Predicting Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions of Excavators in Earthwork Operations: An Artificial Neural Network Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
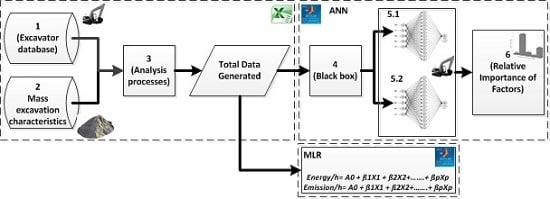
2. Methodology of the Proposed Model for Forecasting the Energy Use and CO2 Emissions
2.1. Extraction of A Database Based on the Excavator Manufacturer’s Handbook
2.2. Collecting Mass Excavation Characteristics of Different Types of Earth
2.3. Generating the Excavator Database Using Different Characteristics of Mass Excavation to Produce the Input Data for the ANN Model
2.4. Designing the Predictive ANN Model with Forwards/Backwards Propagation Learning Algorithms
2.4.1. Matrix Expressions and Final Formula for Energy Prediction from the Proposed ANN Model
2.4.2. Matrix Expressions and Final Formula for CO2 Emission Prediction from the Proposed ANN Model
2.5. Relative Importance and Sensitivity Analysis of Excavator Input Factor on Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions
3. Multivariate Linear Regression Formulae for Predicting Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions Compared with ANN Models
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




| Case | C * | N * | L * | Straining | Stesting | MSE | Epochs | Rtraining | Rtesting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00001974 | 79 | 0.99755 | 0.98361 |
| 2 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00007876 | 91 | 0.99715 | 0.99748 | |
| 3 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00007665 | 76 | 0.99718 | 0.99743 | |
| 4 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00007479 | 71 | 0.99724 | 0.99712 | |
| 5 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00026406 | 63 | 0.98964 | 0.98722 | |
| 6 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00000995 | 85 | 0.99967 | 0.99968 | |
| B | 7 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00000987 | 71 | 0.99755 | 0.98362 |
| 8 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00007876 | 64 | 0.99715 | 0.99748 | |
| 9 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00007665 | 81 | 0.99718 | 0.99743 | |
| 10 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00029514 | 78 | 0.98904 | 0.99048 | |
| 11 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00098040 | 38 | 0.96099 | 0.95960 | |
| 12 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00000994 | 11 | 0.99795 | 0.99821 | |
| C | 13 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00001660 | 38 | 0.99755 | 0.98361 |
| 14 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00007876 | 42 | 0.99715 | 0.99748 | |
| 15 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00007665 | 63 | 0.99718 | 0.99743 | |
| 16 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00007479 | 44 | 0.99724 | 0.99712 | |
| 17 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00007118 | 73 | 0.99723 | 0.99650 | |
| 18 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00001840 | 60 | 0.99053 | 0.98910 | |
| D | 19 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00001970 | 31 | 0.99910 | 0.99034 |
| 20 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00002102 | 26 | 0.99924 | 0.99934 | |
| 21 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00002886 | 22 | 0.99894 | 0.99887 | |
| 22 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00001811 | 28 | 0.99933 | 0.99940 | |
| 23 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00002936 | 25 | 0.99885 | 0.99865 | |
| 24 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00000976 | 16 | 0.99921 | 0.99921 | |
| E | 25 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00000928 | 27 | 0.99926 | 0.99357 |
| 26 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00001489 | 19 | 0.99946 | 0.99954 | |
| 27 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00003063 | 14 | 0.99887 | 0.99881 | |
| 28 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00001585 | 22 | 0.99942 | 0.99935 | |
| 29 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00001616 | 45 | 0.99937 | 0.99933 | |
| 30 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00001847 | 34 | 0.99939 | 0.99945 | |
| F | 31 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00001991 | 33 | 0.99879 | 0.99269 |
| 32 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00004490 | 67 | 0.99837 | 0.99840 | |
| 33 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00001674 | 42 | 0.99938 | 0.99944 | |
| 34 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00001441 | 25 | 0.99947 | 0.99951 | |
| 35 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00001963 | 42 | 0.99873 | 0.99805 | |
| 36 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00000970 | 43 | 0.99897 | 0.99912 | |
| G | 37 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00000999 | 14 | 0.99964 | 0.99967 |
| 38 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00000930 | 43 | 0.99969 | 0.99971 | |
| 39 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00000925 | 17 | 0.99968 | 0.99969 | |
| 40 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00000851 | 15 | 0.99972 | 0.99974 | |
