Spinal Vascular Shunts: Single-Center Series and Review of the Literature of Their Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
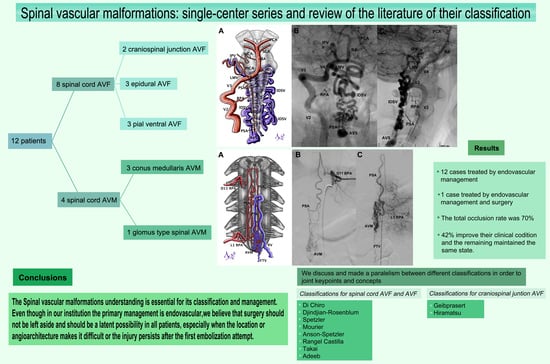
3.1. Clinical Series
3.2. AVMs
3.3. AVFs
3.4. Management and Outcome
3.5. Clinical Cases
3.5.1. Case 4
3.5.2. Case 7
3.5.3. Case 8
3.5.4. Case 10
3.5.5. Case 11
4. Discussion
4.1. Pathophysiology and Clinics
4.2. Classification
4.3. Management
4.4. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaloupka, J.C. Future directions in the evaluation and management of spinal cord vascular malformations. Semin. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Stroke 2002, 2, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Castilla, L.; Russin, J.J.; Zaidi, H.A.; Martinez-del-Campo, E.; Park, M.S.; Albuquerque, F.C.; McDougall, C.G.; Nakaji, P.; Spetzler, R.F. Contemporary management of spinal AVFs and AVMs: Lessons learned from 110 cases. Neurosurg. Focus 2014, 37, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kendall, B.; Logue, V. Spinal epidural angiomatous malformations draining into intrathecal veins. Neuroradiology 1977, 13, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbertson, J.R.; Miller, G.M.; Goldman, M.S.; Marsh, W.R. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: MR and myelographic findings. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1995, 16, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, C. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistula. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugate, J.E.; Lanzino, G.; Rabinstein, A.A. Clinical presentation and prognostic factors of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: An overview. Neurosurg. Focus 2012, 32, E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, E.H. Surgical treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. Semin. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Stroke 2002, 2, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, B.C.; Klinger, D.R.; White, J.A.; Batjer, H.H. Spinal vascular malformations: Treatment strategies and outcome. Neurosurg. Rev. 2017, 40, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, B.; Oldfield, E.H.; Doppman, J.L.; Di Chiro, G. Spinal arteriovenous malformations: A comparison of dural arteriovenous fistulas and intradural AVM’s in 81 patients. J. Neurosurg. 1987, 67, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.L.; Piepgras, D.G. Surgical treatment of spinal cord arteriovenous malformations and arteriovenous fistulas. Semin. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Stroke 2002, 5, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, B.A.; Du, R. Spinal Glomus (Type II) Arteriovenous Malformations A Pooled Analysis of Hemorrhage Risk and Results of Intervention. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascitelli, J.R.G.Y.; Patel, A.B. Endovascular Treatment of Spinal Vascular Malformations. In Youmans & Winn Neurological Surgery, 7th ed.; Winn, H.R., Ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; Volume 4, pp. 3568–3578. [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu, M.; Sugiu, K.; Ishiguro, T.; Kiyosue, H.; Sato, K.; Takai, K.; Niimi, Y.; Matsumaru, Y. Angioarchitecture of arteriovenous fistulas at the craniocervical junction: A multicenter cohort study of 54 patients. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 128, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, F.; Ren, J.; Manjila, S.; Bambakidis, N.C. Dural arteriovenous fistulas at the craniocervical junction: A systematic review. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2016, 8, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consoli, A.; Coskun, O.; Di Maria, F.; Gratieux, J.; Condette-Auliac, S.; Smadja, S.; Boulin, A.; Rodesch, G. Spinal cord arterio-venous shunts: From classification to therapeutic management. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 177, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehresman, J.; Catapano, J.S.; Baranoski, J.F.; Jadhav, A.P.; Ducruet, A.F.; Albuquerque, F.C. Treatment of Spinal Arteriovenous Malformation and Fistula. