Transdermal Delivery of Drugs with Microneedles—Potential and Challenges
Abstract
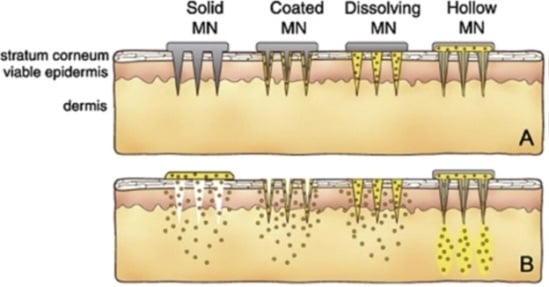
:1. Introduction

2. Hollow Microneedles
3. Solid Microneedles

4. Dissolving Microneedles
5. Coated Microneedles
6. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles
7. Clinical Trials
8. Challenges
9. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lhernould, M.S.; Deleers, M.; Delchambre, A. Hollow polymer microneedles array resistance and insertion tests. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 480, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Ita, K.; Simon, L. Modelling of dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: theoretical and experimental aspects. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 68, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danso, M.O.; Berkers, T.; Mieremet, A.; Hausil, F.; Bouwstra, J.A. An ex vivo human skin model for studying skin barrier repair. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danso, M.O.; van Drongelen, V.; Mulder, A.; Gooris, G.; van Smeden, J.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. Exploring the potentials of nurture: 2nd and 3rd generation explant human skin equivalents. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 77, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.N.; Jeong, E.; Prausnitz, M.R. Transdermal delivery of molecules is limited by full epidermis, not just stratum corneum. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jepps, O.G.; Dancik, Y.; Anissimov, Y.G.; Roberts, M.S. Modeling the human skin barrier—Towards a better understanding of dermal absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaten, G.E.; Palac, Z.; Engesland, A.; Filipović-Grčić, J.; Vanić, Ž.; Škalko-Basnet, N. In vitro skin models as a tool in optimization of drug formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 75, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby, E.; Jarrahian, C.; Hull, H.F.; Zehrung, D. Opportunities and challenges in deliveringinfluenza vaccineby microneedle patch. Vaccine 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.Y.; Choi, S.O.; Prausnitz, M.R. Fabrication of dissolving polymer microneedles for controlled drug encapsulation and delivery: Bubble and pedestal microneedle designs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4228–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Moffatt, K.; Alkilani, A.Z.; Vicente-Pérez, E.M.; Barry, J.; McCrudden, M.T.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays can be effectively inserted in skin by self-application: A pilot study centred on pharmacist intervention and a patient information leaflet. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 1989–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olatunji, O.; Das, D.B.; Garland, M.J.; Belaid, L.; Donnelly, R.F. Influence of array interspacing on the force required for successful microneedle skin penetration: Theoretical and practical approaches. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, K.; Han, T.; Das, D.B. Effect of Force of Microneedle Insertion on the Permeability of Insulin in Skin. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Ita, K.B.; Popova, I.E.; Parikh, S.J.; Bair, D.A. Microneedle-assisted delivery of verapamil hydrochloride and amlodipine besylate. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Park, J.H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbaan, F.J.; Bal, S.M.; van den Berg, D.J.; Dijksman, J.A.; van Hecke, M.; Verpoorten, H.; van den Berg, A.; Luttge, R.; Bouwstra, J.A. Improved piercing of microneedle arrays in dermatomed human skin by an impact insertion method. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.; Das, D.B. Microneedles for drug delivery: Trends and progress. Drug Deliv. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuzhakov, V.V. The AdminPen™ microneedle device for painless & convenient drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2010, 10, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, B.J.; Aria, A.I.; Gharib, M. Fabrication of carbon nanotube-polyimide composite hollow microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Biomed. Microdevices 2014, 16, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Maaden, K.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J. Microneedle technologies for (trans)dermal drug and vaccine delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardeniers, H.J.G.E.; Luttge, R.; Berenschot, E.J.W.; de Boer, M.J.; Yeshurun, S.Y.; Hefetz, M.; van’t Oever, R.; van den Berg, A. Silicon micromachined hollow microneedles for transdermal liquid transport. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perennes, F.; Marmiroli, B.; Matteucci, M.; Tormen, M.; Vaccari, L.; Di Fabrizio, E. Sharp beveled tip hollow microneedle arrays fabricated by LIGA and 3D soft lithography with polyvinyl alchohol. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayakumar, K.B.; Hegde, G.M.; Nayak, M.M.; Dinesh, N.S.; Rajanna, K. Fabrication and characterization of gold coated hollow silicon microneedle array for drug delivery. Microelectron. Eng. 2014, 128, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, H.; Han, M.-R.; Kang, N.-G.; Park, J.-H.; Park, J.H. Use of hollow microneedles for targeted delivery of phenylephrine to treat fecal incontinence. J. Control. Release 2015, 207, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kher, G.; Trehan, S.; Misra, A. Antisense Oligonucleotides and RNA Interference. In Challenges in Delivery of Therapeutic Genomics and Proteomics; Misra, A., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2011; pp. 325–386. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Ye, T.; Ma, Y.; Gill, H.S.; Nitin, N. Microprecision delivery of oligonucleotides in a 3D tissue model and its characterization using optical imaging. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 2868–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, J.; Gill, H.S.; Andrews, S.N.; Prausnitz, M.R. Kinetics of skin resealing after insertion of microneedles in human subjects. J. Control. Release 2011, 154, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, S.; McAllister, D.V.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated microneedles: A novel approach to transdemal drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayakumar, K.B.; Hegde, G.M.; Ramachandra, S.G.; Nayak, M.M.; Dinesh, N.S.; Rajanna, K. Development of cup shaped microneedle array for transdermal drug delivery. Biointerphases 2015, 10, 021008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Coated microneedles for transdermal delivery. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-C.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-N.; Hwang, H.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.S.; Montemagno, C.; Prausnitz, M.R.; et al. Microneedle patch delivery to the skin of virus-like particles containing heterologous M2e extracellular domains of influenza virus induces broad heterosubtypic cross-protection. J. Control. Release 2015, 210, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olatunji, O.; Igwe, C.C.; Ahmed, A.S.; Alhassan, D.O.A.; Asieba, G.O.; Das, D.B. Microneedles from fish scale biopolymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.T.; Ita, K.B.; Parikh, S.J.; Popova, I.E.; Bair, D.A. Transdermal Delivery of Captopril and Metoprolol Tartrate with Microneedles. Drug Deliv. Lett. 2014, 4, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalluri, B.N.; Sai Sri Anusha, V.; Sri Bramhini, R.; Amulya, J.; Ashraf Sultana, S.K.; Chandra Teja, U.; Das, D.B. In Vitro Skin Permeation Enhancement of Sumatriptan by Microneedle Application. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edens, C.; Collins, M.L.; Goodson, J.L.; Rota, P.A.; Prausnitz, M.R. A microneedle patch containing measles vaccine is immunogenic in non-human primates. Vaccine 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yao, G.; Dong, P.; Gong, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C. Investigation on fabrication process of dissolving microneedle arrays to improve effective needle drug distribution. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 66, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, S.P.; Koutsonanos, D.G.; del Pilar Martin, M.; Lee, J.W.; Zarnitsyn, V.; Choi, S.-O.; Murthy, N.; Compans, R.W.; Skountzou, I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for influenza vaccination. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Wei, L.; Wu, F.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. Dissolving and biodegradable microneedle technologies for transdermal sustained delivery of drug and vaccine. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 945–952. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-C.; Huang, S.-F.; Lai, K.-Y.; Ling, M.-H. Fully embeddable chitosan microneedles as a sustained release depot for intradermal vaccination. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3077–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Park, S.H.; Seo, I.H.; Lee, K.J.; Ryu, W.H. Rapid and repeatable fabrication of high A/R silk fibroin microneedles using thermally-drawn micromolds. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 94, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Jin, M.; Quan, Y.; Kamiyama, F.; Kusamori, K.