Assessing Carbon Footprint and Inter-Regional Carbon Transfer in China Based on a Multi-Regional Input-Output Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MRIO Model
2.2. Inter-Regional Carbon Transfer Accounting
2.3. Data Sources and Processing
3. Results
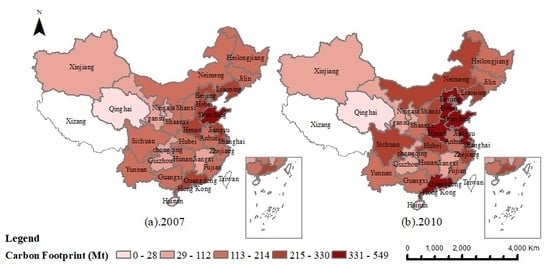
3.1. Provincial Carbon Footprints and Changes
3.2. Direct Carbon Emissions and Embodied Carbon Emissions
3.3. Embodied Carbon Composition in Inter-Provincial Trade
3.4. Inter-Regional Carbon Transfer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, Z.; Huang, R.; Tang, Q.; Cong, X.; Wang, Z. China’s provincial CO2 emissions embodied in trade with implications for regional climate policy. Front. Earth. Sci-PRC. 2015, 9, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Winchester, N.; Karplus, V.J.; Zhang, X. Will economic restructuring in China reduce trade-embodied CO2 emissions? Energy Econ. 2014, 42, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Liang, H. Spatial analysis on China’s regional air pollutants and CO2 emissions: Emission pattern and regional disparity. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, D.; Shan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cong, R.; Yuan, X.C.; Wei, Y.M. Consumption-based emission accounting for Chinese cities. Appl. Energ. 2016, 184, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Guan, D.; Wei, W.; Davis, S.J.; Ciais, P.; Bai, J.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Hubacek, K.; Marland, G. Reduced carbon emission estimates from fossil fuel combustion and cement production in China. Nature 2015, 524, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Qiao, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, B. Growth in embodied energy transfers via China’s domestic trade: Evidence from multi-regional input-output analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, T.; Lenzen, M. Environmental and social footprints of international trade. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Chen, B.; Feng, K.; Liu, Z.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Ahmad, B. Interregional carbon flows of China. Appl. Energ. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.A.; Coello, J.; Kemp, S.; Williams, I. Carbon footprinting for climate change management in cities. Carbon. Manag. 2011, 2, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, T.; Minx, J. A definition of “carbon footprint”. In Ecological Economics Research Trends; Pertsova, C.C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kitzes, J. An introduction to environmentally-extended input-output analysis. Resources. 2013, 2, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schandl, H.; Hatfield-Dodds, S.; Wiedmann, T.; Geschke, A.; Cai, Y.; West, J.; Newth, D.; Baynes, T.; Lenzen, M.; Owen, A. Decoupling global environmental pressure and economic growth: Scenarios for energy use, materials use and carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 132, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukker, A.; Poliakov, E.; Heijungs, R.; Hawkins, T.; Neuwahl, F.; Rueda-Cantuche, J.M.; Giljum, S.; Moll, S.; Oosterhaven, J.; Bouwmeester, M. Towards a global multi-regional environmentally extended input-output database. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.E.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, L. China’s provincial CO2 emissions embodied in international and interprovincial trade. Energ. Policy. 2012, 42, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liang, S.; Xu, M.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Nielsen, C.P.; Bi, J. Temporal and spatial variations in consumption-based carbon dioxide emissions in China. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2014, 40, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemoto, K.; Moran, D.; Hertwich, E.G. Mapping the Carbon Footprint of Nations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10512–10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leontief, W.W. Quantitative Input and Output Relations in the Economic Systems of the United States. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1936, 18, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, R.; Kagawa, S.; Tsukui, M. Carbon footprint analysis through constructing a multi-region input-output table: A case study of Japan. J. Econ. Struct. 2015, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.J.; Caldeira, K. Consumption-based accounting of CO2 emissions. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2010, 107, 5687–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, T. A first empirical comparison of energy Footprints embodied in trade-MRIO versus PLUM. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1975–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Junguo, L.; Qingying, L.; R, T.M.; Dabo, G.; Klaus, H. Physical and virtual water transfers for regional water stress alleviation in China. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 112, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Shi, M. Analyses of water footprint of Beijing in an interregional input–output framework. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 2494–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Dunford, M.; Chen, G.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Global water transfers embodied in Mainland China’s foreign trade: Production- and consumption-based perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.; Griffin, W.M.; Matthews, H.S.; Weber, C.L. Inventory development and input-output model of U.S. land use: Relating land in production to consumption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4937–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinzettel, J.; Hertwich, E.G.; Peters, G.P.; Steen-Olsen, K.; Galli, A. Affluence drives the global displacement of land use. Global. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, M.; Moran, D.; Kanemoto, K.; Foran, B.; Lobefaro, L.; Geschke, A. International trade drives biodiversity threats in developing nations. Nature 2012, 486, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, M. Tele-connecting China’s future urban growth to impacts on ecosystem services under the shared socioeconomic pathways. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 652, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Tang, Z.; Liu, H.; Han, D.; Li, F. China’s 30 Provincial Multi-regional Input-Output Table Theory and Practice in 2007; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Tang, Z.; Chen, J. China’s 30 Provincial Multi-regional Input-output Table Theory and Practice in 2010. China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- IPCC. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/support/Primer_2006GLs.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2018).