| 41 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00000944 | 19 | 0.99962 | 0.99973 | |
| 42 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00000937 | 47 | 0.99968 | 0.99968 |
| Case | C * | N * | L * | Straining | Stesting | MSE | Epochs | Rtraining | Rtesting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00001990 | 41 | 0.99755 | 0.98361 |
| 2 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00007876 | 69 | 0.99715 | 0.99748 | |
| 3 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00007665 | 66 | 0.99718 | 0.99743 | |
| 4 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00007479 | 71 | 0.99724 | 0.99712 | |
| 5 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00026406 | 63 | 0.98964 | 0.98722 | |
| 6 | 5-3-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00000996 | 84 | 0.99967 | 0.99968 | |
| B | 7 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00008863 | 53 | 0.99755 | 0.98362 |
| 8 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00007876 | 64 | 0.99715 | 0.99748 | |
| 9 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00007665 | 68 | 0.99718 | 0.99743 | |
| 10 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00029514 | 78 | 0.98904 | 0.99048 | |
| 11 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00098040 | 38 | 0.96099 | 0.95960 | |
| 12 | 5-6-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00002858 | 48 | 0.99795 | 0.99821 | |
| C | 13 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00009781 | 71 | 0.99755 | 0.98361 |
| 14 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00007876 | 64 | 0.99715 | 0.99748 | |
| 15 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00007665 | 70 | 0.99718 | 0.99743 | |
| 16 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00007479 | 74 | 0.99724 | 0.99712 | |
| 17 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00007118 | 73 | 0.99723 | 0.99650 | |
| 18 | 5-7-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00009549 | 42 | 0.99053 | 0.98910 | |
| D | 19 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00009714 | 49 | 0.99910 | 0.99034 |
| 20 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00002102 | 62 | 0.99924 | 0.99934 | |
| 21 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00002886 | 22 | 0.99894 | 0.99887 | |
| 22 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00001811 | 28 | 0.99933 | 0.99940 | |
| 23 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00002936 | 39 | 0.99885 | 0.99865 | |
| 24 | 5-9-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00001938 | 69 | 0.99921 | 0.99921 | |
| E | 25 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00000999 | 26 | 0.99926 | 0.99357 |
| 26 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00001489 | 37 | 0.99946 | 0.99954 | |
| 27 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00003063 | 45 | 0.99887 | 0.99881 | |
| 28 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00001585 | 28 | 0.99942 | 0.99935 | |
| 29 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00001616 | 41 | 0.99937 | 0.99933 | |
| 30 | 5-11-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00000938 | 24 | 0.99939 | 0.99945 | |
| F | 31 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00000963 | 18 | 0.99879 | 0.99269 |
| 32 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00001990 | 27 | 0.99837 | 0.99840 | |
| 33 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00001674 | 29 | 0.99938 | 0.99944 | |
| 34 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00001441 | 25 | 0.99947 | 0.99951 | |
| 35 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00003263 | 42 | 0.99873 | 0.99805 | |
| 36 | 5-13-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00000923 | 52 | 0.99897 | 0.99912 | |
| G | 37 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4073 | 1019 | 0.00000993 | 28 | 0.99964 | 0.99967 |
| 38 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4364 | 728 | 0.00000930 | 43 | 0.99969 | 0.99971 | |
| 39 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4526 | 566 | 0.00000925 | 17 | 0.99968 | 0.99969 | |
| 40 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4629 | 463 | 0.00000895 | 21 | 0.99970 | 0.99975 | |
| 41 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4700 | 392 | 0.00000944 | 19 | 0.99962 | 0.99973 | |
| 42 | 5-15-1 | 0.1 | 4752 | 340 | 0.00000966 | 23 | 0.99968 | 0.99968 |
References
