Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors Contribute to Cisplatin-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy in Male Mice
Abstract
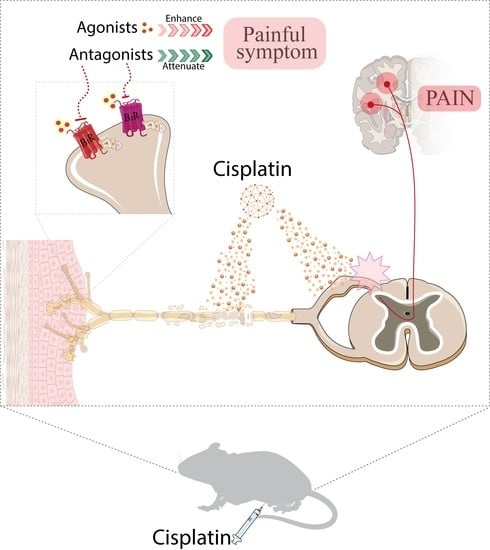
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Cisplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Model
2.4. Study Design for Behavioural Assessment
2.5. Study Design for the Assessment of Kinin B1 and B2 Receptor Involvement in Cisplatin-Induced Painful Behaviours
2.5.1. Therapeutic Protocol
2.5.2. Preventive Protocol
2.5.3. Effects of Sub-Nociceptive Doses of Kinin B1 and B2 Receptor Agonists on Mechanical Allodynia in Mice with Cisplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
2.5.4. Effects of Antisense Oligonucleotides for Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors on Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical and Cold Sensitivity in Mice
2.6. Behavioural Experiments
2.6.1. Mechanical Allodynia Assessment
2.6.2. Cold Sensitivity
2.6.3. Voluntary Wheel Activity
2.6.4. Nesting Behaviour Test
2.6.5. Thigmotaxis Behaviour
2.6.6. Forced Swimming Test
2.6.7. Novel Object/Place Recognition Test
2.7. Evaluation of Other Possible Adverse Effects
2.7.1. Physical and Behavioural Changes
2.7.2. Locomotor Activity
2.7.3. Biochemical Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cisplatin Induces Prolonged Painful Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice
3.2. Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors Contribute to Mechanical Allodynia in Cisplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice
3.3. Kinin B1 and B2 Receptor Agonists Enhanced Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Nociception, Which Was Reversed by B1 and B2 Receptor Antagonists
3.4. Antisense Oligonucleotides for Kinin B1 or B2 Receptors Attenuated the Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Allodynia
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerns, S.L.; Fung, C.; Monahan, P.O.; Ardeshir-Rouhani-Fard, S.; Abu Zaid, M.I.; Williams, A.L.M.; Stump, T.E.; Sesso, H.D.; Feldman, D.R.; Hamilton, R.J.; et al. Cumulative Burden of Morbidity among Testicular Cancer Survivors after Standard Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy: A Multi-Institutional Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, L.B.; Fossa, S.D.; Sesso, H.D.; Frisina, R.D.; Herrmann, D.N.; Beard, C.J.; Feldman, D.R.; Pagliaro, L.C.; Miller, R.C.; Vaughn, D.J.; et al. Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity and Ototoxicity: New Paradigms for Translational Genomics. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, K.D.; Nogueira, L.; Devasia, T.; Mariotto, A.B.; Yabroff, K.R.; Jemal, A.; Kramer, J.; Siegel, R.L. Cancer Treatment and Survivorship Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 409–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, L.A. Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Where Are We Now? Pain 2019, 160, S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starobova, H.; Vetter, I. Pathophysiology of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, E.Y.; Ehrlich, B.E. Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Review of Recent Findings. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 145, 102831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staff, N.P.; Grisold, A.; Grisold, W.; Windebank, A.J. Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Current Review. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calls, A.; Carozzi, V.; Navarro, X.; Monza, L.; Bruna, J. Pathogenesis of Platinum-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity: Insights from Preclinical Studies. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 325, 113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seretny, M.; Currie, G.L.; Sena, E.S.; Ramnarine, S.; Grant, R.; Macleod, M.R.; Colvin, L.A.; Fallon, M. Incidence, Prevalence, and Predictors of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain 2014, 155, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staff, N.P.; Cavaletti, G.; Islam, B.; Lustberg, M.; Psimaras, D.; Tamburin, S. Platinum-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity: From Pathogenesis to Treatment. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2019, 24, S26–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, P. Platinum-Drugs Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity: Clinical Course and Preclinical Evidence. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathinam, R.; Ghosh, S.; Neumann, W.; Jamesdaniel, S. Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis in Auditory, Renal, and Neuronal Cells Is Associated with Nitration and Downregulation of LMO4. Cell Death Discov. 