Optimization of a siRNA Carrier Modified with a pH-Sensitive Cationic Lipid and a Cyclic RGD Peptide for Efficiently Targeting Tumor Endothelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Ligand Conjugated PEG-Lipid
2.3. Preparation of MENDs
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Measurement of Cellular Uptake
2.6. In Vitro Knockdown Experiment
2.7. Animal Experiments
2.8. Quantification of mRNA Expression Level with Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.9. Measurement of Tumor Accumulation of MENDs
2.10. In Vivo Observation of MENDs with Con-Focal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
3. Results and Discussion
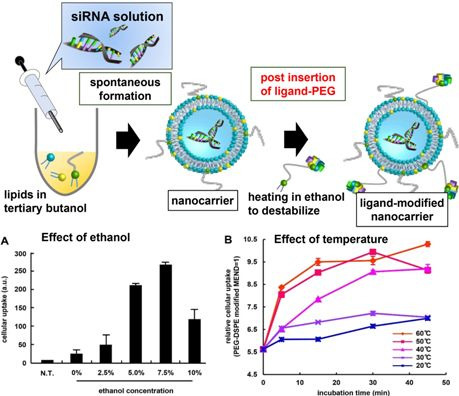
3.1. Optimization of Ligand Modification Method
| Carrier Name | Lipid Composition | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| MENDvivo | YSK05/POPE/chol (50/25/25) + 3 mol% PEG-DMG | [7] |
| MENDvitro | YSK05/chol (70/30) + 3 mol% PEG-DMG | [11,14] |


3.2. Effect of PEG Linker and Ligand Density on in Vitro siRNA Delivery Using MENDvivo
3.3. Effect of PEG-Linker and Ligand Density on in Vivo siRNA Delivery

3.4. Evaluation for the Gene Silencing Ability of Optimized MENDvivo in the Human Carcinoma Model
| Sample Name | Size (nm) | ZP (mV) | PdI | EE (%) | RR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimized RGD-modified MENDvivo (new one) | 84 ± 6 | −21 ± 14 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | 99 ± 2 | 84 ± 5 |
| RGD-modified MENDvitro (previous one) | 92 ± 3 | −14 ± 9 | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 95 ± 1 | 88 ± 7 |