- Lewis, P.; Rasdorf, W.; Frey, H.C.; Pang, S.; Kim, K. Requirements and incentives for reducing construction vehicle emissions and comparison of nonroad diesel engine emissions data sources. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2009, 135, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waris, M.; Liew, M.S.; Khamidi, M.F.; Idrus, A. Criteria for the selection of sustainable onsite construction equipment. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2014, 3, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, B.; Marr, L.C. Real-time emissions from construction equipment compared with model predictions. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guggemos, A.A.; Horvath, A. Decision-support tool for assessing the environmental effects of constructing commercial buildings. J. Archit. Eng. 2006, 12, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K. Modelling of on-site energy consumption profile in construction sites and a case study of earth moving. J. Constr. Eng. Proj. Manag. 2013, 3, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lee, H.; Park, H.; Kim, H. Greenhouse gas emissions from onsite equipment usage in road construction. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2011, 138, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther, M.; Nielsen, O. Fuel use and emissions from non-road machinery in Denmark from 1985–2004-and projections from 2005–2030. Environ. Proj. 2006, 1092, 238. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt, M.; Kühlen, A.; Haghsheno, S. Developing a pollution measuring system to manage demolition projects complying with legal regulations. In Proceedings of the 2014 (5th) International Conference on Engineering, Project, and Production Management (EPPM), Port Elizabeth, South Africa, 30 November–2 December 2014; p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Sandanayake, M.; Zhang, G.; Setunge, S.; Thomas, C.M. Environmental emissions of construction equipment usage in pile foundation construction process—A case study. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium on Advancement of Construction Management and Real Estate; Shen, L., Ye, K., Mao, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 327–339. [Google Scholar]
- Dallmann, T.; Menon, A. Technology Pathways for Diesel Engines Used in Non-Road Vehicles and Equipment; International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT): Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.K.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, T.; Luo, E.; Li, V. Toward low-carbon construction processes: The visualisation of predicted emission via virtual prototyping technology. Autom. Constr. 2013, 33, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhasani, S. Assessment of on-Board Emissions and Energy use of Nonroad Construction Vehicles. Master’s Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Fan, M.; Gupta, R.; Slimane, R.B.; Bland, A.E.; Wright, I. Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrell, E.; Price, L.; Martin, N.; Hendriks, C.; Meida, L.O. Carbon dioxide emissions from the global cement industry. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 2001, 26, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Quéré, C.; Andrew, R.; Canadell, J.; Sitch, S.; Korsbakken, J.; Peters, G.; Manning, A.; Boden, T.; Tans, P.; Houghton, R. Global carbon budget 2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 605–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, A. An overview of CO2 mitigation options for global warming—Emphasizing CO2 sequestration options. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2003, 36, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enevoldsen, M.K.; Ryelund, A.V.; Andersen, M.S. Decoupling of industrial energy consumption and CO2-emissions in energy-intensive industries in Scandinavia. Energy Econ. 2007, 29, 665–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Swedish Transport Administration. The Swedish Transport Administration’s Efforts for Improving Energy Efficiency and for Climate Mitigation; Trafikverket: Karlstad, Sweden, 2012.
- Ainslie, B.; Rideout, G.; Cooper, C.; McKinnon, D. The impact of retrofit exhaust control technologies on emissions from heavy-duty diesel construction equipment. SAE 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbitt, G.R.; Moskwa, J.J. Implementation details and test results for a transient engine dynamometer and hardware in the loop vehicle model. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE International Symposium on Computer Aided Control System Design, Kohala Coast, HI, USA, 27 August 1999; pp. 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren, M.; Hansson, P. Effects of Transient conditions on exhaust emissions from two non-road diesel engines. Biosyst. Eng. 2004, 87, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, U.; Siegmann, H.; Burtscher, H. Dynamic field measurements of submicron particles from diesel engines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanowitz, J.; McCormick, R.L.; Graboski, M.S. In-use emissions from heavy-duty diesel vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Riccobono, F.; Vlachos, T.; Mendoza-Villafuerte, P.; Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Fontaras, G.; Bonnel, P.; Weiss, M. Vehicle emission factors of solid nanoparticles in the laboratory and on the road using Portable Emission Measurement Systems (PEMS). Front. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, H.C.; Rasdorf, W.; Kim, K.; Pang, S.; Lewis, P.; Abolhassani, S. Real-World Duty Cycles and Utilization for Construction Equipment in North Carolina; North Carolina Department of Transportation: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2008.
