Site-Specific Impact of a Regional Hydrodynamic Injection: Computed Tomography Study during Hydrodynamic Injection Targeting the Swine Liver
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Venography of the Hepatic Vein in the Right Medial Lobe

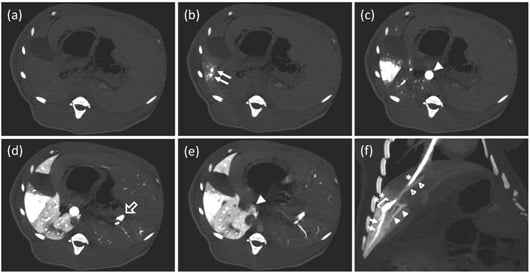
3.2. Single-Level Computed Tomography


3.3. Conventional Enhanced Computed Tomography

3.4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Budker, V.; Wolff, J. A High levels of foreign gene expression in hepatocytes after tail vein injections of naked plasmid DNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 1735–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliño, S.F.; Crespo, A.; Dasí, F. Long-term therapeutic levels of human alpha-1 antitrypsin in plasma after hydrodynamic injection of nonviral DNA. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyros, O.; Wong, S.P.; Niceta, M.; Waddington, S.N.; Howe, S.J.; Coutelle, C.; Miller, A.D.; Harbottle, R.P. Persistent episomal transgene expression in liver following delivery of a scaffold/matrix attachment region containing non-viral vector. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Kamimura, K.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D. Intracellular gene transfer in rats by tail vein injection of plasmid DNA. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Xue, W.; Chen, S.; Bogorad, R.L.; Benedetti, E.; Grompe, M.; Koteliansky, V.; Sharp, P.A.; Jacks, T.; Anderson, D.G. Genome editing with Cas9 in adult mice corrects a disease mutation and phenotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gao, X.; Song, Y.K.; Vollmer, R.; Stolz, D.B.; Gasiorowski, J.Z.; Dean, D.A.; Liu, D. Hydroporation as the mechanism of hydrodynamic delivery. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, A.; Peydró, A.; Dasí, F.; Benet, M.; Calvete, J.J.; Revert, F.; Aliño, S.F. Hydrodynamic liver gene transfer mechanism involves transient sinusoidal blood stasis and massive hepatocyte endocytic vesicles. Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budker, V.G.; Subbotin, V.M.; Budker, T.; Sebestyén, M.G.; Zhang, G.; Wolff, J.A. Mechanism of plasmid delivery by hydrodynamic tail vein injection. II. Morphological studies. J. Gene Med. 2006, 8, 874–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Gao, X.; Stolz, D.B.; Liu, D. Structural impact of hydrodynamic injection on mouse liver. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, G.J.; Dong, X.; Whitehorne, M.; Grehan, A.; Seddon, M.; Shah, A.M.; Zhang, X.; Fabre, J.W. Cardiovascular function following acute volume overload for hydrodynamic gene delivery to the liver. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanefuji, T.; Yokoo, T.; Suda, T.; Abe, H.; Kamimura, K.; Liu, D. Hemodynamics of a hydrodynamic injection. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, H.; Hashizume, K.; Kobayashi, E. Naked plasmid DNA transfer to the porcine liver using rapid injection with large volume. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, K.; Kanefuji, T.; Yokoo, T.; Abe, H.; Suda, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Zhang, G.; Aoyagi, Y.; Liu, D. Safety Assessment of Liver-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery in Dogs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.J.; Sabater, L.; Guenechea, G.; Sendra, L.; Montilla, A.I.; Abargues, R.; Navarro, V.; Alino, S.F. DNA delivery to “ex vivo” human liver segments. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, T.; Suda, K.; Liu, D. Computer-assisted hydrodynamic gene delivery. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoo, T.; Kamimura, K.; Suda, T.; Kanefuji, T.; Oda, M.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D.; Aoyagi, Y. Novel electric power-driven hydrodynamic injection system for gene delivery: Safety and efficacy of human factor IX delivery in rats. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, K.; Suda, T.; Zhang, G.; Aoyagi, Y.; Liu, D. Parameters Affecting Image-guided, Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery to Swine Liver. Mol. Ther. Acids 2013, 2, e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Von Kalle, C.; Schmidt, M.; McCormack, M.P.; Wulffraat, N.; Leboulch, P.; Lim, A.; Osborne, C.S.; Pawliuk, R.; Morillon, E.; et al. LMO2-associated clonal T cell proliferation in two patients after gene therapy for SCID-X1. Science 2003, 302, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, S.J.; Mansour, M.R.; Schwarzwaelder, K.; Hubank, M.; Kempski, H.; Brugman, M.H.; Ridder, D.D.; Gilmour, K.C.; Adams, S.; Thornhill, S.I.; et al. Insertional mutagenesis in combination with acquired somatic mutations leads to leukemogenesis following gene therapy of SCID-X1. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 44, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Manno, C.S.; Pierce, G.F.; Arruda, V.R.; Glader, B.; Ragni, M.; Rasko, J.J.; Ozelo, M.C.; Hoots, K.; Blatt, P.; Konkle, B.; et al. Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastman, S.J.; Baskin, K.M.; Hodges, B.L.; Chu, Q.; Gates, A.; Dreusicke, R.; Anderson, S.; Scheule, R.K. Development of catheter-based procedures for transducing the isolated rabbit liver with plasmid DNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendra, L.; Pérez, D.; Miguel, A.; Herrero, M.J.; Noguera, I.; Díaz, A.; Barettino, D.; Martí-Bonmatí, L.; Aliño, S.F. Human AAT gene transfer to pig liver improved by using a perfusion isolated organ endovascular procedure. Eur. Radiol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, M.C.; Chuang, M.T.; Lin, X.Z.; Tsai, H.M.; Chen, S.Y.; Liu, Y.S. A novel method for the angiographic estimation of the percentage of spleen volume embolized during partial splenic embolization. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yokoo, T.; Kanefuji, T.; Suda, T.; Kamimura, K.; Liu, D.; Terai, S. Site-Specific Impact of a Regional Hydrodynamic Injection: Computed Tomography Study during Hydrodynamic Injection Targeting the Swine Liver. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 334-343. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030334
Yokoo T, Kanefuji T, Suda T, Kamimura K, Liu D, Terai S. Site-Specific Impact of a Regional Hydrodynamic Injection: Computed Tomography Study during Hydrodynamic Injection Targeting the Swine Liver. Pharmaceutics. 2015; 7(3):334-343. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030334
Chicago/Turabian StyleYokoo, Takeshi, Tsutomu Kanefuji, Takeshi Suda, Kenya Kamimura, Dexi Liu, and Shuji Terai. 2015. "Site-Specific Impact of a Regional Hydrodynamic Injection: Computed Tomography Study during Hydrodynamic Injection Targeting the Swine Liver" Pharmaceutics 7, no. 3: 334-343. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030334
APA StyleYokoo, T., Kanefuji, T., Suda, T., Kamimura, K., Liu, D., & Terai, S. (2015). Site-Specific Impact of a Regional Hydrodynamic Injection: Computed Tomography Study during Hydrodynamic Injection Targeting the Swine Liver. Pharmaceutics, 7(3), 334-343. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030334