Chlorhexidine–Silver Nanoparticle Conjugation Leading to Antimicrobial Synergism but Enhanced Cytotoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.1.2. Bacteria and Fungi
2.1.3. Virus
2.1.4. Cells
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Green Tea Total Polyphenols Extraction
2.2.2. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (SN)
2.2.3. Determination of SN Concentration
2.2.4. Conjugation of SN and Chlorhexidine
2.2.5. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
2.2.6. Dynamic Light Scattering/Laser Doppler Electrophoresis
2.2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.2.8. FT-IR Study
2.2.9. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.2.10. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity
2.2.11. Cytotoxicity (CC50) and Antiviral Effect (IC50 and SI) Evaluation via a Neutral Red (NR) Uptake Assay
2.2.12. Determination of the Effect on Extracellular Virions—Virucidal Effect
- SN 35 μg/mL (MTC) or 350 μg/mL (2-fold dilution of stock solution);
- Cx 2 μg/mL (MTC) or 113 μg/mL (10-fold dilution of stock solution);
- SN-Cx 1.2/2 μg/mL (MTC) or 70/113 μg/mL (10-fold dilution of stock solution).
2.2.13. Statistical Data Processing
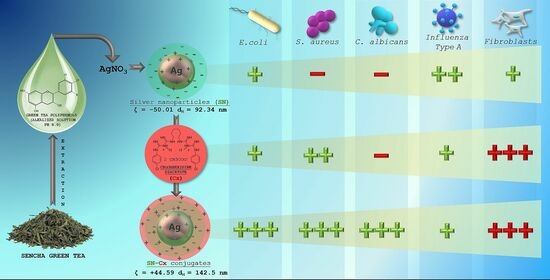
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Silver Nanoparticle Synthesis, Optimization, and Conjunction
3.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.4. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity
3.4.1. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
3.4.2. Minimal Bactericidal/Fungicidal Concentration (MBC/MFC)
3.5. Cytotoxicity, Antiviral, and Virucidal Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, K.; Guo, Z.; Fang, K.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Gu, N. PLLA microcapsules combined with silver nanoparticles and chlorhexidine acetate showing improved antibacterial effect. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myronov, P.; Sulaieva, O.; Korniienko, V.; Banasiuk, R.; Vielikov, M.; Husak, Y.; Pernakov, M.; Deineka, V.; Yusupova, A.; Hristova, M.-T.; et al. Combination of Chlorhexidine and Silver Nanoparticles: An Efficient Wound Infection and Healing Control System. BioNanoScience 2021, 11, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernakov, M.; Ermini, M.L.; Sulaieva, O.; Cassano, D.; Santucci, M.; Husak, Y.; Korniienko, V.; Giannone, G.; Yusupova, A.; Liubchak, I.; et al. Complementary Effect of Non-Persistent Silver Nano-Architectures and Chlorhexidine on Infected Wound Healing. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, D.R.; Silva, S.; Negri, M.; Gorup, L.F.; de Camargo, E.R.; Oliveira, R.; Barbosa, D.B.; Henriques, M. Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles in combination with nystatin and chlorhexidine digluconate against Candida albicans and Candida glabrata biofilms. Mycoses 2013, 56, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charannya, S.; Duraivel, D.; Padminee, K.; Poorni, S.; Nishanthine, C.; Srinivasan, M. Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of silver nanoparticles and 2% chlorhexidine gluconate when used alone and in combination assessed using agar diffusion method: An In vitro study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2018, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckiewicz, K.P.; Cieciórski, P.; Barcińska, E.; Jaśkiewicz, M.; Narajczyk, M.; Bauer, M.; Kamysz, W.; Megiel, E.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I. Silver Nanoparticles as Chlorhexidine and Metronidazole Drug Delivery Platforms: Their Potential Use in Treating Periodontitis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 495–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Ghezelbash, K.; Asheghi, B.; Abbaszadegan, A.; Amini, A. An In Vitro Study on the Antibacterial Effects of Chlorhexidine-Loaded Positively Charged Silver Nanoparticles on Enterococcus faecalis. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 6405772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Knaz, R.; Pedahzur, R.; Avnir, D. Bioactive doped metals: High synergism in the bactericidal activity of chlorhexidine@silver towards wound pathogenic bacteria. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ge, Y.; Qiu, J.; Shao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, J.; Zheng, X.; Chang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Dong, W.; et al. Redox/pH dual-controlled release of chlorhexidine and silver ions from biodegradable mesoporous silica nanoparticles against oral biofilms. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 7697–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Khan, F.; Alshehri, S.; Khan, A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Wu, H.