- Abolhasani, S.; Frey, H.C.; Kim, K.; Rasdorf, W.; Lewis, P.; Pang, S. Real-world in-use activity, fuel use, and emissions for nonroad construction vehicles: A case study for excavators. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2008, 58, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Ge, Y.; Tan, J.; Zeng, T.; Liang, B. Characteristics of typical non-road machinery emissions in China by using Portable Emission Measurement System. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 437, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P.; Leming, M.; Rasdorf, W. Impact of engine idling on fuel use and CO2 emissions of nonroad diesel construction equipment. J. Manag. Eng. 2011, 28, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriani, H.; Lewis, P. Comparison of predictive modeling methodologies for estimating fuel use and emission rates for wheel loaders. In Proceedings of the 2014 Construction Research Congress: Construction in A Global Network, Atlanta, GA, USA, 19–21 May 2014; pp. 613–622. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari Haratmeh, B. New Framework for Real-Time Measurement, Monitoring, and Benchmarking of Construction Equipment Emissions. Master’s Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 7 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lijewski, P.; Merkisz, J.; Fuc, P.; Kozak, M.; Rymaniak, L. Air pollution by the exhaust emissions from construction machinery under actual operating conditions. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 390, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, A.M.; Lewis, P. Development of productivity-based estimating tool for energy and air emissions from earthwork construction activities. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2013, 2, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.; Rasdorf, W. Fuel use and pollutant emissions taxonomy for heavy duty diesel construction equipment. J. Manag. Eng. 2017, 33, 04016038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, A.M.; Muladi, M.; Larasati, A. ‘ENPROD’ MODEL–estimating the energy impact of the use of heavy duty construction equipment by using productivity rate. In Proceedings of the International Mechanical Engineering and Engineering Education Conferences (IMEEEC), Malang, Indonesia, 7–8 October 2016; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1778. [Google Scholar]
- Trani, M.L.; Bossi, B.; Gangolells, M.; Casals, M. Predicting fuel energy consumption during earthworks. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3798–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori, G.; Gang, G.; Briffett, C. Implementing environmental management systems in construction: Lessons from quality systems. Build. Environ. 2002, 37, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Wong, C.T. EnvironalPlanning: Analytic network process model for environmentally conscious construction planning. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2005, 131, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Z. Environmental Management in Construction: A Quantitative Approach; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Braganca, L.; Vieira, S.M.; Andrade, J.B. Early Stage design decisions: The way to achieve sustainable buildings at lower costs. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 365364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robichaud, L.B.; Anantatmula, V.S. Greening project management practices for sustainable construction. J. Manag. Eng. 2010, 27, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterpillar. Caterpillar Performance Handbook, 42th ed.; Caterpillar Inc.: Peoria, IL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Filas, F.J. Excavation, loading, and material transport. In SME Mining Reference Hand Book; Lowrie, R.L., Ed.; Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration: Littleton, CO, USA, 2002; pp. 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- Klanfar, M.; Korman, T.; Kujundžić, T. Fuel consumption and engine load factors of equipment in quarrying of crushed stone. Tech. Gaz. 2016, 23, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T. Military Technologies of the World [2 Volumes]; ABC-CLIO: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Median Life, Annual Activity, and Load Factor Values for Nonroad Engine Emissions Modeling; National Service Center for Environmental Publications (NSCEP): College Park, MD, USA, 2010.