3.5. Knockdown Efficiency in Off-Target Tissues
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergers, G.; Hanahan, D. Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, N.; Manabe, I.; Tottori, T.; Ishihara, A.; Ogata, F.; Kim, J.H.; Nishimura, S.; Fujiu, K.; Oishi, Y.; Itaka, K.; et al. A nanoparticle system specifically designed to deliver short interfering RNA inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6531–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudev, N.S.; Reynolds, A.R. Anti-angiogenic therapy for cancer: Current progress, unresolved questions and future directions. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faruque, L.I.; Lin, M.; Battistella, M.; Wiebe, N.; Reiman, T.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Thomas, C.; Tonelli, M. Systematic review of the risk of adverse outcomes associated with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, M.S.; Cunningham, D. Managing patients treated with bevacizumab combination therapy. Oncology 2005, 69, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hida, K.; Hida, Y.; Shindoh, M. Understanding tumor endothelial cell abnormalities to develop ideal anti-angiogenic therapies. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Hyodo, M.; Akita, H.; Harashima, H. A pH-sensitive cationic lipid facilitates the delivery of liposomal siRNA and gene silencing activity in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Sato, Y.; Hyodo, M.; Akita, H.; Ohga, N.; Hida, K.; Harashima, H. RNAi-mediated gene knockdown and anti-angiogenic therapy of RCCs using a cyclic RGD-modified liposomal-siRNA system. J. Control Release 2014, 173, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhier, F.; Le Breton, A.; Preat, V. RGD-based strategies to target Alpha(v) Beta(3) integrin in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Suemitsu, E.; Kajimoto, K.; Sato, Y.; Akhter, A.; Sakurai, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Hyodo, M.; Kaji, N.; Baba, Y.; et al. Hepatic monoacylglycerol o-acyltransferase 1 as a promising therapeutic target for steatosis, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Hatakeyama, H.; Matsuda-Yasui, C.; Sato, Y.; Sudoh, M.; Takagi, A.; Hirata, Y.; Ohtsuki, T.; Arai, M.; Inoue, K.; et al. In vivo therapeutic potential of dicer-hunting sirnas targeting infectious hepatitis c virus. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, N.; Wong, K.F.; Stark, H.; Louie, L.; McIntosh, D.; Wong, T.; Scherrer, P.; Semple, S.C.; Cullis, P.R. Spontaneous entrapment of polynucleotides upon electrostatic interaction with ethanol-destabilized cationic liposomes. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 2310–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Akita, H.; Harashima, H. Improvement of doxorubicin efficacy using liposomal anti-polo-like kinase 1 siRNA in human renal cell carcinomas. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2713–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Sato, Y.; Hyodo, M.; Akita, H.; Harashima, H. Gene silencing via RNAi and siRNA quantification in tumor tissue using mend, a liposomal siRNA delivery system. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Huang, Y.Y. Encapsulating protein into preformed liposomes by ethanol-destabilized method. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 2003, 31, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Yamashita, K.; Itoh, Y.; Yoshino, K.; Nozawa, S.; Kasukawa, H. Comparative studies of polyethylene glycol-modified liposomes prepared using different PEG-modification methods. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 2801–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Jayaraman, M.; Ansell, S.M.; Du, X.; Tam, Y.Y.; Lin, P.J.; Chen, S.; Narayanannair, J.K.; Rajeev, K.G.; et al. Influence of polyethylene glycol lipid desorption rates on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of siRNA lipid nanoparticles. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibria, G.; Hatakeyama, H.; Ohga, N.; Hida, K.; Harashima, H. The effect of liposomal size on the targeted delivery of doxorubicin to integrin αvβ3-expressing tumor endothelial cells. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5617–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleku, M.; Schulz, P.; Keil, O.; Santel, A.; Schaeper, U.; Dieckhoff, B.; Janke, O.; Endruschat, J.; Durieux, B.; Roder, N.; et al. Atu027, a liposomal small interfering RNA formulation targeting protein kinase n3, inhibits cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9788–9798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smedsrod, B.; De Bleser, P.J.; Braet, F.; Lovisetti, P.; Vanderkerken, K.; Wisse, E.; Geerts, A. Cell biology of liver endothelial and kupffer cells. Gut 1994, 35, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leeuw, A.M.; Brouwer, A.; Knook, D.L. Sinusoidal endothelial cells of the liver: Fine structure and function in relation to age. J. Electron. Microsc. Tech. 1990, 14, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hada, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Harashima, H. Optimization of a siRNA Carrier Modified with a pH-Sensitive Cationic Lipid and a Cyclic RGD Peptide for Efficiently Targeting Tumor Endothelial Cells. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 320-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030320
Hada T, Sakurai Y, Harashima H. Optimization of a siRNA Carrier Modified with a pH-Sensitive Cationic Lipid and a Cyclic RGD Peptide for Efficiently Targeting Tumor Endothelial Cells. Pharmaceutics. 2015; 7(3):320-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030320
Chicago/Turabian StyleHada, Tomoya, Yu Sakurai, and Hideyoshi Harashima. 2015. "Optimization of a siRNA Carrier Modified with a pH-Sensitive Cationic Lipid and a Cyclic RGD Peptide for Efficiently Targeting Tumor Endothelial Cells" Pharmaceutics 7, no. 3: 320-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030320
APA StyleHada, T., Sakurai, Y., & Harashima, H. (2015). Optimization of a siRNA Carrier Modified with a pH-Sensitive Cationic Lipid and a Cyclic RGD Peptide for Efficiently Targeting Tumor Endothelial Cells. Pharmaceutics, 7(3), 320-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030320