-F.; Taha, E.I.; Elbagory, I. Unique Properties of Surface-Functionalized Nanoparticles for Bio-Application: Functionalization Mechanisms and Importance in Application. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, N.; Gugleva, V.; Dobreva, M.; Pehlivanov, I.; Stefanov, S.; Andonova, V. Silver Nanoparticles as Multi-Functional Drug Delivery Systems; Farrukh, M.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Liu, Z.-G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Harper, B.J.; Harper, S.L. Differential dissolution and toxicity of surface functionalized silver nanoparticles in small-scale microcosms: Impacts of community complexity. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noah, N. Green synthesis: Characterization and application of silver and gold nanoparticles. In Green Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of Nanoparticles; Shukla, A.K., Iravani, S., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.T.J.; Nyam, K.L. Evaluation of silver nanoparticles in cosmeceutical and potential biosafety complications. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallineni, S.K.; Sakhamuri, S.; Kotha, S.L.; AlAsmari, A.R.G.M.; AlJefri, G.H.; Almotawah, F.N.; Mallineni, S.; Sajja, R. Silver Nanoparticles in Dental Applications: A Descriptive Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Cai, Y.; Chen, X.; Ke, Y. Silver-based nanocomposite for fabricating high performance value-added cotton. Cellulose 2021, 29, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Das, S.S.; Khatoon, A.; Ansari, M.T.; Afzal, M.; Hasnain, M.S.; Nayak, A.K. Bactericidal activity of silver nanoparticles: A mechanistic review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanath, R.; Negi, B. Conventional and green methods of synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial properties. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilger-Casagrande, M.; Lima, R.D. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Mediated by Fungi: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasher, P.; Sharma, M. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Functionalization and Applications; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2022; pp. 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, V.; Weddell, J.A.; Shin, D.E.; Jones, J.E. Gingivitis and Periodontal Disease. In McDonald and Avery’s Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent; Dean, J.A., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 243–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.S. Topical dermatological therapy. In Small Animal Clinical Pharmacology; Maddison, J.E., Page, S.W., Church, D.B., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, S.K.; Malek, N.A.N.N. Characterization and antibacterial activity of chlorhexidine loaded silver-kaolinite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 127, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Hobden, J.; Warner, I. Recycling Antibiotics into GUMBOS: A New Combination Strategy to Combat Multi-Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Molecules 2015, 20, 6466–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Mutreja, V.; Sareen, S.; Ahmad, B.; Faheem, M.; Zahid, N.; Jabbour, G.; Park, J. Exceptional antibacterial and cytotoxic potency of monodisperse greener AgNPs prepared under optimized pH and temperature. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesaragandla, B.; Hayet, S.; Fine, T.; Janke, U.; Chai, L.; Delcea, M. Inhibitory Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate-Silver Nanoparticles and Their Lysozyme Bioconjugates on Biofilm Formation and Cytotoxicity. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 4213–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Luan, S.; Yin, Z.; He, M.; He, C.; Yin, L.; Zou, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, L.; Song, X.; et al. Recent advances in the medical use of silver complex. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hussein, G.; Brza, M.A.; Mohammed, S.J.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Raza Saeed, S.; Hassanzadeh, A. Fabrication of Interconnected Plasmonic Spherical Silver Nanoparticles with Enhanced Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR) Peaks Using Quince Leaf Extract Solution. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemčeková, K.; Svitková, V.; Sochr, J.; Gemeiner, P.; Labuda, J. Gallic acid-coated silver nanoparticles as perspective drug nanocarriers: Bioanalytical study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5493–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, N.H.; Buazar, F.; Matroodi, S. Synergistic effects of combinatorial chitosan and polyphenol biomolecules on enhanced antibacterial activity of biofunctionalized silver nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Khatir, N.M.; Kiarostami, K. Synthesis and Characterization of 𝒌-Carrageenan/PVA Nanocomposite Hydrogels in Combination with MgZnO Nanoparticles to Evaluate the Catechin Release. Polymers 2023, 15, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, N.; Andonova, V.; Jelev, I.; Dimova, G. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles with green tea-extracted reductants: A preliminary study for optimization of the preparation technique. Scr. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 8, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy, N.R. Chemistry of Natural Products: A Laboratory Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Faleiro, M.L.; Miguel, M.G. Use of Essential Oils and Their Components against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. In Fighting Multidrug Resistance with Herbal Extracts, Essential Oils and Their Components; Rai, M.K., Kon, K.V., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repetto, G.; del Peso, A.; Zurita, J.L. Neutral red uptake assay for the estimation of cell viability/cytotoxicity. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, C.S.; Geldart, S.E.; Seelenbinder, J.A.; Brown, P.R. Analysis of Green Tea Constituents by HPLC-FTIR. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2002, 25, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wang, D.; Liang, P.; Zhang, D.; Du, X.; Ni, D.; Yu, Z. Vibrational (FT-IR, Raman) analysis of tea catechins based on both theoretical calculations and experiments. Biophys. Chem. 2020, 256, 106282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theivasanthi, T.; Alagar, M. Electrolytic Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanopowder. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2012, 4, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardhanan, R.; Karuppaiah, M.; Hebalkar, N.; Rao, T.N. Synthesis and surface chemistry of nano silver particles. Polyhedron 2009, 28, 2522–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, K.; Sandeep, B.V.; Pola, S. Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of Allophylus serratus Leaf and Leaf Derived Callus Extracts Mediated Silver Nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 4213275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, B.K.; Chhajlani, M.; Shrivastava, B.D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their characterization by XRD. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 836, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, B.; Selvan, S.; Narayanan, K.; Fawzy, A. Characterization of Chlorhexidine-Loaded Calcium-Hydroxide Microparticles as a Potential Dental Pulp-Capping Material. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barot, T.; Rawtani, D.; Kulkarni, P. Development of Chlorhexidine Loaded Halloysite Nanotube Based Experimental Resin Composite with Enhanced Physico-Mechanical and Biological Properties for Dental Applications. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raso, E.M.G.; Cortes, M.E.; Teixeira, K.I.; Franco, M.B.; Mohallem, N.D.S.; Sinisterra, R.D. A new controlled release system of chlorhexidine and chlorhexidine: βcd inclusion compounds based on porous silica. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2009, 67, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.-Y.; Wang, S.-Y.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.-X.; Zhang, R.-J.; Zhou, P.; Yang, Y.-M.; Chen, L.-Y. Study of structure and optical properties of silver oxide films by ellipsometry, XRD and XPS methods. Thin Solid Films 2004, 455, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeung, D.-G.; Lee, M.; Paek, S.-M.; Oh, J.-M. Controlled Growth of Silver Oxide Nanoparticles on the Surface of Citrate Anion Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxide. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhoondia, Z.H.; Chakraborty, H. Lactobacillus Mediated Synthesis of Silver Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, J.; Kan, J.; Wen, X.; Jin, C. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro anti-diabetic activity of catechin grafted inulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roell, K.R.; Reif, D.M.; Motsinger-Reif, A.A. An Introduction to Terminology and Methodology of Chemical Synergy—Perspectives from Across Disciplines. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The Antibacterial Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Application in Dentistry. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic Basis of Antimicrobial Actions of Silver Nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Formulation Code | Silver Nitrate Conc., mM | Reductant (C8) conc., mg/mL * | Day 2 | Day 7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λmax, nm | Abs ± SD | λmax, nm | Abs ± SD | |||