- Clement, S.; Evans, N.; ICLEI-Local Governments for Sustainability. Clean Fleets guide. In Procuring Clean and Efficient Road Vehicles; International Council for Local Environmental Initiatives (ICLEI-Europe) Local Governments for Sustainability: Freiburg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tyson, K.S.; McCormick, R.L. Biodiesel Handling and Use Guidelines; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, C.; Auld, D.; Korus, R. Winter rape oil fuel for diesel engines: Recovery and utilization. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1983, 60, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A.V. Renewable fuels and chemicals by thermal processing of biomass. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 91, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Leick, M.; Liu, Y.; Chia-fon, F.L. Effect of EGR and injection timing on combustion and emission characteristics of split injection strategy DI-diesel engine fueled with biodiesel. Fuel 2011, 90, 1884–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, R.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Fu, L.; Hao, J. Real-world fuel consumption and CO2 emissions of urban public buses in Beijing. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, C.S. Experimental investigation on the fuel properties of biodiesel and its blends at various temperatures. Energy Fuels 2007, 22, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Energy and Climate Change (DECC); Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra). Guidelines to Defra/DECC’s GHG Conversion Factors for Company Reporting; Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs: London, UK, 2011.
- Burgess, J.W. Material properties. In SME Mining Reference Hand Book; Lowrie, R.L., Ed.; Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration: Littleton, CO, USA, 2002; pp. 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Scesi, L.; Papini, M. Geologia Applicata. Vol. 1: Il Rilevamento Geologico-Tecnico; Città Studi: Milan, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gottfried, A. Ergotecnica Edile; Hoepli: Milan, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, S.S.; Harrison, R.F.; Kennedy, R.L. Introduction to neural networks. Lancet 1995, 346, 1075–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuth, H.; Beale, M. Neural Network Toolbox; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Patuwo, B.E.; Hu, M.Y. Forecasting with artificial neural networks: The state of the art. Int. J. Forecast. 1998, 14, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreta, A.W.C. Simulating size effect on shear strength of RC beams without stirrups using neural networks. Eng. Struct. 2004, 26, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, B.R.; Eryurek, E. Application of neural networks for sensor validation and plant monitoring. Nucl. Technol. 1992, 97, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Siami-Irdemoosa, E.; Dindarloo, S.R. Prediction of fuel consumption of mining dump trucks: A neural networks approach. Appl. Energy 2015, 151, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šibalija, T.V.; Majstorović, V.D. Advanced Multiresponse Process. Optimisation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gulcicek, U.; Ozkan, O.; Gunduz, M.; Demir, I.H. Cost assessment of construction projects through neural networks. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2013, 40, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, S.C.; Sinha, S.K. Construction equipment productivity estimation using artificial neural network Model. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2006, 24, 1029–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.; Tong, T.K.; Tse, S.L. Artificial neural networks model for predicting excavator productivity. Eng. Constr. Arch. Manag. 2002, 9, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garson, D.G. Interpreting neural network connection weights. AI Expert 1991, 6, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, A. Back-propagation neural networks for modeling complex systems. Artif. Intell. Eng. 1995, 9, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.H. Multiple linear regression analysis: A matrix approach with MATLAB. Ala. J. Math. 2009, 34, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht-Nielsen, R. Neurocomputing; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Caudill, M. Neural network training tips and techniques. AI Expert 1991, 6, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, T. Practical Neural Network Recipes in C++; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, D.; Goss, E. Forecasting with neural networks: An application using bankruptcy data. Inf. Manag. 1993, 24, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, T.; Fazio, P.; Moselhi, O. Developing practical neural network applications using back-propagation. Compu. Aided Civil Infrastruct. Eng. 1994, 9, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadid, M.N.; Fairbairn, D.R. Neural-network applications in predicting moment-curvature parameters from experimental data. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 1996, 9, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gis, W.; Bielaczyc, P. Emission of CO2 and fuel consumption for automotive vehicles. Emiss. Tech. Meas. Test. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Checkel, M.D. Experimental measurement of on-road CO2 emission and fuel consumption functions. Trans. J. Eng. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, I.; Peurifoy, P.; Clifford, J.; Schexnayder, P.; Shapira, A. Construction Planning, Equipment and Methods; McGrow-Hill Higher Education: Boston, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Barati, K.; Shen, X. Emissions modelling of earthmoving equipment. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, Auburn, AL, USA, 18–21 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, F.; Harding, J.A.; Glass, J. An eco-approach to optimise efficiency and productivity of a hydraulic excavator. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3966–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, A.S. Characterizing the Operation of a Large Hydraulic Excavator. Master’s Thesis, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 28 January 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fuel Economy. Fuelling Savings in Tough Times; Blutip Power Technologies: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 2015; pp. 38–46.