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 33, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodesch, G.; Hurth, M.; Alvarez, H.; Tadié, M.; Lasjaunias, P. Classification of spinal cord arteriovenous shunts: Proposal for a reappraisal-the Bicêtre experience with 155 consecutive patients treated between 1981 and 1999. Neurosurgery 2002, 51, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodesch, G.; Lasjaunias, P. Spinal cord arteriovenous shunts: From imaging to management. Eur. J. Radiol. 2003, 46, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, T.H.; Alexander, L. Vascular system of the human spinal cord. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1939, 41, 659–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalani, M.Y.S.; Mendes, G.A.; Kalani, M.A.; Spetzler, R.F. Surgery of spinal arteriovenous malformations. Compr. Manag. Arter. Malform. Brain Spine 2015, 171, 4–49. [Google Scholar]
- Niimi, Y.; Berenstein, A. Endovascular treatment of spinal vascular malformations. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 10, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Berenstein, A. Surgical neuroangiography of the spine and spinal cord. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 1988, 26, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amenta, M.R.; Singh, M.K.; Dumont, A.S.; Oldfield, E.H. Microsurgical Treatment of Spinal Vascular Malformations. In Youmans & Winn Neurological Surgery, 7th ed.; Winn, H.R., Ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; Volume 4, pp. 3579–3605. [Google Scholar]
- Abecassis, I.J.; Osbun, J.W.; Kim, L. Classification and pathophysiology of spinal vascular malformations. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 143, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Djindjian, M.; Djindjian, R.; Rey, A.; Hurth, M.; Houdart, R. Intradural extramedullary spinal arterio-venous malformations fed by the anterior spinal artery. Surg. Neurol. 1977, 8, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mourier, K.; Gobin, Y.; George, B.; Lot, G.; Merland, J. Intradural perimedullary arteriovenous fistulae: Results of surgical and endovascular treatment in a series of 35 cases. Neurosurgery 1993, 32, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozpinar, A.; Weiner, G.M.; Ducruet, A.F. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation, and prognosis of spinal arteriovenous malformations. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 143, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Spetzler, R.F.; Detwiler, P.W.; Riina, H.A.; Porter, R.W. Modified classification of spinal cord vascular lesions. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2002, 96, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rangel-Castilla, L.; Holman, P.J.; Krishna, C.; Trask, T.W.; Klucznik, R.P.; Diaz, O.M. Spinal extradural arteriovenous fistulas: A clinical and radiological description of different types and their novel treatment with Onyx. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2011, 15, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TaKai, K. Spinal arteriovenous shunts: Angioarchitecture and historical changes in classification. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2017, 57, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adeeb, N.; Moore, J.M.; Alturki, A.Y.; Bulsara, K.R.; Griessenauer, C.J.; Patel, A.S.; Gupta, R.; Tubbs, R.S.; Ogilvy, C.S.; Thomas, A.J. Type I spinal arteriovenous fistula with ventral intradural venous drainage: A proposal of a modified classification. Asian. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 13, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Osbun, N.J.; Kim, L.J. Classification of Spinal Arteriovenous Lesions: Arterivenous Fistulas and Arteriovenous Malformations. In Youmans & Winn Neurological Surgery, 7th ed.; Winn, H.R., Ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; Volume 4, pp. 3563–3566. [Google Scholar]
