Instantaneous 3D Continental-Shelf Scale Imaging of Oceanic Fish by Multi-Spectral Resonance Sensing Reveals Group Behavior during Spawning Migration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. OAWRS Gulf of Maine 2006 Experiment
2.2. Instantaneous Multi-Spectral OAWRS Scattering Strength Images of Large Herring Groups
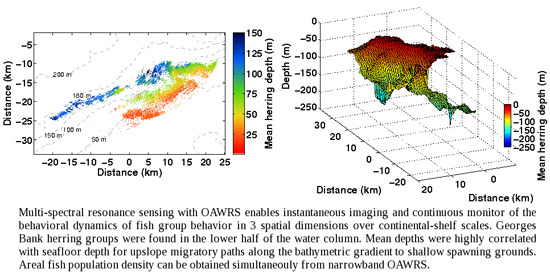
2.3. Instantaneous 3D Imaging via Multi-Spectral Resonance Sensing
2.4. Spatial Shoal Segmentation
2.5. Modeled Resonant Scattering from Herring in a Uniform Vertical Layer
2.6. Least Squares Estimation of Herring Group Parameters
2.7. Estimation Uncertainty Measure from Cost Function
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Makris, N.; Ratilal, P.; Jagannathan, S.; Gong, Z.; Andrews, M.; Bertsatos, I.; Godø, O.; Nero, R.; Jech, J. Critical population density triggers rapid formation of vast oceanic fish shoals. Science 2009, 323, 1734–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, G.A. Cod spawning on a migration highway in the north-west Atlantic. Nature 1993, 366, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakken, O. Norwegian Spring-Spawning Herring & Northeast Arctic Cod: 100 Years of Research Management; Tapir Academic Press: Trondheim, Norway, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Makris, N.; Ratilal, P.; Symonds, D.; Jagannathan, S.; Lee, S.; Nero, R. Fish population and behavior revealed by instantaneous continental shelf-scale imaging. Science 2006, 311, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Andrews, M.; Jagannathan, S.; Patel, R.; Jech, J.; Makris, N.; Ratilal, P. Low-frequency target strength and abundance of shoaling Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus) in the Gulf of Maine during the Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing 2006 Experiment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Jain, A.D.; Tran, D.; Yi, D.H.; Wu, F.; Zorn, A.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Ecosystem scale acoustic sensing reveals humpback whale behavior synchronous with herring spawning processes and re-evaluation finds no effect of sonar on humpback song occurrence in the Gulf of Maine in Fall 2006. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Garcia, H.; Huang, W.; Tran, D.D.; Jain, A.D.; Yi, D.H.; Gong, Z.; Jech, J.M.; Godø, O.R.; Makris, N.C.; et al. Vast assembly of vocal marine mammals from diverse species on fish spawning ground. Nature 2016, 531, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Preston, J. The ONR five octave research array (FORA) at Penn State. In Proceedings of the Oceans 2003, Celebrating the Past ... Teaming Toward the Future (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37492), San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 September 2003; Volume 5, pp. 2607–2610. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Ratilal, P. Angular Resolution Enhancement Provided by Nonuniformly-Spaced Linear Hydrophone Arrays in Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.D.; Makris, N.C. Maximum Likelihood Deconvolution of Beamformed Images with Signal-Dependent Speckle Fluctuations from Gaussian Random Fields: With Application to Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing (OAWRS). Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, S.; Bertsatos, I.; Symonds, D.; Chen, T.; Nia, H.; Jain, A.; Andrews, M.; Gong, Z.; Nero, R.; Ngor, L.; et al. Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing (OAWRS) of marine ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 395, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; Chen, T.; Ratilal, P. Empirical dependence of acoustic transmission scintillation statistics on bandwidth, frequency, and range in New Jersey continental shelf. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.D. A split-step Padé solution for the parabolic equation method. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Mean and variance of the forward field propagated through three-dimensional random internal waves in a continental-shelf waveguide. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 118, 3560–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, N. The effect of saturated transmission scintillation on ocean acoustic intensity measurements. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 100, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Andrews, M.; Ratilal, P. Probability distribution for energy of saturated broadband ocean acoustic transmission: Results from Gulf of Maine 2006 experiment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3659–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, R. Resonant acoustic scattering by swimbladder-bearing fish. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1978, 64, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.H.; Makris, N.C. Feasibility of acoustic remote sensing of large herring shoals and seafloor by baleen whales. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Statistical Optics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Uslenghi, P.L.E.; Senoor, T.B.A.; Bowman, J.; Asvestas, J.S. Electromagnetic and Acoustic Scattering by Simple Shapes; Bowman, J.J., Senior, T.B.A., Uslenghi, P.L.E., Eds.; North-Holland Publishing Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, F.H.; Scholes, P. Gas secretion and resorption in the swimbladder of the cod (Gadus morhua). J. Comp. Physiol. B 1985, 155, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, D.; Simmonds, E.J. Fisheries Acoustics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Nero, R.W.; Thompson, C.H.; Jech, J.M. In situ acoustic estimates of the swimbladder volume of Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2004, 61, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, D.E. Sound propagation in the presence of bladder fish. In Underwater Acoustics; Albers, V.M., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1967; Volume 2, pp. 55–88. [Google Scholar]
- Brawn, V.M. Physical properties and hydrostatic function of the swimbladder of herring (Clupea harengus L.). J. Fish. Board Can. 1962, 19, 635–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, G.; Walker, M.G. Vertical movements of cod (Gadus morhua L.) in the open sea and the hydrostatic function of the swimbladder. ICES J. Mar. Sci. J. Conseil 1992, 49, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, D.K.; Scott, M.L. Essential Fish Habitat Source Document: Atlantic Herring, Clupea Harengus, Life History and Habitat Characteristics; NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-NE-192; Northeast Fisheries Science Center, National Marine Fisheries Service, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, U.S. Department of Commerce: Woods Hole, MA, USA, 2005.
- Slotte, A. Effects of fish length and condition on spawning migration in Norwegian spring spawning herring (Clupea harengus L.). Sarsia 1999, 84, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nøttestad, L. Extensive gas bubble release in Norwegian spring-spawning herring (Clupea harengus) during predator avoidance. ICES J. Mar. Sci. J. Conseil 1998, 55, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, R.; Thomas, G. Acoustic observations of gas bubble release by Pacific herring (Clupea harengus pallasi). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 47, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlberg, M.; Westerberg, H. Sounds produced by herring (Clupea harengus) bubble release. Aquat. Living Resour. 2003, 16, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Batty, R.; Dill, L. Pacific and Atlantic herring produce burst pulse sounds. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, S95–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.D.; Ignisca, A.; Yi, D.H.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Feasibility of Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing (OAWRS) of Atlantic cod with seafloor scattering limitations. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 180–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fässler, S.M.M.; Santos, R.; García-núñez, N.; Fernandes, P.G. Multifrequency backscattering properties of Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus) and Norway pout (Trisopterus esmarkii). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 64, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jech, J.M. Interpretation of multi-frequency acoustic data: Effects of fish orientation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, R.H. Dorsal-aspect target strength of an individual fish. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1971, 49, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorska, N.; Ona, E. Modelling the acoustic effect of swimbladder compression in herring. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 60, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, D.H.; Gong, Z.; Jech, J.M.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Instantaneous 3D Continental-Shelf Scale Imaging of Oceanic Fish by Multi-Spectral Resonance Sensing Reveals Group Behavior during Spawning Migration. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010108
Yi DH, Gong Z, Jech JM, Ratilal P, Makris NC. Instantaneous 3D Continental-Shelf Scale Imaging of Oceanic Fish by Multi-Spectral Resonance Sensing Reveals Group Behavior during Spawning Migration. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(1):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010108
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Dong Hoon, Zheng Gong, J. Michael Jech, Purnima Ratilal, and Nicholas C. Makris. 2018. "Instantaneous 3D Continental-Shelf Scale Imaging of Oceanic Fish by Multi-Spectral Resonance Sensing Reveals Group Behavior during Spawning Migration" Remote Sensing 10, no. 1: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010108
APA StyleYi, D. H., Gong, Z., Jech, J. M., Ratilal, P., & Makris, N. C. (2018). Instantaneous 3D Continental-Shelf Scale Imaging of Oceanic Fish by Multi-Spectral Resonance Sensing Reveals Group Behavior during Spawning Migration. Remote Sensing, 10(1), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010108