Effect of Crosslinking Agent Concentration on the Properties of Unmedicated Hydrogels †
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
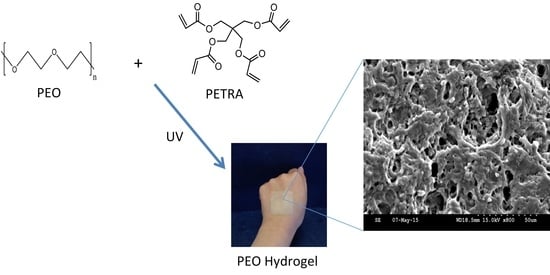
2.2.1. Synthesis of PEO Hydrogel Films
2.2.2. UV Irradiation of PEO Hydrogel Films
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Swelling Behavior
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.3. Tensile Testing
2.3.4. Measurement of Rheological Properties
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of PETRA Content on the Swelling Properties
| PEO (Mw = 1,000,000 g/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent Parameter | ||||
| PETRA Conc. (% w/w) | 1 | 2.5 | 5 | 10 |
| Dependent Parameters | ||||
| Thickness of dry film (µm) | 210 | 200 | 200 | 230 |
| Thickness of swollen film (µm) | 470 | 350 | 320 | 320 |
| Equilibrium swelling (%) | 598.60 (±23.29) * | 336.02 (±16.93) * | 199.82 (±9.24) * | 130.21 (±12.78) * |
| Equilibrium water content (%) | 85.67 (±0.48) * | 77.04 (±0.87) * | 66.84 (±1.30) * | 56.56 (±0.53) * |
| Gel fraction (%) | 67.02 (±1.38) * | 79.69 (±2.40) * | 85.84 (±1.65) * | 89.47 (±0.36) * |
| Average molecular weight between crosslinks, (g/mol) | 6643.65 (±516.21) * | 2073.79 (±214.80) * | 734.48 (±62.36) * | 323.30 (±11.87) * |
| Crosslink density, ρc × 10−4 (mol/cm3) | 1.79 (±0.15) * | 5.835 (±0.57) * | 16.45 (±1.56) * | 38.39 (±2.71) * |
| Mesh size, ξ (nm) | 10.72 (±0.41) * | 4.98 (±0.08) * | 2.73 (±0.08) * | 1.64 (±0.04) * |
| Average elastic modulus within LVR, G’ (Pa × 105) | – | 1.23 (±0.34) a | 0.99 (±0.37) a | 1.12 (±0.37) a |
| Average viscous modulus within LVR, G’’ (Pa × 104) | – | 1.80 (±0.83) a | 2.02 (±0.28) a | 2.19 (±0.50) a |

