Insights into the Virulence of Campylobacter jejuni Associated with Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems and Single Regulators
Abstract
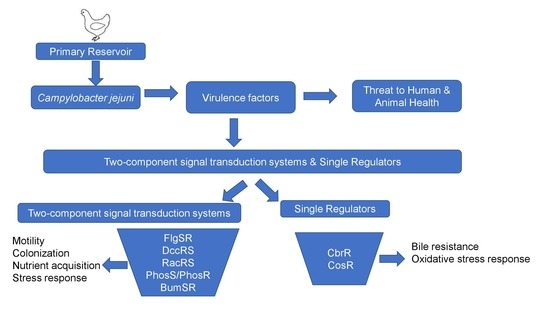
:1. Introduction
2. Detailed Description of TCSs and Single Regulators of Campylobacter jejuni
2.1. Two-Component Systems of Campylobacter jejuni
2.1.1. FlgS/FlgR TCS and Campylobacter jejuni Motility
2.1.2. Campylobacter jejuni DccR/DccS (Diminished Capacity to Colonise) Is Involved in Chicken Colonisation
2.1.3. Campylobacter jejuni PhosSR TCS and Phosphate Acquisition
2.1.4. Campylobacter jejuni CprRS (Planktonic Growth Regulation) TCS Regulation of Biofilm Formation and Chicken Colonisation
2.1.5. Campylobacter jejuni RacRS (Reduced Ability to Colonise) TCS Controls Physiology and Metabolism
2.1.6. Campylobacter jejuni BumSR (Butyrate Modulated) TCS Regulates Transcription and Colonisation
2.2. Single Regulators
2.2.1. Campylobacter jejuni CbrR (Bile Resistance Regulator) Modulates Sodium Deoxycholate Resistance and Chicken Colonisation
2.2.2. Campylobacter jejuni CosR (Oxidative Stress Regulator) controls Oxidative Stress Response and Expulsion of Toxic Substances
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirakawa, H.; Kurushima, J.; Hashimoto, Y.; Tomita, H. Progress Overview of Bacterial Two-Component Regulatory Systems as Potential Targets for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefers, M.M. Regulation of Virulence by Two-Component Systems in Pathogenic Burkholderia. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00927-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zschiedrich, C.P.; Keidel, V.; Szurmant, H. Molecular Mechanisms of Two-Component Signal Transduction. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 3752–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laub, M.T.; Goulian, M. Specificity in Two-Component Signal Transduction Pathways. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2007, 41, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhate, M.P.; Molnar, K.S.; Goulian, M.; DeGrado, W.F. Signal Transduction in Histidine Kinases: Insights from New Structures. Structure 2015, 23, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Sun, D.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W. Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems: A Major Strategy for Connecting Input Stimuli to Biofilm Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.N.; Stewart, V. Negative control in two-component signal transduction by transmitter phosphatase activity. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 82, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowland, M.A.; Deeds, E.J. Crosstalk and the evolution of specificity in two-component signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5550–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agrawal, R.; Sahoo, B.K.; Saini, D.K. Cross-talk and specificity in two-component signal transduction pathways. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procaccini, A.; Lunt, B.; Szurmant, H.; Hwa, T.; Weigt, M. Dissecting the Specificity of Protein-Protein Interaction in Bacterial Two-Component Signaling: Orphans and Crosstalks. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Stock, A.M. Biological Insights from Structures of Two-Component Proteins. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 63, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beier, D.; Gross, R. Regulation of bacterial virulence by two-component systems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Jamal, S.B.; Hassan, S.S.; Carvalho, P.V.S.D.; Almeida, S.; Barh, D.; Ghosh, P.; Silva, A.; Castro, T.L.P.; Azevedo, V. Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems of Pathogenic Bacteria As Targets for Antimicrobial Therapy: An Overview. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States-major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umaraw, P.; Prajapati, A.; Verma, A.K.; Pathak, V.; Singh, V.P. Control of Campylobacter in poultry industry from farm to poultry processing unit: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhill, J.; Wren, B.W.; Mungall, K.; Ketley, J.M.; Churcher, C.; Basham, D.; Chillingworth, T.; Davies, R.M.; Feltwell, T.; Holroyd, S.; et al. The genome sequence of the food-borne pathogen Campylobacter jejuni reveals hypervariable sequences. Nature 2000, 403, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svensson, S.L.; Hyunh, S.; Parker, C.T.; Gaynor, E.C. The Campylobacter jejuni CprRS two-component regulatory system regulates aspects of the cell envelope. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 96, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, P.M.; Hendrixson, D.R. Campylobacter jejuni: Collective components promoting a successful enteric lifestyle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagieva, E.; Teren, M.; Michova, H.; Strakova, N.; Karpiskova, R.; Demnerova, K. Adhesion, Biofilm Formation, and luxS Sequencing of Campylobacter jejuni Isolated From Water in the Czech Republic. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 596613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, S.L.; Davis, L.M.; MacKichan, J.K.; Allan, B.J.; Pajaniappan, M.; Thompson, S.A.; Gaynor, E.C. The CprS sensor kinase of the zoonotic pathogen Campylobacter jejuni influences biofilm formation and is required for optimal chick colonization. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 71, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luethy, P.M.; Huynh, S.; Parker, C.T.; Hendrixson, D.R. Analysis of the Activity and Regulon of the Two-Component Regulatory System Composed by Cjj81176_1484 and Cjj81176_1483 of Campylobacter jejuni. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 1592–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouts, D.E.; Mongodin, E.F.; Mandrell, R.E.; Miller, W.G.; Rasko, D.A.; Ravel, J.; Brinkac, L.M.; DeBoy, R.T.; Parker, C.T.; Daugherty, S.C.; et al. Major Structural Differences and Novel Potential Virulence Mechanisms from the Genomes of Multiple Campylobacter Species. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wösten, M.M.S.M.; Wagenaar, J.A.; van Putten, J.P.M. The FlgS/FlgR Two-component Signal Transduction System Regulates the fla Regulon in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 16214–16222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacKichan, J.K.; Gaynor, E.C.; Chang, C.; Cawthraw, S.; Newell, D.G.; Miller, J.F.; Falkow, S. The Campylobacter jejuni dccRS two-component system is required for optimal in vivo colonization but is dispensable for in vitro growth. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1269–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, D.; Ellermeier, J.; Pryjma, M.; DiRita, V.J.; Gaynor, E.C. Characterization of Campylobacter jejuni RacRS Reveals Roles in the Heat Shock Response, Motility, and Maintenance of Cell Length Homogeneity. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2342–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joslin, S.N.; Hendrixson, D.R. Activation of the Campylobacter jejuni FlgSR Two-Component System Is Linked to the Flagellar Export Apparatus. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2656–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wosten, M.M.S.M.; van Dijk, L.; Parker, C.T.; Guilhabert, M.R.; van der Meer-Janssen, Y.P.M.; Wagenaar, J.A.; van Putten, J.P.M. Growth Phase-Dependent Activation of the DccRS Regulon of Campylobacter jejuni. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Stel, A.-X.; van Mourik, A.; Heijmen-van Dijk, L.; Parker, C.T.; Kelly, D.J.; van de Lest, C.H.A.; van Putten, J.P.M.; Wosten, M.M.S.M. The Campylobacter jejuni RacRS system regulates fumarate utilization in a low oxygen environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Stel, A.-X.; van Mourik, A.; Laniewski, P.; van Putten, J.P.M.; Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E.K.; Wosten, M.M.S.M. The Campylobacter jejuni RacRS two-component system activates the glutamate synthesis by directly upregulating gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT). Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wösten, M.M.S.M.; Parker, C.T.; Mourik, A.V.; Guilhabert, M.R.; Dijk, L.V.; Putten, J.P.M.V. The Campylobacter jejuni PhosS/PhosR operon represents a non-classical phosphate-sensitive two-component system. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, K.N.; Powers, M.J.; Crofts, A.A.; Trent, M.S.; Hendrixson, D.R. Campylobacter jejuni BumSR directs a response to butyrate via sensor phosphatase activity to impact transcription and colonization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11715–11726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphael, B.H.; Pereira, S.; Flom, G.A.; Zhang, Q.; Ketley, J.M.; Konkel, M.E. The Campylobacter jejuni Response Regulator, CbrR, Modulates Sodium Deoxycholate Resistance and Chicken Colonization. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3662–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garénaux, A.; Guillou, S.; Ermel, G.; Wren, B.; Federighi, M.; Ritz, M. Role of the Cj1371 periplasmic protein and the Cj0355c two-component regulator in the Campylobacter jejuni NCTC 11168 response to oxidative stress caused by paraquat. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Kim, M.; Ryu, S.; Jeon, B. Regulation of Oxidative Stress Response by CosR, an Essential Response Regulator in Campylobacter jejuni. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hendrixson, D.R.; DiRita, V.J. Transcription of σ54-dependent but not σ28-dependent flagellar genes in Campylobacter jejuni is associated with formation of the flagellar secretory apparatus. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuijten, P.J.M.; Márquez-Magaña, L.; van der Zeijst, B.A.M. Analysis of flagellin gene expression in flagellar phase variants ofCampylobacter jejuni 81116. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1995, 67, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerry, P. Campylobacter flagella: Not just for motility. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Levine, M.M.; Clements, M.L.; Hughes, T.P.; Blaser, M.J. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni Infection in Humans. J. Infect. Dis. 1988, 157, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachamkin, I.; Yang, X.H.; Stern, N.J. Role of Campylobacter jejuni flagella as colonization factors for three-day-old chicks: Analysis with flagellar mutants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hendrixson, D.R.; Akerley, B.J.; DiRita, V.J. Transposon mutagenesis of Campylobacter jejuni identifies a bipartite energy taxis system required for motility. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 40, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, N.J.; Acheson, D.W.K. Identification of Motility and Autoagglutination Campylobacter jejuni Mutants by Random Transposon Mutagenesis. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.; Lara-Tejero, M.; Lefebre, M.; Goodman, A.L.; Galán, J.E. Novel Components of the Flagellar System in Epsilonproteobacteria. mBio 2014, 5, e01349-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sperandio, V.; Torres, A.G.; Kaper, J.B. Quorum sensing Escherichia coli regulators B and C (QseBC): A novel two-component regulatory system involved in the regulation of flagella and motility by quorum sensing in E. coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 43, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ren, F.; Cai, G.; Huang, P.; Chai, Q.; Gundogdu, O.; Jiao, X.; Huang, J. Investigating the Role of FlhF Identifies Novel Interactions With Genes Involved in Flagellar Synthesis in Campylobacter jejuni. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lertsethtakarn, P.; Ottemann, K.M.; Hendrixson, D.R. Motility and chemotaxis in Campylobacter and Helicobacter. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnham, P.M.; Kolar, W.P.; Hendrixson, D.R. A Polar Flagellar Transcriptional Program Mediated by Diverse Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems and Basal Flagellar Proteins Is Broadly Conserved in Polar Flagellates. mBio 2020, 11, e03107-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boll, J.M.; Hendrixson, D.R. A Regulatory Checkpoint during Flagellar Biogenesis in Campylobacter jejuni Initiates Signal Transduction To Activate Transcription of Flagellar Genes. mBio 2013, 4, e00432-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, F.; Lei, T.; Song, Z.; Yu, T.; Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Jiao, X. Could FlhF be a key element that controls Campylobacter jejuni flagella biosynthesis in the initial assembly stage? Microbiol. Res. 2018, 207, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, M.; Joslin, S.N.; Hendrixson, D.R. FlhF and Its GTPase Activity Are Required for Distinct Processes in Flagellar Gene Regulation and Biosynthesis in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 6602–6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gulbronson, C.J.; Ribardo, D.A.; Balaban, M.; Knauer, C.; Bange, G.; Hendrixson, D.R. FlhG employs diverse intrinsic domains and influences FlhF GTPase activity to numerically regulate polar flagellar biogenesis in Campylobacter jejuni. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riedel, C.; Förstner, K.U.; Püning, C.; Alter, T.; Sharma, C.M.; Gölz, G. Differences in the Transcriptomic Response of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter lari to Heat Stress. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, A.; Butcher, J.; Clarke, C.; Marlow, D.; Stintzi, A. Use of a Rabbit Soft Tissue Chamber Model to Investigate Campylobacter Jejuni–Host Interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2010, 1, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ioannidis, A.; Magiorkinis, E.; Ioannidou, V.; Perlorentzou, S.; Chatzipanagiotou, S. Campylobacter Infections: Epidemiology, Clinical Management and Prevention. Our Twenty Five-Year Experience in Greece. In Campylobacter Infections: Epidemiology, Clinical Management and Prevention; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 109–127. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Beneit, F. The Pho regulon: A huge regulatory network in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drozd, M.; Gangaiah, D.; Liu, Z.; Rajashekara, G. Contribution of TAT System Translocated PhoX to Campylobacter jejuni Phosphate Metabolism and Resilience to Environmental Stresses. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Gangaiah, D.; Torrelles, J.B.; Rajashekara, G. Polyphosphate and associated enzymes as global regulators of stress response and virulence in Campylobacter jejuni. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7402–7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Mourik, A.; Bleumink-Pluym, N.M.C.; van Dijk, L.; van Putten, J.P.M.; Wosten, M.M.S.M. Functional analysis of a Campylobacter jejuni alkaline phosphatase secreted via the Tat export machinery. Microbiol.-SGM 2008, 154, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martín, J.F. Phosphate Control of the Biosynthesis of Antibiotics and Other Secondary Metabolites Is Mediated by the PhoR-PhoP System: An Unfinished Story. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5197–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azeredo, J.; Azevedo, N.F.; Briandet, R.; Cerca, N.; Coenye, T.; Costa, A.R.; Desvaux, M.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Hébraud, M.; Jaglic, Z.; et al. Critical review on biofilm methods. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 313–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaynor, E.C.; Wells, D.H.; MacKichan, J.K.; Falkow, S. The Campylobacter jejuni stringent response controls specific stress survival and virulence-associated phenotypes. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 56, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, A.; Nasher, F.; Dorrell, N.; Wren, B.; Gundogdu, O. Revisiting Campylobacter jejuni Virulence and Fitness Factors: Role in Sensing, Adapting, and Competing. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, A.M.; Chatterjee, S.; Wren, B.W.; Newell, D.G.; Ketley, J.M. A Novel Campylobacter jejuni Two-Component Regulatory System Important for Temperature-Dependent Growth and Colonization. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3298–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barnes, I.H.A.; Bagnall, M.C.; Browning, D.D.; Thompson, S.A.; Manning, G.; Newell, D.G. γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase has a role in the persistent colonization of the avian gut by Campylobacter jejuni. Microb. Pathog. 2007, 43, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gripp, E.; Hlahla, D.; Didelot, X.; Kops, F.; Maurischat, S.; Tedin, K.; Alter, T.; Ellerbroek, L.; Schreiber, K.; Schomburg, D.; et al. Closely related Campylobacter jejuni strains from different sources reveal a generalist rather than a specialist lifestyle. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hofreuter, D.; Tsai, J.; Watson, R.O.; Novik, V.; Altman, B.; Benitez, M.; Clark, C.; Perbost, C.; Jarvie, T.; Du, L.; et al. Unique Features of a Highly Pathogenic Campylobacter jejuni Strain. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4694–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alemka, A.; Corcionivoschi, N.; Bourke, B. Defense and Adaptation: The Complex Inter-Relationship between Campylobacter jejuni and Mucus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hazeleger, W.C.; Wouters, J.A.; Rombouts, F.M.; Abee, T. Physiological Activity of Campylobacter jejuni Far below the Minimal Growth Temperature. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3917–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wouters, J.A.; Rombouts, F.M.; Kuipers, O.P.; de Vos, W.M.; Abee, T. The Role of Cold-Shock Proteins in Low-Temperature Adaptation of Food-Related Bacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 23, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guccione, E.; Leon-Kempis, M.D.R.; Pearson, B.M.; Hitchin, E.; Mulholland, F.; Diemen, P.M.V.; Stevens, M.P.; Kelly, D.J. Amino acid-dependent growth of Campylobacter jejuni: Key roles for aspartase (AspA) under microaerobic and oxygen-limited conditions and identification of AspB (Cj0762), essential for growth on glutamate. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 69, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhon, S.D.; Maurer, R.; Suyemoto, M.; Altier, C. Intestinal short-chain fatty acids alter Salmonella typhimurium invasion gene expression and virulence through BarA/SirA. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crofts, A.A.; Poly, F.M.; Ewing, C.P.; Kuroiwa, J.M.; Rimmer, J.E.; Harro, C.; Sack, D.; Talaat, K.R.; Porter, C.K.; Gutierrez, R.L.; et al. Campylobacter jejuni transcriptional and genetic adaptation during human infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, J.S. Mechanisms of bacterial resistance and response to bile. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Akiba, M.; Sahin, O.; Zhang, Q. CmeR Functions as a Transcriptional Repressor for the Multidrug Efflux Pump CmeABC in Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelliciari, S.; Pinatel, E.; Vannini, A.; Peano, C.; Puccio, S.; De Bellis, G.; Danielli, A.; Scarlato, V.; Roncarati, D. Insight into the essential role of the Helicobacter pylori HP1043 orphan response regulator: Genome-wide identification and characterization of the DNA-binding sites. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ryu, S.; Jeon, B. Transcriptional Regulation of the CmeABC Multidrug Efflux Pump and the KatA Catalase by CosR in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 6883–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fields, J.A.; Thompson, S.A. Campylobacter jejuni CsrA mediates oxidative stress responses, biofilm formation, and host cell invasion. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 3411–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duqué, B.; Rezé, S.; Rossero, A.; Membré, J.-M.; Guillou, S.; Haddad, N. Quantification of Campylobacter jejuni gene expression after successive stresses mimicking poultry slaughtering steps. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vliet, A.H.M.V.; Ketley, J.M. Pathogenesis of enteric Campylobacter infection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| TCS Name | Genes | Alias | Identity | Role | Stimulus | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FlgSR | flgS | Cj0793 | HK | Regulation of fla regulon | FlhF/Flagella export apparatus (FEA) | [23,26,35,49] |
| flgR | Cj1024 | RR | ||||
| DccRS | dccS | Cj1222c | HK | Chicken colonisation | Unknown (product of metabolism) | [24,27] |
| dccR | Cj1223c | RR | ||||
| PhosSR | phosS | Cj0889 | HK | Regulation of pho regulon | Phosphate limitation | [30] |
| phosR | Cj0890 | RR | ||||
| CprRS | cprS | Cj1226c | HK | Regulation of envelope-related genes | Environmental (unknown) | [17,20] |
| cprR | Cj1227c | RR | ||||
| RacRS | racS | Cj1262 | HK | Regulation of temperature-dependent growth and colonisation | Unknown | [25,28,58,63] |
| racR | Cj1261 | RR | ||||
| BumRS | bumS | Cjj1484 | HK | Regulation of transcription and colonisation | Exogenous butyrate | [21,31] |
| bumR | Cjj1483 | RR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gahamanyi, N.; Song, D.-G.; Mboera, L.E.G.; Matee, M.I.; Mutangana, D.; Amachawadi, R.G.; Komba, E.V.G.; Pan, C.-H. Insights into the Virulence of Campylobacter jejuni Associated with Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems and Single Regulators. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 188-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13020016
Gahamanyi N, Song D-G, Mboera LEG, Matee MI, Mutangana D, Amachawadi RG, Komba EVG, Pan C-H. Insights into the Virulence of Campylobacter jejuni Associated with Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems and Single Regulators. Microbiology Research. 2022; 13(2):188-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleGahamanyi, Noel, Dae-Geun Song, Leonard E. G. Mboera, Mecky I. Matee, Dieudonné Mutangana, Raghavendra G. Amachawadi, Erick V. G. Komba, and Cheol-Ho Pan. 2022. "Insights into the Virulence of Campylobacter jejuni Associated with Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems and Single Regulators" Microbiology Research 13, no. 2: 188-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13020016
APA StyleGahamanyi, N., Song, D. -G., Mboera, L. E. G., Matee, M. I., Mutangana, D., Amachawadi, R. G., Komba, E. V. G., & Pan, C. -H. (2022). Insights into the Virulence of Campylobacter jejuni Associated with Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems and Single Regulators. Microbiology Research, 13(2), 188-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13020016