Design, Characterization, and In Vitro Assays on Muscle Cells of Endocannabinoid-like Molecule Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles for a Therapeutic Anti-Inflammatory Approach to Sarcopenia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
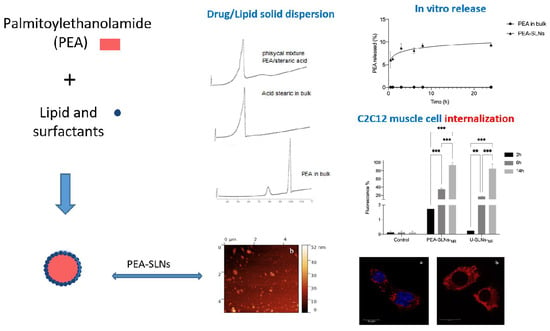
2.2. PEA Solubility in the Lipids
2.3. SLNs Preparation
2.4. Particle Size, Z-Potential, and Morphology
2.5. SLNs Stability
2.6. Drug Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
2.7. In Vitro PEA Release
2.8. Thermal Analysis
2.9. Cell Culture
2.10. Cytotoxicity Test
2.11. Cell Internalization by Flow Cytometry
2.12. Confocal Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Formulation Parameters
3.2. SLNs Characterization
3.3. Cell Culture Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balogun, S.; Winzenberg, T.; Wills, K.; Scott, D.; Jones, G.; Callisaya, M.L.; Aitken, D. Prospective Associations of Low Muscle Mass and Strength with Health-Related Quality of Life over 10-Year in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 118, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E. Treatment of Sarcopenia: The Road to the Future. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.T.; Ling, S.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Bartlett, S.J.; Andersen, R.E.; Towns, M.; Muller, D.; Fontaine, K.R.; Bathon, J.M. Abnormal Body Composition Phenotypes in Older Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Association with Disease Characteristics and Pharmacotherapies. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lo, J.H.-T.; Yiu, T.; Ong, M.T.-Y.; Lee, W.Y.-W. Sarcopenia: Current Treatments and New Regenerative Therapeutic Approaches. J. Orthop. Translat. 2020, 23, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.Y.; Kwon, K.-S. Pharmacological Interventions for Treatment of Sarcopenia: Current Status of Drug Development for Sarcopenia. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2019, 23, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guglielmi, V.; Carton, F.; Vattemi, G.; Arpicco, S.; Stella, B.; Berlier, G.; Marengo, A.; Boschi, F.; Malatesta, M. Uptake and Intracellular Distribution of Different Types of Nanoparticles in Primary Human Myoblasts and Myotubes. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 560, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondo, T.M.; Mooney, D.J. Functional Muscle Recovery with Nanoparticle-Directed M2 Macrophage Polarization in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10648–10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishikawa, H.; Fukunishi, S.; Asai, A.; Yokohama, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; Higuchi, K. Pathophysiology and Mechanisms of Primary Sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 48, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle, S.; Rossmeislova, L.; Koppo, K. The Role of Inflammation in Age-Related Sarcopenia. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, S.-Z.; No, M.-H.; Heo, J.-W.; Park, D.-H.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Kwak, H.-B. Role of Exercise in Age-Related Sarcopenia. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2018, 14, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, S.; Alalwan, T.A.; Al-Thawadi, S.; Negro, M.; Parimbelli, M.; Cerullo, G.; Gasparri, C.; Guerriero, F.; Infantino, V.; Diana, M.; et al. Evidence-Based Role of Nutrients and Antioxidants for Chronic Pain Management in Musculoskeletal Frailty and Sarcopenia in Aging. Geriatrics 2020, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landi, F.; Marzetti, E.; Liperoti, R.; Pahor, M.; Russo, A.; Martone, A.M.; Colloca, G.; Capoluongo, E.; Bernabei, R. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID) Use and Sarcopenia in Older People: Results from the IlSIRENTE Study. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 626.e9–626.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trappe, T.A.; Ratchford, S.M.; Brower, B.E.; Liu, S.Z.; Lavin, K.M.; Carroll, C.C.; Jemiolo, B.; Trappe, S.W. COX Inhibitor Influence on Skeletal Muscle Fiber Size and Metabolic Adaptations to Resistance Exercise in Older Adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uchitomi, R.; Oyabu, M.; Kamei, Y. Vitamin D and Sarcopenia: Potential of Vitamin D Supplementation in Sarcopenia Prevention and Treatment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keppel Hesselink, J.M.; de Boer, T.; Witkamp, R.F. Palmitoylethanolamide: A Natural Body-Own Anti-Inflammatory Agent, Effective and Safe against Influenza and Common Cold. Int. J. Inflam. 