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Transdermal delivery of relatively high molecular weight drugs using novel self-dissolving microneedle arrays fabricated from hyaluronic acid and their characteristics and safety after application to the skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 86, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-C.; Ling, M.-H.; Wang, K.-W.; Lin, Z.-W.; Lai, B.-H.; Chen, D.-H. Near-infrared light-responsive composite microneedles for on-demand transdermal drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, H.; Zheng, J.; Mou, D.; Wan, J.; Zhang, J.; Shi, T.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, X. Iontophoresis-driven penetration of nanovesicles through microneedle-induced skin microchannels for enhancing transdermal delivery of insulin. J. Control. Release 2009, 139, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.W.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, K.R.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, K.; Park, J.S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Jo, D.-G.; Lee, H.; Lee, D.S.; et al. Polyplex-releasing microneedles for enhanced cutaneous delivery of DNA vaccine. J. Control. Release 2014, 179, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearton, M.; Saller, V.; Coulman, S.A.; Gateley, C.; Anstey, A.V.; Zarnitsyn, V.; Birchall, J.C. Microneedle delivery of plasmid DNA to living human skin: Formulation coating, skin insertion and gene expression. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Mehta, P.; Msallam, H.; Armitage, D.; Ahmad, Z. Smart microneedle coatings for controlled delivery and biomedical analysis. J. Drug Target 2014, 22, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Gill, H.S. Coating solid dispersions on microneedles via a molten dip-coating method: development and in vitro evaluation for transdermal delivery of a water-insoluble drug. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3621–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Raj Singh, T.R.; Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; O’Neill, S.; O’Mahony, C.; Armstrong, K.; McLoone, N.; Kole, P.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays exhibit antimicrobial properties: Potential for enhanced patient safety. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 451, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Alkilani, A.Z.; Larrañeta, E.; McAlister, E.; Courtenay, A.J.; Kearney, M.-C.; Raj Singh, T.R.; McCarthy, H.O.; Kett, V.L.; et al. Hydrogel-forming microneedles prepared from “super swelling” polymers combined with lyophilised wafers for transdermal drug delivery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Mooney, K.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Vicente-Pérez, E.M.; Belaid, L.; González-Vázquez, P.; McElnay, J.C.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-forming microneedles increase in volume during swelling in skin, but skin barrier function recovery is unaffected. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Raj Singh, T.R.; Garland, M.J.; Migalska, K.; Majithiya, R.; McCrudden, C.M.; Kole, P.L.; Tuan-Mahmood, T.-M.; McCarthy, H.O.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caffarel-Salvador, E.; Tuan-Mahmood, T.-M.; McElnay, J.C.; McCarthy, H.O.; Mooney, K.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Potential of hydrogel-forming and dissolving microneedles for use in paediatric populations. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 489, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ita, K. Transdermal delivery of drugs with microneedles: Strategies and outcomes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daddona, P.E.; Matriano, J.A.; Mandema, J.; Maa, Y.-F. Parathyroid hormone (1–34)-coated microneedle patch system: clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics for treatment of osteoporosis. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ita, K. Transdermal Delivery of Drugs with Microneedles—Potential and Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 90-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030090
Ita K. Transdermal Delivery of Drugs with Microneedles—Potential and Challenges. Pharmaceutics. 2015; 7(3):90-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030090
Chicago/Turabian StyleIta, Kevin. 2015. "Transdermal Delivery of Drugs with Microneedles—Potential and Challenges" Pharmaceutics 7, no. 3: 90-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030090
APA StyleIta, K. (2015). Transdermal Delivery of Drugs with Microneedles—Potential and Challenges. Pharmaceutics, 7(3), 90-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030090