Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the Stratum Corneum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Transdermal Drug Delivery (TDD)
3. A Brief Review of Skin Structure

3.1. Epidermis
3.2. Dermis
3.3. Hypodermis
3.4. Drug Penetration Routes

3.5. Kinetics of TDD
- Penetration: The entry of a substance into a particular layer of the skin;
- Partitioning from the stratum corneum into the aqueous viable epidermis;
- Diffusion through the viable epidermis and into the upper dermis;
- Permeation: The penetration of molecules from one layer into another, which is different both functionally and structurally from the first layer;
- Absorption: The uptake of a substance into the systemic circulation.


| Drug (Year of Approval) | Dose/Day (mg) | MW (Da) | Log P a | Cl (L/h) | T1/2 (h)b | F (%) c | Cp,eff (ng/mL) e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scopolamine (1979) | 0.3 | 303 | 0.98 | 672 | 2.9 | 27 | 0.04 |
| Glyceryl trinitrate (1981) | 2.4–15 | 227 | 01.62 | 966 | 0.04 | <1 | 0.1–5 |
| Clonidine (1984) | 0.1–0.3 | 230 | 2.42 ± 0.52 | 13 | 6–20 | 95 | 0.2–2.0 |
| Estradiol (1986) | 0.025–0.1 | 272 | 4.01 | 615–790 | 0.05 | 3-5 | 0.04–0.06 |
| Fentanyl (1990) | 0.288–2.4 | 337 | 4.05 | 27–75 | 3–12 | 32 | 1.0 |
| Nicotine (1991) | 7–21 | 162 | 1.17 | 78 | 2 | 30 | 10–30 |
| Testosterone (1993) | 0.3–5 | 288 | 3.32 | 0.17–1.7 | <1 | 10–100 | |
| Estradiol & Norethisterone Acetate (1998) | 0.025–0.050 0.125–0.250 | 272 340 | 4.01 3.99 | 2–3 6–8 d | 3–5 64 | 0.04–0.07 0.8–1.1 | |
| Norelgestromin & EthinylEstradiol (2001) | 0.025–0.050 0.125–0.250 | 327 296 | 3.90 ± 0.47 3.67 | 28 17 d | 40 | 0.8 0.05 | |
| Estradiol & Levonorgestrel (2003) | 0.025–0.050 0.125–0.250 | 272 312 | 4.01 3.72 ± 0.49 | 3 28 d | 3-5 | 0.03–0.05 0.1–0.2 | |
| Oxybutynin (2003) | 3.9 | 357 | 4.02 ± 0.52 | 2 | 6 | 1.0–5.0 | |
| Selegeline (2006) | 6–12 | 187 | 2.90 | 84 | 10 | 10 | 2.0–3.0 |
| Methylphenidate (2006) | 26–80 | 233 | 2.15 ± 0.42 | 20 | 2–3 | 5–20 | 5.0–25 |
| Rotigotine (2007) | 1–3 | 315 | 4.58 ± 0.72 | 600 | 5–7 d | n/a | ~1.0 |
| Rivastigmine (2007) | 4.6–9.5 | 250 | 2.34 ± 0.16 | 108 | 1.5 | 40 | ~10 |
| Granisetron (2008) | 3.1 | 312 | 2.55 ± 0.28 | 33–76 healthy 15–34 patients | 4–6 healthy 9–12 patients | 60 | 0.7–9.5 |
| Buprenorphine (2010) | 0.12–1.68 | 468 | 4.98 | 55 | 22–36 d | n/a | 0.1–0.4 |
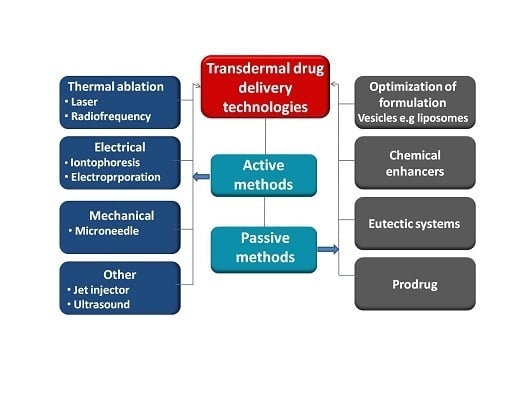
4. Techniques for Enhancement of Skin Permeabilisation


4.1. Ultrasound Devices

4.2. Electrical Techniques
4.2.1. Electroporation
4.2.2. Iontophoresis


4.3. Velocity Based Devices


4.4. Thermal Approaches (Lasers and Radio-Frequency Heating)
4.4.1. Laser Thermal Ablation
4.4.2. Radiofrequency (RF) Thermal Ablation

4.5. Mechanical Approaches to Mediate Skin Permeation
4.5.1. Tape Stripping
4.5.2. Microneedle (MN) Arrays




5. MN Overcome Many of the Limitations Associated with Other TDD Methodologies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. An Overview of Clinical and Commercial Impact of Drug Delivery Systems. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Das, D.B. Potential of Combined Ultrasound and Microneedles for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Permeation: A Review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brambilla, D.; Luciani, P.; Leroux, J. Breakthrough Discoveries in Drug Delivery Technologies: The Next 30 years. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ita, K. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoellhammer, C.M.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Skin Permeabilization for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrudden, M.T.; Singh, T.R.R.; Migalska, K.; Donnelly, R.F. Strategies for Enhanced Peptide and Protein Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2013, 4, 593–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermode, M. Unsafe Injections in Low-Income Country Health Settings: Need for Injection Safety Promotion to Prevent the Spread of Blood-Borne Viruses. Health Promot. Int. 2004, 19, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Morrow, D.I.; Woolfson, A.D. Microneedle-Mediated Transdermal and Intradermal Drug Delivery; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kretsos, K.; Kasting, G.B. A Geometrical Model of Dermal Capillary Clearance. Math. Biosci. 2007, 208, 430–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Garland, M.J.; Migalska, K.; Majithiya, R.; McCrudden, C.M.; Kole, P.L.; Mahmood, T.M.T.; McCarthy, H.O.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arora, A.