Nanonization and Deformable Behavior of Fattigated Peptide Drug in Mucoadhesive Buccal Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
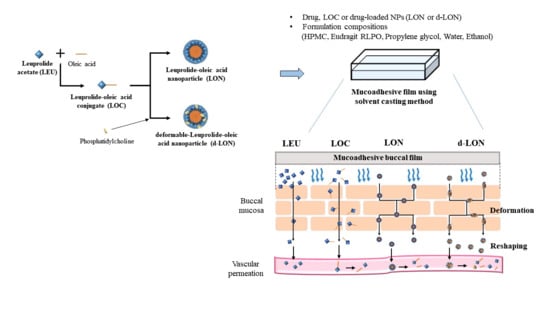
2.2. Preparation of LOC, LON, d-LON, and the MBFs
2.2.1. Preparation of LOC, LON, and d-LON
2.2.2. Preparation of MBFs
2.3. Physicochemical Characterizations of LON and d-LON
2.3.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.3.2. Deformability Index (DI)
2.4. Physicochemical Characterizations of MBF
2.4.1. Weight and Thickness Variations
2.4.2. HPLC Analysis
2.4.3. Drug Content
2.4.4. Folding Endurance
2.4.5. Surface pH
2.4.6. Swelling Study
2.4.7. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM)
2.4.8. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrometer
2.4.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4.10. In Vitro Residence Time
2.4.11. In Vitro Dissolution Study
2.4.12. In Vitro Permeability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of LON and d-LON
3.2. Formulation Optimization of MBF
3.2.1. Physical Properties of MBF
3.2.2. Swelling Study and In Vitro Residence Time
3.2.3. In Vitro Dissolution Study of Formulations
3.2.4. In Vitro Permeability of Formulations
3.3. Physicochemical Characterization of the Optimized MBF
3.3.1. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM)
3.3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrometer
3.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.3.4. In Vitro Dissolution Study
3.3.5. In Vitro Permeability Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MBFs | Mucoadhesive buccal films |
| LEU | Leuprolide |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| LOC | LEU-oleic acid conjugate |
| d-LON | Deformable variant of LON |
| DI | Deformability index |
| GnRH | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| FT-IR | Fourier-transform infrared |
| FE-SEM | Field-emission scanning electron microscopy |
| RP | Reversed-phase |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatographic system |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Fluoride |
References
- Zou, W.; Mourad, F.K.; Zhang, X.; Ahn, D.U.; Cai, Z.; Jin, Y. Phase separation behavior and characterization of ovalbumin and propylene glycol alginate complex coacervates. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 105978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.F.; Lee, D.; Carlson, R.; Rao, G.S.; Hui, H.W.; Adjei, L.; Herrin, M.; Sundberg, D.; Hsu, L. The effects of formulation variables on iontophoretic transdermal delivery of leuprolide to humans. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1993, 19, 1557–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Ngo, H.V.; Park, C.; Lee, B.-J. Mucoadhesive buccal tablet of leuprolide and its fatty acid conjugate: Design, in vitro evaluation and formulation strategies. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 639, 122963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Okada, H.; Yashiki, T.; Shimamoto, T. A new technique to efficiently entrap leuprolide acetate into microcapsules of polylactic acid or copoly(lactic/glycolic) acid. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.C.; Meethal, S.V.; Bowen, R.L.; Atwood, C.S. Leuprolide acetate: A drug of diverse clinical applications. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J.S.; Missmer, S.A.; Hornstein, M.D.; Laufer, M.R.; Gordon, C.M.; DiVasta, A.D. Long-term effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and add-back in adolescent endometriosis. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 2018, 31, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, O. Eligard: Leuprolide acetate in a novel sustained-release delivery system. Urology 2003, 61, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, K.; Doty, A.C.; Ackermann, R.; Zhou, J.; Olsen, K.F.; Feng, M.R.; Wang, Y.; Choi, S.; Qu, W.; Schwendeman, A.S. Characterizing release mechanisms of leuprolide acetate-loaded PLGA microspheres for IVIVC development I: In vitro evaluation. J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, M.; Wan, B.; Bao, Q.; Burgess, D.J. Influence of PLGA molecular weight distribution on leuprolide release from microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, T.; Guan, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y. PEGylated leuprolide with improved pharmacokinetic properties. