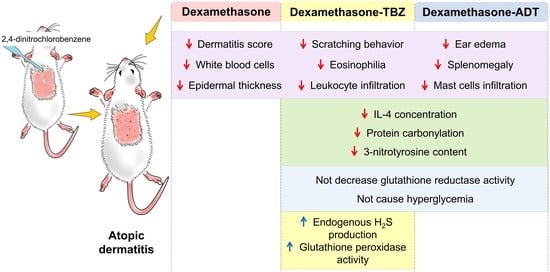
Beneficial Effects of Two Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)-Releasing Derivatives of Dexamethasone with Antioxidant Activity on Atopic Dermatitis in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs
2.3. Induction of Experimental AD and Drug Treatment
2.4. Clinical Assessment of Dermatitis Severity
2.5. Evaluation of Itching
2.6. Ear Edema
2.7. Histopathological Analysis
2.8. Circulating Leukocyte Counting
2.9. Spleen Weight Measurement
2.10. ELISA Measurements
2.11. Measurement of Endogenous H2S Production
2.12. Antioxidants Enzymes
2.13. Analysis of Protein 3-Nitrotyrosine Residues and Carbonyl Groups
2.14. Clinical Biochemistry
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Treatments on Clinical AD Signs
3.2. Histopathological Analysis
3.3. Effects of Treatments on DNCB-Induced Eosinophilia and Splenomegaly
3.4. Plasma IgE Concentration and Skin IL-4 and Eotaxin-1 Contents
3.5. Effects of Treatments on Skin H2S Production
3.6. Antioxidant and Oxidative Stress Markers
3.7. Clinical Biochemistry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakahara, T.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Tsuji, G.; Furue, M. Basics and Recent Advances in the Pathophysiology of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 2020, 48, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, S.; Beck, L.A.; Bieber, T.; Kabashima, K.; Irvine, A.D. Atopic Dermatitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Boguniewicz, M.; Howell, M.D.; Nomura, I.; Hamid, Q.A. New Insights into Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tollefson, M.M.; Bruckner, A.L. Section on Dermatology Atopic Dermatitis: Skin-Directed Management. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e1735-44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wollenberg, A.; Kinberger, M.; Arents, B.; Aszodi, N.; Avila Valle, G.; Barbarot, S.; Bieber, T.; Brough, H.A.; Calzavara Pinton, P.; Christen-Zäch, S.; et al. European Guideline (EuroGuiDerm) on Atopic Eczema—Part II: Non-Systemic Treatments and Treatment Recommendations for Special AE Patient Populations. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1904–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollenberg, A.; Kinberger, M.; Arents, B.; Aszodi, N.; Avila Valle, G.; Barbarot, S.; Bieber, T.; Brough, H.A.; Calzavara Pinton, P.; Christen-Zäch, S.; et al. European Guideline (EuroGuiDerm) on Atopic Eczema: Part I—Systemic Therapy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1409–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Topete, D.; Cidlowski, J.A. One Hormone, Two Actions: Anti- and pro-Inflammatory Effects of Glucocorticoids. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 22, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The Anti-Inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Effects of Glucocorticoids, Recent Developments and Mechanistic Insights. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Kimura, H. The Possible Role of Hydrogen Sulfide as an Endogenous Neuromodulator. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Ding, L.; Xie, Z.Z.; Yang, Y.; Whiteman, M.; Moore, P.K.; Bian, J.S. A Review of Hydrogen Sulfide Synthesis, Metabolism, and Measurement: Is Modulation of Hydrogen Sulfide a Novel Therapeutic for Cancer? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 31, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coavoy-Sánchez, S.A.; Costa, S.K.P.; Muscará, M.N. Hydrogen Sulfide and Dermatological Diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, L.; Ekundi-Valentim, E.; Florenzano, J.; Cerqueira, A.R.A.; Soares, A.G.; Schmidt, T.P.; Santos, K.T.; Teixeira, S.A.; Ribela, M.T.C.P.; Rodrigues, S.F.; et al. Protective Effects of Exogenous and Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide in Mast Cell-Mediated Pruritus and Cutaneous Acute Inflammation in Mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 115, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coavoy-Sánchez, S.A.; Rodrigues, L.; Teixeira, S.A.; Soares, A.G.; Torregrossa, R.; Wood, M.E.; Whiteman, M.; Costa, S.K.P.; Muscará, M.N. Hydrogen Sulfide Donors Alleviate Itch Secondary to the Activation of Type-2 Protease Activated Receptors (PAR-2) in Mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magli, E.; Perissutti, E.; Santagada, V.; Caliendo, G.; Corvino, A.; Esposito, G.; Esposito, G.; Fiorino, F.; Migliaccio, M.; Scognamiglio, A.; et al. H2S Donors and Their Use in Medicinal Chemistry. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.L.; Caliendo, G.; Santagada, V.; Cirino, G. Markedly Reduced Toxicity of a Hydrogen Sulphide-Releasing Derivative of Naproxen (ATB-346). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, J.L.; Nagy, P.; Feener, T.D.; Allain, T.; Ditrói, T.; Vaughan, D.J.; Muscara, M.N.; de Nucci, G.; Buret, A.G. A Proof-of-Concept, Phase 2 Clinical Trial of the Gastrointestinal Safety of a Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Anti-Inflammatory Drug. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvino, A.; Citi, V.; Fiorino, F.; Frecentese, F.; Magli, E.; Perissutti, E.; Santagada, V.; Calderone, V.; Martelli, A.; Gorica, E.; et al. H2S Donating Corticosteroids: Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation in a Murine Model of Asthma. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 35, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, F.; Corvino, A.; Scognamiglio, A.; Citi, V.; Gorica, E.; Fattorusso, C.; Persico, M.; Caliendo, G.; Fiorino, F.; Magli, E.; et al. Hybrids between H2S-Donors and Betamethasone 17-Valerate or Triamcinolone Acetonide Inhibit Mast Cell Degranulation and Promote Hyperpolarization of Bronchial Smooth Muscle Cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 221, 113517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Watanabe, N.; Geba, G.P.; Sperl, J.; Tsudzuki, M.; Hiroi, J.; Matsumoto, M.; Ushio, H.; Saito, S.; Askenase, P.W.; et al. Development of Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesion with IgE Hyperproduction in NC/Nga Mice. Int. Immunol. 1997, 9, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xian, Y.F.; Loo, S.; Chan, W.Y.; Liu, L.; Lin, Z.X. Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effects of Dictamni Cortex: Studies on In Vitro and In Vivo Experimental Models. Phytomedicine 2021, 82, 153453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva Gonçalves, V.; Ortega, A.A.C.; Steffens, J.P.; Spolidorio, D.M.P.; Rossa, C.; Spolidorio, L.C. Long-Term Testosterone Depletion Attenuates Inflammatory Bone Resorption in the Ligature-Induced Periodontal Disease Model. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ukeda, H.; Maeda, S.; Ishii, T.; Sawamura, M. Spectrophotometric Assay for Superoxide Dismutase Based on Tetrazolium Salt 3′-1-(Phenylamino)-Carbonyl-3, 4-Tetrazolium]-Bis(4-Methoxy-6-Nitro)Benzenesulfonic Acid Hydrate Reduction by Xanthine-Xanthine Oxidase. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 251, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, P.; Prencipe, L.; Berti, G. Use of 3,5-Dichloro-2-Hydroxybenzenesulfonic Acid/4-Aminophenazone Chromogenic System in Direct Enzymic Assay of Uric Acid in Serum and Urine. Clin. Chem. 1980, 26, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flohé, L.; Günzler, W.A. Assays of Glutathione Peroxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlberg, I.; Mannervik, B. Purification and Characterization of the Flavoenzyme Glutathione Reductase from Rat Liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, 5475–5480. [Google Scholar]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione S Transferases. The First Enzymatic Step in Mercapturic Acid Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuhako, M.H.; Augusto, O.; Linares, E.; Chadi, G.; Giorgio, S.; Pereira, C.A. Tempol Ameliorates Murine Viral Encephalomyelitis by Preserving the Blood-Brain Barrier, Reducing Viral Load, and Lessening Inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.E.; Keshavarzian, A.; Pasco, D.S.; Frommel, T.O.; Winship, D.H.; Holmes, E.W. Determination of Protein Carbonyl Groups by Immunoblotting. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 266, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshorafa, A.K.H.; Guo, Q.; Zeng, F.; Chen, M.; Tan, G.; Tang, Z.; Yin, R. Psoriasis Is Associated with Low Serum Levels of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Potential Anti-Inflammatory Molecule. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2012, 228, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Yao, W.; Chen, Y.; Geng, B.; Tang, C. Plasma Level of Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide in Patients with Acute Asthma. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2008, 40, 505–508. [Google Scholar]