- Zozulya, Y.P.; Slin’ko, E.I.; Al-Qashqish, I.I. Spinal arteriovenous malformations: New classification and surgical treatment. Neurosurg. Focus 2006, 20, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Choi, I.S.; David, C.A. Spinal arteriovenous fistulas of the filum terminale. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryu, B.; Sato, S.; Mochizuki, T.; Niimi, Y. Spinal arteriovenous fistula located in the filum terminale externa: A case report and review of the literature. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2021, 27, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenck, S.; Nicholson, P.; Tymianski, R.; Hilditch, C.; Nouet, A.; Patel, K.; Krings, T.; Tymianski, M.; Radovanovic, I.; Pereira, V.M. Spinal and Paraspinal Arteriovenous Lesions. Stroke 2019, 50, 2259–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, J.; Xu, J.; He, C.; Bian, L.; Li, G.; Ye, M.; Hu, P.; Sun, L.; Jiang, N.; et al. Natural History and Clinical Outcomes of Paravertebral Arteriovenous Shunts. Stroke 2021, 52, 3873–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geibprasert, S.; Pereira, V.; Krings, T.; Jiarakongmun, P.; Toulgoat, F.; Pongpech, S.; Lasjaunias, P. Dural arteriovenous shunts: A new classification of craniospinal epidural venous anatomical bases and clinical correlations. Stroke 2008, 39, 2783–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, D.A.; Abla, A.A.; Uschold, T.D.; McDougall, C.G.; Albuquerque, F.C.; Spetzler, R.F. Multimodality treatment of conus medullaris arteriovenous malformations: 2 decades of experience with combined endovascular and microsurgical treatments. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narvid, J.; Hetts, S.W.; Larsen, D.; Neuhaus, J.; Singh, T.P.; McSwain, H.; Lawton, M.T.; Dowd, C.F.; Higashida, R.T.; Halbach, V.V. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae: Clinical features and long-term results. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.L.; Miller, G.M.; Krauss, W.E.; Marsh, W.R.; Piepgras, D.G.; Atkinson, P.P.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Lane, J.I. Clinical and radiographic features of dural arteriovenous fistula, a treatable cause of myelopathy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2001, 76, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.S.; Sun, H.; Spetzler, R.F. Spinal arteriovenous malformations: Surgical management. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 143, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Day, A.L.; Turkmani, A.H.; Chen, P.R. Spinal arteriovenous fistulae: Surgical management. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 143, 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Tykocki, T.; Poniatowski, Ł.A.; Czyz, M.; Wynne-Jones, G. Oblique corpectomy in the cervical spine. Spinal Cord. 2018, 56, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, N.A.; Khanna, R.K.; Batzdorf, U. Posterolateral cervical or thoracic approach with spinal cord rotation for vascular malformations or tumors of the ventrolateral spinal cord. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 83, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.; Sekhar, L. Surgical management of anteriorly placed lesions at the craniocervical junction—an alternative approach. Acta Neurochir. 1991, 108, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garling, R.J.; Rajah, G.; Narayanan, S.; Rangel-Castilla, L.; Haridas, A. Pial resection technique of a cervical spinal arteriovenous malformation in a pediatric patient. Oper Neurosurg. 2018, 14, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velat, G.J.; Chang, S.W.; Abla, A.A.; Albuquerque, F.C.; McDougall, C.G.; Spetzler, R.F. Microsurgical management of glomus spinal arteriovenous malformations: Pial resection technique. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2012, 16, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, S.L.; Kadkhodayan, Y.; Ray, W.Z.; Zipfel, G.J.; Cross, D.T.; Moran, C.J.; Derdeyn, C.P. Onyx is associated with poor venous penetration in the treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2014, 6, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, C.G.; Deshmukh, V.R.; Fiorella, D.J.; Albuquerque, F.C.; Spetzler, R.F. Endovascular techniques for vascular malformations of the spinal axis. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 16, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, B.; Chavda, V.; Lu, B.; Garg, K.; Montemurro, N. Cognitive deficits and memory impairments after COVID-19 (Covishield) vaccination. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2022, 22, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symon, L.; Kuyama, H.; Kendall, B. Dural arteriovenous malformations of the spine: Clinical features and surgical results in 55 cases. J. Neurosurg. 1984, 60, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuoka, S.; Peterson, H.A.; MacCarty, C.S. Incidence of spinal column deformity after multilevel laminectomy in children and adults. J. Neurosurg. 1982, 57, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haynes, J.; Nossek, E.; Shapiro, M.; Chancellor, B.; Frempong-Boadu, A.; Peschillo, S.; Alves, H.; Tanweer, O.; Gordon, D.; Raz, E. Radial Arterial Access for Thoracic Intraoperative Spinal Angiography in the Prone Position. World Neurosurg. 2020, 137, e358–e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Szu-Kai, H.; Chih-Ju, C.; Ming-Hong, C.; Chih-Ta, H.; Jing-Shan, H.; Su, I. Transfemoral Approach for Intraoperative Angiography in the Prone or Three-quarter Prone Position. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2020, 30, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, T.; Koyanagi, I.; Kaneko, T.; Iihoshi, S.; Houkin, K. Intraoperative indocyanine green videoangiography for spinal vascular lesions: Case report. Oper Neurosurg. 2011, 68, onsE241–onsE245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodesch, G.; Hurth, M.; Ducot, B.; Alvarez, H.; David, P.; Tadie, M.; Lasjaunias, P. Embolization of spinal cord arteriovenous shunts: Morphological and clinical follow-up and results—review of 69 consecutive cases. Neurosurgery 2003, 53, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, W.; Zada, G.; Yashar, P.; Giannotta, S.L.; Teitelbaum, G.; Larsen, D.W. Endovascular management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: A review. Neurosurg. Focus 2009, 26, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eskandar, E.N.; Borges, L.F.; Budzik, R.F.; Putman, C.M.; Ogilvy, C.S. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Experience with endovascular and surgical therapy. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2002, 96, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarençon, F.; Parat, D.; Shotar, E.; Premat, K.; Lenck, S.; Drir, M.; Maillart, E.; Boch, A.-L.; Sourour, N. ’Balloon pressure technique’ for endovascular treatment of spinal cord arteriovenous fistulas: Preliminary results in 10 cases. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2022, 28, 018807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinjikji, W.; Lanzino, G. Endovascular treatment of spinal arteriovenous malformations. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 143, 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Ohata, K.; Takami, T.; El-Naggar, A.; Morino, M.; Nishio, A.; Inoue, Y.; Hakuba, A. Posterior approach for cervical intramedullary arteriovenous malformation with diffuse-type nidus: Report of three cases. J. Neurosurg. Spine 1999, 91, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillevin, R.; Vallee, J.; Cormier, E.; Lo, D.; Dormont, D.; Chiras, J. N-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate embolization of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae: CT evaluation, technical features, and outcome prognosis in 26 cases. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 929–935. [Google Scholar]
- Takai, K.; Endo, T.; Seki, T.; Inoue, T.; Koyanagi, I.; Mitsuhara, T.; the Neurospinal Society of Japan CCJ AVF Study Investigators; Neurospinal Society of Japan CCJ AVF Investigators. Ischemic complications in the neurosurgical and endovascular treatments of craniocervical junction arteriovenous fistulas: A multicenter study. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, K.; Endo, T.; Seki, T.; Inoue, T.; Koyanagi, I.; Mitsuhara, T.; the Neurospinal Society of Japan CCJ AVF Study Investigators. Neurosurgical versus endovascular treatment of craniocervical junction arteriovenous fistulas: A multicenter cohort study of 97 patients. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, D.H.; Cho, Y.D.; Boonchai, T.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, W.-S.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, C.K.; Kang, H.