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunn, U.; Wiedey, K. Safety and clinical efficacy of a new 6-month depot formulation of leuprorelin acetate in patients with prostate cancer in Europe. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2009, 12, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.O.; Huang, S.; Williams Iii, R.O.; McConville, J.T. Films loaded with insulin-coated nanoparticles (ICNP) as potential platforms for peptide buccal delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 122, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caon, T.; Pan, Y.; Simões, C.M.O.; Nicolazzo, J.A. Exploiting the buccal mucosa as an alternative route for the delivery of donepezil hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.G.H.; Pramod Kumar, T.M. Preparation and evaluation of a novel buccal adhesive system. AAPS Pharmscitech 2004, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, Y.; Kuotsu, K.; Bandyopadhyay, A.K. Buccal bioadhesive drug delivery—A promising option for orally less efficient drugs. J Control. Release 2006, 114, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Nair, A.B.; Kumria, R.; Attimarad, M.; Harsha, S. Development and evaluation of nebivolol hydrochloride nanocrystals impregnated buccal film. Farmacia 2019, 67, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamat-Miller, N.; Chittchang, M.; Johnston, T.P. The use of mucoadhesive polymers in buccal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1666–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, J.C.; Eugresya, G.; Hinrichs, W.L.J.; Tjandrawinata, R.R.; Avanti, C.; Frijlink, H.W.; Woerdenbag, H.J. Development of orodispersible films with selected Indonesian medicinal plant extracts. J. Herb. Med. 2017, 7, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Scarpa, M.; Kamlow, M.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W.; Orlu, M. Patient acceptability of 3D printed medicines. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 530, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Ngo, H.V.; Jin, H.-E.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, B.-J. Hydroxyl group-targeted conjugate and its self-assembled nanoparticle of peptide drug: Effect of degree of saturation of fatty acids and modification of physicochemical properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 2243–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, M.B.; Banka, A.L.; Braunreuther, M.; Fromen, C.A.; Kelley, W.J.; Lee, J.; Adili, R.; Holinstat, M.; Eniola-Adefeso, O. Deformable microparticles for shuttling nanoparticles to the vascular wall. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe0143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Tian, F.; Shi, X. Diffusion of deformable nanoparticles in adhesive polymeric gels. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2022, 167, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Xiao, S.; Liang, H. Morphological and mechanical determinants of cellular uptake of deformable nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 11969–11979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, C.N.; Priya, R.; Swain, S.; Jena, G.K.; Panigrahi, K.C.; Ghose, D. Pharmaceutical significance of Eudragit: A review. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 3, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrani, M.; Garbuzenko, O.B.; Minko, T.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Development of edge-activated liposomes for siRNA delivery to human basal epidermis for melanoma therapy. J. Control. Release 2016, 228, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, A.; Qureshi, O.S.; Kim, H.-S.; Cha, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.-K. Improved skin permeation of methotrexate via nanosized ultradeformable liposomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 3813–3824. [Google Scholar]
