Brown, T.; Clark, C.; Campbell, M.; Gore, C.; Hardman, C.; Langford, A.; et al. Emollients, education and quality of life: The RCPCH care pathway for children with eczema. Arch. Dis. Child. 2011, 96, i19–i24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudney, P.D.A.; Mélot, M.; Caspers, P.J.; van der Pol, A.; Puppels, G.J. An In Vivo Confocal Raman Study of the Delivery of Trans-Retinol to the Skin. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 61, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pot, L.M.; Coenraads, P.-J.; Blömeke, B.; Puppels, G.J.; Caspers, P.J. Real-time detection of p-phenylenediamine penetration into human skin by in vivo Raman spectroscopy. Contact Dermat. 2016, 74, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, F.; Caspers, P.J.; Puppels, G.J.; Lane, M.E. Franz Cell Diffusion Testing and Quantitative Confocal Raman Spectroscopy: In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Iliopoulos, F.; Caspers, P.J.; Puppels, G.J.; Lane, M.E. In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation in Dermal Delivery: The Role of Excipients. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatas, G.N.; Bensaci, J.; Greugny, E.; Kaur, S.; Wang, H.; Dizon, M.V.; Cork, M.J.; Friedman, A.J.; Oddos, T. A Predictive Self-Organizing Multicellular Computational Model of Infant Skin Permeability to Topically Applied Substances. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 2049–2055.e2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Category | Definition |
|---|---|
| Neonatal/newborn | the first 4 week after birth |
| Infancy | the whole first year after birth |
| Full-term infants | infants born between 37th–42nd week of gestation age |
| Preterm infants | infants born before the 37th week of gestation age |
| Low birth-weight infants | infants born with a birth weight of lower than 2.5 kg |
| Parameters | Properties |
|---|---|
| Structure | |
| Epidermis—cell size | Smaller corneocytes and keratinocytes [2] |
| Epidermis—surface | Higher density of skin microrelief network [2] |
| Epidermis—thickness | SC: 30% thinner [36]; Epidermis: 20% thinner [2] |
| Dermis—organization | More homogenous dermal papilla [2]; Extensive but disorganized vascular network [37]; Lower density of collagen fiber bundles [37] |
| Composition | |
| NMF | Lower [13] |
| Melanin | Lower [38] |
| Water | Lower at birth, gradually increasing throughout the first year [2] |
| Function | |
| Cell turnover | Higher [2] |
| Hydration and water-holding capacity | Lower hydration at birth, peaks between 3–12 months [13]; lower water holding capacity [2] |
| Immunological barrier | Epidermal LC are not fully mature [38] |
| pH | Higher [2] |
| Photoprotection | Melanocytes are not fully mature [38] |
| Sebaceous activity | Higher at birth; decreases drastically within the first few days [27] |
| TEWL | Higher at birth, gradually decreases throughout the first few years [38] |
| Parameters | Properties |
|---|---|
| Blood-brain barrier | Less developed |
| Conjugation reactions | Lower rate |
| Cytochrome P450 biotransformation | Lower rate |
| Glomerular filtration | Lower rate |
| Liver mass | Higher |
| Plasma protein binding | Lower |
| Water content per body weight | Higher |
| Parameter | Findings | Subject | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | pH was comparable ** in both groups | Newborns (n = 280) | [98] |
| Higher * skin pH in water-and-cloth group | Infants (n = 15) | [105] | |
| pH was comparable ** in both groups | Newborns (n = 44) | [107] | |
| Hydration | Skin hydration was comparable ** in both groups | Newborns (n = 280) | [98] |
| Skin hydration was comparable ** in both groups | Newborns (n = 44) | [107] | |
| TEWL | TEWL was comparable ** in both groups | Newborns (n = 280) | [98] |
| Lower * TEWL in baby wipes group | Newborns (n = 44) | [107] | |
| Erythema | Erythema score around genitals, perianal area, and buttock was comparable* in both groups; lower* erythema score around the skin folds in baby wipes group | Infants (n = 102) | [103] |
| lower * erythema score in baby wipes group | Preterm infants (n = 130) | [106] | |
| lower * erythema score around perianal area in baby wipes group | Infants (n = 82) | [104] | |
| IL-1α expression was comparable ** in both groups | Newborns (n = 44) | [107] |
| Ingredient | Rationale | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Water | As the vehicle for the cleansing ingredients [102] | Highly purified [102] |
| Preservatives | To prevent microbial growth in the products [102] | Should not alter the normal cutaneous microbiome; use only regulator-approved ingredients [108] |
| Surfactants | Water alone is ineffective in removing water-insoluble skin soil; for optimal cleaning [102] | Should effectively remove faeces and urine; should not include harsh surfactants, particularly sodium lauryl sulphate [108] |
| Emollients | To minimize friction and to replenish the SC lipids [102] | Should exert positive effect on skin barrier function [108] |
| pH buffering compounds | To maintain a healthy skin pH [102] | Should maintain the skin pH at ±5.5 [108] |
| Ingredient | Frequency (%) 1 |
|---|---|
| Sodium citrate/citric acid | 69 |
| Sodium benzoate | 62 |
| Phenoxyethanol | 48 |
| Iodopropyl butylcarbamate | 23.5 |
| Ethylhexylglycerin | 6.5 |
| Surfactant | Type | Typical Concentration (% w/w) |
|---|---|---|
| Coco-betaine (cocoamidopropyl betaine) | Amphoteric | <0.5% [126] |
| Coco-glucoside, or decyl glucoside, or lauryl glucoside | Non-ionic | <0.5% [126] |
| Glyceryl stearate | Non-ionic | 1.0–2.0% [127] |
| Glyceryl stearate citrate | Anionic | 0.5–2.0% [127] |
| PEG-40 hydrogenated castor oil | Non-ionic | <0.8% [128] |
| Polysorbate 20 | Non-ionic | <0.5% [126] |
| Sodium cocoamphoacetate or disodium cocoamphodiacetate | Amphoteric | <0.5% [126] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahma, A.; Lane, M.E. Skin Barrier Function in Infants: Update and Outlook. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020433
Rahma A, Lane ME. Skin Barrier Function in Infants: Update and Outlook. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(2):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020433
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahma, Annisa, and Majella E. Lane. 2022. "Skin Barrier Function in Infants: Update and Outlook" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 2: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020433
APA StyleRahma, A., & Lane, M. E. (2022). Skin Barrier Function in Infants: Update and Outlook. Pharmaceutics, 14(2), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020433