2015, 1, 15052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loprinzi, C.L.; Lacchetti, C.; Bleeker, J.; Cavaletti, G.; Chauhan, C.; Hertz, D.L.; Kelley, M.R.; Lavino, A.; Lustberg, M.B.; Paice, J.A.; et al. Prevention and Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Survivors of Adult Cancers: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3325–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.M.L.; Pang, H.; Cirrincione, C.; Fleishman, S.; Paskett, E.D.; Ahles, T.; Bressler, L.R.; Gilman, P.B.; Shapiro, C.L.; Chemotherapy-induced, W.; et al. Effect of Duloxetine on Pain, Function, and Quality of Life among Patients with Chemotherapy-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 309, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatters, S.J.L.; Dougherty, P.M.; Colvin, L.A. Clinical and Preclinical Perspectives on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN): A Narrative Review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, J.; Trichês, K.M.; Medeiros, R.; Cabrini, D.A.; Mori, M.A.S.; Pesquero, J.B.; Bader, M.; Calixto, J.B. The Role of Kinin B1 Receptors in the Nociception Produced by Peripheral Protein Kinase C Activation in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, E.C.D.; Vieira, G.; Gonçalves, T.R.; Simões, R.R.; Brusco, I.; Oliveira, S.M.; Calixto, J.B.; Cola, M.; Santos, A.R.S.; Dutra, R.C. Bradykinin Receptors Play a Critical Role in the Chronic Post-Ischaemia Pain Model. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 41, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintão, N.L.M.; Rocha, L.W.; da Silva, G.F.; Paszcuk, A.F.; Manjavachi, M.N.; Bento, A.F.; da Silva, K.A.B.S.; Campos, M.M.; Calixto, J.B. The Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors and TNFR1/P55 Axis on Neuropathic Pain in the Mouse Brachial Plexus. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintão, N.L.M.; Passos, G.F.; Medeiros, R.; Paszcuk, A.F.; Motta, F.L.; Pesquero, J.B.; Campos, M.M.; Calixto, J.B. Neuropathic Pain-like Behavior after Brachial Plexus Avulsion in Mice: The Relevance of Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2856–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, C.R.; Oliveira, S.M.; Hoffmeister, C.; Funck, V.; Guerra, G.P.; Trevisan, G.; Tonello, R.; Rossato, M.F.; Pesquero, J.B.; Bader, M.; et al. The Role of Kinin B1 Receptor and the Effect of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibition on Acute Gout Attacks in Rodents. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, M.F.P.; Kassuya, C.A.L.; Ferreira, J.; Zampronio, A.R.; Calixto, J.B.; Rae, G.A. Peripheral Kinin B1 and B2 Receptor-Operated Mechanisms Are Implicated in Neuropathic Nociception Induced by Spinal Nerve Ligation in Rats. Neuropharmacology 2007, 53, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusco, I.; Benatti, A.; Regina, C.; Fischer, S.; Mattar, T.; Scussel, R.; Machado-de-ávila, R.A.; Ferreira, J.; Marchesan, S. Kinins and Their B 1 and B 2 Receptors Are Involved in Fibromyalgia-like Pain Symptoms in Mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 168, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.P.; Heavens, R. Basal Expression of Bradykinin B1 Receptor in the Spinal Cord in Humans and Rats. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 2311–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.P. The Expression of Bradykinin B1 Receptors on Primary Sensory Neurones That Give Rise to Small Caliber Sciatic Nerve Fibres in Rats. Neuroscience 2001, 107, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marceau, F.; Regoli, D. Bradykinin Receptor Ligands: Therapeutic Perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusco, I.; Silva, C.R.; Trevisan, G.; de Campos Velho Gewehr, C.; Rigo, F.K.; La Rocca Tamiozzo, L.; Rossato, M.F.; Tonello, R.; Dalmolin, G.D.; de Almeida Cabrini, D.; et al. Potentiation of Paclitaxel-Induced Pain Syndrome in Mice by Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Inhibition and Involvement of Kinins. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7824–7837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, J.B.; Medeiros, R.; Fernandes, E.S.; Ferreira, J.; Cabrini, D.A.; Campos, M.M. Kinin B 1 Receptors: Key G-Protein-Coupled Receptors and Their Role in Inflammatory and Painful Processes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, J.; Campos, M.M.; Araújo, R.; Bader, M.; Pesquero, J.B.; Calixto, J.B. The Use of Kinin B1 and B2 Receptor Knockout Mice and Selective Antagonists to Characterize the Nociceptive Responses Caused by Kinins at the Spinal Level. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintão, N.L.M.; Santin, J.R.; Stoeberl, L.C.; Corrêa, T.P.; Melato, J.; Costa, R. Pharmacological Treatment of Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain: PPARγ Agonists as a Promising Tool. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bujalska, M.; Tatarkiewicz, J.; Gumułka, S.W. Effect of Bradykinin Receptor Antagonists on Vincristine- and Streptozotocin-Induced Hyperalgesia in a Rat Model of Chemotherapy-Induced and Diabetic Neuropathy. Pharmacology 2008, 81, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujalska, M.; Makulska-Nowak, H. Bradykinin Receptor Antagonists and Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors in Vincristine- and Streptozotocin-Induced Hyperalgesia. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Motta, E.M.; Dutra, R.C.; Manjavachi, M.N.; Bento, A.F.; Malinsky, F.R.; Pesquero, J.B.; Calixto, J.B. Anti-nociceptive Effect of Kinin B1 and B2 Receptor Antagonists on Peripheral Neuropathy Induced by Paclitaxel in Mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Estrela, G.R.; Wasinski, F.; Almeida, D.C.; Amano, M.T.; Castoldi, A.; Dias, C.C.; Malheiros, D.M.A.C.; Almeida, S.S.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J.; Pesquero, J.B.; et al. Kinin B1 Receptor Deficiency Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Modulating Immune Cell Migration. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrela, G.R.; Wasinski, F.; Bacurau, R.F.; Malheiros, D.M.A.C.; Câmara, N.O.S.; Araújo, R.C. Kinin B2 Receptor Deletion and Blockage Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Renal Injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, M.; das, C.T. e I. Resolução Normativa no 39, De 20 De Junho De 2018. Diário Of. da União 2018, 120, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, M. Ethical Guidelines for Investigations of Experimental Pain in Conscious Animals. Pain 1983, 16, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, J.C.; Lilley, E. Implementing Guidelines on Reporting Research Using Animals (ARRIVE Etc.): New Requirements for Publication in BJP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3189–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, R.; Bicca, M.A.; Manjavachi, M.N.; Segat, G.C.; Dias, F.C.; Fernandes, E.S.; Calixto, J.B. Kinin Receptors Sensitize TRPV4 Channel and Induce Mechanical Hyperalgesia: Relevance to Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 2150–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meotti, F.C.; Campos, R.; Da Silva, K.A.B.S.; Paszcuk, A.F.; Costa, R.; Calixto, J.B. Inflammatory Muscle Pain Is Dependent on the Activation of Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors and Intracellular Kinase Pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.J.; Stokes, J.A.; Corr, M.; Yaksh, T.L. Toll-like Receptor Signaling Regulates Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Mice. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 73, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, H.J.; Stokes, J.A.; Pirie, E.; Skahen, J.; Shtaerman, Y.; Yaksh, T.L. Persistent Hyperalgesia in the Cisplatin-Treated Mouse as Defined by Threshold Measures, the Conditioned Place Preference Paradigm, and Changes in Dorsal Root Ganglia Activated Transcription Factor 3: The Effects of Gabapentin, Ketorolac, and Etanercept. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 116, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- John, T.; Lomeli, N.; Bota, D.A. Systemic Cisplatin Exposure during Infancy and Adolescence Causes Impaired Cognitive Function in Adulthood. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 319, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative Assessment of Tactile Allodynia in the Rat Paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.M.; Silva, C.R.; Ferreira, J. Critical Role of Protease-Activated Receptor 2 Activation by Mast Cell Tryptase in the Development of Postoperative Pain. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva Brum, E.; Fialho, M.F.P.; Fischer, S.P.M.; Hartmann, D.D.; Gonçalves, D.F.; Scussel, R.; Machado-de-Ávila, R.A.; Dalla Corte, C.L.; Soares, F.A.A.; Oliveira, S.M. Relevance of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Reserpine-Induced Experimental Fibromyalgia Model. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 4202–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobos, E.J.; Ghasemlou, N.; Araldi, D.; Segal, D.; Duong, K.; Woolf, C.J. Inflammation-Induced Decrease in Voluntary Wheel Running in Mice: A Non-Reflexive Test for Evaluating Inflammatory Pain and Analgesia. Pain 2012, 153, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negus, S.S.; Neddenriep, B.; Altarifi, A.A.; Carroll, F.I.; Leitl, M.D.; Miller, L.L. Effects of Ketoprofen, Morphine, and Kappa Opioids On Pain- Related Depression of Nesting in Mice. Pain 2015, 156, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, H.F.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lai, C.L.; Chen, C.C. Activation of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3 by Lysophosphatidylcholine 16:0 Mediates Psychological Stress-Induced Fibromyalgia-like Pain. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1644–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.P.M.; Brusco, I.; Brum, E.S.; Fialho, M.F.P.; Camponogara, C.; Scussel, R.; Machado-de-Ávila, R.A.; Trevisan, G.; Oliveira, S.M. Involvement of TRPV1 and the Efficacy of α-Spinasterol on Experimental Fibromyalgia Symptoms in Mice. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 134, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yankelevitch-yahav, R.; Franko, M.; Huly, A.; Doron, R. The Forced Swim Test as a Model of Depressive-like Behavior. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 97, e52587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, G.S.; Maj, M.A.; Rivzi, S.; Dantzer, R.; Vichaya, E.G.; Laumet, G.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J. Pifithrin-µ Prevents Cisplatin-Induced Chemobrain by Preserving Neuronal Mitochondrial Function. Cancer Res. 2017, 3, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, J.F.; Seua, A.V.; Arroyo, L.D.; Ray, P.R.; Wangzhou, A.; Heiβ-Lückemann, L.; Schedlowski, M.; Price, T.J.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J. Nasal Administration of Mitochondria Reverses Chemotherapy-Induced Cognitive Deficits. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3109–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, G.S.; Boukelmoune, N.; Chiang, A.C.A.; Peng, B.; Rao, V.; Kingsley, C.; Liu, H.L.; Kavelaars, A.; Kesler, S.R.; Heijnen, C.J. Nasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Restores Cisplatin-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Brain Damage in Mice. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 35581–35597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brum, S.; Moreira, R.; Regina, A.; Augusti, A.; Barbosa, F.; Linde, M.; Brandão, R.; Marchesan, S. Tabernaemontana Catharinensis Ethyl Acetate Fraction Presents Antinociceptive Activity without Causing Toxicological Effects in Mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 191, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Du, W.; Acklin, S.; Jin, S.; Xia, F. SIRT2 Protects Peripheral Neurons from Cisplatin-Induced Injury by Enhancing Nucleotide Excision Repair. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2953–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavaletti, G.; Marzorati, L.; Bogliun, G.; Colombo, N.; Marzola, M.; Pittelli, M.R.; Tredici, G. Cisplatin-lnduced Peripheral Neurotoxicity Is Dependent on Total-dose Intensity and Single-dose Intensity. Cancer 1992, 69, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glendenning, J.L.; Barbachano, Y.; Norman, A.R.; Dearnaley, D.P.; Horwich, A.; Huddart, R.A. Long-Term Neurologic and Peripheral Vascular Toxicity after Chemotherapy Treatment of Testicular Cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 2322–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woller, S.A.; Corr, M.; Yaksh, T.L. Differences in Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Male and Female Mice. Eur. J. Pain 2015, 19, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khasabova, I.A.; Khasabov, S.G.; Olson, J.K.; Uhelski, M.L.; Kim, A.H.; Albino-Ramírez, A.M.; Wagner, C.L.; Seybold, V.S.; Simone, D.A. Pioglitazone, a PPARγ Agonist, Reduces Cisplatin-Evoked Neuropathic Pain by Protecting against Oxidative Stress. Pain 2019, 160, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, J.; Deng, L.; Fan, B.; Wager-miller, J.; Hohmann, A.G. Optimization of a Cisplatin Model of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice: Use of Vitamin C and Sodium Bicarbonate Pretreatments to Reduce Nephrotoxicity and Improve Animal Health Status. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 1744-8069-10-56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alotaibi, M.; Al-Aqil, F.; Alqahtani, F.; Alanazi, M.; Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.F.; Lapresa, R.; Alharbi, M.; Alshammari, A.; Alotaibi, M.; et al. Alleviation of Cisplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain, Neuronal Apoptosis, and Systemic Inflammation in Mice by Rapamycin. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 891593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Krukowski, K.; Laumet, G.O.; Weis, D.; Alexander, J.F.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A. CD8+ T Cell-Derived IL-13 Increases Macrophage IL-10 to Resolve Neuropathic Pain. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e154194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukelmoune, N.; Laumet, G.; Tang, Y.; Ma, J.; Mahant, I.; Singh, S.K.; Nijboer, C.; Benders, M.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J. Nasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reverses Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 93, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumet, G.; Edralin, J.D.; Dantzer, R.