2013, 2013, 151028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uberti, F.; Ruga, S.; Farghali, M.; Galla, R.; Molinari, C. A Combination of α-Lipoic Acid (ALA) and Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) Blocks Endotoxin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Cytokine Storm: A Possible Intervention for COVID-19. J. Diet. Suppl. 2021, 18, 1966152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielsson, L.; Gouveia-Figueira, S.; Häggström, J.; Alhouayek, M.; Fowler, C.J. The Anti-Inflammatory Compound Palmitoylethanolamide Inhibits Prostaglandin and Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid Production by a Macrophage Cell Line. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2017, 5, e00300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heide, E.C.; Bindila, L.; Post, J.M.; Malzahn, D.; Lutz, B.; Seele, J.; Nau, R.; Ribes, S. Prophylactic Palmitoylethanolamide Prolongs Survival and Decreases Detrimental Inflammation in Aged Mice with Bacterial Meningitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orefice, N.S.; Alhouayek, M.; Carotenuto, A.; Montella, S.; Barbato, F.; Comelli, A.; Calignano, A.; Muccioli, G.G.; Orefice, G. Oral Palmitoylethanolamide Treatment Is Associated with Reduced Cutaneous Adverse Effects of Interferon-Β1a and Circulating Proinflammatory Cytokines in Relapsing–Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Paracetamol, a New Association to Relieve Hyperalgesia and Pain in a Sciatic Nerve Injury Model in Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Masuda, A.; Chen, G.; Bushra, S.; Kamon, M.; Araki, T.; Kinoshita, M.; Ohkawara, B.; Ito, M.; Ohno, K. Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase-1 by Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Demethylates MeR2 Enhancer and Promotes Mbnl1 Transcription in Myogenic Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastbergen, S.C.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G.; Bijlsma, J.W.J. Selective COX-2 Inhibition Prevents Proinflammatory Cytokine-Induced Cartilage Damage. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trappe, T.A.; Liu, S.Z. Effects of Prostaglandins and COX-Inhibiting Drugs on Skeletal Muscle Adaptations to Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1985, 115, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beggiato, S.; Tomasini, M.C.; Ferraro, L. Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) as a Potential Therapeutic Agent in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordaro, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Crupi, R. An Update of Palmitoylethanolamide and Luteolin Effects in Preclinical and Clinical Studies of Neuroinflammatory Events. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Therapeutic Efficacy of Palmitoylethanolamide and Its New Formulations in Synergy with Different Antioxidant Molecules Present in Diets. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering Precision Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.d.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano Based Drug Delivery Systems: Recent Developments and Future Prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puglia, C.; Santonocito, D.; Ostacolo, C.; Maria Sommella, E.; Campiglia, P.; Carbone, C.; Drago, F.; Pignatello, R.; Bucolo, C. Ocular Formulation Based on Palmitoylethanolamide-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Technological and Pharmacological Profile. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tronino, D.; Offerta, A.; Ostacolo, C.; Russo, R.; De Caro, C.; Calignano, A.; Puglia, C.; Blasi, P. Nanoparticles Prolong N-Palmitoylethanolamide Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects in Vivo. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, K.M.; Sindi, A.M.; Ali, S.; Alharbi, W.S.; Hajjaj, M.S.; Bukhary, H.A.; Badr, M.Y.; Mushtaq, R.Y.; Murshid, S.S.A.; Almehmady, A.M.; et al. Development, optimization, and evaluation of a nanostructured lipid carrier of sesame oil loaded with miconazole for the treatment of oral candidiasis. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maretti, E.; Costantino, L.; Buttini, F.; Rustichelli, C.; Leo, E.; Truzzi, E.; Iannuccelli, V. Newly Synthesized Surfactants for Surface Mannosylation of Respirable SLN Assemblies to Target Macrophages in Tuberculosis Therapy. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maretti, E.; Rustichelli, C.; Romagnoli, M.; Balducci, A.G.; Buttini, F.; Sacchetti, F.; Leo, E.; Iannuccelli, V. Solid Lipid Nanoparticle Assemblies (SLNas) for an Anti-TB Inhalation Treatment—A Design of Experiments Approach to Investigate the Influence of Pre-Freezing Conditions on the Powder Respirability. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacchetti, F.; Marraccini, C.; D’Arca, D.; Pelà, M.; Pinetti, D.; Maretti, E.; Hanuskova, M.; Iannuccelli, V.; Costi, M.P.; Leo, E. Enhanced Anti-Hyperproliferative Activity of Human Thymidylate Synthase Inhibitor Peptide by Solid Lipid Nanoparticle Delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 136, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurakula, M.; Ahmed, O.A.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Ahmed, T.A. Solid lipid nanoparticles for transdermal delivery of avanafil: Optimization, formulation, in-vitro and ex-vivo studies. J. Liposome Res. 2016, 26, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaffe, D.; Saxel, O. Serial Passaging and Differentiation of Myogenic Cells Isolated from Dystrophic Mouse Muscle. Nature 1977, 270, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenchov, R.; Bird, R.; Curtze, A.E.; Zhou, Q. Lipid Nanoparticles—From Liposomes to MRNA Vaccine Delivery, a Landscape of Research Diversity and Advancement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16982–17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, S.S.; Anderson, B.D. What Determines Drug Solubility in Lipid Vehicles: Is It Predictable? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 638–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, D.M.; Vandevoorde, S.; Diependaele, G.; Govaerts, S.J.; Robert, A.R. Anticonvulsant Activity of N-Palmitoylethanolamide, a Putative Endocannabinoid, in Mice. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vighi, E.; Montanari, M.; Hanuskova, M.; Iannuccelli, V.; Coppi, G.; Leo, E. Design Flexibility Influencing the in Vitro Behavior of Cationic SLN as a Nonviral Gene Vector. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 440, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrstensen, H.; Müller, R.H.; Müller, B.W. Particle Size, Surface Hydrophobicity and Interaction with Serum of Parenteral Fat Emulsions and Model Drug Carriers as Parameters Related to RES Uptake. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 11, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S.A.; Kayser, O.; Müller, R.H. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Parenteral Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar Shekoufeh Bahari, L.; Hamishehkar, H. The Impact of Variables on Particle Size of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siekmann, B.; Westesen, K. Submicron-Sized Parenteral Carrier Systems Based on Solid Lipids. Pharm. Pharmacol. Lett. 1992, 1, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; de Haan, L.H.J.; Evers, N.M.; Jiang, X.; Marcelis, A.T.M.; Zuilhof, H.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Alink, G.M. Role of Surface Charge and Oxidative Stress in Cytotoxicity of Organic Monolayer-Coated Silicon Nanoparticles towards Macrophage NR8383 Cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foroozandeh, P.; Aziz, A.A. Insight into Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Trafficking of Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E. The Role of Surface Charge in Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Medical Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5577–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, C.; Jefferies, C.; Cryan, S.-A. Targeted Liposomal Drug Delivery to Monocytes and Macrophages. J. Drug Deliv. 2010, 2011, e727241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Pinho, S.C.; Souto, E.B.; Santana, M.H.A. Polymorphism, Crystallinity and Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance of Stearic Acid and Stearic Acid-Capric/Caprylic Triglyceride Matrices for Production of Stable Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 86, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campardelli, R.; Oleandro, E.; Scognamiglio, M.; Della Porta, G.; Reverchon, E. Palmitoylethanolamide Sub-Micronization Using Fast Precipitation Followed by Supercritical Fluids Extraction. Powder Technol. 2017, 305, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.E.; Bucarey, J.L.; Espinosa, A. Muscle Lipid Metabolism: Role of Lipid Droplets and Perilipins. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1789395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, M.J.; Hoy, A.J. Lipid Metabolism in Skeletal Muscle: Generation of Adaptive and Maladaptive Intracellular Signals for Cellular Function. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E1315–E1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouchaala, R.; Anton, N.; Anton, H.; Vandamme, T.; Vermot, J.; Smail, D.; Mély, Y.; Klymchenko, A.S. Light-Triggered Release from Dye-Loaded Fluorescent Lipid Nanocarriers In Vitro and In Vivo. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 156, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, P.; Mayer, E.P.; Fowler, S.D. Nile Red: A Selective Fluorescent Stain for Intracellular Lipid Droplets. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 100, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vighi, E.; Montanari, M.; Ruozi, B.; Tosi, G.; Magli, A.; Leo, E. Nuclear Localization of Cationic Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Protamine as Transfection Promoter. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zhu, L.; Dong, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, W. Preparation, Characterization and Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Influences of Fatty Acids. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 83, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich, C.; Kayser, O.; Müller, R.H. Lipase Degradation of Dynasan 114 and 116 Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN)—Effect of Surfactants, Storage Time and Crystallinity. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 237, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, T.; Kinugawa, S.; Takada, S.; Furihata, T.; Fukushima, A.; Yokota, T.; Anzai, T.; Hibino, M.; Harashima, H.; Yamada, Y. A Mitochondrial Delivery System Using Liposome-Based Nanocarriers That Target Myoblast Cells. Mitochondrion 2019, 49, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Maity, S.; Ghosh, B.; Chakraborty, T.; Mondal, A.; Bishayee, A. Assessment of the Antidiabetic Potentiality of Glyburide Loaded Glyceryl Monostearate Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Jiang, C.; Wu, L.; Bai, X.; Zhai, S. Cytotoxicity-Related Bioeffects Induced by Nanoparticles: The Role of Surface Chemistry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morsanuto, V.; Galla, R.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. A New Palmitoylethanolamide Form Combined with Antioxidant Molecules to Improve Its Effectivess on Neuronal Aging. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Sample | Size (nm) | PDI | Z Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-SLNs | 214 ± 19 | 0.244 ± 0.050 | −32.3 ± 2.5 |
| PEA-SLNs | 253 ± 15 | 0.185 ± 0.100 | −39.5 ± 2.1 |
| PEA-SLNs-NR | 258 ± 12 | 0.197 ± 0.080 | −40.2 ± 2.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maretti, E.; Molinari, S.; Battini, R.; Rustichelli, C.; Truzzi, E.; Iannuccelli, V.; Leo, E. Design, Characterization, and In Vitro Assays on Muscle Cells of Endocannabinoid-like Molecule Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles for a Therapeutic Anti-Inflammatory Approach to Sarcopenia. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030648
Maretti E, Molinari S, Battini R, Rustichelli C, Truzzi E, Iannuccelli V, Leo E. Design, Characterization, and In Vitro Assays on Muscle Cells of Endocannabinoid-like Molecule Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles for a Therapeutic Anti-Inflammatory Approach to Sarcopenia. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(3):648. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030648
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaretti, Eleonora, Susanna Molinari, Renata Battini, Cecilia Rustichelli, Eleonora Truzzi, Valentina Iannuccelli, and Eliana Leo. 2022. "Design, Characterization, and In Vitro Assays on Muscle Cells of Endocannabinoid-like Molecule Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles for a Therapeutic Anti-Inflammatory Approach to Sarcopenia" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 3: 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030648
APA StyleMaretti, E., Molinari, S., Battini, R., Rustichelli, C., Truzzi, E., Iannuccelli, V., & Leo, E. (2022). Design, Characterization, and In Vitro Assays on Muscle Cells of Endocannabinoid-like Molecule Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles for a Therapeutic Anti-Inflammatory Approach to Sarcopenia. Pharmaceutics, 14(3), 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030648