-S. Endovascular treatment of medullary bridging vein-draining dural arteriovenous fistulas: Foramen magnum vs. craniocervical junction lesions. Neuroradiology 2022, 64, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavda, V.; Chaurasia, B.; Fiorindi, A.; Umana, G.E.; Lu, B.; Montemurro, N. Ischemic Stroke and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The Bidirectional Pathology and Risk Morbidities. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.X.; He, C.; Ye, M.; Li, G.-L.; Bian, L.-S.; Yang, F.; Zhai, X.-D.; Ling, F.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Hong, T. The efficacy and deficiency of contemporary treatment for spinal cord arteriovenous shunts. Brain 2021, 144, 3381–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojdasiewicz, P.; Poniatowski, Ł.A.; Turczyn, P.; Frasuńska, J.; Paradowska-Gorycka, A.; Tarnacka, B. Significance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Prophylaxis and Treatment after Spinal Cord Injury in Rodent Models. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 29, 3164260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, N.; Condino, S.; Carbone, M.; Cattari, N.; D’Amato, R.; Cutolo, F.; Ferrari, V. Brain Tumor and Augmented Reality: New Technologies for the Future. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, N. Telemedicine: Could it represent a new problem for spine surgeons to solve? Global Spine J. 2022, 12, 1306–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprengel, U.; Saalfeld, P.; Stahl, J.; Mittenentzwei, S.; Drittel, M.; Behrendt, B.; Kaneko, N.; Behme, D.; Berg, P.; Preim, B.; et al. Virtual embolization for treatment support of intracranial AVMs using an interactive desktop and VR application. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 16, 2119–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Spinal AVFs | Spinal AVMs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | Epidural AVF | CCJ AFV | Pial Ventral AVF | CM AVM | Other AVM | Total |
| Age <18 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 4 |
| Age 18–59 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| >60 | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| Total | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 12 |
| Age/Sex | Symptoms | Admission mRS | Classification | Afferents | Ostium/Nidus | Aneurysms | Venous Drainage | Management | Outcome | Last Follow-Up mRS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 44/F | Chronic myelopathy (paraparesis 2/5, paresthesia, sphincter incontinence) | 4 | AVF extradural epidural lateral subtype B1 (Rangel-Castilla) | Right L1 radiculomeningeal artery | Small ostium D12 | No | Ventral epidural venous plexus | Embolized with Histoacryl | Complete occlusion. Without improvement of the sequel | 4 |
| Case 2 | 18/F | Chronic myelopathy, left leg monoparesis 2/5 | 3 | AVF extradural epidural dorsal sub type A (Rangel-Castilla) | Right radiculopial L1 and D9 left radiculopial D7 | Shunt and epidural venous pouch D9 | No | Intradural vein | Through right L1 radiculomedullary artery with Histoacryl | Partial occlusion, without neurological changes | 3 |
| Case 3 | 51/F | Acute myelopathy, paraparesis (1/5 right leg; 2/5 left leg), sphincter incontinence | 4 | AVF extradural epidural dorsal sub type A (Rangel-Castilla). Unexpected diagnosis during spine surgery | Right D9 radiculomeningeal and radiculopial artery | Shunt and epidural venous pouch D9 | No | Intradural vein | Through right D9 radiculopial artery with Histoacryl | Total occlusion, without neurological changes | 4 |
| Case 4 | 3/F | Chronic myelopathy (paraparesis 4/5) and lumbar pain | 3 | AVF pial ventral at conus medullaris | Right D11 and L2 radiculomedullary arteries | Intradural fistulous ostium at D12–L1 with venous aneurism (15 mm × 20 mm) | Venous aneurysm | L3 radiculomedullary vein | Embolized with coils and Histoacryl | Complete occlusion. Almost without sequel, paraparesis (4+/5) | 1 |
| Case 5 | 6/M | Chronic myelopathy (paraparesis 4/5), history of AVF embolization 5 years ago | 2 | AVF type IV (Di Chiro)/intradural ventral subtype A (Anson-Spetzler) | Right D9 and left D10 radiculomedullary arteries | Small ostium at D11–D12 | Venous aneurysm | Venous drainage runs to anterior spinal vein | Embolized with Histoacryl | There is no evidence of AVF, same neurological status | 2 |