- Karki, S.; Kim, H.; Na, S.-J.; Shin, D.; Jo, K.; Lee, J. Thin films as an emerging platform for drug delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, J.G.; Tarai, M.; Yadav, N.P.; Patnaik, A.; Mishra, P.; Yadav, K.S. Development and characterization of cellulose–polymethacrylate mucoadhesive film for buccal delivery of carvedilol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shnoudeh, A.J.; Hamad, I.; Abdo, R.W.; Qadumii, L.; Jaber, A.Y.; Surchi, H.S.; Alkelany, S.Z. Chapter 15—Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Metal Nanoparticles. In Biomaterials and Bionanotechnology; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 527–612. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, J.; Wang, H.-L.; Xia, X.; Liu, Y. Mechanisms of deformable nanovesicles based on insulin-phospholipid complex for enhancing buccal delivery of insulin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 7319–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.J.; Eum, J.Y.; Park, S.H.; Kang, M.H.; Park, K.H.; Choi, S.E.; Lee, M.W.; Kang, K.H.; Oh, C.H.; Choi, Y.W. Pep-1 peptide-conjugated elastic liposomal formulation of taxifolin glycoside for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 402, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avachat, A.M.; Gujar, K.N.; Wagh, K.V. Development and evaluation of tamarind seed xyloglucan-based mucoadhesive buccal films of rizatriptan benzoate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andhariya, J.V.; Jog, R.; Shen, J.; Choi, S.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Burgess, D.J. Development of Level A in vitro-in vivo correlations for peptide loaded PLGA microspheres. J. Control. Release 2019, 308, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Kumria, R.; Harsha, S.; Attimarad, M.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Alhaider, I.A. In vitro techniques to evaluate buccal films. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanker, G.; Kumar, C.K.; Gonugunta, C.S.; Kumar, B.V.; Veerareddy, P.R. Formulation and evaluation of bioadhesive buccal drug delivery of tizanidine hydrochloride tablets. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohyagi, N.; Ueda, K.; Higashi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawakami, K.; Moribe, K. Synergetic role of hypromellose and methacrylic acid copolymer in the dissolution improvement of amorphous solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Thakur, N.; Goswami, M. FTIR spectroscopy based identification and compatibility studies of Gamma Oryzanol with various polymers. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Weng, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J. Influence of metal ions on phosphatidylcholine–bovine serum albumin model membrane, an FTIR study. J. Mol. Struct. 2006, 794, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá-Alcalá, S.; Urbán-Morlán, Z.; Aguilar-Rosas, I.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. A biodegradable polymeric system for peptide–protein delivery assembled with porous microspheres and nanoparticles, using an adsorption/infiltration process. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.; An, J.; Park, C.; Kim, D.; Lee, J. Design and characterization of phosphatidylcholine-based solid dispersions of aprepitant for enhanced solubility and dissolution. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Cagno, M.; Bibi, H.A.; Bauer-Brandl, A. New biomimetic barrier Permeapad™ for efficient investigation of passive permeability of drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 73, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevc, G.; Blume, G. Lipid vesicles penetrate into intact skin owing to the transdermal osmotic gradients and hydration force. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 1992, 1104, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padula, C.; Pescina, S.; Nicoli, S.; Santi, P. New insights on the mechanism of fatty acids as buccal permeation enhancers. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Potential of nanoparticles as permeation enhancers and targeted delivery options for skin: Advantages and disadvantages. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3271–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Ye, J.; Xia, X.; Liu, Y. Deformable Nanovesicle-Loaded Gel for Buccal Insulin Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yin, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Shao, L. Understanding the interactions between inorganic-based nanomaterials and biological membranes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 175, 113820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, H.V.; Bak, H.