Mutational Profile and Pathological Features of a Case of Interleukin-10 and RGS1-Positive Spindle Cell Variant Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Histological Procedures
2.2. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing
- 1st.
- Variants identified by at least three programs, mutation caller (num.caller 2 to 5).
- 2nd.
- Exonic, exonic;splicing, and splicing calls (Func.refGene).
- 3rd.
- Allele Frequency VAF >3.5% (AlleleFreq > 0.035).
- 4th.
- Nonsynonymous mutations and damaging in at least 2 of 4 softwares (SIFT, Polyphen2_HVAR, mutation assessor, and CADD_phred). In SIFT, the calls that were selected were the “D” (damaging); in Polyphen2, the “D”; in Mutation Assessor, the “H” (high functional impact) and “M” (medium), the low and neutral (nonfunctional) were discarded; and in CADD phred ≥ 20.
- 5th.
- Avsp150 all sites ≤1% (i.e., avsp150 >1% were excluded).
- 6th.
- Not synonymous (ExonicFunc.refGene) (i.e., synonymous were excluded).
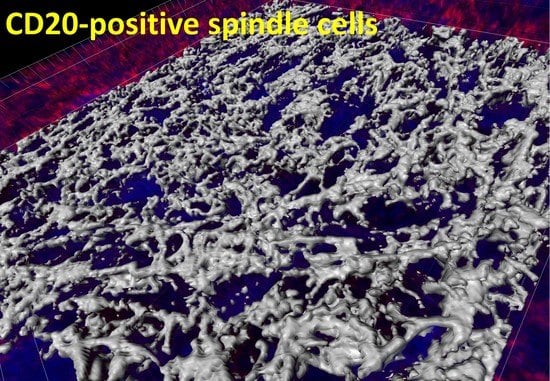
3. Case Report
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| ACTB | ARID1A | ARID1B | ARID5B | ATM | ATP10A | B2M | BCL10 | BCL2 | BCL6 |
| BCL7A | BCOR | BLNK | BRAF | BTG1 | BTG2 | BTK | CARD11 | CCL22 | CCND3 |
| CD22 | CD274 | CD276 | CD28 | CD36 | CD40 | CD40LG | CD58 | CD70 | CD79A |
| CD79B | CD80 | CD83 | CD86 | CDKN2A | CDKN2B | CIITA | CREBBP | CSF1R | CTLA4 |
| CXCR4 | CXCR5 | DDX3X | DIS3 | DTX1 | DUSP2 | EBF1 | EP300 | ETS1 | ETV6 |
| EZH2 | FAS | FBXW7 | FOXO1 | GNA13 | GNAI2 | HAVCR2 | HIST1H1B | HIST1H1C | HIST1H1D |
| HIST1H1E | HIST1H3G | HLA-A | HLA-B | HLA-C | HVCN1 | ICOS | ICOSLG | ID3 | IDO1 |
| IKZF1 | IL10 | IRF2BP2 | IRF4 | IRF8 | ITPKB | JUNB | KLHL14 | KLHL6 | KMT2D |
| KRAS | LAG3 | LGALS9 | LPHN2 | LYN | MALT1 | MAML1 | MAP2K1 | MAPK1 | MCL1 |
| MEF2B | MFHAS1 | MYC | MYD88 | NFKB1 | NFKB2 | NFKBIA | NFKBIE | NFKBIZ | NOTCH1 |
| NOTCH2 | NRAS | OSBPL10 | P2RY8 | PARP2 | PAX5 | PCBP1 | PDCD1 | PDCD1LG2 | PIK3CA |
| PIK3CD | PIK3R1 | PIM1 | PLCG2 | PLOD2 | POU2AF1 | POU2F2 | PRDM1 | PRKCB | PTEN |
| PTPN6 | PTPRD | REL | RELA | RGS1 | RHOA | RRAGC | S1PR1 | S1PR2 | SETD1B |
| SETD2 | SF3B1 | SGK1 | SMARCA4 | SOCS1 | SPEN | SPIB | STAT3 | STAT6 | SYK |
| TBL1XR1 | TCF3 | TET2 | TGFB1 | TMEM30A | TMSB4X | TNFAIP3 | TNFRSF14 | TNFRSF18 | TNFRSF4 |
| TNFRSF9 | TNFSF18 | TNFSF4 | TNFSF9 | TNIP1 | TOX | TP53 | TP53BP1 | TP63 | TREML2 |
| TYRO3 | UBE2A | VSIR | VTCN1 | XBP1 | XPO1 | ZEB2 | ZFP36L1 |


References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Wang, S.A.; Bagg, A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; et al. International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias: Integrating morphologic, clinical, and genomic data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S.; Cook, J.R.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Anderson, K.C.; Brousset, P.; Cerroni, L.; de Leval, L.; Dirnhofer, S.; et al. The International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms: A Report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood 2022, 140, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Leval, L.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Campo, E.; Davies, A.; Dogan, A.; Fitzgibbon, J.; Horwitz, S.M.; Melnick, A.M.; Morice, W.G.; et al. Genomic profiling for clinical decision making in lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2022, 140, 2193–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leval, L.; Jaffe, E.S. Lymphoma Classification. Cancer J. 2020, 26, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, L.M.; Wang, S.S.; Devesa, S.S.; Hartge, P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Linet, M.S. Lymphoma incidence patterns by WHO subtype in the United States, 1992–2001. Blood 2006, 107, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moller, M.B.; Pedersen, N.T.; Christensen, B.E. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Clinical implications of extranodal versus nodal presentation--a population-based study of 1575 cases. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 124, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pileri, S.A.; Tripodo, C.; Melle, F.; Motta, G.; Tabanelli, V.; Fiori, S.; Vegliante, M.C.; Mazzara, S.; Ciavarella, S.; Derenzini, E. Predictive and Prognostic Molecular Factors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. Cells 2021, 10, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, A.S.; Aster, J.C. Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, Pathologic Features, and Diagnosis of Diffuse Large B cell Lymphoma; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- De Paepe, P.; Achten, R.; Verhoef, G.; Wlodarska, I.; Stul, M.; Vanhentenrijk, V.; Praet, M.; De Wolf-Peeters, C. Large cleaved and immunoblastic lymphoma may represent two distinct clinicopathologic entities within the group of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7060–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Miyaoka, M.