Innovative Recycling of Lime Slaker Grits from Paper-Pulp Industry Reused as Aggregate in Ambient Cured Biomass Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers for Sustainable Construction Material
Abstract
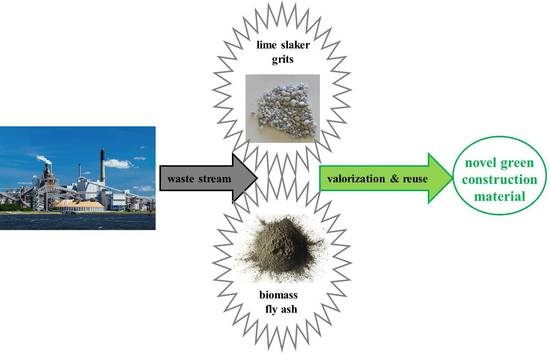
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Processing Details
2.3. Characterisation of the Materials
2.4. Tested Formulations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Waste Characterisation
3.2. Mortar Characterisation
3.2.1. Physical Properties
3.2.2. Mechanical Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32008L0098 (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Kumar, S.A. Entrepreneurship Development; New Age Int.: New Delhi, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Martin Hirschnitz-Garbers, A.R.T.; Gradmann, A.; Srebotnjak, T. Key drivers for unsustainable resource use–categories, effects and policy pointers. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 132, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C. Sustainable Construction Methods and Processes. In Encyclopedia of Sustainable Technologies, Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Abraham, M.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Kylili, A.; Fokaides, P.A. Policy trends for the sustainability assessment of construction materials: A review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 35, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K. Sustainable cements and concrete for the climate change era—A review. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies, Ancona, Italy, 28–30 June 2010; Zachar, J., Claisse, P., Naik, T.R., Ganjian, E., Eds.; Università Politecnica Delle Marche: Ancona, Italy, 2010; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, M.; Romer, M.; Tschudin, M.; Bolio, H. Sustainable cement production–present and future. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, H.G. Background Facts and Issues Concerning Cement and Cement Data. U.S. Department of the Interior and U.S Geological Survey, 2005. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2005/1152/2005-1152.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Singh, B.; Ishwarya, G.; Gupta, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.K. Geopolymer concrete: A review of some recent developments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 85, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, Y.J.; Shah, N. Development of self-compacting geopolymer concrete as a sustainable construction material. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2018, 28, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Arif, M.; Shariq, M. Use of geopolymer concrete for a cleaner and sustainable environment-A review of mechanical properties and microstructure. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 704–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.K. Structural and material performance of geopolymer concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connie, N.G.; Johnson Alengaram, U.; Wong, L.S.; Mo, K.H.; Ramesh, S. A review on microstructural study and compressive strength of geopolymer mortar, paste and concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 550–576. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J. A review on properties of fresh and hardened geopolymer mortars. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 152, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Abdollahnejad, Z.; Camões, A.F.; Jamshidi, M.; Ding, Y. Durability of alkali-activated binders: A clear advantage over Portland cement or an unproven issue? Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.; Collins, F.G. Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2-e) emissions: A comparison between geopolymer and OPC cement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandanayake, M.; Gunasekara, C.; Law, D.; Zhang, G.; Setunge, S. Greenhouse gas emissions of different fly ash based geopolymer concretes in building construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Synthesis of New High Temperature Geo-Polymers for Reinforced Plastics/Composites; Society of Plastic Engineers, Brookfield Center: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 79, pp. 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymer Chemistry and Applications; Institut Géopolymère: Saint-Quentin, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Duxson, P.; Fernandez-Jimenez, A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Palomo, A.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymer technology: The current state of the art. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2917–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komnitsas, K.; Zaharaki, D. Geopolymerisation: A review and prospects for the minerals industry. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, T.M.; Leopold, B.; Malcolm, E.W. Alkaline Pulping. In Pulp and Paper Manufacture; Kocurek, M.J., Stevens, F., Eds.; Joint Textbook Committee of the Paper Industry of the United States and Canada: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1991; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Sixta, H. Handbook of Pulp; Wiley-VHC: Weinheim, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ek, M.; Gellerstedt, G.; Henriksson, G. Pulping Chemistry and Technology; de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Council Directive 1999/31/EC of 26 April 1999 on the Landfill of Waste. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A31999L0031 (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Naik, T.R. Tests of Wood Ash as a Potential Source for Construction Materials; Report, No. CBU-1999-09; UWM Center for by-Products Utilization, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Baxter, L. Comprehensive study of biomass fly ash in concrete: Strength, microscopy, kinetics and durability. Fuel Process Technol. 2007, 88, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamma, R.; Ball, R.J.; Tarelho, L.A.; Allen, G.C.; Labrincha, J.A.; Ferreira, V.M. Characterisation and use of biomass fly ash in cement-based materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardjito, D.; Wallah, S.E.; Sumajouw, D.M.J.; Rangan, B.V. On the development of fly ash based geopolymer concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2004, 101, 467–472. [Google Scholar]