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Mitragotri, S. Micro-Scale Devices for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuan-Mahmood, T.; McCrudden, M.T.; Torrisi, B.M.; McAlister, E.; Garland, M.J.; Singh, T.R.R.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedles for Intradermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Langer, R. Transdermal Drug Delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, H.; Shin, J.; Kim, Y. Microneedle Patches for Vaccine Delivery. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2014, 3, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peasah, S.K.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Breese, J.; Meltzer, M.I.; Widdowson, M. Influenza Cost and Cost-Effectiveness Studies globally—A Review. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5339–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, G.K. New Insights into Skin Structure: Scratching the Surface. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, S3–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kruger, P.; Maibach, H.; Colditz, P.B.; Roberts, M.S. Using Skin for Drug Delivery and Diagnosis in the Critically Ill. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 77, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration Enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, H.A.; Watkinson, A.C. Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery: Principles and Practice; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gratieri, T.; Alberti, I.; Lapteva, M.; Kalia, Y.N. Next Generation Intra-and Transdermal Therapeutic Systems: Using Non-and Minimally-Invasive Technologies to Increase Drug Delivery into and Across the Skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, P.H.; Laurent, P.E. Intradermal Vaccine Delivery: Will New Delivery Systems Transform Vaccine Administration? Vaccine 2008, 26, 3197–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Maaden, K.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J. Microneedle Technologies for (Trans) Dermal Drug and Vaccine Delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Delgado, C.L.; Rodríguez-Cruz, I.M.; López-Cervantes, M.; Escobar-Chávez, J.; Merino, V. The Skin a Valuable Route for Administration of Drugs. Current Technologies to Increase the Transdermal Delivery of Drugs; Bentham Science: Sharjah, UAE, 2010; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- El Maghraby, G.; Barry, B.; Williams, A. Liposomes and Skin: From Drug Delivery to Model Membranes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, K.A. Dermatological and Transdermal Formulations; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, A.; Dwivedi, S.; Giri, T.K.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S.; Tripathi, D.K. Approaches for Breaking the Barriers of Drug Permeation through Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, A.; Bower, J.K.; McFetridge-Durdle, J.; Blumenthal, J.A.; Newby, L.K.; Hinderliter, A.L. Age Moderates the Short-Term Effects of Transdermal 17β-Estradiol on Endothelium-Dependent Vascular Function in Postmenopausal Women. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1782–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLennan, D.N.; Porter, C.J.; Charman, S.A. Subcutaneous Drug Delivery and the Role of the Lymphatics. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2005, 2, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, Y.B.; Naik, A.; Guy, R.H.; Kalia, Y.N. Emerging Strategies for the Transdermal Delivery of Peptide and Protein Drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, Y.; Louw, R.; Gerber, M.; du Plessis, J. Breaching the Skin Barrier through Temperature Modulations. J. Control. Release 2015, 202, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhote, V.; Bhatnagar, P.; Mishra, P.K.; Mahajan, S.C.; Mishra, D.K. Iontophoresis: A Potential Emergence of a Transdermal Drug Delivery System. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 80, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragicevic, N.; Maibach, H.I. Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Chemical Methods in Penetration Enhancement: Drug Manipulation Strategies and Vehicle Effects; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Subramony, J.A. Needle Free Parenteral Drug Delivery: Leveraging active transdermal technologies for pediatric use. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 455, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedersberg, S.; Guy, R.H. Transdermal Drug Delivery: 30 Years of War and Still Fighting! J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, T.K.; Jasti, B.R. Theory and Practice of Contemporary Pharmaceutics; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, Y.B.; Prausnitz, M.R. The Rule of Five for Non-Oral Routes of Drug Delivery: Ophthalmic, Inhalation and Transdermal. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, B. Novel Mechanisms and Devices to Enable Successful Transdermal Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 14, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Park, H.; Seo, J.; Lee, S. Sonophoresis in Transdermal Drug Deliverys. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, A.; Kalia, Y.N.; Guy, R.H. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Overcoming the skin’s Barrier Function. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 2000, 3, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Ma, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Wen, L. Transdermal Protein Delivery by a Coadministered Peptide Identified Via Phage Display. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maghraby, G.M.; Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Can drug-bearing Liposomes Penetrate Intact Skin? J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.; Zulfakar, M.H. Recent Advances in Gel Technologies for Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 40, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorec, B.; Préat, V.; Miklavčič, D.; Pavšelj, N. Active Enhancement Methods for Intra-and Transdermal Drug Delivery: A Review. Zdravniški Vestnik 2013, 82, 339–356. (In Slovenian) [Google Scholar]
- Paudel, K.S.; Milewski, M.; Swadley, C.L.; Brogden, N.K.; Ghosh, P.; Stinchcomb, A.L. Challenges and Opportunities in dermal/transdermal Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2010, 1, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marianecci, C.; Di Marzio, L.; Rinaldi, F.; Celia, C.; Paolino, D.; Alhaique, F.; Esposito, S.; Carafa, M. Niosomes from 80s to Present: The State of the Art. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 205, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karande, P.; Mitragotri, S. Enhancement of Transdermal Drug Delivery via Synergistic Action of Chemicals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 2362–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitragotri, S. Devices for Overcoming Biological Barriers: The use of physical forces to disrupt the barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Gadiraju, P.; Park, J.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microsecond Thermal Ablation of Skin for Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2011, 154, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azagury, A.; Khoury, L.; Enden, G.; Kost, J. Ultrasound Mediated Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 72, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Rielly, C.D.; Das, D.B. Microneedle-Assisted Microparticle Delivery by Gene Guns: Experiments and Modeling on the Effects of Particle Characteristics. Drug Deliv. 2014, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsumi, H.; Liu, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Hitomi, K.; Hayashi, R.; Hirai, Y.; Kusamori, K.; Quan, Y.; Kamiyama, F.; Sakane, T. Development of a Novel self-dissolving Microneedle Array of Alendronate, a nitrogen-containing Bisphosphonate: Evaluation of Transdermal Absorption, Safety, and Pharmacological Effects After Application in Rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 3230–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonin, J. On the Mechanisms of in Vitro and in Vivo Phonophoresis. J. Control. Release 1995, 33, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skauen, D.M.; Zentner, G.M. Phonophoresis. Int. J. Pharm. 1984, 20, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, B.E.; Hart, D.; Langer, R.; Blankschtein, D. Ultrasound-Mediated Transdermal Drug Delivery: Mechanisms, Scope, and Emerging Trends. J. Control. Release 2011, 152, 330–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, A.J.; Homan, C.S.; Church, A.L.; McClain, S.A. Low-frequency Sonophoresis: Pathologic and Thermal Effects in Dogs. Acad. Emerg. Med. 1998, 5, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamo, A.; Roushdy, O.; Dokov, R.; Sharei, A.; Jensen, K. Microfluidic Jet Injection for Delivering Macromolecules into Cells. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 35026–35033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, S.; Gupta, G.K.; Avci, P.; Chandran, R.; Sadasivam, M.; Jorge, A.E.S.; Hamblin, M.R. Physical Energy for Drug Delivery; Poration, Concentration and Activation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 71, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, E.; Schaefer-Ridder, M.; Wang, Y.; Hofschneider, P.H. Gene Transfer into Mouse Lyoma Cells by Electroporation in High Electric Fields. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Preat, V.; Vanbever, R. Skin Electroporation for Transdermal and Topical Drug Delivery. Transdermal Drug Deliv. 2002, 123, 227–254. [Google Scholar]
