An Aptamer against MNK1 for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.3. Protein and RNA Extraction
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Cell Viability (MTT) and Cell Toxicity (LDH) Assays
2.6. Trypan Blue Exclusion Test of Cell Viability
2.7. Cell Cycle Assay
2.8. Apoptosis Assay
2.9. Clonogenic Assays
2.10. Migration Assays
2.11. Cell Adhesion Assays
2.12. Zymography
2.13. Aptamer Quantification
2.14. Quantification of mRNA
2.15. Tolerability Study
2.16. In Vivo Efficacy Assays
2.17. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
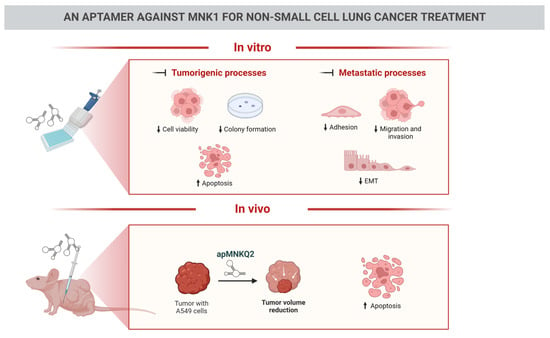
3.1. apMNKQ2 Inhibits Cell Viability in NSCLC Cell Lines
3.2. apMNKQ2 Induces Apoptosis, Cell Cycle Arrest, and Inhibits Colony Formation in Lung Cancer Cells
3.3. apMNKQ2 Inhibits Migration, Invasion, Cell Adhesion, and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Lung Cancer Cells
3.4. Effect of apMNKQ2 on MNK1 Isoforms
3.5. apMNKQ2 Reduces Tumor Growth In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, W.; Liu, X.; Zhong, R.; Cheng, B.; Zhu, F.; Xiang, Y.; He, J.; et al. Advances in lung cancer screening and early detection. Cancer Biol. Med. 2022, 19, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, R.; Hunter, T. MNK1, a new MAP kinase-activated protein kinase, isolated by a novel expression screening method for identifying protein kinase substrates. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskiewicz, A.J.; Flynn, A.; Proud, C.G.; Cooper, J.A. Mitogen-activated protein kinases activate the serine/threonine kinases Mnk1 and Mnk2. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loghlen, A.; Gonzalez, V.M.; Pineiro, D.; Perez-Morgado, M.I.; Salinas, M.; Martin, M.E. Identification and molecular characterization of Mnk1b, a splice variant of human MAP kinase-interacting kinase Mnk1. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 299, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loghlen, A.; González, V.M.; Jurado, T.; Salinas, M.; Martín, M.E. Characterization of the activity of human MAP kinase-interacting kinase Mnk1b. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1416–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskiewicz, A.J.; Johnson, J.C.; Penn, B.; Mahalingam, M.; Kimball, S.R.; Cooper, J.A. Phosphorylation of the cap-binding protein eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E by protein kinase Mnk1 in vivo. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shveygert, M.; Kaiser, C.; Bradrick, S.S.; Gromeier, M. Regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase occurs through modulation of Mnk1-eIF4G interaction. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 30, 5160–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxade, M.; Parra, J.L.; Rousseau, S.; Shpiro, N.; Marquez, R.; Morrice, N.; Bain, J.; Espel, E.; Proud, C.G. The Mnks are novel components in the control of TNF alpha biosynthesis and phosphorylate and regulate hnRNP A1. Immunity 2005, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefner, Y.; Borsch-Haubold, A.G.; Murakami, M.; Wilde, J.I.; Pasquet, S.; Schieltz, D.; Ghomashchi, F.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Armstrong, C.G.; Paterson, A.; et al. Serine 727 phosphorylation and activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 by MNK1-related protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 37542–37551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DaSilva, J.; Xu, L.; Kim, H.J.; Miller, W.T.; Bar-Sagi, D. Regulation of sprouty stability by Mnk1-dependent phosphorylation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxadé, M.; Morrice, N.; Krebs, D.L.; Proud, C.G. The PSF.p54nrb complex is a novel Mnk substrate that binds the mRNA for tumor necrosis factor alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, D.; Kaspar, R.; Rosenwald, I.; Gehrke, L.; Sonenberg, N. Translation initiation of ornithine decarboxylase and nucleocytoplasmic transport of cyclin D1 mRNA are increased in cells overexpressing eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culjkovic, B.; Topisirovic, I.; Borden, K.L. Controlling gene expression through RNA regulons: The role of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furic, L.; Rong, L.; Larsson, O.; Koumakpayi, I.H.; Yoshida, K.; Brueschke, A.; Petroulakis, E.; Robichaud, N.; Pollak, M.; Gaboury, L.A.; et al. eIF4E phosphorylation promotes tumorigenesis and is associated with prostate cancer progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14134–14139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, N.; del Rincon, S.V.; Huor, B.; Alain, T.; Petruccelli, L.A.; Hearnden, J.; Goncalves, C.; Grotegut, S.; Spruck, C.H.; Furic, L.; et al. Phosphorylation of eIF4E promotes EMT and metastasis via translational control of SNAIL and MMP-3. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2032–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, N.; Hsu, B.E.; Istomine, R.; Alvarez, F.; Blagih, J.; Ma, E.H.; Morales, S.V.; Dai, D.L.; Li, G.; Souleimanova, M.; et al. Translational control in the tumor microenvironment promotes lung metastasis: Phosphorylation of eIF4E in neutrophils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2202–E2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhong, W.; Cao, R. Phosphorylation of the mRNA cap-binding protein eIF4E and cancer. Cell Signal. 2020, 73, 109689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheater, M.J.; Johnson, P.W.; Blaydes, J.P. The role of MNK proteins and eIF4E phosphorylation in breast cancer cell proliferation and survival. Cancer Biol. 2010, 10, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzmil, M.; Morin, P., Jr.; Lino, M.M.; Merlo, A.; Frank, S.; Wang, Y.; Moncayo, G.; Hemmings, B.A. MAP kinase-interacting kinase 1 regulates SMAD2-dependent TGF-β signaling pathway in human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2392–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Peng, G.; Li, E.; Xi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, G.; Wu, Q.; He, J. MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine kinase 2 promotes proliferation, metastasis, and predicts poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Du, P.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Liu, P.; Liu, H. Significance of MNK1 in prognostic prediction and chemotherapy development of epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 19, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Díez, C.; García-Recio, E.M.; Pérez-Morgado, M.I.; García-Hernández, M.; Sanz-Criado, L.; Sacristán, S.; Toledo-Lobo, M.V.; Pérez-Mies, B.; Esteban-Rodríguez, I.; Pascual, A.; et al. Increased expression of MNK1b, the spliced isoform of MNK1, predicts poor prognosis and is associated with triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13501–13516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhuang, H.; Chen, B. MAP Kinase-Interacting Kinase 1 Promotes Proliferation and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Is an Unfavorable Prognostic Biomarker. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto-Díez, C.; Ferreras-Martín, R.; Carrión-Marchante, R.; González, V.M.; Martín, M.E. Deeping in the Role of the MAP-Kinases Interacting Kinases (MNKs) in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santag, S.; Siegel, F.; Wengner, A.M.; Lange, C.; Bömer, U.; Eis, K.; Pühler, F.; Lienau, P.; Bergemann, L.; Michels, M.; et al. BAY 1143269, a novel MNK1 inhibitor, targets oncogenic protein expression and shows potent anti-tumor activity. Cancer Lett. 2017, 390, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, S.H.; Sprengeler, P.A.; Chiang, G.G.; Appleman, J.R.; Chen, J.; Clarine, J.; Eam, B.; Ernst, J.T.; Han, Q.; Goel, V.K.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Pyridone-Aminal eFT508 Targeting Dysregulated Translation by Selective Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Interacting Kinases 1 and 2 (MNK1/2) Inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3516–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Kannan, S.; Verma, C.S.; Nacro, K. Update on the Development of MNK Inhibitors as Therapeutic Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 983–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Watanabe-Fukunaga, R.; Fukuyama, H.; Nagata, S.; Fukunaga, R. Mnk2 and Mnk1 are essential for constitutive and inducible phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E but not for cell growth or development. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 6539–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J. Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: Current potential and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.W.; Shima, D.T.; Calias, P.; Cunningham, E.T., Jr.; Guyer, D.R.; Adamis, A.P. Pegaptanib, a targeted anti-VEGF aptamer for ocular vascular disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.K.; Lu, A.; Zhang, B.T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, G. Structural Biology for the Molecular Insight between Aptamers and Target Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xiang, J. Aptamers, the Nucleic Acid Antibodies, in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Recio, E.M.; Pinto-Díez, C.; Pérez-Morgado, M.I.; García-Hernández, M.; Fernández, G.; Martín, M.E.; González, V.M. Characterization of MNK1b DNA Aptamers That Inhibit Proliferation in MDA-MB231 Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Díez, C.; Ferreras-Martín, R.; Carrión-Marchante, R.; Klett-Mingo, J.I.; García-Hernández, M.; Pérez-Morgado, M.I.; Sacristán, S.; Barragán, M.; Seijo-Vila, M.; Tundidor, I.; et al. An optimized MNK1b aptamer, apMNKQ2, and its potential use as a therapeutic agent in breast cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 30, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Biswas, S.; Oki, Y.; Issa, J.P.; Berry, D.A. A parallel phase I/II clinical trial design for combination therapies. Biometrics 2007, 63, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Tourneau, C.; Lee, J.J.; Siu, L.L. Dose escalation methods in phase I cancer clinical trials. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, K.J.; Mulero-Sanchez, A.; Berninger, A.; Ruiz-Canas, L.; Bosma, A.; Gorgulu, K.; Wu, N.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Kaya-Aksoy, E.; Ruess, D.A.; et al. Extensive preclinical validation of combined RMC-4550 and LY3214996 supports clinical investigation for KRAS mutant pancreatic cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendel, H.G.; Silva, R.L.; Malina, A.; Mills, J.R.; Zhu, H.; Ueda, T.; Watanabe-Fukunaga, R.; Fukunaga, R.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Pelletier, J.; et al. Dissecting eIF4E action in tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.K.; Brown, M.C.; Geradts, J.; Bao, X.; Robinson, T.J.; Jolly, M.K.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Palmer, G.M.; Gromeier, M.; Levine, H.; et al. XIAP Regulation by MNK Links MAPK and NFκB Signaling to Determine an Aggressive Breast Cancer Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1726–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Kim, S.Y.; Cheng, H. Update 2020: Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung 2020, 198, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Wang, W.; Luo, J.; Chu, S.; Chen, L.; Xu, L.; Zang, H.; Alnemah, M.M.; Ma, J.; Fan, S. CGP57380 enhances efficacy of RAD001 in non-small cell lung cancer through abrogating mTOR inhibition-induced phosphorylation of eIF4E and activating mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27787–27801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, R.; Iwakawa, R.; Tang, M.; Kohno, T.; Angulo, B.; Pio, R.; Montuenga, L.M.; Minna, J.D.; Yokota, J.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M. A gene-alteration profile of human lung cancer cell lines. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korrodi-Gregório, L.; Soto-Cerrato, V.; Vitorino, R.; Fardilha, M.; Pérez-Tomás, R. From Proteomic Analysis to Potential Therapeutic Targets: Functional Profile of Two Lung Cancer Cell Lines, A549 and SW900, Widely Studied in Pre-Clinical Research. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chan, D.W.H.; Ma, Y.; Lu, A.; Yu, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, G. Strategies for developing long-lasting therapeutic nucleic acid aptamer targeting circulating protein: The present and the future. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1048148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guttikonda, S.; Roberts, L.; Uziel, T.; Semizarov, D.; Elmore, S.W.; Leverson, J.D.; Lam, L.T. Mcl-1 is critical for survival in a subgroup of non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1963–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelaziz, A.M.; Basnet, S.K.C.; Islam, S.; Li, M.; Tadesse, S.; Albrecht, H.; Gerber, C.; Yu, M.; Wang, S. Synthesis and evaluation of 2′H-spiro[cyclohexane-1,3′-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine]-1′,5′-dione derivatives as Mnk inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 2650–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.; Gediya, L.; Kwegyir-Afful, A.K.; Ramamurthy, V.P.; Purushottamachar, P.; Mbatia, H.; Njar, V.C. First MNKs degrading agents block phosphorylation of eIF4E, induce apoptosis, inhibit cell growth, migration and invasion in triple negative and Her2-overexpressing breast cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, J.E.; Tian, S.; Jones, G.G.; Xie, J.; Iadevaia, V.; Jenei, V.; Thomas, G.; Proud, C.G. The MAP kinase-interacting kinases regulate cell migration, vimentin expression and eIF4E/CYFIP1 binding. Biochem. J. 2015, 467, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwegyir-Afful, A.K.; Bruno, R.D.; Purushottamachar, P.; Murigi, F.N.; Njar, V.C. Galeterone and VNPT55 disrupt Mnk-eIF4E to inhibit prostate cancer cell migration and invasion. Febs J. 2016, 283, 3898–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Guo, J.; Yang, W.; Goncalves, C.; Rzymski, T.; Dreas, A.; Żyłkiewicz, E.; Mikulski, M.; Brzózka, K.; Golas, A.; et al. MNK1/2 inhibition limits oncogenicity and metastasis of KIT-mutant melanoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 4179–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, F.; Cai, Y.; Liu, T. Expression profiling of integrins in lung cancer cells. Pathol. Res. Pr. 2009, 205, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, K.S.; Idevall-Hagren, O.; Stefansson, A.; Velling, T.; Jackson, S.P.; Downward, J.; Tengholm, A.; Johansson, S. PI3-kinase p110α mediates β1 integrin-induced Akt activation and membrane protrusion during cell attachment and initial spreading. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 1838–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iksen; Pothongsrisit, S.; Pongrakhananon, V. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Lung Cancer: An Update Regarding Potential Drugs and Natural Products. Molecules 2021, 26, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, V.P.; Ramalingam, S.; Gediya, L.K.; Njar, V.C.O. The retinamide VNLG-152 inhibits f-AR/AR-V7 and MNK-eIF4E signaling pathways to suppress EMT and castration-resistant prostate cancer xenograft growth. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puisieux, A.; Brabletz, T.; Caramel, J. Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.; Ramamurthy, V.P.; Gediya, L.K.; Murigi, F.N.; Purushottamachar, P.; Huang, W.; Choi, E.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Vasaitis, T.S.; Kane, M.A.; et al. The Novel Mnk1/2 Degrader and Apoptosis Inducer VNLG-152 Potently Inhibits TNBC Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Cancers 2019, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Merrett, J.; Tong, S.; Flower, B.; Xie, J.; Yu, R.; Tian, S.; Gao, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Design, synthesis and activity of Mnk1 and Mnk2 selective inhibitors containing thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine scaffold. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 162, 735–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, M.; Blyth, G.T.; Mina, A.A.; Kosciuczuk, E.M.; Dolniak, B.; Dinner, S.; Altman, J.K.; Eklund, E.A.; Saleiro, D.; Beauchamp, E.M.; et al. Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansook, S.; Lineham, E.; Hassell-Hart, S.; Tizzard, G.J.; Coles, S.J.; Spencer, J.; Morley, S.J. Probing the Anticancer Action of Novel Ferrocene Analogues of MNK Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimon, A.; Mogilevsky, M.; Shilo, A.; Golan-Gerstl, R.; Obiedat, A.; Ben-Hur, V.; Lebenthal-Loinger, I.; Stein, I.; Reich, R.; Beenstock, J.; et al. Mnk2 alternative splicing modulates the p38-MAPK pathway and impacts Ras-induced transformation. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, V.Z.; Nichol, J.N.; Huang, F.; Yang, W.; Preston, S.E.J.; Talat, Z.; Lefrère, H.; Yu, H.; Zhang, G.; et al. MNK1/NODAL Signaling Promotes Invasive Progression of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1646–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Wang, X.; Proud, C.G. Oncogenic MNK signalling regulates the metastasis suppressor NDRG1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46121–46135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Khoury, E.; Guo, Q.; Prabhu, S.A.; Emond, A.; Huang, F.; Gonçalves, C.; Zhan, Y.; Plourde, D.; Nichol, J.N.; et al. MNK1 signaling induces an ANGPTL4-mediated gene signature to drive melanoma progression. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3650–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Di Maio, M. Platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Optimal number of treatment cycles. Expert Rev. Anticancer 2016, 16, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barquín-García, A.; Molina-Cerrillo, J.; Garrido, P.; Garcia-Palos, D.; Carrato, A.; Alonso-Gordoa, T. New oncologic emergencies: What is there to know about inmunotherapy and its potential side effects? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.H.; Yang, J.C.; Mok, T.S.; Loong, H.H. Overview of current systemic management of EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, i3–i9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steurer, M.; Montillo, M.; Scarfò, L.; Mauro, F.R.; Andel, J.; Wildner, S.; Trentin, L.; Janssens, A.; Burgstaller, S.; Frömming, A.; et al. Olaptesed pegol (NOX-A12) with bendamustine and rituximab: A phase IIa study in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carrión-Marchante, R.; Pinto-Díez, C.; Klett-Mingo, J.I.; Palacios, E.; Barragán-Usero, M.; Pérez-Morgado, M.I.; Pascual-Mellado, M.; Alcalá, S.; Ruiz-Cañas, L.; Sainz, B., Jr.; et al. An Aptamer against MNK1 for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041273
Carrión-Marchante R, Pinto-Díez C, Klett-Mingo JI, Palacios E, Barragán-Usero M, Pérez-Morgado MI, Pascual-Mellado M, Alcalá S, Ruiz-Cañas L, Sainz B Jr., et al. An Aptamer against MNK1 for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(4):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041273
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrión-Marchante, Rebeca, Celia Pinto-Díez, José Ignacio Klett-Mingo, Esther Palacios, Miriam Barragán-Usero, M. Isabel Pérez-Morgado, Manuel Pascual-Mellado, Sonia Alcalá, Laura Ruiz-Cañas, Bruno Sainz, Jr., and et al. 2023. "An Aptamer against MNK1 for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 4: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041273
APA StyleCarrión-Marchante, R., Pinto-Díez, C., Klett-Mingo, J. I., Palacios, E., Barragán-Usero, M., Pérez-Morgado, M. I., Pascual-Mellado, M., Alcalá, S., Ruiz-Cañas, L., Sainz, B., Jr., González, V. M., & Martín, M. E. (2023). An Aptamer against MNK1 for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics, 15(4), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041273