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Hiraiwa, S.; Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Kawada, H.; Nakamura, N. The multilobated morphology is still a better prognosis factor of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the R-CHOP era. Pathol. Int. 2022, 72, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Arakawa, F.; Kiyasu, J.; Miyoshi, H.; Yoshida, M.; Ichikawa, A.; Nakashima, S.; Ishibashi, Y.; Niino, D.; Sugita, Y.; et al. A spindle cell variant of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is characterized by T-cell/myofibrohistio-rich stromal alterations: Analysis of 10 cases and a review of the literature. Eur. J. Haematol. 2012, 89, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, S.; Bozdag, Z.; Karadag, N.; Akbulut, S. Spindle Variant Primary Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma of the Colon: Case Report and Literature Review. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2022. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wobser, M.; Schummer, P.; Appenzeller, S.; Kneitz, H.; Roth, S.; Goebeler, M.; Geissinger, E.; Rosenwald, A.; Maurus, K. Panel Sequencing of Primary Cutaneous B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhirev, A.G.; Vasef, M.A.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Reichard, K.K.; Czuchlewski, D.R. Fluorescence immunophenotyping and interphase cytogenetics (FICTION) detects BCL6 abnormalities, including gene amplification, in most cases of nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Ramirez, A.; Cigudosa, J.C.; Maestre, L.; Rodriguez-Perales, S.; Haralambieva, E.; Benitez, J.; Roncador, G. Simultaneous detection of the immunophenotypic markers and genetic aberrations on routinely processed paraffin sections of lymphoma samples by means of the FICTION technique. Leukemia 2004, 18, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyaoka, M.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Carreras, J.; Ito, A.; Ikoma, H.; Tomita, S.; Kawada, H.; Roncador, G.; Bea, S.; Campo, E.; et al. Copy Number Alteration and Mutational Profile of High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 Rearrangements, Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Rearrangement, and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Cluster Amplification. Cancers 2022, 14, 5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, J.; Roncador, G.; Hamoudi, R. Artificial Intelligence Predicted Overall Survival and Classified Mature B-Cell Neoplasms Based on Immuno-Oncology and Immune Checkpoint Panels. Cancers 2022, 14, 5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, J.; Hiraiwa, S.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Miyaoka, M.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Ito, A.; Kondo, Y.; Roncador, G.; Garcia, J.F.; et al. Artificial Neural Networks Predicted the Overall Survival and Molecular Subtypes of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Using a Pancancer Immune-Oncology Panel. Cancers 2021, 13, 6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, J.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Itoh, J.; Masashi, M.; Ikoma, H.; Tomita, S.; Hiraiwa, S.; Hamoudi, R.; Rosenwald, A.; et al. High TNFRSF14 and low BTLA are associated with poor prognosis in Follicular Lymphoma and in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma transformation. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2019, 59, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langerak, A.W.; Groenen, P.J.; Bruggemann, M.; Beldjord, K.; Bellan, C.; Bonello, L.; Boone, E.; Carter, G.I.; Catherwood, M.; Davi, F.; et al. EuroClonality/BIOMED-2 guidelines for interpretation and reporting of Ig/TCR clonality testing in suspected lymphoproliferations. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2159–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karube, K.; Enjuanes, A.; Dlouhy, I.; Jares, P.; Martin-Garcia, D.; Nadeu, F.; Ordonez, G.R.; Rovira, J.; Clot, G.; Royo, C.; et al. Integrating genomic alterations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies new relevant pathways and potential therapeutic targets. Leukemia 2018, 32, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, J.A.; Bonneau, P.; Prieto, V.; Sangueza, M.; Mackinnon, A.; Suster, D.; Bacchi, C.; Estrozi, B.; Kazakov, D.; Kacerovska, D.; et al. Desmoplastic melanoma: An updated immunohistochemical analysis of 40 cases with a proposal for an additional panel of stains for diagnosis. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2016, 43, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissinger, S.E.; Keil, P.; Silvers, D.N.; Klaus, B.M.; Moller, P.; Horst, B.A.; Lennerz, J.K. A diagnostic algorithm to distinguish desmoplastic from spindle cell melanoma. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mantese, G. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor: Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 35, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Sobin, L.H.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M. Immunohistochemical spectrum of GISTs at different sites and their differential diagnosis with a reference to CD117 (KIT). Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miettinen, M.; Wang, Z.F.; Lasota, J. DOG1 antibody in the differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A study of 1840 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009, 33, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, B.P.; Heinrich, M.C. Genotyping and immunohistochemistry of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: An update. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 32, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surbhi; Metgud, R.; Naik, S.; Patel, S. Spindle cell lesions: A review on immunohistochemical markers. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2017, 13, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, W.; Woodroof, J.M.; Zhang, D. Extranodal B Cell Lymphoma with Prominent Spindle Cell Features Arising in Uterus and in Maxillary Sinus: Report of Two Cases and Literature Review. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 46, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, N.C.; Nozawa, Y.; Arber, D.A.; Chu, P.; Chang, K.L.; Weiss, L.M. Histological and immunohistochemical characterization of extranodal diffuse large-cell lymphomas with prominent spindle cell features. Histopathology 2001, 39, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Bea, S.; Miyaoka, M.; Hiraiwa, S.; Ikoma, H.; Nagao, R.; Tomita, S.; Martin-Garcia, D.; Salaverria, I.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and genomic profile of primary sinonasal tract diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) reveals gain at 1q31 and RGS1 encoding protein; high RGS1 immunohistochemical expression associates with poor overall survival in DLBCL not otherwise specified (NOS). Histopathology 2017, 70, 595–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Hiraiwa, S.; Miyaoka, M.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Ito, A.; Kondo, Y.; Itoh, J.; Roncador, G.; et al. High PTX3 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, J.; Nakamura, N.; Hamoudi, R. Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Gene Expression Predicted the Overall Survival of Mantle Cell Lymphoma and a Large Pan-Cancer Series. Healthcare 2022, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Marker | Leiomyosarcoma | Angiosarcoma | Fibrous Histiocytoma | Spindle Cell Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Desmoplastic Melanoma | Spindle Cell Variant DLBCL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMA | + | +/− | − | |||
| Desmin | + | +/− | − | |||
| CD34 | + | − | ||||
| S100 | − | |||||
| Endothelial (CD31) | + | − | ||||
| Melanocytic(HMB-45, Melan–A) | +/− | − | ||||
| Epithelial(CK AE1/AE3, EMA) | +/− | +/− | + | +/− | − | |
| Macrophage markers (CD68) | + | − | − | − | ||
| B-cell marker (CD20) | − | − | − | − | − | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Miyaoka, M.; Hiraiwa, S.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Kondo, Y.; Ito, A.; Nagase, S.; Miura, H.; et al. Mutational Profile and Pathological Features of a Case of Interleukin-10 and RGS1-Positive Spindle Cell Variant Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Hematol. Rep. 2023, 15, 188-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep15010020
Carreras J, Kikuti YY, Miyaoka M, Hiraiwa S, Tomita S, Ikoma H, Kondo Y, Ito A, Nagase S, Miura H, et al. Mutational Profile and Pathological Features of a Case of Interleukin-10 and RGS1-Positive Spindle Cell Variant Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Hematology Reports. 2023; 15(1):188-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep15010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarreras, Joaquim, Yara Yukie Kikuti, Masashi Miyaoka, Shinichiro Hiraiwa, Sakura Tomita, Haruka Ikoma, Yusuke Kondo, Atsushi Ito, Shunsuke Nagase, Hisanobu Miura, and et al. 2023. "Mutational Profile and Pathological Features of a Case of Interleukin-10 and RGS1-Positive Spindle Cell Variant Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma" Hematology Reports 15, no. 1: 188-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep15010020
APA StyleCarreras, J., Kikuti, Y. Y., Miyaoka, M., Hiraiwa, S., Tomita, S., Ikoma, H., Kondo, Y., Ito, A., Nagase, S., Miura, H., Roncador, G., Colomo, L., Hamoudi, R., Campo, E., & Nakamura, N. (2023). Mutational Profile and Pathological Features of a Case of Interleukin-10 and RGS1-Positive Spindle Cell Variant Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Hematology Reports, 15(1), 188-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep15010020