- Denet, A.; Preat, V. Transdermal Delivery of Timolol by Electroporation through Human Skin. J. Control. Release 2003, 88, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Bose, V.G.; Langer, R.; Weaver, J.C. Electroporation of Mammalian Skin: A Mechanism to Enhance Transdermal Drug Delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10504–10508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Edelman, E.; Gimm, J.; Langer, R.; Weaver, J. Transdermal Delivery of Heparin by Skin Electroporation. Biotechnology 1995, 13, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommannan, D.B.; Tamada, J.; Leung, L.; Potts, R.O. Effect of Electroporation on Transdermal Lontophoretic Delivery of Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Hormone (LHRH) in Vitro. Pharm. Res. 1994, 11, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Hofmann, G.A.; Zhang, L.; Deftos, L.J.; Banga, A.K. The Effect of Electroporation on Iontophoretic Transdermal Delivery of Calcium Regulating Hormones. J. Control. Release 2000, 66, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombry, C.; Dujardin, N.; Préat, V. Transdermal Delivery of Macromolecules using Skin Electroporation. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Barrow, A.J.; Yu, N.; O'Neill, B.E. Efficient Electroporation of Liposomes Doped with Pore Stabilizing Nisin. J. Liposome Res. 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badkar, A.V.; Banga, A.K. Electrically Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of a Macromolecule. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzki, S.; Roustit, M.; Arnaud, C.; Godin-Ribuot, D.; Cracowski, J. Effect of Continuous Vs Pulsed Iontophoresis of Treprostinil on Skin Blood Flow. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 72, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratieri, T.; Kalia, Y.N. Mathematical Models to Describe Iontophoretic Transport in Vitro and in Vivo and the Effect of Current Application on the Skin Barrier. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, M.; Hama, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kogure, K. Anti-Cancer Vaccination by Transdermal Delivery of Antigen Peptide-Loaded Nanogels via Iontophoresis. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 483, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, N.; Bali, V.; Baboota, S.; Ahuja, A.; Ali, J. Iontophoresis—An Approach for Controlled Drug Delivery: A Review. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2007, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Yasir, M.; Asif, M.; Chauhan, I.; Singh, A.P.; Sharma, R.; Singh, P.; Rai, S. Iontophoretic Drug Delivery: History and Applications. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, L.L.; Blankespoor, R.L.; Zinger, B. Electrochemical controlled release drug delivery system. U.S. Patent 4585652 A, 29 April 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Green, P.G.; Hinz, R.S.; Cullander, C.; Yamane, G.; Guy, R.H. Lontophoretic Delivery of Amino Acids and Amino Acid Derivatives Across the Skin in Vitro. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.G.; Hinz, R.S.; Kim, A.; Cullander, C.; Yamane, G.; Szoka Jr, F.C.; Guy, R.H. Transdermal Iontophoresis of Amino Acids and Peptides in Vitro. J. Control. Release 1992, 21, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnette, R.R.; Ongpipattanakul, B. Characterization of the Permselective Properties of Excised Human Skin during Iontophoresis. J. Pharm. Sci. 1987, 76, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Geest, R.; Hueber, F.; Szoka Jr, F.C.; Guy, R.H. Iontophoresis of Bases, Nucleosides, and Nucleotides. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banga, A.K. Electrically Assisted Transdermal and Topical Drug Delivery; Taylor & Francis: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Roustit, M.; Gaillard-Bigot, F.; Blaise, S.; Stanke-Labesque, F.; Cracowski, C.; Seinturier, C.; Jourdil, J.; Imbert, B.; Carpentier, P.H.; Cracowski, J. Cutaneous Iontophoresis of Treprostinil in Systemic Sclerosis: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 95, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, O.; Nair, V.; Panchagnula, R. Transdermal Iontophoresis of Insulin: IV. Influence of Chemical Enhancers. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 269, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cázares-Delgadillo, J.; Naik, A.; Ganem-Rondero, A.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Kalia, Y. Transdermal Delivery of Cytochrome C—A 12.4 kDa protein—across Intact Skin by constant–current Iontophoresis. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gratieri, T.; Kalia, Y.N. Targeted Local Simultaneous Iontophoresis of Chemotherapeutics for Topical Therapy of Head and Neck Cancers. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 460, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.; Kalia, Y. Non-Invasive Iontophoretic Delivery of Enzymatically Active Ribonuclease A (13.6 kDa) Across Intact Porcine and Human Skins. J. Control. Release 2010, 145, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.; Perozzo, R.; Scapozza, L.; Kalia, Y. Non-Invasive Electrically-Assisted Transdermal Delivery of Human Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.; Kalia, Y. Understanding the Poor Iontophoretic Transport of Lysozyme across the Skin: When High Charge and High Electrophoretic Mobility are not enough. J. Control. Release 2014, 183, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeGrys, V.A.; Yankaskas, J.R.; Quittell, L.M.; Marshall, B.C.; Mogayzel Jr, P.J. Diagnostic Sweat Testing: The Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Guidelines. J. Pediatr. 2007, 151, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Shieh, H.; Ching, C.T. Carbon Nanotube Composites for Glucose Biosensor Incorporated with Reverse Iontophoresis Function for Noninvasive Glucose Monitoring. Inter. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3069–3076. [Google Scholar]
- Krueger, E.; Claudino Junior, J.L.; Scheeren, E.M.; Neves, E.B.; Mulinari, E.; Nohama, P. Iontophoresis: Principles and Applications. Fisioterapia Movimento 2014, 27, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, Y.; Naik, A.; Garrison, J.; Guy, R.; Naik, A.; Garrison, J.; Guy, R. Iontophoretic Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 619–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitragotri, S. Current Status and Future Prospects of Needle-Free Liquid Jet Injectors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachowiak, J.C.; Li, T.H.; Arora, A.; Mitragotri, S.; Fletcher, D.A. Dynamic Control of Needle-Free Jet Injection. J. Control. Release 2009, 135, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitragotri, S. Immunization without Needles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, A.; Hakim, I.; Baxter, J.; Rathnasingham, R.; Srinivasan, R.; Fletcher, D.A.; Mitragotri, S. Needle-Free Delivery of Macromolecules Across the Skin by Nanoliter-Volume Pulsed Microjets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4255–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.; Loskutov, A.; Zehrung, D.; Puaa, K.; LaBarre, P.; Muller, N.; Guiqiang, W.; Ding, H.; Hu, D.; Blackwelder, W.C. Preventing Contamination between Injections with Multiple-use Nozzle Needle-Free Injectors: A Safety Trial. Vaccine 2008, 26, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassaday, R.D.; Sondel, P.M.; King, D.M.; Macklin, M.D.; Gan, J.; Warner, T.F.; Zuleger, C.L.; Bridges, A.J.; Schalch, H.G.; Kim, K.M. A Phase I Study of Immunization using Particle-Mediated Epidermal Delivery of Genes for gp100 and GM-CSF into Uninvolved Skin of Melanoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarno, M.J.; Blase, E.; Galindo, N.; Ramirez, R.; Schirmer, C.L.; Trujillo-Juarez, D.F. Clinical Immunogenicity of Measles, Mumps and Rubella Vaccine Delivered by the Injex Jet Injector: Comparison with Standard Syringe Injection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2000, 19, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, L.A.; Austin, G.; Chen, R.T.; Stout, R.; DeStefano, F.; Gorse, G.J.; Newman, F.K.; Yu, O.; Weniger, B.G.; Vaccine Safety Datalink Study Group. Safety and Immunogenicity of Varying Dosages of Trivalent Inactivated Influenza Vaccine Administered by Needle-Free Jet Injectors. Vaccine 2001, 19, 4703–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.; Mitchell, T.; Wrighton-Smith, P. Intradermal Ballistic Delivery of Micro-Particles into Excised Human Skin for Pharmaceutical Applications. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Wahab, G.M.K.A.; ur Rahman, M.A.S.; Altaf, H.; Akhtar, N.; Qayyum, M.I. Potential Enhancers for Transdermal Drug Delivery: A Review. Inter. J. Basic Med. Sci. Pharm. 2014, 4, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sklar, L.R.; Burnett, C.T.; Waibel, J.S.; Moy, R.L.; Ozog, D.M. Laser Assisted Drug Delivery: A Review of an Evolving Technology. Lasers Surg. Med. 2014, 46, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannos, S. Skin Microporation: Strategies to Enhance and Expand Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.B.; Traynor, M.J.; Martin, G.P.; Akomeah, F.K. Transdermal drug delivery systems: Skin perturbation devices. In Drug Delivery Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, C.; Costela, A.; García-Moreno, I.; Llanes, F.; Teijon, J.M.; Blanco, D. Laser Treatments on Skin Enhancing and Controlling Transdermal Delivery of 5-fluorouracil. Lasers Surg. Med. 2008, 40, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.S.; McCullough, J.L.; Glenn, T.C.; Wright, W.H.; Liaw, L.L.; Jacques, S.L. Mid-Infrared Laser Ablation of Stratum Corneum Enhances in Vitro Percutaneous Transport of Drugs. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 97, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, E.D.; Harris, L.; Redpath, W.S.; Shapiro, H.; Hetzel, F.; Morley, G.; Bar-Or, D.; Stevens, S.R. Laser-Assisted Penetration of Topical Anesthetic in Adults. Arch. Dermatol. 2003, 139, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhamecha, D.L.; Rajendra, V.B.; Rathi, A.A.; Ghadlinge, S.V.; Saifee, M.; Dehghan, M.H.G. Physical Approaches to Penetration Enhancement. Inter. J. Health Res. 2010, 3, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Philip, A. Modified Transdermal Technologies: Breaking the Barriers of Drug Permeation via the Skin. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2007, 6, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Fang, J.; Hu, C.; Lee, W. Erbium: YAG Laser Pretreatment Accelerates the Response of Bowen’s Disease Treated by Topical 5-Fluorouracil. Dermatol. Surg. 2004, 30, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.H.; Aljuffali, I.A.; Fang, J.Y. Lasers as an Approach for Promoting Drug Delivery via Skin. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, F.; Wei, L.; Yuan, W. Hydrogel Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Nano-Micro Lett. 2014, 6, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indermun, S.; Luttge, R.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Modi, G.; Pillay, V. Current Advances in the Fabrication of Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lademann, J.; Jacobi, U.; Surber, C.; Weigmann, H.; Fluhr, J. The Tape Stripping procedure—Evaluation of some Critical Parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar-Chavez, J.J.; Merino-Sanjuán, V.; López-Cervantes, M.; Urban-Morlan, Z.; Pinon-Segundo, E.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Ganem-Quintanar, A. The Tape-Stripping Technique as a Method for Drug Quantification in Skin. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 11, 104–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Jin, M.; Quan, Y.; Kamiyama, F.; Kusamori, K.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Transdermal Delivery of Relatively High Molecular Weight Drugs using Novel Self-Dissolving Microneedle Arrays Fabricated from Hyaluronic Acid and their Characteristics and Safety after Application to the Skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, A.; Babla, H.; Han, T.; Das, D.B. Lidocaine Carboxymethylcellulose with Gelatine Co-Polymer Hydrogel Delivery by Combined Microneedle and Ultrasound. Drug Deliv. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAllister, D.V.; Wang, P.M.; Davis, S.P.; Park, J.H.; Canatella, P.J.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated Needles for Transdermal Delivery of Macromolecules and Nanoparticles: Fabrication Methods and Transport Studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, K.; Xu, Y.; Kang, C.; Liu, H.; Tam, K.; Ko, S.; Kwan, F.; Lee, T.M.H. Sharp Tipped Plastic Hollow Microneedle Array by Microinjection Moulding. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 015016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Biodegradable Polymer Microneedles: Fabrication, Mechanics and Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattani, A.; McKay, P.F.; Garland, M.J.; Curran, R.M.; Migalska, K.; Cassidy, C.M.; Malcolm, R.K.; Shattock, R.J.