- Komatsu (Ed.) Komatsu Specification and Application Handbook, 30th ed.; Komatsu Limited: Tokyo, Japan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kecojevic, V.; Komljenovic, D. Impact of bulldozer’s engine load factor on fuel consumption, CO2 emission and cost. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavlik, J.W.; Mooney, R.J.; Towell, G.G. Symbolic and neural learning algorithms: An experimental comparison. Mach. Learn. 1991, 6, 111–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiono, R.; Leow, W.K.; Zurada, J.M. Extraction of rules from artificial neural networks for nonlinear regression. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.D.; Davis, R.; Meyer, M.; Turner, A.; Turner, S.; Withers, G.; Kam, L.; Banker, G.; Craighead, H.; Issacson, M. Aligned microcontact printing of micrometer-scale poly-l-lysine structures for controlled growth of cultured neurons on planar microelectrode arrays. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 47, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajji, A.M.; Lewis, P. Development of productivity-based estimating tool for fuel use and emissions from earthwork construction activities. KICEM J. Constr. Eng. Proj. Manag. 2013, 3, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Caterpillar Excavator Model | Suitable Type of Earth | Bank Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| 307C, 308D CR, 308D CR SB, 311D LRR, 312D, 312D L, 315D L, 319D L, 319D LN | Decomposed Rock-Packed Earth | 960–2260 |
| M313D, M315D, M316D, M318D, M322D | Sand/Gravel | 1370–2082 |
| 320D, 320D RR, 321D CR, 323D, 324D, 328D LCR, 329D, 336D, 345D, 365C L and 385C | Hard Clay | 1089–2415 |
| Excavator Model | Dp (m) | Tc (min) | Bs (m3) | Bf (%) | Hp (kW) | Lf (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 307C, 308D CR, 308D CR SB, 311D LRR, 312D, 312D L, 315D L, 319D L, 319D LN | 1.5–3.0 | 0.22–0.28 | 0.37–1.05 | 0.8–1.1 | 41–93 | 0.15–0.91 |
| M313D, M315D, M316D, M318D, M322D | 2.0–4.0 | 0.17–0.23 | 0.8–1.37 | 0.9–1.0 | 95–123 | 0.15–0.91 |
| 320D, 320D RR, 321D CR, 323D, 324D, 328D LCR, 329D, 336D, 345D, 365C L and 385C | 2.3–5.6 | 0.23–0.35 | 1.05–5.0 | 0.65–0.95 | 103–355 | 0.15–0.91 |
| Items | A | ß1 | ß2 | ß3 | ß4 | ß5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EnR | n | −562.921 | −5.79 × 10−9 | 8.14 × 10−9 | 3.25 × 10−10 | 4.45274 | 1177.95 |
| EmR | m | −42.1721 | 1.51 × 10−10 | 3.16 × 10−9 | 6.31 × 10−10 | 0.33359 | 88.2478 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jassim, H.S.H.; Lu, W.; Olofsson, T. Predicting Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions of Excavators in Earthwork Operations: An Artificial Neural Network Model. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071257
Jassim HSH, Lu W, Olofsson T. Predicting Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions of Excavators in Earthwork Operations: An Artificial Neural Network Model. Sustainability. 2017; 9(7):1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071257
Chicago/Turabian StyleJassim, Hassanean S. H., Weizhuo Lu, and Thomas Olofsson. 2017. "Predicting Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions of Excavators in Earthwork Operations: An Artificial Neural Network Model" Sustainability 9, no. 7: 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071257
APA StyleJassim, H. S. H., Lu, W., & Olofsson, T. (2017). Predicting Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions of Excavators in Earthwork Operations: An Artificial Neural Network Model. Sustainability, 9(7), 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071257