| Case 6 | 28/M | Chronic myelopathy, paraparesis (2/5 right leg; 4/5 left leg) | 3 | AVF type IV (Di Chiro)/intradural ventral subtype A (Anson-Spetzler) associated with tumor | Left D12 and D9 radiculomedullary arteries | Small ostium at D11 | 2 arterial aneurysms | Anterior spinal vein/filum terminal vein | Spontaneous thrombosis | Spontaneous thrombosis without neurological changes | 3 |
| Case 7 | 15/F | SAH Fisher IV, headache, neck stiffness | 3 | Type V dorsal CCJ AVF (Hiramatsu) | Posterior spinal artery | Middle ostium at C3 | Venous aneurysm | Venous drainage to intradural varicose veins–inferior petrous vein | Embolized with Histoacryl | Complete occlusion, without neurological deficit | 0 |
| Case 8 | 26/F | 2 episodes of syncope, chronic headache | 1 | Type V perimedullary CCJ AVF (Hiramatsu)/epidural dorsal (Geibprasert) | Posterior meningeal arteries, PSA, and radiculomeningeal branch from V3 on the left side | 2 small ostia at foramen magnum | 2 arterial aneurysm | Venous drainage to marginal sinus–epidural plexus | Embolized with Histoacryl in 2 sessions | Almost complete occlusion, without neurological deficit | 0 |
| Case 9 | 51/F | Chronic myelopathy, spastic paraparesis 2/5 | 4 | Type II (Di Chiro)/compact spinal AVM (Spetzler) | Right and left D10 radiculomedullary arteries, left D9 radiculomedullary artery | Compact nidus at D10 | No | Left D9 radiculomedullary vein and anterior spinal vein | Partially embolized with Histoacryl through D9 radiculomedullary artery, a second unsuccessful embolization attempt | Partial occlusion, without neurological changes | 4 |
| Case 10 | 18/M | Lumbar pain, acute myelopathy, paraparesis (2/5), headache, vomiting, and SAH at cranial base and perimedullary | 4 | Conus medullaris compact AVM (Spetzler) | Radiculomedullary arteries at left D11 and L1 | Compact nidus from D12 to L2 | No | Toward varicose perimedullary vein–lumbar segmentary vein | Embolized with Histoacryl in 2 sessions | Complete occlusion without sequel | 0 |
| Case 11 | 5/M | Acute myelopathy, hematomyelia, paraplegia, sphincter incontinence, and lumbar pain | 4 | Conus medullaris diffuse AVM | Right D10 and L2 RMA, left L3 RMA, right L4 RPA | Diffuse nidus with various high-flow fistulas | Arterial aneurysm at right L2 and venous aneurysm at left L2 | Venous drainage runs to radiculomedullary veins and filum terminale vein | Embolized with Histoacryl (2 sessions), laminoplasty with partial resection of AVM, and hematoma evacuation | There is no evidence of AVM, clinical improvement, still with paraparesis (4/5) | 2 |
| Case 12 | 74/F | Chronic myelopathy, paraparesis (2/5 right leg; 4/5 left leg), sensitive level at D8, sphincter incontinence | 3 | Conus medullaris diffuse AVM | D7 radiculomedullary | Nidus from D11 to L1 | No | Filum terminal vein and venous reflux to anterior spinal vein | Through right D7 radiculomedullary artery with Histoacryl | Total occlusion, without neurological changes | 3 |
| Sessions of Embolization | Total Occlusion | Partial Occlusion | Total Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| 1 Session | 5 (50) | 1 (10) | 6 (60) |
| 2 Sessions | 2 (20) | 2 (20) | 4 (40) |
| Total | 7 (70) | 3 (30) | 10 (100) |
| Type of Lesion | Arteriovenous Fistulas | Arteriovenous Malformations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subtypes by Spetzler | Extradural Epidural AVM | Intradural Dorsal AVM | Intradural Ventral AVM | Extradural Intradural | Intramedullary | Medullary Conus AVM |
| Pathogeny | Radicular artery to epidural venous plexus | Radicular artery to radicular or medullary vein | Anterior spinal artery to radicular or medullary vein | Metameric effect on skin, bone, muscle, and nerve tissue | 1 or multiple feeders from anterior or posterior spinal arteries | 1 or multiple feeders from anterior or posterior spinal arteries, 1 or multiple nidi around conus |
| Pathophysiology | Venous hypertension (A subtype), compression (A subtype), vascular steal, B subtype is associated with Von Recklinghausen disease | Venous congestion, rare hemorrhage | Compression (venous aneurysm), hemorrhage and vascular steal, arterial aneurysms (10%) | Compression, hemorrhage, and vascular steal | Compression, 50% debut with hemorrhage (glomus 4% to 10%), and vascular steal | Venous hypertension, compression, hemorrhage |