3.2. Effect of PETRA Content on the Morphology Characteristics


3.3. Effect of PETRA Content on the Mechanical Properties

3.4. Effect of PETRA Content on the Rheological Properties


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Symbols and Abbreviations
average molecular weight between crosslinks | |
| ρc | crosslinking density |
| ζ | mesh size |
| EWC | equilibrium water content |
| G’ | elastic shear modulus |
| G’’ | viscous shear modulus |
| LVR | linear viscoelastic region |
| PEO | polyethylene oxide |
| PETRA | pentaerythritol tetra-acrylate |
| UV | ultraviolet |
References
- Stephen, H.; Mandy, M.D. A new primary wound dressing made of polyethylene oxide gel. J. Dermatol. Surg. Onc. 1983, 9, 153–155. [Google Scholar]
- Stringer, J.L.; Peppas, N.A. Diffusion of small molecular weight drugs in radiation-crosslinked poly(ethylene oxide) hydrogels. J. Control. Release 1996, 42, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapar, E.A.; İnal, Ö. Poly(ethylene oxide)–poly(propylene oxide)-based copolymers for transdermal drug delivery: An overview. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 855–866. [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan, S.; Varma, M.; Sinha, V.R. High molecular weight poly(ethylene oxide)-based drug delivery systems. Part I: hydrogels and hydrophilic matrix systems. Pharm. Technol. 2005, 29, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- King, P.A. Ionizing radiation of water solution of polyalkylene oxide and product thereof. U.S. Patent 3,264,202, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Doytcheva, M.; Dotcheva, D.; Stamenova, R.; Tsvetanov, C. UV-initiated crosslinking of poly(ethylene oxide) with pentaerythritol triacrylate in solid state. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2001, 286, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidian, H.; Hashemi, S.A.; Askari, F.; Nafisi, S. Swelling and crosslink density measurements for hydrogels. Iran. J. Polym. Sci. Tech. 1994, 3, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Tighe, B.J. The role of permeability and related properties in the design of synthetic hydrogels for biomedical applications. Brit. Polym. J. 1986, 18, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, F.; Zhanshan, Y.; Isobe, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Makuuchi, K. Electron beam cross-linked PEO and PEO/PVA hydrogels for wound dressing. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1999, 55, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J.; Rehner, J.R. Statistical mechanics of cross-linked polymer networks. II. Swelling. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandrup, J.; Immergut, E.H. Polymer Handbook, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Peppas, N.A.; Huang, Y.; Torres-Lugo, M.; Ward, J.H.; Zhang, J. Physicochemical foundations and structural design of hydrogels in medicine and biology. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rixman, M.A.; Dean, D.; Ortiz, C. Nanoscale intermolecular interactions between human serum albumin and low density surfaces of poly(ethylene oxide). Langmuir 2003, 19, 9357–9372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Barr-Howell, B.D. Characterization of the crosslinked structure of hydrogels. In Hydrogels in Medicine and Pharmacy; Peppas, N.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986; pp. 27–56. [Google Scholar]
- Horkay, F.; Zrinyi, M. Studies on mechanical and swelling behavior of polymer network on the basis of the scaling concept. Macromolecules 1988, 21, 3260–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.L.; Topgaard, D.; Kocherbitov, V.; Sousa, J.J.S.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Sparr, E. Stratum corneum hydration: Phase transformations and mobility in the stratum corneum, extracted lipids and isolated corneocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 2647–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancer. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ende, M.T.; Peppas, N.A. Transport of ionizable drugs and proteins in crosslinked poly(acrylic acid) and poly(acrylic acid-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels. II. Diffusion and release studies. J. Control. Release 1997, 48, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Keys, K.B.; Torres-Lugo, M.; Lowman, A.M. Poly(ethylene glycol)-containing hydrogels in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 1999, 62, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruise, G.M.; Sharp, D.S.; Hubbell, J.A. Characterization of permeability and network structure of interracially photopolymerized poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Uda, H.; Tanaka, S.; Shimamura, H.; Aramaki, Y.; Tsuchiya, S. Hydrogel formation of the pH response polymer polyvinylacetal diethylaminoacetate (AEA). Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 167, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Weiss, R.A. Viscoelastic and mechanical behavior of hydrophobically modified hydrogels. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 9390–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haryanto; Kim, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, O.J.; Ku, S.K.; Cho, H.; Han, D.H.; Huh, P. Fabrication of poly (ethylene oxide) hydrogels for wound dressing application using e-beam. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manschot, J.F.; Brakkee, A.J. The measurement and modeling of the mechanical properties of human skin in vivo I. The measurement. J. Biomech. 1986, 19, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Raza, A.; Shih, H. PEG hydrogels formed by thiol-ene photo-click chemistry and their effect on the formation and recovery of insulin-secreting cell spheroids. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9685–9695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.Y.; Dodou, K. Rheological studies on pressure-sensitive silicone adhesives and drug-in-adhesive layers as a means to characterise adhesive performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 333, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, J.L.; Xu, H.Y. Volume confinement induced microstructural transitions and property enhancements of supramolecular soft materials. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, S.F.; Nguyen, D.C.; Kochhar, J.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Kang, L. Dissipative interactions in cell-matrix adhesion. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 6270–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, R.S.H.; Ashton, M.; Dodou, K. Effect of Crosslinking Agent Concentration on the Properties of Unmedicated Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 305-319. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030305
Wong RSH, Ashton M, Dodou K. Effect of Crosslinking Agent Concentration on the Properties of Unmedicated Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics. 2015; 7(3):305-319. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030305
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Rachel Shet Hui, Mark Ashton, and Kalliopi Dodou. 2015. "Effect of Crosslinking Agent Concentration on the Properties of Unmedicated Hydrogels" Pharmaceutics 7, no. 3: 305-319. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030305
APA StyleWong, R. S. H., Ashton, M., & Dodou, K. (2015). Effect of Crosslinking Agent Concentration on the Properties of Unmedicated Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics, 7(3), 305-319. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030305