- Rajamma, R.; Labrincha, J.A.; Ferreira, V.M. Alkali activation of biomass fly ash–metakaolin blends. Fuel 2012, 98, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yliniemi, J.; Paiva, H.; Ferreira, V.M.; Tiainen, O.Y.; Illikainen, M. Development and incorporation of lightweight waste-based geopolymer aggregates in mortar and concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.; Tan, M.J. Experimental study on mix proportion and fresh properties of fly ash based geopolymer for 3D concrete printing. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 10258–10265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.; Paul, S.C.; Hui, L.J.; Tay, Y.W.D.; Tan, M.J. Additive manufacturing of geopolymer for sustainable built environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Ascensão, G.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Biomass fly ash geopolymer monoliths for effective methylene blue removal from wastewaters. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Carvalheiras, J.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Pullar, R.C.; Labrincha, J.A. Synthesis of porous biomass fly ash-based geopolymer spheres for efficient removal of methylene blue from wastewaters. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhmayies, S.; Li, B.; Carpenter, J.S.; Li, J.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Monteiro, S.N.; Firrao, D.; Zhang, M.; Peng, Z.; Escobedo-Diaz, J.P.; et al. Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, F.B.; Holanda, J.N.F. Reuse of grits waste for the production of soil-cement bricks. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, F.B.; Holanda, J.N.F. Efeito da incorporação de resíduo grits sobre o comportamento de densificação de tijolo solo-cimento. Cerâmica 2015, 61, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeli, M.; Novais, R.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Mix design and mechanical performance of geopolymer binder for sustainable construction and building material. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 264, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeli, M.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Mix design and mechanical performance of geopolymeric binders and mortars using biomass fly ash and alkaline effluent from paper-pulp industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeli, M.; Novais, R.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Green geopolymeric concrete using grits for applications in construction. Mater. Lett. 2018, 233, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudley, R.; Greeno, R. Building Construction Handbook; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sleiman, H.; Perrot, A.; Amziane, S. A new look at the measurement of cementitious paste setting by Vicat test. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Mortar Family | Specimen N. | B/A Ratio | Aggregate Nature | L/S Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | 1 | 1:1 | sand | 0.391 |
| 2 | 1:2 | 0.261 | ||
| 3 | 1:3 | 0.196 | ||
| 4 | 1:4 | 0.156 | ||
| 5 | 1:5 | 0.130 | ||
| (II) | 6 | 1:1 | sand + grits | 0.391 |
| 7 | 1:2 | 0.261 | ||
| 8 | 1:3 | 0.196 | ||
| 9 | 1:4 | 0.156 | ||
| 10 | 1:5 | 0.130 | ||
| (III) | 11 | 1:1 | grits | 0.391 |
| 12 | 1:2 | 0.261 | ||
| 13 | 1:3 | 0.196 | ||
| 14 | 1:4 | 0.156 | ||
| 15 | 1:5 | 0.130 |
| Oxides [wt.%] | BFA | Grits |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 38.5 | 0.47 |
| CaO | 16.7 | 49.45 |
| Al2O3 | 14.8 | 0.29 |
| K2O | 5.97 | 0.27 |
| Fe2O3 | 5.94 | 0.05 |
| MgO | 3.44 | 0.45 |
| SO3 | 2.66 | 1.86 |
| Na2O | 1.53 | 5.52 |
| P2O5 | 1.12 | 0.38 |
| TiO2 | 0.76 | - |
| MnO | 0.50 | - |
| LOI | 6.39 | 41.1 * |
| Mortar Family | Aggregate Nature | Setting Time [min] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | ||
| (I) | sand | 140 | 195 |
| (II) | sand + grits | 145 | 205 |
| (III) | grits | 155 | 215 |
| Mortar Family | Specimen N. | B/A Ratio | Aggregate Nature | UCS [MPa] | Class of Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | 1 | 1:1 | sand | 17.81 ± 0.91 | M15 |
| 2 | 1:2 | 18.03 ± 0.71 | M15 | ||
| 3 | 1:3 | 22.01 ± 0.03 | M20 | ||
| 4 | 1:4 | 16.88 ± 0.95 | M15 | ||
| 5 | 1:5 | 14.14 ± 0.93 | M10 | ||
| (II) | 6 | 1:1 | sand + grits | 20.09 ± 0.46 | M20 |
| 7 | 1:2 | 19.62 ± 1.28 | M15 | ||
| 8 | 1:3 | 22.86 ± 0.72 | M20 | ||
| 9 | 1:4 | 20.85 ± 1.04 | M20 | ||
| 10 | 1:5 | 23.17 ± 1.17 | M20 | ||
| (III) | 11 | 1:1 | grits | 14.71 ± 1.09 | M10 |
| 12 | 1:2 | 14.29 ± 1.72 | M10 | ||
| 13 | 1:3 | 16.05 ± 1.13 | M15 | ||
| 14 | 1:4 | 16.24 ± 0.24 | M15 | ||
| 15 | 1:5 | 18.89 ± 1.26 | M15 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saeli, M.; Senff, L.; Tobaldi, D.M.; La Scalia, G.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Innovative Recycling of Lime Slaker Grits from Paper-Pulp Industry Reused as Aggregate in Ambient Cured Biomass Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers for Sustainable Construction Material. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123481
Saeli M, Senff L, Tobaldi DM, La Scalia G, Seabra MP, Labrincha JA. Innovative Recycling of Lime Slaker Grits from Paper-Pulp Industry Reused as Aggregate in Ambient Cured Biomass Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers for Sustainable Construction Material. Sustainability. 2019; 11(12):3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123481
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaeli, Manfredi, Luciano Senff, David Maria Tobaldi, Giada La Scalia, Maria Paula Seabra, and João Antonio Labrincha. 2019. "Innovative Recycling of Lime Slaker Grits from Paper-Pulp Industry Reused as Aggregate in Ambient Cured Biomass Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers for Sustainable Construction Material" Sustainability 11, no. 12: 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123481
APA StyleSaeli, M., Senff, L., Tobaldi, D. M., La Scalia, G., Seabra, M. P., & Labrincha, J. A. (2019). Innovative Recycling of Lime Slaker Grits from Paper-Pulp Industry Reused as Aggregate in Ambient Cured Biomass Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers for Sustainable Construction Material. Sustainability, 11(12), 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123481