- Wang, P.; Dai, H.C.; Ren, S.Y.; Zhao, D.Q.; Masui, T. Achieving Copenhagen target through carbon emission trading: Economic impacts assessment in Guangdong Province of China. Energy 2015, 79, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen-Olsen, K.; Weinzettel, J.; Cranston, G.; Ercin, A.E.; Hertwich, E.G. Carbon, land, and water footprint accounts for the European Union: Consumption, production, and displacements through international trade. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10883–10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Chang, M.; Lin, C.; Tanikawa, H. China’s carbon footprint: A regional perspective on the effect of transitions in consumption and production patterns. Appl. Energ. 2014, 123, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, B. Greenhouse gas emissions in China 2007: Inventory and input–output analysis. Energ. Policy. 2010, 38, 6180–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| 2007 | 2010 | Change in Rank | Growth (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province | CF (Mt) | Rank | CF (Mt) | Rank | ||
| Total | 4578.27 | - | 6251.67 | - | - | 36.57 |
| Shandong | 413.35 | 1 | 548.85 | 1 | - | 32.78 |
| Henan | 315.70 | 2 | 415.53 | 3 | 1 | 31.62 |
| Jiangsu | 309.56 | 3 | 426.70 | 2 | −1 | 37.84 |
| Guangdong | 292.54 | 4 | 387.69 | 4 | - | 32.53 |
| Hebei | 272.66 | 5 | 375.21 | 5 | - | 37.61 |
| Liaoning | 215.84 | 6 | 329.97 | 6 | - | 52.88 |
| Zhejiang | 210.13 | 7 | 283.08 | 7 | - | 34.72 |
| Shanxi | 179.93 | 8 | 228.26 | 11 | 3 | 26.86 |
| Hubei | 170.85 | 9 | 249.73 | 8 | −1 | 46.16 |
| Inner Mongolia | 169.05 | 10 | 248.76 | 9 | −1 | 47.15 |
| Shanghai | 165.81 | 11 | 214.02 | 12 | 1 | 29.08 |
| Hunan | 164.12 | 12 | 208.47 | 13 | 1 | 27.03 |
| Sichuan | 147.40 | 13 | 229.80 | 10 | −3 | 55.90 |
| Jilin | 137.32 | 14 | 184.04 | 14 | - | 34.02 |
| Beijing | 131.34 | 15 | 172.50 | 15 | - | 31.34 |
| Anhui | 124.79 | 16 | 162.89 | 18 | 2 | 30.53 |
| Shaanxi | 121.66 | 17 | 170.21 | 16 | −1 | 39.90 |
| Heilongjiang | 121.45 | 18 | 154.99 | 21 | 3 | 27.62 |
| Guangxi | 119.29 | 19 | 164.75 | 17 | −2 | 38.11 |
| Yunnan | 115.89 | 20 | 155.49 | 20 | - | 34.16 |
| Tianjin | 114.11 | 21 | 159.71 | 19 | −2 | 39.96 |
| Fujian | 112.10 | 22 | 153.92 | 22 | - | 37.30 |
| Xinjiang | 79.18 | 23 | 108.41 | 24 | 1 | 36.92 |
| Guizhou | 77.55 | 24 | 99.95 | 26 | 2 | 28.89 |
| Jiangxi | 74.32 | 25 | 100.72 | 25 | - | 35.53 |
| Chongqing | 74.11 | 26 | 112.42 | 23 | −3 | 51.69 |
| Gansu | 67.96 | 27 | 93.58 | 27 | - | 37.70 |
| Ningxia | 43.74 | 28 | 61.62 | 28 | - | 40.88 |
| Qinghai | 20.59 | 29 | 28.11 | 29 | - | 36.55 |
| Hainan | 15.95 | 30 | 22.28 | 30 | - | 39.71 |
| 2007 | 2010 | |||||
| Provinces | PGDP | PCF | Urban Rate | PGDP | PCF | Urban Rate |
| (104 CNY) | (t) | (%) | (104 CNY) | (t) | (%) | |
| Shanghai | 6.05 | 8.03 | 0.89 | 7.45 | 9.29 | 0.89 |
| Beijing | 5.88 | 7.84 | 0.84 | 7.19 | 8.79 | 0.86 |
| Tianjin | 4.71 | 10.23 | 0.76 | 7.10 | 12.29 | 0.80 |
| Zhejiang | 3.64 | 4.08 | 0.57 | 5.09 | 5.20 | 0.62 |
| Jiangsu | 3.37 | 4.01 | 0.53 | 5.26 | 5.42 | 0.61 |
| Guangdong | 3.29 | 3.03 | 0.63 | 4.41 | 3.71 | 0.66 |
| Shandong | 2.75 | 4.41 | 0.47 | 4.09 | 5.72 | 0.50 |
| Inner Mongolia | 2.64 | 6.96 | 0.50 | 4.72 | 10.06 | 0.56 |
| Liaoning | 2.60 | 5.02 | 0.59 | 4.22 | 7.54 | 0.62 |
| Fujian | 2.56 | 3.10 | 0.51 | 3.99 | 4.17 | 0.57 |