| Di Chiro classification | Without definition | Type I (dural fistula) | Type IV (Djindjian and Rosemblum) | Type III | Type II | Without definition |
| Subclassifications and other characteristics | By Rangel-Castilla: A: epidural drainage and perimedullary B: to Batson venous plexus B1 with compression or myelopathy B2 without compression or myelopathy | By Spetzler: A: 1 feeder B: multiple feeders By Adeeb: IA: dorsal venous plexus IB: ventral venous plexus | By Mourier and Anson-Spetzler: I/A: 1 small feeder II/B: medium size main feeder and others small feeders III/C: multipedicle lesion with great venous ectasia Associated with no metameric genetic diseases | Cobb syndrome | Compact nidus Diffuse nidus Associated with no metameric genetic diseases | Compact nidus. Glomus-like, pial perimedullary, complex venous drainage, associated with tethered cord |
| Subtypes by Takai | Type V (extradural) A: intradural venous drainage B: without intradural venous drainage | Type I (dural) | Type IV (perimedullary) Subtypes A, B, and C by Mourier | Type III (juvenile intramedullary) | Type II (glomus intramedullary) | Without definition |
| Ventral Epidural | Dorsal Epidural | Lateral Epidural | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Venous embryology | Osteo cartilaginous (notochord) Ventral osseous drainage | Osteo membranous Osseous dorsal and leptomeningeal drainage | Leptomeningeal drainage (not related to nerves) |
| Localization of the shunt | Vertebral body, basioccipital sinus, sigmoid sinus, petrous pyramid, basi-sphenoidal sinus, cavernous sinus, and sphenoidal wing | Dorsal epidural spinal, dorsal part of the marginal sinus, occipital sinus, torcula, transverse sinus, superior sagittal sinus | Lateral dural spinal, lateral part of marginal sinus with emissary condylar vein, vein of Galen, basitentorial sinus, sphenoparietal sinus, paracavernous region, intraorbital and cribriform lamina |
| Clinics and behavior | Female (2:1), rare cortical reflux unless there is thrombosis distal to the shunt | Pediatrics, epidural hematoma, cortical reflux could occur if there is a high flow shunt or restriction of efferents | Male (4:1), elderly, aggressive behavior. Always perimedullary or cortical reflux |
| by Hiramatsu | Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV | Type V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Denomination | Dural fistula | Radicular fistula | Epidural with pial afferents | Epidural | Perimedullary |
| Angioarchitecture | Meningeal afferent to intradural veinsAnd dura mater shunt | Radicular or meningeal afferents with drainage to radicular veins, Radicular shunt | Radicular or meningeal afferent with pial afferents also and epidural drainage. Shunt outside the dura mater | Radicular or meningeal afferent and epidural drainage Shunt outside the dura mater | Pial afferents with drainage to intradural veins Intradural shunt |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lizana, J.; Aliaga, N.; Marani, W.; Escribano, A.; Montemurro, N. Spinal Vascular Shunts: Single-Center Series and Review of the Literature of Their Classification. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 581-599. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14030047
Lizana J, Aliaga N, Marani W, Escribano A, Montemurro N. Spinal Vascular Shunts: Single-Center Series and Review of the Literature of Their Classification. Neurology International. 2022; 14(3):581-599. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14030047
Chicago/Turabian StyleLizana, Jafeth, Nelida Aliaga, Walter Marani, Amanda Escribano, and Nicola Montemurro. 2022. "Spinal Vascular Shunts: Single-Center Series and Review of the Literature of Their Classification" Neurology International 14, no. 3: 581-599. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14030047
APA StyleLizana, J., Aliaga, N., Marani, W., Escribano, A., & Montemurro, N. (2022). Spinal Vascular Shunts: Single-Center Series and Review of the Literature of Their Classification. Neurology International, 14(3), 581-599. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14030047