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle Mediated Intradermal Delivery of Adjuvanted Recombinant HIV-1 CN54gp140 Effectively Primes Mucosal Boost Inoculations. J. Control. Release 2012, 162, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomaa, Y.A.; Garland, M.J.; McInnes, F.; El-Khordagui, L.K.; Wilson, C.; Donnelly, R.F. Laser-Engineered Dissolving Microneedles for Active Transdermal Delivery of Nadroparin Calcium. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, Y.; Hirono, M.; Fukushima, K.; Sugioka, N.; Takada, K. Two-Layered Dissolving Microneedles Formulated with Intermediate-Acting Insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Park, J.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for Drug and Vaccine Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrudden, M.T.; Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, C.M.; McAlister, E.; McCarthy, H.O.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Design and Physicochemical Characterisation of Novel Dissolving Polymeric Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Delivery of High Dose, Low Molecular Weight Drugs. J. Control. Release 2014, 180, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, H.S.; Denson, D.D.; Burris, B.A.; Prausnitz, M.R. Effect of Microneedle Design on Pain in Human Subjects. Clin. J. Pain 2008, 24, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameri, M.; Kadkhodayan, M.; Nguyen, J.; Bravo, J.A.; Su, R.; Chan, K.; Samiee, A.; Daddona, P.E. Human Growth Hormone Delivery with a Microneedle Transdermal System: Preclinical Formulation, Stability, Delivery and PK of Therapeutically Relevant Doses. Pharmaceutics 2014, 6, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.; O’Neill, S.; O’Mahony, C.; Armstrong, K.; McLoone, N.; Kole, P.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays Exhibit Antimicrobial Properties: Potential for Enhanced Patient Safety. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 451, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, S.P.; Koutsonanos, D.G.; del Pilar Martin, M.; Lee, J.W.; Zarnitsyn, V.; Choi, S.; Murthy, N.; Compans, R.W.; Skountzou, I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Dissolving Polymer Microneedle Patches for Influenza Vaccination. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, J.J.; Arya, J.M.; McClain, M.A.; Frew, P.M.; Meltzer, M.I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedle Patches: Usability and Acceptability for Self-Vaccination Against Influenza. Vaccine 2014, 32, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, J.; Guy, B. Intradermal, Epidermal and Transcutaneous Vaccination: From Immunology to Clinical Practice. Expert Rev. Vaccine 2008, 7, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Moffatt, K.; Alkilani, A.Z.; Vicente-Pérez, E.M.; Barry, J.; McCrudden, M.T.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays can be Effectively Inserted in Skin by Self-Application: A Pilot Study Centred on Pharmacist Intervention and a Patient Information Leaflet. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 1989–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, P.E.; Bonnet, S.; Alchas, P.; Regolini, P.; Mikszta, J.A.; Pettis, R.; Harvey, N.G. Evaluation of the Clinical Performance of a New Intradermal Vaccine Administration Technique and Associated Delivery System. Vaccine 2007, 25, 8833–8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daddona, P.E.; Matriano, J.A.; Mandema, J.; Maa, Y. Parathyroid Hormone (1–34)-Coated Microneedle Patch System: Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics for Treatment of Osteoporosis. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Brown, K.; Siebenaler, K.; Determan, A.; Dohmeier, D.; Hansen, K. Development of Lidocaine-Coated Microneedle Product for Rapid, Safe, and Prolonged Local Analgesic Action. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Woolfson, A.D. Microneedle-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Microfabrication, Drug Delivery, and Safety. Drug Deliv. 2010, 17, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, T.; Hagino, K.; Sato, T. Evaluation of the Effect of Polymeric Microneedle Arrays of Varying Geometries in Combination with a High-Velocity Applicator on Skin Permeability and Irritation. Biomed. Microdevices 2014, 16, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yao, G.; Dong, P.; Gong, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C. Investigation on Fabrication Process of Dissolving Microneedle Arrays to Improve Effective Needle Drug Distribution. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 66, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, N.; Yuan, W.; Jin, T. A Scalable Fabrication Process of Polymer Microneedles. Inter. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1415. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, R.; Majithiya, R.; Thakur, R.; Morrow, D.; Garland, M.; Demir, Y.; Migalska, K.; Ryan, E.; Gillen, D.; Scott, C. Design and Physicochemical Characterisation of Optimised Polymeric Microneedle Arrays Prepared by a Novel Laser-Based Micromoulding Technique. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.W.; Tayyaba, S.; Afzulpurkar, N.; Nisar, A.; Punyasai, C.; Saejok, K.; Supadech, J.; Atthi, N.; Hruanun, C. Optimization of Fabrication Process for MEMS Based Microneedles using ICP Etching Technology. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 403, 4611–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardeniers, H.J.; Luttge, R.; Berenschot, E.J.; De Boer, M.J.; Yeshurun, S.Y.; Hefetz, M.; van’t Oever, R.; van den Berg, A. Silicon Micromachined Hollow Microneedles for Transdermal Liquid Transport. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martanto, W.; Moore, J.S.; Kashlan, O.; Kamath, R.; Wang, P.M.; O’Neal, J.M.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microinfusion using Hollow Microneedles. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, J.; Felner, E.I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Minimally Invasive Insulin Delivery in Subjects with Type 1 Diabetes using Hollow Microneedles. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2009, 11, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirouche, F.; Zhou, Y.; Johnson, T. Current Micropump Technologies and their Biomedical Applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2009, 15, 647–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariya, S.H.; Gohel, M.C.; Mehta, T.A.; Sharma, O.P. Microneedles: An Emerging Transdermal Drug Delivery System. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Coated Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Yoo, D.G.; Bondy, B.J.; Quan, F.S.; Compans, R.W.; Kang, S.M.; Prausnitz, M.R. Stability of Influenza Vaccine Coated onto Microneedles. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3756–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrdoljak, A.; McGrath, M.G.; Carey, J.B.; Draper, S.J.; Hill, A.V.; O’Mahony, C.; Crean, A.M.; Moore, A.C. Coated Microneedle Arrays for Transcutaneous Delivery of Live Virus Vaccines. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, Y.K.; Akan, Z.; Kerimoglu, O. Sodium Alginate Microneedle Arrays Mediate the Transdermal Delivery of Bovine Serum Albumin. PLoS ONE 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolli, C.S.; Xiao, J.; Parsons, D.L.; Babu, R.J. Microneedle Assisted Iontophoretic Transdermal Delivery of Prochlorperazine Edisylate. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.D.; Banga, A.K. Controlled Delivery of Ropinirole Hydrochloride through Skin using Modulated Iontophoresis and Microneedles. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Jin, M.; Quan, Y.; Kamiyama, F.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. The Development and Characteristics of Novel Microneedle Arrays Fabricated from Hyaluronic Acid, and their Application in the Transdermal Delivery of Insulin. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ita, K. Transdermal Delivery of Drugs with Microneedles—Potential and Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R. Novel Delivery Systems for Transdermal and Intradermal Drug Delivery; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the Stratum Corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438-470. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7040438
Alkilani AZ, McCrudden MTC, Donnelly RF. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the Stratum Corneum. Pharmaceutics. 2015; 7(4):438-470. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7040438
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkilani, Ahlam Zaid, Maelíosa T. C. McCrudden, and Ryan F. Donnelly. 2015. "Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the Stratum Corneum" Pharmaceutics 7, no. 4: 438-470. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7040438
APA StyleAlkilani, A. Z., McCrudden, M. T. C., & Donnelly, R. F. (2015). Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the Stratum Corneum. Pharmaceutics, 7(4), 438-470. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7040438