| Hebei | 1.96 | 3.93 | 0.40 | 2.83 | 5.22 | 0.44 |
| Jilin | 1.94 | 5.03 | 0.53 | 3.16 | 6.70 | 0.53 |
| Heilongjiang | 1.86 | 3.18 | 0.54 | 2.71 | 4.04 | 0.56 |
| Shanxi | 1.78 | 5.30 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 6.39 | 0.48 |
| Xinjiang | 1.68 | 3.78 | 0.39 | 2.49 | 4.96 | 0.43 |
| Chongqing | 1.66 | 2.63 | 0.48 | 2.75 | 3.90 | 0.53 |
| Hubei | 1.64 | 3.00 | 0.44 | 2.79 | 4.36 | 0.50 |
| Henan | 1.60 | 3.37 | 0.34 | 2.46 | 4.42 | 0.39 |
| Shaanxi | 1.55 | 3.28 | 0.41 | 2.71 | 4.56 | 0.46 |
| Ningxia | 1.51 | 7.17 | 0.44 | 2.67 | 9.74 | 0.48 |
| Hunan | 1.49 | 2.58 | 0.40 | 2.44 | 3.17 | 0.43 |
| Hainan | 1.48 | 1.89 | 0.47 | 2.38 | 2.56 | 0.50 |
| Qinghai | 1.44 | 3.73 | 0.40 | 2.40 | 4.99 | 0.45 |
| Jiangxi | 1.33 | 1.70 | 0.40 | 2.12 | 2.26 | 0.44 |
| Sichuan | 1.30 | 1.81 | 0.36 | 2.14 | 2.86 | 0.40 |
| Guangxi | 1.22 | 2.50 | 0.36 | 2.08 | 3.57 | 0.40 |
| Anhui | 1.20 | 2.04 | 0.39 | 2.07 | 2.73 | 0.43 |
| Gansu | 1.06 | 2.67 | 0.32 | 1.61 | 3.66 | 0.36 |
| Yunnan | 1.06 | 2.57 | 0.32 | 1.57 | 3.38 | 0.35 |
| Guizhou | 0.79 | 2.14 | 0.28 | 1.32 | 2.87 | 0.34 |
| 2007 | 2010 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-value | p-value | |||
| Spearman’s rank coefficient | 0.7735 | - | 0.7651 | - |
| Intercept | 1.41** | 0.01 | 1.52** | 0.04 |
| PGDP | 1.17*** | 0.00 | 1.12*** | 0.00 |
| Provinces | DCEG (%) | ECEG (%) | Provinces | DCEG (%) | ECEG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sichuan | 66.31 | 33.08 | Xinjiang | 37.75 | 35.86 |
| Chongqing | 65.97 | 35.97 | Jiangxi | 36.93 | 33.11 |
| Liaoning | 63.96 | 33.41 | Zhejiang | 35.41 | 34.14 |
| Inner Mongolia | 57.99 | 35.46 | Yunnan | 33.64 | 34.77 |
| Tianjin | 55.94 | 34.88 | Shandong | 32.44 | 34.06 |
| Hubei | 49.72 | 32.95 | Guangdong | 30.58 | 34.13 |
| Shaanxi | 49.11 | 35.39 | Henan | 29.41 | 34.91 |
| Guangxi | 43.71 | 32.51 | Jilin | 26.57 | 39.15 |
| Ningxia | 43.31 | 36.54 | Anhui | 25.94 | 35.08 |
| Jiangsu | 42.22 | 33.28 | Guizhou | 24.46 | 36.83 |
| Hainan | 42.14 | 34.01 | Hunan | 23.61 | 34.59 |
| Hebei | 40.85 | 33.39 | Beijing | 23.06 | 36.24 |
| Fujian | 40.55 | 33.2 | Shanxi | 22.07 | 36.56 |
| Qinghai | 39.08 | 34.35 | Shanghai | 18.23 | 34.28 |
| Gansu | 37.78 | 37.56 | Heilongjiang | 11.59 | 41.51 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Assessing Carbon Footprint and Inter-Regional Carbon Transfer in China Based on a Multi-Regional Input-Output Model. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4626. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124626
Huang M, Chen Y, Zhang Y. Assessing Carbon Footprint and Inter-Regional Carbon Transfer in China Based on a Multi-Regional Input-Output Model. Sustainability. 2018; 10(12):4626. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124626
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Min, Yimin Chen, and Yuanying Zhang. 2018. "Assessing Carbon Footprint and Inter-Regional Carbon Transfer in China Based on a Multi-Regional Input-Output Model" Sustainability 10, no. 12: 4626. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124626
APA StyleHuang, M., Chen, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Assessing Carbon Footprint and Inter-Regional Carbon Transfer in China Based on a Multi-Regional Input-Output Model. Sustainability, 10(12), 4626. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124626