- Moniaga, C.S.; Kamata, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Suga, Y.; Tominaga, M.; Takamori, K. Hydrogen Sulfide Modulates the Expression of Axon-Guidance Molecules in Human Keratinocytes. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 97, 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-L.; Tian, B.; Huang, Y.; Peng, X.-Y.; Chen, L.-H.; Li, J.-C.; Liu, T. Hydrogen Sulfide-Induced Itch Requires Activation of Cav3.2 T-Type Calcium Channel in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerő, D.; Torregrossa, R.; Perry, A.; Waters, A.; Le-Trionnaire, S.; Whatmore, J.L.; Wood, M.; Whiteman, M. The Novel Mitochondria-Targeted Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Donors AP123 and AP39 Protect against Hyperglycemic Injury in Microvascular Endothelial Cells in Vitro. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.L.; Caliendo, G.; Santagada, V.; Cirino, G.; Fiorucci, S. Gastrointestinal Safety and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Diclofenac Derivative in the Rat. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekundi-Valentim, E.; Mesquita, F.P.; Santos, K.T.; de Paula, M.A.V.; Florenzano, J.; Zanoni, C.I.; Rodrigues, L.; de Nucci, G.; Teixeira, S.A.; Ferreira, H.H.; et al. A Comparative Study on the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Single Oral Doses of Naproxen and Its Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)-Releasing Derivative ATB-346 in Rats with Carrageenan-Induced Synovitis. Med. Gas Res. 2013, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piloto Valdés, L.; Gómez Echevarría, A.H.; Valdés Sánchez, A.F.; Ochoa Ochoa, C.; Chong López, A.; Mier Naranjo, G. Atopic Dermatitis. Findings of Skin Biopsies. Allergol. Immunopathol. 1990, 18, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Zanardo, R.C.O.; Brancaleone, V.; Distrutti, E.; Fiorucci, S.; Cirino, G.; Wallace, J.L. Hydrogen Sulfide Is an Endogenous Modulator of Leukocyte-Mediated Inflammation. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2118–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Goodarzi, H.; Chen, H.Y. IgE, Mast Cells, and Eosinophils in Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 41, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druilhe, A.; Létuvé, S.; Pretolani, M. Glucocorticoid-Induced Apoptosis in Human Eosinophils: Mechanisms of Action. Apoptosis 2003, 8, 481–495. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Wu, R.; Geng, B.; Qi, Y.-F.; Wang, P.-P.; Yao, W.-Z.; Tang, C.-S. Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Reduces Airway Inflammation and Remodeling in a Rat Model of Asthma. Cytokine 2009, 45, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benetti, L.R.; Campos, D.; Gurgueira, S.A.; Vercesi, A.E.; Guedes, C.E.V.; Santos, K.L.; Wallace, J.L.; Teixeira, S.A.; Florenzano, J.; Costa, S.K.P.; et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Inhibits Oxidative Stress in Lungs from Allergic Mice In Vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 698, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, P.; Yang, G.; Cao, Q.; Wang, R. The Inhibitory Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Asthma. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, D.; Ravagnani, F.G.; Gurgueira, S.A.; Vercesi, A.E.; Teixeira, S.A.; Costa, S.K.P.; Muscará, M.N.; Ferreira, H.H.A. Increased Glutathione Levels Contribute to the Beneficial Effects of Hydrogen Sulfide and Inducible Nitric Oxide Inhibition in Allergic Lung Inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 39, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frew, A.J. Allergen Immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S306–S313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, N.A.; Bennett, B.L.; Graham, N.M.H.; Pirozzi, G.; Stahl, N.; Yancopoulos, G.D. Targeting Key Proximal Drivers of Type 2 Inflammation in Disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.K.; Marshall, J.D. Dexamethasone Promotes Type 2 Cytokine Production Primarily through Inhibition of Type 1 Cytokines. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2001, 21, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Corticosteroids, IgE, and Atopy. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chu, L. Hydrogen Sulfide Protects against Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats by Inhibiting NF-ΚB Expression and Regulating Th1/Th2 Balance. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 224, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Hou, C.L.; Mu, X.P.; Sun, C.; Zhu, Y.C.; Wang, M.J.; Lv, Q.Z. H2S Donor NaHS Changes the Production of Endogenous H2S and NO in D-Galactose-Induced Accelerated Ageing. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 5707830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertino, L.; Guarneri, F.; Cannavò, S.P.; Casciaro, M.; Pioggia, G.; Gangemi, S. Oxidative Stress and Atopic Dermatitis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omata, N.; Tsukahara, H.; Ito, S.; Ohshima, Y.; Yasutomi, M.; Yamada, A.; Jiang, M.; Hiraoka, M.; Nambu, M.; Deguchi, Y.; et al. Increased Oxidative Stress in Childhood Atopic Dermatitis. Life Sci. 2001, 69, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Oh, S.-Y.; Shin, Y.-K. Association of Glutathione-S-Transferase Polymorphisms with Atopic Dermatitis Risk in Preschool Age Children. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2009, 47, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaranjani, N.; Rao, S.V.; Rajeev, G. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidants in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 2683–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsello, T.; Komaravelli, N.; Casola, A. Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Nrf2-and Sirtuin-Dependent Maintenance of Cellular Redox Balance. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Bełtowski, J. Synthesis, Metabolism, and Signaling Mechanisms of Hydrogen Sulfide: An Overview. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 2007, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, B.; Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Hydrogen Sulfide Signaling in Mitochondria and Disease. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 13098–13125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schäfer, M.; Farwanah, H.; Willrodt, A.H.; Huebner, A.J.; Sandhoff, K.; Roop, D.; Hohl, D.; Bloch, W.; Werner, S. Nrf2 Links Epidermal Barrier Function with Antioxidant Defense. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Peng, G.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, Z.; Han, X. Sulforaphane Has a Therapeutic Effect in an Atopic Dermatitis Murine Model and Activates the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, M.; Lee, T.H.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, H.; Son, Y.; Lee, E.H.; Kim, J. Inhibitory Effect of 5,6-Dihydroergosteol-Glucoside on Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions via Suppression of NF-ΚB and STAT Activation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 79, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-G.; Lee, J.-E.; Jeong, D.-G.; Lee, Y.-H.; Park, S.-I.; Lee, D.-G.; Han, C.-H.; Kang, S.-J.; Song, C.-H.; Choi, S.-H.; et al. Bathing Effects of East Saline Groundwater Concentrates on Allergic (Atopic) Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions Induced by 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene in Hairless Mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3448–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ku, J.M.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, H.I.; Seo, H.S.; Shin, Y.C.; Ko, S.-G. Effects of Angelicae Dahuricae Radix on 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions in Mice Model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rooman, R.; Koster, G.; Bloemen, R.; Gresnigt, R.; van Buul-Offers, S.C. The Effect of Dexamethasone on Body and Organ Growth of Normal and IGF-II-Transgenic Mice. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 163, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, T.; McQueen, A.; Chen, T.C.; Wang, J.C. Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis by Glucocorticoids. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 872, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piragine, E.; Calderone, V. Pharmacological Modulation of the Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) System by Dietary H2S-Donors: A Novel Promising Strategy in the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Phyther. Res. 2021, 35, 1817–1846. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, N.; Wei, F.Y.; Watanabe, S.; Hirayama, M.; Ohuchi, Y.; Fujimura, A.; Kaitsuka, T.; Ishii, I.; Sawa, T.; Nakayama, H.; et al. Reactive Sulfur Species Regulate TRNA Methylthiolation and Contribute to Insulin Secretion. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichette, J.; Fynn-Sackey, N.; Gagnon, J. Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfate Prebiotic Stimulates the Secretion of GLP-1 and Improves Glycemia in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 3416–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, D.; You, V.; Li, W.; Hu, B.; Zhang, S.; Miao, L.; Xian, M.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, X. Cystathionine γ-Lyase Deficiency Aggravates Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance via FoxO1-Dependent Hepatic Gluconeogenesis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 4212–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Feng, Y.; Lin, X.; Yang, J.; Cui, Q.; Tang, C.; Xu, G.; et al. Cystathionine γ Lyase-Hydrogen Sulfide Increases Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Activity by Sulfhydration at C139 Site Thereby Promoting Glucose Uptake and Lipid Storage in Adipocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Hao, D.D.; Sun, J.P.; Li, W.W.; Zhao, M.M.; Li, X.H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Ding, Y.J.; Liu, J.; et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Treatment Promotes Glucose Uptake by Increasing Insulin Receptor Sensitivity and Ameliorates Kidney Lesions in Type 2 Diabetes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, W.; Wang, C.; Li, D. The Content of Hydrogen Sulfide in Plasma of Cirrhosis Rats Combined with Portal Hypertension and the Correlation with Indexes of Liver Function and Liver Fibrosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5022–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coavoy-Sánchez, S.A.; Cerqueira, A.R.A.; Teixeira, S.A.; Santagada, V.; Andreozzi, G.; Corvino, A.; Scognamiglio, A.; Sparaco, R.; Caliendo, G.; Severino, B.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Two Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)-Releasing Derivatives of Dexamethasone with Antioxidant Activity on Atopic Dermatitis in Mice. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071907
Coavoy-Sánchez SA, Cerqueira ARA, Teixeira SA, Santagada V, Andreozzi G, Corvino A, Scognamiglio A, Sparaco R, Caliendo G, Severino B, et al. Beneficial Effects of Two Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)-Releasing Derivatives of Dexamethasone with Antioxidant Activity on Atopic Dermatitis in Mice. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(7):1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071907
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoavoy-Sánchez, Silvia Abigail, Anderson Romério Azevedo Cerqueira, Simone Aparecida Teixeira, Vincenzo Santagada, Giorgia Andreozzi, Angela Corvino, Antonia Scognamiglio, Rosa Sparaco, Giuseppe Caliendo, Beatrice Severino, and et al. 2023. "Beneficial Effects of Two Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)-Releasing Derivatives of Dexamethasone with Antioxidant Activity on Atopic Dermatitis in Mice" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 7: 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071907
APA StyleCoavoy-Sánchez, S. A., Cerqueira, A. R. A., Teixeira, S. A., Santagada, V., Andreozzi, G., Corvino, A., Scognamiglio, A., Sparaco, R., Caliendo, G., Severino, B., Costa, S. K. P., Spolidorio, L. C., & Muscará, M. N. (2023). Beneficial Effects of Two Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)-Releasing Derivatives of Dexamethasone with Antioxidant Activity on Atopic Dermatitis in Mice. Pharmaceutics, 15(7), 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071907