| 1C8R0.6 | 1 | 0.6 | 426 | 0.307 ± 0.001 | 430 | 0.481 ± 0.001 |
| 2C8R0.6 | 2 | 0.6 | 425 | 0.435 ± 0.002 | 429 | 0.571 ± 0.001 |
| 1C8R1 | 1 | 1.0 | 423 | 0.617 ± 0.001 | 429 | 0.744 ± 0.002 |
| 2C8R1 | 2 | 1.0 | 425 | 0.776 ± 0.002 | 428 | 0.889 ± 0.002 |
| 1C8R1.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 425 | 0.753 ± 0.002 | 429 | 0.913 ± 0.002 |
| 2C8R1.5 | 2 | 1.5 | 425 | 0.948 ± 0.001 | 430 | 1.125 ± 0.003 |
| 1C8R3 | 1 | 3 | 417 | 1.350 ± 0.003 | 418 | 1.395 ± 0.005 |
| 2C8R3 | 2 | 3 | 421 | 1.828 ± 0.003 | 424 | 1.904 ± 0.002 |
| 1C8R4.5 | 1 | 4.5 | 416 | 1.379 ± 0.004 | 415 | 1.367 ± 0.003 |
| 2C8R4.5 | 2 | 4.5 | 421 | 2.374 ± 0.003 | 422 | 2.386 ± 0.002 |
| 1C8R6 | 1 | 6 | 413 | 1.448 ± 0.004 | 415 | 1.498 ± 0.002 |
| 2C8R6 ** | 2 | 6 | 417 | 2.584 ± 0.004 | 420 | 2.758 ± 0.003 |
| Formulation Code | Cx 3.75 mg/mL vol. (mL) | Cx Final Conc. in Solution, mg/mL | Zeta Potential, mV |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2C8R1.5 | n/a * | n/a | −43.45 |
| 2C8R3 | n/a | n/a | −39.06 |
| 2C8R4.5 | n/a | n/a | −50.01 |
| 2C8R1.5 Cx+ | 0.5 | 0.47 | +31.24 |
| 2C8R1.5 Cx++ | 1.0 | 0.83 | +33.74 |
| 2C8R1.5 Cx+++ | 1.5 | 1.13 | +36.2 |
| 2C8R3 Cx+ | 0.5 | 0.47 | +40.02 |
| 2C8R3 Cx++ | 1.0 | 0.83 | +44.34 |
| 2C8R3 Cx+++ | 1.5 | 1.13 | +42.44 |
| 2C8R4.5 Cx+ | 0.5 | 0.47 | +41.22 |
| 2C8R4.5 Cx++ | 1.0 | 0.83 | +43.78 |
| 2C8R4.5 Cx+++ | 1.5 | 1.13 | +44.59 |
| Infectious Strain | MIC | MBC/MFC | FICSN | FICCx | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SN (µg/mL) | Cx (µg/mL) | SN + Cx (µg/mL) | SN (µg/mL) | Cx (µg/mL) | SN + Cx (µg/mL) | |||
| E. coli | 175 | 35.3 | SN 5.5 + Cx 8.8 | 175 | 141.3 | SN 5.5 + Cx 8.8 | 0.031 | 0.023 |
| S. aureus | n.e.* | 17.7 | SN 5.5 + Cx 8.8 | n.e. | 35.3 | SN 10.9 + Cx 17.7 | <<0.016 ** | 0.497 |
| C. albicans | n.e.* | 17.7 | SN 5.5 + Cx 8.8 | n.e. | n.e. | SN 10.9 + Cx 17.7 | <<0.016 | 0.497 |
| Active Agent | Cell Line | Cytotoxicity | Antiviral Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC50 (μg/mL) ± SD | IC50 (μg/mL) | SI | ||
| SN | MDCK | 56.4 ± 0.4 | 43.6 ± 16.6 | 1.29 |
| Cx | MDCK | 2.5 ± 0.7 | - | - |
| SN-Cx | MDCK | 1.6/2.6 ± 0.1 | - | - |
| SN | A549 | 60.7 ± 0.3 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Cx | A549 | 5.3 ± 0.7 | n.d. | n.d. |
| SN-Cx | A549 | 3.6/5.8 ± 0.2 | n.d. | n.d. |
| SN | BJ | 16.9 ± 0.4 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Cx | BJ | 2.2 ± 0.1 | n.d. | n.d. |
| SN-Cx | BJ | 1.5/2.4 ± 0.5 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Active Agent | Δlg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 min | 15 min | 30 min | 60 min | |
| SN 35 μg/mL | 2.5 | 2.66 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Cx 2.0 μg/mL | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SN-Cx 1.2/2.0 μg/mL | 0 | 0 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| Active Agent | Δlg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 min | 15 min | 30 min | 60 min | |
| SN 350 μg/mL | 2 | 2.33 | 2.5 | 3 |
| Cx 113 μg/mL | 1 | 1.33 | 1.66 | 1.66 |
| SN-Cx 70.0/113.0 μg/mL | 1 | 1.33 | 1.66 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivanova, N.; Ermenlieva, N.; Simeonova, L.; Kolev, I.; Slavov, I.; Karashanova, D.; Andonova, V. Chlorhexidine–Silver Nanoparticle Conjugation Leading to Antimicrobial Synergism but Enhanced Cytotoxicity. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092298
Ivanova N, Ermenlieva N, Simeonova L, Kolev I, Slavov I, Karashanova D, Andonova V. Chlorhexidine–Silver Nanoparticle Conjugation Leading to Antimicrobial Synergism but Enhanced Cytotoxicity. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(9):2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092298
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvanova, Nadezhda, Neli Ermenlieva, Lora Simeonova, Iliyan Kolev, Iliya Slavov, Daniela Karashanova, and Velichka Andonova. 2023. "Chlorhexidine–Silver Nanoparticle Conjugation Leading to Antimicrobial Synergism but Enhanced Cytotoxicity" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 9: 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092298
APA StyleIvanova, N., Ermenlieva, N., Simeonova, L., Kolev, I., Slavov, I., Karashanova, D., & Andonova, V. (2023). Chlorhexidine–Silver Nanoparticle Conjugation Leading to Antimicrobial Synergism but Enhanced Cytotoxicity. Pharmaceutics, 15(9), 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092298