-E.; Nguyen, H.D.; Kye Wan Lee, K.W.; Park, C.; Lee, B.-J. Physicochemical and Biopharmaceutical Controllability of New Self-Assembled Fatty Acid Conjugated Leuprolide for the Enhanced Anticancer Activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 2325–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, P.J.; Carolina, M.-J.; Angeles, P.B. Understanding human salivary esterase activity and its variation under wine consumption conditions. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 24352–24361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Factor | Leuprolide Acetate |
|---|---|
| 2D structure |  |
| Physical appearance | White solid |
| Molecular weight | 1269.45 g/mol |
| Chemical formula | C59H84N16O12 ∙ C2H4O2 |
| Melting point | 150–155 °C (https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB7174300.htm (accessed on 20 March 2024)) |
| Half-life | 3 h |
| Drug class | GnRH analogue; GnRH agonist; Antigonadotropin |
| Route of administration | IM, SC injection |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Solubility in water | Highly water-soluble, ≥66.66 mg/mL |
| log P | −2.7 |
| Dose strength | 3.75, 7.5 mg per month |
| Code | Drug Type | Eudragit RLPO | HPMC | Propylene Glycol | Ethanol | DW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.5 (LEU) | 21 | - | 28 | 0.3 mL | 0.2 mL |
| F2 * | 0.5 (LEU) | 14 | 7 | 28 | 0.3 mL | 0.2 mL |
| 1.0 (LEU) | 14 | 7 | 28 | 0.3 mL | 0.2 mL | |
| 2.0 (LEU) | 14 | 7 | 28 | 0.3 mL | 0.2 mL | |
| 1.22 (LOC) | 14 | 7 | 28 | 0.3 mL | 0.2 mL | |
| 1.22 (LON) | 14 | 7 | 28 | 0.3 mL | 0.2 mL | |
| 1.34 (d-LON) | 14 | 7 | 28 | 0.3 mL | 0.2 mL | |
| F3 | 0.5 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 28 | 0.3 mL | 0.2 mL |
| F4 | 0.5 | 7 | 14 | 28 | 0.3 mL | 0.2 mL |
| F5 | 0.5 | - | 21 | 28 | 0.3 mL | 0.2 mL |
| NPs | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | DI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LON | 251.57 ± 5.52 | 0.263 ± 0.006 | 71.69 ± 2.01 | 9.76 ± 1.24 |
| d-LON | 269.43 ± 5.46 | 0.168 ± 0.059 | 63.69 ± 4.56 | 55.99 ± 5.33 |
| Code | Film Weight (mg) | Film Thickness (μm) | Drug Content (%) | Folding Endurance | Surface pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 57.23 ± 6.48 | 246.87 ± 22.25 | 102.50 ± 18.83 | >300 | 5.72 ± 0.18 |
| F2 | 55.83 ± 2.57 | 222.97 ± 10.27 | 103.78 ± 4.21 | >300 | 5.96 ± 0.08 |
| F3 | 53.97 ± 5.15 | 213.33 ± 22.36 | 108.85 ± 8.60 | >300 | 6.11 ± 0.11 |
| F4 | 51.63 ± 6.84 | 271.93 ± 52.23 | 106.63 ± 14.21 | >300 | 5.79 ± 0.38 |
| F5 | 49.57 ± 12.14 | 312.10 ± 69.82 | 96.18 ± 16.96 | >300 | 6.24 ± 0.16 |
| Code | Residence Time (h) |
|---|---|
| F1 | 3.74 ± 0.58 |
| F2 | 7.41 ± 0.55 |
| F3 | 6.83 ± 0.30 |
| F4 | 6.57 ± 0.47 |
| F5 | 2.23 ± 0.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, W.; Ngo, H.V.; Nguyen, H.D.; Park, J.-M.; Lee, K.W.; Park, C.; Park, J.-B.; Lee, B.-J. Nanonization and Deformable Behavior of Fattigated Peptide Drug in Mucoadhesive Buccal Films. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040468
Kim W, Ngo HV, Nguyen HD, Park J-M, Lee KW, Park C, Park J-B, Lee B-J. Nanonization and Deformable Behavior of Fattigated Peptide Drug in Mucoadhesive Buccal Films. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(4):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040468
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Woojun, Hai V. Ngo, Hy D. Nguyen, Ji-Min Park, Kye Wan Lee, Chulhun Park, Jun-Bom Park, and Beom-Jin Lee. 2024. "Nanonization and Deformable Behavior of Fattigated Peptide Drug in Mucoadhesive Buccal Films" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 4: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040468
APA StyleKim, W., Ngo, H. V., Nguyen, H. D., Park, J. -M., Lee, K. W., Park, C., Park, J. -B., & Lee, B. -J. (2024). Nanonization and Deformable Behavior of Fattigated Peptide Drug in Mucoadhesive Buccal Films. Pharmaceutics, 16(4), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040468