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A. Cisplatin Educates CD8+ T Cells to Prevent and Resolve Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice. Pain 2019, 160, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cano, R.; Montilla-García, Á.; Ruiz-Cantero, M.C.; Bravo-Caparrós, I.; Tejada, M.; Nieto, F.R.; Cobos, E.J. The Search for Translational Pain Outcomes to Refine Analgesic Development: Where Did We Come from and Where Are We Going? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 113, 238–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, L.A.; Duggett, N.A.; Pitcher, A.L.; Flatters, S.J.L. Evoked and Ongoing Pain-Like Behaviours in a Rat Model of Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Pain Res. Manag. 2018, 2018, 821763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cauli, O. Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Alterations Induced by Cancer Chemotherapy Drugs: A Scoping Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouten-Kemperman, M.M.; de Ruiter, M.B.; Caan, M.W.A.; Boogerd, W.; Kerst, M.J.; Reneman, L.; Schagen, S.B. Lower Cognitive Performance and White Matter Changes in Testicular Cancer Survivors 10 Years after Chemotherapy. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 4638–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumagalli, G.; Monza, L.; Cavaletti, G.; Rigolio, R.; Meregalli, C. Neuroinflammatory Process Involved in Different Preclinical Models of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 626687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surah, A.; Baranidharan, G.; Morley, S. Chronic Pain and Depression. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 2014, 14, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, W.; Vodermaier, A.; MacKenzie, R.; Greig, D. Anxiety and Depression after Cancer Diagnosis: Prevalence Rates by Cancer Type, Gender, and Age. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 141, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, A.Y.; Hameed, A.N.; Mustafa, N.; Alwafi, H.; Dahmash, E.Z.; Alyami, H.S.; Khalil, H. Depression and Anxiety in Patients with Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 585534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, L.; Wang, J.; Cao, B.; Jelfs, B.; Chan, R.H.M.; Xu, X.; Hasan, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Impairment of Cognitive Function by Chemotherapy: Association with the Disruption of Phase-Locking and Synchronization in Anterior Cingulate Cortex. Mol. Brain 2015, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelkader, N.F.; Saad, M.A.; Abdelsalam, R.M. Neuroprotective Effect of Nebivolol against Cisplatin-Associated Depressive-like Behavior in Rats. J. Neurochem. 2017, 141, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saadati, H.; Noroozzadeh, S.; Esmaeili, H.; Amirshahrokhi, K.; Shadman, J.; Niapour, A. The Neuroprotective Effect of Mesna on Cisplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity: Behavioral, Electrophysiological, and Molecular Studies. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 826–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.D.; Guginski, G.; Sato, K.L.; Sanada, L.S.; Sluka, K.A.; Santos, A.R.S. Persistent Pain Induces Mood Problems and Memory Loss by the Involvement of Cytokines, Growth Factors, and Supraspinal Glial Cells. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2020, 7, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calls, A.; Torres-Espin, A.; Navarro, X.; Yuste, V.J.; Udina, E.; Bruna, J. Cisplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Is Associated with Neuronal Senescence-like Response. Neuro. Oncol. 2021, 23, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, M.E.; Garbacki, N.; Molinaro, G.; Brown, N.J.; Marceau, F.; Adam, A. The Kallikrein-Kinin System: Current and Future Pharmacological Targets. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 99, 6–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutra, R.C. Kinin Receptors: Key Regulators of Autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couture, R.; Harrisson, M.; Vianna, R.M.; Cloutier, F. Kinin Receptors in Pain and Inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 429, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, M.; Kariura, Y.; Amano, T.; Manago, Y.; Nishikawa, K.; Aoki, S.; Wada, K. Kinin Receptors in Cultured Rat Microglia. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, W.Q.; Hu, X.M.; Du, L.X.; Mi, W.L.; Chu, Y.X.; Wu, G.C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Mao-Ying, Q.L. Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells 2 (TREM2) Dependent Microglial Activation Promotes Cisplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2018, 68, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusco, I.; Justino, A.B.; Silva, C.R.; Scussel, R.; Machado-de-Ávila, R.A.; Oliveira, S.M. Inhibitors of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Potentiate Fibromyalgia-like Pain Symptoms via Kinin Receptors in Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 895, 173870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.; Inoue, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Ueda, H. Switching of Bradykinin-Mediated Nociception Following Partial Sciatic Nerve Injury in Mice. 2004, 308, 1158–1164. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cernit, V.; Sénécal, J.; Othman, R.; Couture, R. Reciprocal Regulatory Interaction between TRPV1 and Kinin B1 Receptor in a Rat Neuropathic Pain Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talbot, S.; Chahmi, E.; Dias, J.P.; Couture, R. Key Role for Spinal Dorsal Horn Microglial Kinin B1receptor in Early Diabetic Pain Neuropathy. J. Neuroinflammation 2010, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Story, G.M.; Peier, A.M.; Reeve, A.J.; Eid, S.R.; Mosbacher, J.; Hricik, T.R.; Earley, T.J.; Hergarden, A.C.; Andersson, D.A.; Hwang, S.W.; et al. ANKTM1, a TRP-like Channel Expressed in Nociceptive Neurons, Is Activated by Cold Temperatures. Cell 2003, 112, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jordt, S.E.; Bautista, D.M.; Chuang, H.H.; McKemy, D.D.; Zygmunt, P.M.; Högestätt, E.D.; Meng, I.D.; Julius, D. Mustard Oils and Cannabinoids Excite Sensory Nerve Fibres through the TRP Channel ANKTM1. Nature 2004, 427, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandell, M.; Story, G.M.; Hwang, S.W.; Viswanath, V.; Eid, S.R.; Petrus, M.J.; Earley, T.J.; Patapoutian, A. Noxious Cold Ion Channel TRPA1 Is Activated by Pungent Compounds and Bradykinin. Neuron 2004, 41, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, J.; Da Silva, G.L.; Calixto, J.B. Contribution of Vanilloid Receptors to the Overt Nociception Induced by B 2 Kinin Receptor Activation in Mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bautista, D.M.; Jordt, S.E.; Nikai, T.; Tsuruda, P.R.; Read, A.J.; Poblete, J.; Yamoah, E.N.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. TRPA1 Mediates the Inflammatory Actions of Environmental Irritants and Proalgesic Agents. Cell 2006, 124, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ta, L.E.; Low, P.A.; Windebank, A.J. Mice with Cisplatin and Oxaliplatin-Induced Painful Neuropathy Develop Distinct Early Responses to Thermal Stimuli. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 1744-8069-5-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estrela, G.R.; Wasinski, F.; Felizardo, R.J.F.; Souza, L.L.; Câmara, N.O.S.; Bader, M.; Araujo, R.C. MATE-1 Modulation by Kinin B1 Receptor Enhances Cisplatin Efflux from Renal Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 428, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.C.; Gera, L.; Stewart, J.M.; Helfrich, B.; Zhao, T.L.; Feng, W.Y.; Chan, K.K.; Covey, J.M.; Bunn, P.A. Bradykinin Antagonist Dimer, CU201, Inhibits the Growth of Human Lung Cancer Cell Lines in Vitro and in Vivo and Produces Synergistic Growth Inhibition in Combination with Other Antitumor Agents. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- da Costa, P.L.N.; Sirois, P.; Tannock, I.F.; Chammas, R. The Role of Kinin Receptors in Cancer and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jutras, S.; Bachvarova, M.; Keita, M.; Bascands, J.L.; Mes-Masson, A.M.; Stewart, J.M.; Bachvarov, D. Strong Cytotoxic Effect of the Bradykinin Antagonist BKM-570 in Ovarian Cancer Cells—Analysis of the Molecular Mechanisms of Its Antiproliferative Action. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 5146–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, H.; Kőhalmi, K.V. Icatibant for the Treatment of Hereditary Angioedema with C1-Inhibitor Deficiency in Adolescents and in Children Aged over 2 Years. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Becker, G.; Fialho, M.F.P.; Brusco, I.; Oliveira, S.M. Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors Contribute to Cisplatin-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy in Male Mice. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030852
Becker G, Fialho MFP, Brusco I, Oliveira SM. Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors Contribute to Cisplatin-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy in Male Mice. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(3):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030852
Chicago/Turabian StyleBecker, Gabriela, Maria Fernanda Pessano Fialho, Indiara Brusco, and Sara Marchesan Oliveira. 2023. "Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors Contribute to Cisplatin-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy in Male Mice" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 3: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030852
APA StyleBecker, G., Fialho, M. F. P., Brusco, I., & Oliveira, S. M. (2023). Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors Contribute to Cisplatin-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy in Male Mice. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030852